
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
What are Fordyce granules?
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
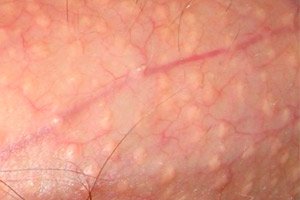
The noticeable sebaceous glands of the skin – in the form of small nodules (papules) of various localizations – were first described in 1861 by the Swiss anatomist Albert Kölliker, but they were named Fordyce granules after another doctor – the American dermatologist John Fordyce, who reported them 45 years later… [ 1 ]
Epidemiology
By some estimates, granules or Fordyce glands, as an anatomical variant, occur in 70-80% of adults and are twice as common in men.
Their most frequent localization (more than 80% of cases) is the red border of the upper or lower lip; then the retromolar region, that is, Fordyce granules on the gums behind the last molars. A significant number of cases also fall on Fordyce granules on the cheeks (on their mucous membrane in the oral cavity).
Causes Fordyce granules
But even today the key reasons for the appearance of Fordyce granules are unknown, although there are several assumptions regarding their origin.
Some researchers believe that the enlargement of sebaceous glands not associated with hair follicles occurs during hormonal changes, especially during puberty. According to another point of view, these fatty nodules begin to form during intrauterine development, and in children before puberty they are simply not visible.
However, most dermatologists consider clusters of sebaceous glands shifted closer to the skin surface (ectopic or heterotopic), covered by intact epithelium or mucous membrane, to be an anatomical variant. That is, in fact, these granules are formed due to the peculiarities of the development of sebaceous glands - their number and depth in the skin - during the embryonic period.
When asked whether Fordyce granules are contagious, experts give a definitive negative answer, although these papules, which are completely harmless to physical health (and not associated with any infection), can cause concern in people. [ 2 ]
Risk factors
Given the rather uncertain etiology, it is difficult for specialists to establish definitive risk factors for the appearance of Fordyce glands.
Most often, the conclusions of clinical observations or assumptions are mentioned as oily skin type with pronounced seborrhea, male gender (sebaceous gland cells are stimulated by testosterone and dihydrotestosterone), elevated blood lipid levels (hyperlipidemia) and age up to 30-35 years, when these glands become noticeable.
Pathogenesis
The sebaceous glands (glandulae sebacea) are located in close proximity to the hair follicles (folliculus pili); they produce sebum, which reaches the surface of the skin through the follicular duct - to protect the epidermis.
Both the size of these glands and the activity of sebum secretion are controlled by male steroid hormones called androgens. The sebaceous glands enlarge in pre-adolescence due to stimulation of the adrenal glands by androgens and reach their full size during puberty, when androgens begin to be produced by the gonads (sex glands).
And the pathogenesis of Fordyce granules on various parts of the body is associated with the displacement and enlargement of sebaceous glands not associated with hair follicles; in this case, their ducts enter the superficial layers of the dermis and mucous membranes, where limited accumulations of sebum are formed (the composition of the granules and sebaceous glands is identical).
It should be borne in mind that most adults have very small sebaceous glands on the red border of the lips, which is why Fordyce granules may appear on the lips.
In addition, tiny sebaceous glands are present on the eyelids, which may explain Fordyce granules under the eyes, and the presence of modified sebaceous glands (called Montgomery glands) on the areolas of the nipples - Fordyce granules on the breasts and nipples.
In men, Fordyce granules on the penis may be associated with ectopia and enlargement of the preputial sebaceous glands - under the foreskin (preputium) of the penis. And in women, Fordyce granules on the labia majora and labia minora, as well as Fordyce granules on the clitoris, are an anatomical feature of the smallest sebaceous glands located in the mucous membrane of the so-called hood of the clitoris - the inner layer of its foreskin. [ 3 ]
Symptoms Fordyce granules
Symptoms of Fordyce granules are limited to the presence of small (1-3 mm in size) isolated papules (tubercles or pimples) of cream or yellowish-white color under the epithelium - on the lips or mucous membrane in the mouth, on the penis, scrotum and labia; often papules cause local elevation of the epithelium covering them.
Nodules located next to each other can sometimes merge, but remain asymptomatic: they do not cause pain, itching, etc. On the shaft of the penis and scrotum, papules become more pronounced when the skin is stretched.
Fordyce granules in the mouth - on the mucous membrane of the cheeks - can be on both sides, single or multiple, but the surrounding mucous membrane remains unchanged. In ICD-10, ectopic Fordyce sebaceous glands in the mouth are classified as congenital anomalies of the oral cavity with the code Q38.6.
By the way, in domestic dermatology, glands or Fordyce granules on the male genitals can be considered sebaceous gland cysts or atheroma of the scrotum, testicles and penis, although cystic formation occurs in the sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles. [ 4 ]
Typically, Fordyce granules in the armpits, groin, and pubic area, where apocrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles (having excretory ducts) predominate, are formed as the primary element of the rash in Fox-Fordyce disease in women - apocrine miliaria (code L75.2 according to ICD-10), which manifests itself as a perifollicular nodular rash with severe itching and the formation of keratin plugs.
Complications and consequences
There are no physical consequences of Fordyce granules, but anxiety and depression are common due to the cosmetic defect. However, when they appear on the penis, discomfort during intercourse is possible.
A complication may be inflammation of Fordyce granules if the skin in the area where they are located is damaged. For example, when there are Fordyce granules on the lips, and permanent lip makeup touches them.
Diagnostics Fordyce granules
Diagnosis of Fordyce granules involves visual inspection and examination of the skin.[ 5 ]
Instrumental diagnostics is usually carried out using dermatoscopy;ultrasound of the skin and subcutaneous fat can also be used.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis includes steatocystomas (congenital sebaceous cysts), epidermoid or dermoid cysts, sebaceous gland hyperplasia, atheroma, xanthomas, whiteheads (milia), syringomas, perioral dermatitis, vegetarian pyostomatitis, leukoplakia, and molluscum contagiosum. [ 6 ]
Who to contact?
Treatment Fordyce granules
Most dermatologists do not consider it necessary to treat ectopic sebaceous glands. However, to eliminate the cosmetic defect, it is possible to use some medications containing retinol (vitamin A).
Thus, local agents with retinoids can be used - an active form of vitamin A (isotretinoin) - in the form of an ointment (cream or gel), that is, retinoic ointment from Fordyce granules; Tretinoin, Atrederm solution or Retin A cream; Adapalene gel or cream (Adaklin, Differin) - with an analogue of retinoic acid. These agents are applied to the skin once a day. However, one should keep in mind their possible side effects, which are manifested by swelling, redness, peeling and itching of the skin. [ 7 ]
Salicylic and bichloroacetic acid, calcipotriol betamethasone are used locally.
Possible physiotherapeutic treatment is photodynamic therapy sessions with 5-aminolevulinic acid. [ 8 ]
Herbal treatment is limited to lotions with tincture of Sanguinaria canadensis root, calendula and celandine. It is recommended to lubricate the granules with a mixture of aloe juice and turmeric (powder of Curcuma longa rhizomes), and also to moisten them with natural apple cider vinegar diluted with water (1:1).
How to remove Fordyce granules? Removal of Fordyce granules is practiced by laser (ablative carbon dioxide or pulsed), as well as by electrocoagulation or cryotherapy. And for large sebaceous papules, surgical treatment is possible - their removal using micropunctures. [ 9 ]
Prevention
There are currently no methods for preventing the appearance of ectopic sebaceous glands.

