
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Viral wart: causes, treatment
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
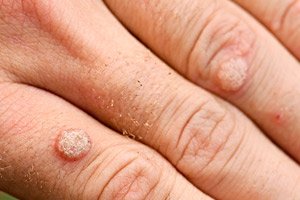
Benign neoplasms in the form of small round growths with a flat surface, nodules on legs or with a sharp tip, flesh-colored, that appeared on the skin or mucous membrane are called differently, depending on their appearance, warts, papillomas, condylomas. Any such formation is a viral wart. And the process of epithelial proliferation begins with infection with papillomavirus infection.
Epidemiology
Statistics show that viral warts can be found on the skin of every third or fourth representative of the planet's population, regardless of gender and race. Clinical manifestations of HPV infection are more common in adults (about 30%) than in childhood and adolescence (from 3 to 9%). In children, vulgar warts are mainly found, in adults - anogenital, and the prevalence of venereal pointed condylomas is growing worldwide.
Oral papillomatosis is quite common. Single large lesions are typical for adults, and women are more susceptible to this pathology (60% of cases). Multiple lesions are typical for children and adolescents. A fifth of viral warts of the oral cavity are detected in this category of the population, more often in 7-12-year-old schoolchildren, and girls suffer from papillomatosis of this localization almost twice as often as boys. [ 1 ]
Causes viral wart
The abbreviation HPV is probably known to everyone nowadays. It stands for human papillomavirus. Many different strains of this virus have already been discovered, about two hundred. They are classified into five genera – α-, β-, γ-, μ- and η-papillomaviruses and 27 species. It is assumed that viruses of different species are characterized by a certain ability to affect specific types of tissue, the so-called tissue specificity. For example, when vulgar warts appear on the soles of the feet, μ-papillomavirus-1, α-papillomavirus-2 or γ-papillomavirus-4 are detected. The last two types are detected in other localizations of common warts (the back of the hands, feet, face), in addition, they can be caused by HPV types 26, 27, 29, 57. [ 2 ] However, usually DNA fragments of several pathogens are found in those infected with the papillomavirus. [ 3 ]
The cause of infection is direct contact of the skin or mucous membranes of a healthy person with virus-affected areas of the epithelium of an infected person. Moreover, infection occurs when virions get on a damaged epithelial surface. These do not necessarily have to be wounds or abrasions, a small inflammation, irritation, or unnoticeable microcracks are enough. The introduced viruses multiply and manifest themselves as excessive proliferation of the epithelium near the site of introduction. They do not migrate throughout the body to distant areas. If several foci of infection appear in different places, this rather indicates self-infection, which is also possible when healthy and infected areas come into contact in the same person.
Outside keratinocytes, the virion remains viable for a short time, up to three hours, and then on damp towels, linen. Therefore, household transmission is also not excluded, but this happens extremely rarely.
HPV is very common in general and it seems that we encounter them often, however, as researchers claim, in the vast majority of cases of such encounters (they cite figures of over 90%) the body copes with the infection itself, and we may not even know about the infection. Many cases indicate that sometimes unexpectedly appeared single warts just as suddenly disappear on their own.
Risk factors
Risk factors for infection and development of the disease, in addition to damaged epithelium, include viral load (the number of viruses that have penetrated the basal layer of the epithelium), the frequency and nature of contacts with a carrier of the papillomavirus, and the immune status of the infected person.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of morphological changes in the epithelium can be triggered by any decrease in the body's defenses, for example, a cold. The human papilloma virus remains in the body for a long time (often for years) without showing any signs of itself, and is activated, beginning to multiply rapidly, in cases of decreased host immunity. In an infected cell, the virus can be in different forms: extrachromosomal (episomal) and embedded in the cell's DNA (intrasomal). The first option is considered more favorable.
