
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Itchy scalp and dandruff: causes, treatment
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
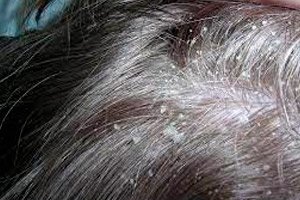
When doctors talk about pruritis and diffuse desquamation of the skin on the scalp, this means that the patient experiences itching and dandruff.
And these non-contagious, but extremely unpleasant symptoms are observed very often and appear for several reasons. [ 1 ]
Epidemiology
According to experts at the American Academy of Dermatology, itching and dandruff usually begin to bother at a young age and the problem continues into later life. And this problem is estimated to affect up to 40% of people aged 30 and older.
As a rule, statistics on the prevalence of dandruff accompanied by itchy scalp are based on foreign data: the USA, Great Britain, Canada and Australia. In this case, precise calculations are not carried out, but an automated extrapolation method of calculation is used, which, naturally, does not give an actual picture.
According to these calculations, one in five Americans has problems with dandruff: this is approximately 50 million people or 18.4% of the entire population. The same figure is in Australia, and in the UK and Canada – approximately 18.2%. [ 2 ]
Causes itchy scalp and dandruff
Experts believe that the main causes of itchy scalp and dandruff are:
- in the development of fungal skin diseases – seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff with excessive production of sebum by sebocytes; [ 3 ]
- in the reaction of sensitive skin to ingredients in hair care products or hair dyes, leading to the development of contact dermatitis;
- in increased dryness of the scalp, when itching and dry dandruff appear - due to insufficient moisture content in its stratum corneum, which cannot fully perform the functions of protecting the epidermis.
Risk factors
Often, the following risk factors are directly related to the process of dandruff and itchy skin:
- oily skin type and increased sweating of the head;
- bathing habits that contribute to dry skin (using inappropriate soaps or detergents, or water that is too hot);
- lack of vitamins and zinc in the body;
- excessive UV radiation;
- hormonal imbalances (in men – problems with androgen production, in women – with the ovaries and the estrogens synthesized in them). By the way, men suffer from dandruff and itching more often, as they have more sweat and sebaceous glands in the scalp;
- immunosuppression and certain diseases, in particular Parkinson's disease, diabetes, severe renal failure, hypothyroidism, Sjogren's syndrome, lymphomas;
- long-term use of certain medications, such as diuretics, powerful systemic antibiotics, corticosteroids, statins;
- long-term stress (accompanied by an increase in the level of cortisol in the blood, as a result of which the functioning of the thymus gland, which ensures the normal immune status of the body, is disrupted). [ 4 ]
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis has been precisely established: the yeast-like fungus Malassezia furfur is the causative agent of seborrhea. [ 5 ]
In the composition of the microflora of the scalp, researchers have discovered opportunistic fungi Malassezia (previously known as Pityrosporum orbiculare). If there is no dandruff, the number of fungi does not exceed 44-46%, however, when their number increases to 74-75%, significant peeling of the skin is observed, and at a level of 85-87%, superficial mycosis is detected, called seborrheic dermatitis. [ 6 ]
These fungi (strains M. restricta and M. globosa) are lipophilic by nature, colonize the stratum corneum and hair follicles, and are present in the scalp microflora as commensals; they feed on saturated fatty acids produced by the sebaceous glands. Under the influence of predisposing factors – high temperature, high humidity, weakened body defenses and barrier functions of the skin – Malassezia are transformed from the blastospore stage to the mycelial form (in which they become pathogenic). This is when itching of the scalp and dandruff appear. [ 7 ]
Fungal cell wall proteins are antigens, and Malassezia may act as a continuous sensitizing factor, causing tissue and humoral immune response, which is manifested by increased production of immunoglobulins (IgE) and interleukins (IL4 and IL5). As a result of the action of IgE on mast cells, histamine is released, and itching occurs. [ 8 ]
And dandruff is a consequence of the “intervention” of Malassezia and the toxins and lipases it produces, leading to increased proliferation, weakening of intercellular connections and migration of corneocytes (dead cells) of the stratum corneum, which, being rejected from it and mixing with sebum, remain on the skin and hair. [ 9 ]
Symptoms itchy scalp and dandruff
The first signs of dandruff are easy to spot: the hair is covered with many white or yellowish flakes of dead skin (oily to the touch), which are usually scattered all over the scalp, falling on the collar and shoulders of clothing, and the scalp is very often itchy. This is oily dandruff and itching.
