
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
A white mole
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
An amelanotic nevus, or, in common parlance, a white birthmark, is a small round or oval spot with clearly defined borders. A white birthmark, unlike other types of birthmarks, is formed as a result of not an increased, but a decreased content of melanocytes in the skin.
An amygdala is considered one of the types of benign neoplasms. It does not disappear on its own, but, as a rule, it does not cause any particular discomfort.
Causes white mole
White moles are a consequence of decreased activity of skin cells responsible for the production of pigment - melanin. Such formations usually differ in size and shape, as they can be large, small, smooth or ellipsoid.
In children, the appearance of non-pigmented moles is most often congenital, which is associated with a failure in the process of melanoblast movement during the intrauterine period.
The appearance of white spots in adult patients may indicate a dermatological disease - vitiligo. Another name for the disease is achromia, the causes of which may be the following:
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- neuroendocrine disorders (diseases of the endocrine glands);
- pathologies of the autonomic nervous system;
- mental trauma, stress;
- autoimmune diseases.
Frequent stress, toxic substances, mechanical damage to the skin, as well as a lack of vitamins and microelements in the skin layers play a huge role in the development of the disease.
If an initially dark mole has become white, the cause may be either a disruption in pigment formation in melanocytes or malignancy of the birthmark, that is, its degeneration into a malignant tumor.
In the event that the lightening of a mole is accompanied by its rapid growth, the appearance of unpleasant sensations (pain, burning) or a change in shape, it is imperative to consult a doctor - a surgeon or a dermatologist.
Pathogenesis
Melanin, the dark pigment of the skin, is formed in melanocyte cells from a special amino acid, tyrosine. Tyrosine enters the human body with food and is produced by the liver from phenylalanine. This transformation can only occur with the participation of tyrosinase, an enzyme containing copper and facilitating the conversion of the amino acid into melanin.
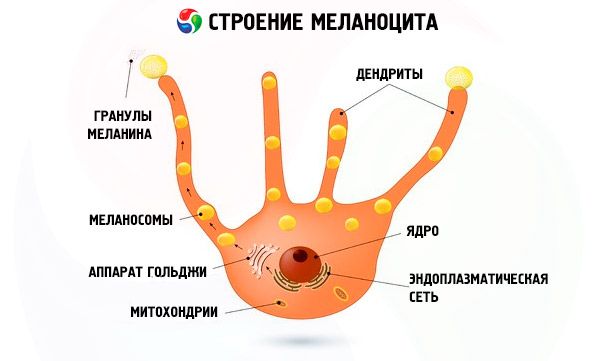
The following stages are distinguished in the formation of melanin:
- melanocytes receive a command from nearby cells to produce the enzyme tyrosinase;
- conversion of tyrosine to melanin;
- transportation and absorption of melanin in cellular structures.
The amount of melanin absorbed by cells may depend on the organism itself, on race, on the frequency and power of solar radiation.
Malfunction of melanocytes or their destruction can lead to a decrease in the level of melanin in epidermal cells, which is the impetus for the appearance of white moles.
Symptoms white mole
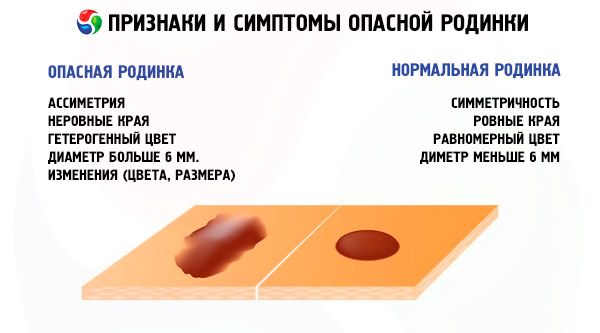
A white mole is noticeably different from an ordinary mole and has the following characteristics:
- the surface of the mole is not hard, but pliable;
- the shade of the spot may be lighter than the surrounding skin;
- the outlines of the formation are smooth and clearly defined;
- there are no signs of surrounding inflammation.
A frequently protruding white mole may resemble a flat wart in appearance, or be similar to a raspberry - for example, this is what white hanging moles look like. The neoplasm can be either single or multiple on the body.
The size of the mole is from 2 mm to 20 mm. Upon closer examination, a capillary network or small brown dots can be found inside it.
The first signs are the appearance of a small spot on the skin, which gradually fades. The rate of growth of a mole may depend on the individual characteristics of the body and the degree of pigment metabolism disorders.
White moles on the skin most often appear on the neck, in the armpits, on the external genitals, on the chest. Less often, they can be found on the stomach or limbs.
