All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Pills for skin fungus
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
Fungal skin lesions are no less common than viral or infectious diseases. Currently, more than 400 varieties of fungi are known that can provoke the development of diseases of the skin and mucous tissues, as well as internal organs. However, modern medicine successfully fights fungal infections using antifungal agents for external and oral use. Creams and ointments act locally when applied to superficial tissues. Tablets for skin fungus have a systemic effect, destroying the infection not only from the outside, but also from the inside of the body.
ATC classification
Pharmacological group
Pharmachologic effect
Indications skin fungus pills
Tablets for skin fungus are intended for the treatment of various types of fungal diseases caused by opportunistic and pathogenic fungi.
- Keratomycosis is a disease of the superficial epidermal layer, stratum corneum and cuticle, without an inflammatory process. Keratomycosis, in turn, is divided into the following types of pathologies:
- versicolor lichen;
- nodular trichosporia.
- Dermatophytosis is a fungal infection of the deep layers of the skin, right down to the appendages of the skin. Dermatophytosis includes:
- Candidiasis is the most common fungal disease that affects the skin, appendages and even internal organs.
- Mycoses are fungal infections of the skin and underlying tissues. The most well-known mycoses are:
- blastomycosis;
- maduromycosis;
- sporotrichosis;
- chromomycosis;
- coccidioidomycosis;
- rhinosporidiosis;
- histoplasmosis.
- Trichomycosis is a fungal infection caused by the fungi Microsporium and Trichophyton.
- Actinomycosis is a disease caused by opportunistic ray fungi.
Dosing and administration
In most cases, at the initial stage of antifungal treatment, the doctor prescribes external medications: ointments, creams, gels. If local treatment does not have the expected effect, then in such a case, tablets are connected and complex therapy is carried out.
Below we offer you a schematic list of the most effective and common tablets for skin fungus.
Tablets for fungus of skin appendages
Itraconazole
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Synthetic tablets for skin fungus with a wide spectrum of activity. The drug is most accessible when taken immediately after meals. The maximum concentration in the blood is detected within 3-4 hours. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
It can be prescribed only for systemic fungal infections when the risk of damage to the fetus exceeds the degree of toxic effect of the drug. |
Contraindications for use |
Allergy. |
Side effects |
Bowel disorders, nausea, hepatitis, headaches, allergies, menstrual irregularities in women. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
The treatment regimen is determined individually. The average dose of the drug is 0.1 to 0.2 g once a day. The treatment is long-term, up to several months. |
Overdose |
No information. |
Interactions with other drugs |
Do not use in combination with terfenadine, midazolam, cyclosporine, vincristine, digoxin. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
Store for up to 2 years at room temperature. |
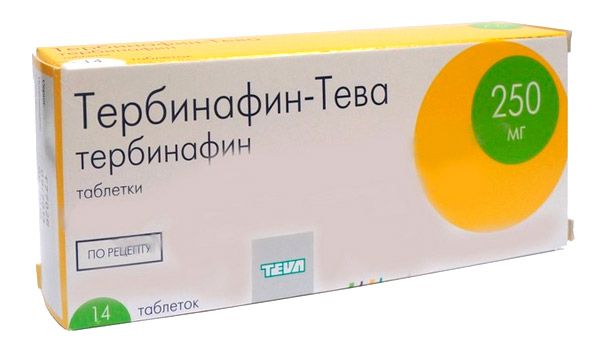
Terbinafine
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Tablets from fungus, representative of allylamines. Well absorbed from the digestive tract, bioavailability is about 50% (regardless of food intake). |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
Clinical data on the use of pills during pregnancy are insufficient to call the drug absolutely safe. Therefore, it is not recommended to take pills for fungus during this period. |
Contraindications for use |
Allergy. |
Side effects |
Allergic reactions, anxiety, depression, taste disturbances, numbness of the extremities, headaches, changes in appetite, hearing and vision impairments, feeling of fatigue. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
Tablets are taken 1 tablet (250 mg) once a day. The average duration of therapy is up to 4-6 weeks. |
Overdose |
Headaches, bouts of nausea, dizziness. |
Interactions with other drugs |
Combination with fluconazole, rifampicin, cyclosporines, and caffeine is undesirable. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
Store for up to 4 years at room temperature, out of reach of children. |
 [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ]
[ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ]
Tablets for foot skin fungus
Ketoconazole
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Antifungal tablets related to imidazole derivatives. The maximum concentration is detected one and a half hours after taking the drug. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
The tablets are contraindicated during pregnancy. |
Contraindications for use |
Possibility of allergy, severe kidney and liver diseases, pregnancy and breastfeeding. The product is not used in pediatrics. |
Side effects |
Abdominal pain, dyspeptic disorders, headaches, impaired consciousness, sleep disorders, allergies, fever, gynecomastia, decreased sexual desire. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
The tablets are prescribed in the amount of 200 mg per day at one time, with food. The duration of antifungal therapy depends on the specific disease. |
Overdose |
There is no description of overdose, however, a certain increase in side effects is allowed. |
Interactions with other drugs |
It is not advisable to take tablets together with antacids, anticholinergic drugs, beta-blockers, isoniazid, rifampicin. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
The drug can be stored for up to 2 years under normal conditions. |