In complicated cases of seborrheic dermatitis, yellowish or hyperemic spots (plaques) may appear at the hairline, inside and around the ears, in the nose area, and on the upper chest.
With dry dandruff, symptoms may be worse in the cold season and slightly weaken in the warm season. In addition, the scales that peel off with dry skin are very small and almost white.
Sometimes an itchy scalp, dandruff and hair loss are linked, although dandruff itself does not cause hair loss, but both conditions have common triggers and risk factors.[ 10 ]
Complications and consequences
Most often, the consequences and complications concern histamine-associated itching: it intensifies, leading to scratching of the skin (excoriation) and loss of the skin's protective mechanism. This facilitates deeper penetration of Malassezia, where the fungi, with the help of their lipase, break down sebum into fatty acids (arachidonic and oleic), which enhance the desquamation of keratinocytes. The process becomes cyclical and is characterized by a high frequency of relapses. [ 11 ]
Also, very oily dandruff and itching are complicated by blockage of the sebaceous and sweat glands of the scalp, which creates conditions for the development of fungal folliculitis (inflammation of the hair follicles).
Diagnostics itchy scalp and dandruff
First of all, the doctor (dermatologist or trichologist) records the patient's complaints, collects anamnesis and visually, as well as using a dermatoscope, examines the scalp. Diagnostics are described in more detail in the publications:
Differential diagnosis
If the slightest doubt arises – in order not to miss the possible presence of atopic dermatitis, lichenoid pityriasis, scalp psoriasis and other dermatological pathologies – differential diagnostics are carried out with identification of the cause of dandruff by laboratory testing of a sample of exfoliated cells or skin scrapings. [ 12 ]
It is important to note that dermatologists insist on the need to differentiate dandruff from dry scalp (since most people find it difficult to tell the difference). It is true that you can have both dandruff and dry scalp at the same time, but the dermatophyte Malassezia furfur is associated with quite intense itching and oily dandruff, which occurs in people with oily scalp and increased hair oiliness. [ 13 ]
Who to contact?
Treatment itchy scalp and dandruff
What to do with dandruff and itching? Be patient and start treatment.
In solving this dermatological problem, the main emphasis is on local treatment aimed at counteracting the activated fungal microbiota (Malassezia furfur), as well as slowing down the proliferation and keratinization of skin cells.
Antifungal agents for dandruff and itching are available in several forms:
- anti-itch and anti-dandruff shampoos that contain pharmacological antifungal agents (imidazole or triazole derivatives), keratolytic agents (salicylates), as well as zinc and selenium. For example, these are special shampoos Seboderm, Nizoral, Mikozoral (with ketoconazole); Dermazole Plus (with ketoconazole and zinc pyrithione); Sulsena (with selenium sulfide and salicylic acid); shampoos with tar, etc.; [ 14 ], [ 15 ]
- externally applied (topical) agents, for more details see - Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis, and also Ointment for dandruff; [ 16 ], [ 17 ]
- tablets for dandruff and scalp itching, in particular, systemic antifungal drugs of the azole group against seborrheic dermatitis (Itraconazole, Fluconazole) - Tablets for skin fungus, as well as antihistamines - Tablets that relieve itching. [ 18 ]
As for oral antifungal agents, they are prescribed when topical antimycotics fail to cope with their task. Thus, Itraconazole (other trade names - Itrakon, Itrazol, Itramikon, Orungal) is taken once a day, one or two capsules (0.1-0.2 g) after meals, the minimum course is one to two weeks. It should be borne in mind that this drug cannot be used to treat children, pregnant and lactating women, with severe pathologies of the stomach, heart and kidneys. And among its side effects are dizziness and tinnitus, nausea and vomiting; headaches, joint, muscle and epigastric pain; problems with the intestines and liver; allergic urticaria, etc. [ 19 ]
In addition, it is important to take vitamins such as beta-carotene (vitamin A), ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), niacin (PP), tocopherol (vitamin E).