Under favorable conditions for virus replication in the macroorganism, under its influence, hyperproliferation of keratinocytes occurs and skin growths appear. Basically, such conditions are: high viral load (regular contacts with virus carriers; entry of physiological fluid or skin flakes abundantly seeded with virions into the wound) and/or infection of a person with a weakened immune system. In the second case, the introduction of single virions is enough for the appearance of clinical symptoms on the skin in the form of viral warts. Virus replication occurs at the level of the basal layer of the integumentary epithelium. [ 4 ]
In these cases, clinical symptoms of infection may appear quite quickly – viral warts. They are most often caused by α-papillomaviruses types 2, 27, 57; γ-papillomavirus-4 and μ-papillomavirus-1. Much less frequently, patients with viral warts are found to have α-papillomaviruses types 3, 7, 10, 28; γ-papillomaviruses types 65, 88, 95; η-papillomavirus-41. [ 5 ]
The immune system's response to the entry of papillomaviruses into the body has not been sufficiently studied. It is known that in response, infected patients produce antibodies - immunoglobulins of the IgM and IgG classes, specific for viral diseases. It is also believed that a more extensive pathological process develops in patients with a low immune status. [ 6 ]
Symptoms viral wart
Viral warts on the hands and fingers usually look like small rounded elevations above the skin surface with a rough and sometimes dry cracked surface. They are painless, do not differ in color from the surrounding skin or are slightly darker. They can merge into fairly large plaques. Often, an impressive mother wart is visible on the skin, surrounded by smaller daughter warts. In most cases, such symptoms indicate that we are dealing with common (simple, vulgar) viral warts. A characteristic, but not obligatory, sign is their symmetrical location relative to the fold of the skin or the extension-bending lines. They are also called "kissing" warts.
The localization of skin growths is varied. They appear not only on the thin skin of the hands, but also on the legs, face, and also on the thick skin of the palms and soles. [ 7 ]
A viral wart on the leg or foot appears when virions from an infected surface get onto damaged skin. On the thin skin of the lower limb, they look exactly the same as on the back of the hands.
If the thick skin covering the soles or palms is infected, a viral plantar wart occurs. These growths are painful because the bundles of filiform papillae grow into the skin, harden, and resemble a callus in appearance. They often appear in places where shoes press on them. Palmar-plantar warts do not rise above the skin, have a granular dry surface covered with small scales. Sometimes a black dot is visible in the center of the plantar wart. This is a thrombosed vessel, which, if damaged, can cause bleeding.
A viral wart may form under the nail or around the nail bed. Such growths are typical for people who have a habit of biting their nails. Hangnails and cracks on the fingers increase the risk of viral warts. More often, according to experts, subungual growths are observed on the hands. The growing growth leads to the nail rising above the bed, peeling off from it. [ 8 ]
For example, a bump under the nail is most likely a viral wart, but if there is swelling and hyperemia, then a bacterial infection is more likely, which could be caused by a piercing injury or a manicure.
Viral warts may appear in the oral cavity. These are painless mucous membrane or whitish soft formations on a stalk (papillomas), detected visually. In half of the known cases, viral warts in the oral cavity were located on the tongue. Another favorite localization is the palate, less often papillomas are found on the inner surface of the cheek, on the bottom of the oral cavity or on the gums. If you accidentally bite a wart, it bleeds.
Anogenital viral condylomas (pointed warts) appear in people who are sexually active. They spread through all types of sexual contact, are painless, and are often discovered during examinations for other reasons, since isolated lesions in hard-to-reach places can remain there unnoticed for a long time.
Viral warts in children and adolescents usually belong to the vulgar varieties. At this age, they often appear on the thin skin of the hands, papillomatosis of the oral cavity occurs, palmar-plantar warts, growths on the face appear. There are sometimes quite a lot of them. Parents often associate the appearance of growths with acute respiratory viral infections, flu, tonsillitis suffered the day before, that is, a temporary decrease in immunity. In most cases, viral warts in children and young people disappear just as unexpectedly as they appeared.
Complications and consequences
Most often, such growths itch, and involuntary scratching can cause damage and bleeding. Palmar-plantar growths can cause discomfort and pain. Formation under the nail - its separation from its bed (onycholysis). Sometimes, although in rare cases, when the wart is damaged, another infection joins - mycosis or bacterial.