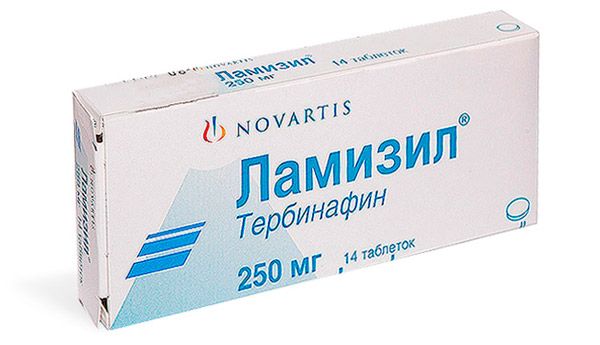
Lamisil
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Antifungal tablets based on terbinafine. Fungicidal activity begins to manifest itself within an hour and a half after internal administration of the drug. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
There have been no full-scale studies on the negative impact of the drug on pregnancy and the fetus. For this reason, taking pills for skin fungus is not recommended for pregnant women. |
Contraindications for use |
Possibility of allergic reaction. |
Side effects |
Anemia, allergic reactions, loss of appetite, anxiety, taste disturbances, headaches, vertigo, taste disturbances, vasculitis, pancreatitis. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
Take 1 tablet (250 mg) once a day. |
Overdose |
Overdose may be accompanied by headache, nausea, stomach pain. |
Interactions with other drugs |
Combination with cimetidine, fluconazole, rifampicin is not recommended. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
Store for up to 3 years at room temperature, out of reach of children. |
Tablets for hand skin fungus
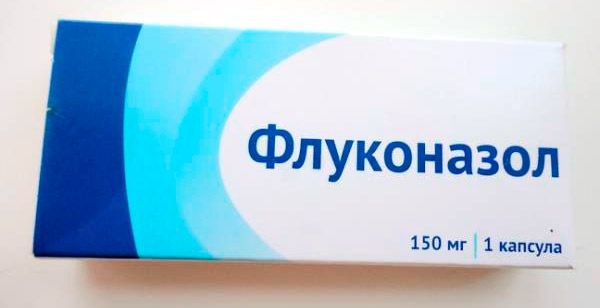
Fluconazole
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Tablets for fungus, are derivatives of triazole. The active substance penetrates into all tissues and fluids in the body. Bioavailability is equal to 90%. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
Fluconazole treatment should be avoided during pregnancy. |
Contraindications for use |
Allergy to fluconazole drugs, pregnancy and breastfeeding. |
Side effects |
Dyspeptic disorders, liver intoxication, skin rashes, allergic reactions, jaundice, tachycardia. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
The average dosage of tablets is 100-200 mg per day. |
Overdose |
No cases have been described. |
Interactions with other drugs |
Interaction with terfenadine and cisapride should be avoided. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
Tablets can be stored for up to 2 years in a dry place. |
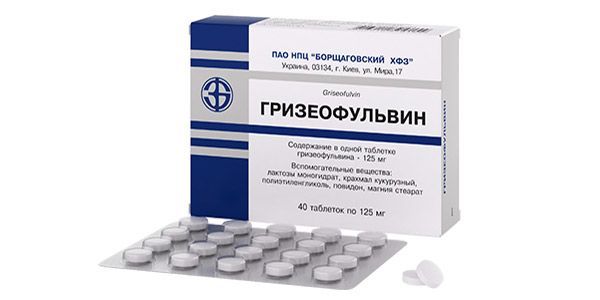
Griseofulvin
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Fungistatic tablets with a cumulative effect, which virtually eliminates the development of fungal resistance. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
The tablets are not used during pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects in the fetus. |
Contraindications for use |
Potential for allergies, significant degree of leukopenia, systemic blood diseases, severe kidney and liver pathologies, autoimmune diseases, malignant tumors, lactase deficiency. |
Side effects |
Dyspeptic disorders, allergies, migraine-like headaches, fatigue, anxiety, depression, renal dysfunction, menstrual irregularities in women, arrhythmia, aversion to alcoholic beverages, eye pain, stomatitis, fever, swelling, muscle pain. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
The tablets are taken 0.5 g twice a day, immediately after meals, with a small amount of vegetable oil (1 teaspoon). |
Overdose |
It didn't happen. |
Interactions with other drugs |
The drug should not be combined with barbiturates, sedatives, alcohol, or contraceptives for internal use. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
The tablets are kept in a place out of reach of children's pranks until the age of 4. |
Tablets for skin fungus in children
Diflucan
|
|
Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics |
Tablets, triazole derivatives. Possess good digestibility and bioavailability. |
Using Skin Fungus Pills During Pregnancy |
A short course of treatment is allowed only in cases of extreme necessity. |
Contraindications for use |
Possibility of allergy. |
Side effects |
Headaches, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, allergic rashes, sleep disorders. |
Method of application and dosage of tablets for skin fungus |
Tablets can be prescribed to children from 5 years of age, in the amount of 3-6 mg per kilogram of body weight per day. |
Overdose |
Disorders of consciousness, disorientation, hallucinations. |
Interactions with other drugs |
Do not prescribe together with erythromycin, quinidine, cisapride, astemizole, pimozide, terfenadine. |
Storage conditions and shelf life |
The drug does not require special storage conditions. It can be stored in the original packaging for up to 5 years. |
Fungal diseases generally require a long course of antifungal therapy. Therefore, the outcome of the disease largely depends on the patient, or rather, on his patience and self-discipline. In order to effectively get rid of skin fungus, it is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations and carefully follow the prescribed treatment regimen. In addition, it is also important to follow the rules of hygiene and sanitation, otherwise re-infection is possible. If you stop taking the pills before the time prescribed by the doctor, then more persistent fungal variations may form, which will be much more difficult to destroy. Remember: for successful treatment, it is very important to take pills for skin fungus exactly as prescribed by the attending physician.
Attention!
To simplify the perception of information, this instruction for use of the drug "Pills for skin fungus" translated and presented in a special form on the basis of the official instructions for medical use of the drug. Before use read the annotation that came directly to medicines.
Description provided for informational purposes and is not a guide to self-healing. The need for this drug, the purpose of the treatment regimen, methods and dose of the drug is determined solely by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous for your health.