Some effective remedies are offered by homeopathy (in individually determined dosage): Armoracia sativa, Badiaga, Kali sulphuricum, Phosphorus, Thuja occidetalis, Graphites, Lycopodium clavatum, Natrum muriaticum, Sanicula, Calcarea carbonica, Calcarea sulphu, Medorrhinum. [ 20 ]
Home Remedies for Dandruff and Itching
For those who prefer folk remedies - using natural products - masks against dandruff and itching can help:
Following Ayurveda, you can try to cleanse your scalp with onion juice, the antibacterial properties of which no one doubts, but in this case the main benefit is the presence of sulfur and vitamin B6 in onions.
Essential oils with antiseptic properties against dandruff and itching have a positive effect: rosemary oil, lemon oil and tea tree oil, which can be added to shampoo and any hair mask - if there is oily dandruff and itching. And to get rid of dandruff with dry skin, essential oils of eucalyptus, lavender and grapefruit are recommended. [ 21 ], [ 22 ]
In addition, when itching and dry dandruff bother you, you can do a very simple but effective procedure at home, using sesame oil as a base. You need to: mix two tablespoons of warm oil with a few drops of essential oil (from those mentioned above) and lemon juice; apply to the skin, massaging for about 10 minutes; wrap your head in a hot towel (for a quarter of an hour); remove the towel and let the oils moisturize the skin well during the night (wash your head in the morning). This procedure should be done every other day for a week.
It is recommended to rinse your hair with water and vinegar after each wash (150 ml per 2 l). Regular or apple cider vinegar for dandruff and itching not only helps clean clogged pores and hair follicles, but also restores the pH balance of the scalp, reducing the growth of fungal infections.
You can enhance the effect of vinegar with aspirin - acetylsalicylic acid (which is an exfoliant): crush two aspirin tablets into powder, mix with a tablespoon of vinegar and apply to the scalp (massaging the skin with your fingers), leave for about half an hour and wash your hair thoroughly.
But trichologists categorically do not recommend using laundry soap for dandruff and itching. The normal pH of the scalp is closer to acidic (5.4-5.6), and fungal microorganisms do not like this; the pH of laundry soap is alkaline (at the level of 11-12), so washing your hair with such soap disrupts the acid mantle of the skin.
Herbal treatment
No one can guarantee that herbal treatment will help with dandruff and itching, but experts in medicinal plants claim that decoctions of some herbs - with their long-term use - will help cope with this problem.
So, herbs that help with dandruff: fireweed, burdock (root), fenugreek (seeds), chamomile (flowers), bearberry, horsetail, yarrow, red clover.
Herbal decoctions are applied externally, thoroughly wetting the scalp with a tampon (dividing the hair into rows with a comb).
Prevention
The main measures to prevent dandruff and itching are:
- compliance with general principles of hair and scalp care;
- proper care for oily hair;
- drinking enough water;
- a balanced diet that provides the body with the necessary substances;
- Eating nuts and seeds, which contain high amounts of alpha-linolenic acid, zinc and selenium, which are important for a healthy scalp.
Forecast
For most people, dandruff is a chronic condition that sometimes goes away, sometimes comes back. So experts do not undertake to give an optimistic forecast regarding the final elimination of dandruff and scalp itching.