Large clusters of genital warts can block a woman's birth canal.
Also, quite rarely, with constant trauma to the formation, malignant degeneration of keratinocytes is possible. [ 9 ]
Diagnostics viral wart
A viral wart has a fairly characteristic appearance and when it is located on visible surfaces, a diagnostic conclusion is made based on anamnestic data and external examination.
If atypical growths are detected, scraping, biopsy and analysis of biological material are performed to confirm the presence of fragments of papillomavirus DNA using the polymerase chain reaction method.
Instrumental diagnostics are not used, except for differentiation of diagnosis (dermatoscopy), taking biopsies from inaccessible places, for example, colposcopy, or to assess the general condition of the patient at the discretion of the doctor.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics are carried out with other diseases of the epidermis - syphilis, neoplasms, mixed skin infections, fibrous polyps, hyperplastic changes caused by chronic somatic diseases.
Who to contact?
Treatment viral wart
Treatment for papillomavirus infection and warts should be prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient and establishing the origin of the growths on the skin. You should not remove warts on your own, since any neoplasm is likely to become malignant. [ 10 ]
Currently, preference is given to conservative methods of treating viral warts.
For example, when treating various types of warts on thin and thick skin, local treatment is used by rubbing ointments with antimitotic, antiviral, keratolytic, and caustic components into the formations. [ 11 ]
Depending on the size, location and number of growths, and the individual sensitivity of the patient, the doctor may prescribe a variety of ointments for viral warts.
Fluorouracil ointment 5% (cream). Its active ingredient fluorouracil is a cytostatic that inhibits the enzymatic activity of thymidylate synthetase, which catalyzes the process of cell division. When the ointment is applied to a wart, the sequence of cell proliferation in the growth is disrupted by blocking the synthesis of viral DNA. Active metabolites accumulate in the tissues of the wart, block cell division in the growths, causing them to disappear. The product also effectively prevents relapses and malignancy.
The drug is very toxic, so even when applied locally, you must strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions. It is strictly contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. Even external use can cause weakness, dizziness, dyspeptic disorders, anorexia, and heart problems. Baldness from local short-term use of the cream is unlikely, but the areas of application must be protected from sunlight. The drug is a prescription drug.
For viral warts, apply the cream with a spatula (cotton swab) in a thin layer directly onto the growth before going to bed every day for seven days. According to another, more gentle scheme, the ointment can be used once a week for ten weeks. In any case, it is necessary to periodically scrape off dead wart particles.
To treat genital or anal condylomas, the ointment is applied directly to the growths or tampons soaked in the ointment are inserted intravaginally.
Colchamine ointment 0.5%. Its main antitumor component is colchamine, an alkaloid of plant origin. It has cytostatic activity. The ointment also contains thymol, an antiseptic and preservative, as well as synthomycin, a component with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Contraindications and precautions for using the ointment are similar to the previous one. It is not recommended to apply Colchamine ointment to mucous membranes, it also contains ethyl alcohol.
The ointment is applied to the skin growths with a spatula once a day for 7-10 days, covered with gauze and sealed with a plaster. Dressings are done daily, simultaneously removing necrotic parts of the wart.
When using ointments with antimitotic activity, it is recommended to periodically monitor the blood composition, as they can cause leukopenia.
Viferon ointment. This product is a stimulant of local immunity, inhibits transcription of viral DNA and due to this action prevents the reproduction of viruses, helping the body to cope with warts of any localization. Tocopherol acetate, which is part of the ointment, due to the ability to stabilize cell membranes and bind free radicals, increases the effectiveness of interferon several times.
The ointment is applied to the affected skin and mucous membranes every 12 hours, i.e. twice a day. Suitable for long-term use. The ointment is applied in a thin layer using a spatula, allowed to soak in and dry. There is no need to remove the remaining ointment.
Oxolinic ointment 0.25% also has antiviral activity, it produces a gentle effect, which allows it to be used for warts of any localization, even on the delicate skin of the face and mucous membranes. However, many experts question its effectiveness. The ointment is applied to the growths and the skin around them two to three times a day. The treatment process is long - from two weeks to two months.
These antiviral ointments have virtually no contraindications, except for hypersensitivity. Reactions are usually limited to a burning sensation at the site of application. It is believed that they can be used by pregnant women and children of any age.
Salicylic ointment: for more delicate skin - 2%, for rougher skin (on the soles) - 5%. The product works due to the keratolytic (exfoliating) properties of salicylic acid. It is not recommended for use by pregnant and lactating women and children under twelve years of age. The ointment can cause burns, so it should be used with caution.
Warts are removed as follows. The limb with warts is steamed in a hot bath. This is especially true for neglected palmoplantar warts or large dry warts. Dry and apply a thin layer of salicylic ointment with a spatula. Small growths on thin skin are simply smeared with ointment without steaming.
Apply a gauze bandage. After about 12 hours, remove the bandage and carefully scrape off the top peeling layer of the wart, then apply the ointment again and cover with a bandage (you can use adhesive tape) for the next 12 hours.
The process of removing warts, especially large ones, is quite lengthy, about a month, and requires daily effort.
To speed up the process, you can combine the use of 5% salicylic ointment with tebrofen (3%). The treatment regimen is the same, only first the exfoliating salicylic ointment is applied to the wart, then, after waiting about a quarter of an hour, tebrofen, which has antiviral activity, is applied on top. It is used independently to remove viral warts in children.
Tretinoin cream 0.05% based on retinoids is used to remove warts on the face. Before treatment, the skin area with warts is thoroughly washed with soap, dried well, then a pea-sized amount of cream is applied to each wart. The procedure is done daily before bedtime. When going outside, protect the treated skin from direct sunlight. In general, this precaution should always be observed, even if it is not indicated in the instructions.
To remove viral warts, not only ointments are used, but also solutions of caustic substances: solcoderm (nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acid and copper trihydrate), betadine (contains iodine), trichloroacetic acid, verrukatsid. Freezing solution cryopharma. The destructive action of solutions is more effective, however, burns and scars with their careless use are also more likely.
There are patches and pencils for treating warts; phonophoresis with interferon is used.
In a medical institution, bleomycin sulfate injections are used to treat large warts. This is a drug with pronounced cytostatic activity. Injections are made directly into the wart. Often one procedure is enough, sometimes it is necessary to make several injections at intervals of three to four weeks. Cytostatics are very toxic drugs, even their local use can lead to a number of complications. Therefore, the possibility of this treatment, the effectiveness of which is high (estimated at 92%), should be discussed with the attending physician.
When treating viral warts, systemic agents that increase the body's immunity are also used, for example, vitamin and mineral complexes, Immunal, Echinacea-Ratiopharm, Immunoplus.
Folk remedies
Viral warts have caused physical and moral discomfort to people at all times. Therefore, there are many folk remedies for their removal. Opinions on their effectiveness vary greatly, however, many very quickly get rid of the growths.
Herbal treatment is mainly used. However, it should be taken into account that the herbs and grasses that can remove warts are poisonous. Therefore, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a herbalist and all recommended precautions should be observed.
Perhaps the most famous and simple remedy for removing warts is fresh celandine juice. In the summer, you need to pick a branch of the plant, a bright yellow liquid will appear on the cut. It is used to lubricate the wart. This treatment should be carried out daily, however, it is possible only in the summer and in places with direct access to the plant, for example, in the country or in the countryside.
You can squeeze the juice out of celandine and dilute it with a small amount of alcohol as a preservative. This solution can also be used to lubricate growths on the skin.
Apple cider vinegar and regular vinegar not only have exfoliating properties, but also virucidal ones.
Even more effective is vinegar essence. It can burn out a wart in one application, but you should be very careful. The skin around it should be lubricated with Vaseline and the essence should be dropped strictly on the neoplasm. It will turn white, loosen, then shrink, darken and fall off.
Many people claim that if you cover a wart with a regular bandage, it will also disappear.
In folk medicine, the following ointment is used to combat warts: two parts of green walnuts, thoroughly crushed, are ground with one part of kerosene. Infuse for a month, squeeze out the resulting liquid. Warts are regularly lubricated with it at least twice a day. They should disappear in about a week.
Also, daily applications of garlic gruel are made, which are applied to the growths under a bandage before going to bed.
In addition, eating vegetables and fruits, freshly squeezed juices from them, vitamin teas from rose hips, leaves and shoots of raspberries and currants, citrus fruits, sprouted grains of buckwheat, wheat and other cereals will help strengthen the immune system, and warts will disappear on their own.
Traditional methods of treatment have helped many people get rid of skin growths, however, before resorting to such treatment, you need to make sure that you have a viral wart and not a malignant neoplasm.
Homeopathy
Hard palmoplantar warts, dry and keratinized require the prescription of Antimony Sulfide (Antimonium crudum). This drug can also be prescribed for growths in other locations - in the nasopharynx, anogenital area.
For papillomatosis of the oral cavity and throat, silver nitrate (Argentum nitricum) is prescribed; for anal condylomas -
hemp (Cannabis), juniper (Sabina); for genitals: for men - more often club moss (Lycopodium), red mercury sulfide (Cinnabaris), for women - juniper (Sabina), gonorrheal nosode (Medorrhinum).
For flat juvenile warts, Celandine (Chelidonium), Nightshade (Dulcamara), Iron (Ferrum metallicum) are indicated; for weeping and itchy warts,
Nitric acid (Nitricum acidum), Thuja (Thuja).
When treating viral warts, many drugs are used, the correct prescription should be made by a doctor who will take into account not only their type and location, but many other symptoms and characteristics of the patient, and also determine the necessary dosage. Then the treatment will be successful and fast.
Removal of viral warts
The most effective and fastest method is destructive therapy. Surgical removal of viral warts with a scalpel is usually resorted to only in cases of atypical formations requiring histological examination. [ 12 ]
If the origin of the growth is not in doubt, then radical methods of removing neoplasms that do not involve surgical interventions are recommended.
Electrocoagulation is the removal of warts with a needle electrode by means of high-frequency currents, or simply cauterization. Allows you to remove several not very large growths in one session. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes. Dry crusts remain in place of the removed warts, which fall off on the second or third day after the procedure. It is considered a fairly gentle method, used on the face and any other accessible places.
Cryodestruction (freezing with liquid nitrogen) - a cryoprobe with a nozzle of the required diameter is pressed tightly against the neoplasm for a period of one to five minutes. If necessary, for example, a large growth, the removal of a viral wart with liquid nitrogen is repeated a week or ten days after the previous procedure. [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
More modern methods include laser removal of viral warts, i.e. their layer-by-layer evaporation. The duration of the procedure, as in other cases, depends on the size and number of warts. It is possible to get rid of all the formations in one session.
Another modern method is radiosurgical destruction using high-power electromagnetic waves that cause tissue destruction at the site of contact with the radio knife electrode. [ 15 ]
The last two methods can result in scarring where large warts are removed.
After removal, the patient is prescribed a course of antiviral drugs to prevent recurrence of the disease.
No method guarantees that warts will not reappear. Firstly, you can become infected again, and secondly, apparently healthy surrounding tissues could be infected.
Prevention
The best method of preventing HPV infection is to strengthen the immune system, then even if warts do appear, they will be isolated and will disappear on their own after some time.
A healthy lifestyle, good nutrition, and adherence to generally known sanitary and hygienic standards – there is no other prevention today.
Forecast
In most cases, our immune system copes with the human papilloma virus on its own.
If the warts do not go away and their number increases, then you need to see a doctor about this problem. Modern medicine, although it does not guarantee complete eradication of the virus, has an extensive arsenal of means to provide assistance in cases of infection.