White birthmarks in a child can appear from birth, or from 2-3 months of age and up to 10 years. Usually, these are benign formations that do not pose a danger to the baby. Congenital birthmarks can increase in diameter over the years, as the body itself grows. If there are no other signs of malignancy, then this is a normal variant and does not require any treatment.
Complications and consequences
The only possible dangerous consequence of a white mole is its malignancy. This complication occurs rarely, but it is important to remember. This is especially true for those patients who are at risk:
- owners of congenital large white moles;
- people who developed moles after 60 years of age;
- owners of white spots larger than 30 mm in diameter;
- owners of multiple white birthmarks (several dozen or more).
Moles that are constantly exposed to injury or contact with clothing, or the periodic appearance of new growths on the body are also considered risk factors.
For example, if a white mole becomes crusty or bleeds, and this is not due to recent injury
Diagnostics white mole
Before starting the diagnosis, the doctor will first ask the patient about the time of the mole's appearance, its possible modifications, and other signs that may bother the patient.
During the examination, the doctor should pay attention to the appearance, shape, diameter of the birthmark, as well as the features of its development or location.
In most cases, additional diagnostic tests may be required to make a definitive diagnosis.
- The tests are prescribed to refute the transformation of a mole into melanoma. When a cancerous tumor develops, specific tumor markers can be detected in the patient’s blood – TA90 and SU100.
The doctor also takes a smear from the surface of the neoplasm. This analysis is especially relevant in the presence of bleeding, bloody discharge or ulcers on the surface of the birthmark. The material taken during the procedure is subjected to a thorough examination, which helps to determine the nature and degree of danger of the birthmark.
- Instrumental diagnostics includes, first of all, fluorescent microscopy - this is an examination of a mole under multiple magnification, directly on the patient's body. A special oily liquid is applied to the spot beforehand, which potentiates the pigment's reflection. The fluorescent microscopy method is considered one of the most accurate and comfortable procedures for the patient.
In addition to microscopy, computer studies may be prescribed – layer-by-layer examination of the mole using a monitor, with subsequent saving of the image on film.
In addition to the above, the direct removal of the birthmark also serves as a diagnostic method. After the operation, the birthmark is necessarily sent for histology - this is done in order to determine with 100% certainty whether the process is malignant or benign.
Who to contact?
Treatment white mole
Prescribing any medications for white moles is practically inappropriate, since it is impossible to slow down or block the development of a benign tumor. The only effective treatment is the removal of the mole by surgery or other available methods.
Is it possible to remove a white mole? And what is the best way to do it?
Before deciding to remove a birthmark, it makes sense to first consult a doctor and undergo the necessary diagnostics. This is done in order to know exactly what kind of neoplasm you will have to deal with. If the doctor recognizes the removal of a white birthmark as possible, then you can use one of the proposed methods.
- The surgical method is the removal of the neoplasm using a scalpel. This type of surgery is especially common in small hospitals and clinics that lack the necessary equipment for other resection methods. In some cases, surgery may be indicated for other reasons, such as removing a large mole.
During the operation, local anesthesia is used in most cases. Small white moles are removed completely, while large neoplasms sometimes have to be excised in parts.
- The cryodestructive method is getting rid of a white mole by freezing it with liquid nitrogen or carbonic acid. The method is quite effective and painless, and does not require anesthesia. However, sometimes it is not possible to remove a spot with cryodestruction in one procedure. Repeated sessions are required.
- The electrocoagulation method is the removal of a neoplasm with an electric knife or electrocoagulator. The procedure may cause some discomfort for the patient, as it is painful and requires local anesthesia. Electrocoagulation is used only to remove small white moles.
- Laser removal is the most common method of getting rid of the hated neoplasm. Laser radiation allows you to accurately outline the tumor borders, practically without affecting the surrounding tissues. In this case, no scars or burn surfaces are formed. Laser removal can be used for small moles.
- The radiosurgery method is the use of the Surgitron device (radioknife), which can remove a tumor with a beam of directed radio waves. This method is relevant if the benign nature of a white birthmark is reliably confirmed. The radioknife is effective and safe, but is not used to remove large-diameter nevi.
Folk treatment of white mole
Herbal and other folk remedies should be used very carefully so as not to harm or provoke malignancy of the mole. The ideal option is traditional treatment in a medical center by a specialist, with mandatory histological examination of the removed mole.
It is not advisable to use the suggested folk remedies without prior consultation with a doctor.
- Take fresh celandine juice, spread it over the surface of the white birthmark and cover it with a bandage or plaster. Repeat the procedure 3 times a day until the nevus falls off.
- First, lubricate the birthmark with garlic juice, and immediately after that with lemon juice. Repeat the procedure 3 times a day for 7-10 days.
- Apply the juice of unripe figs to the stain once a day.
- Prepare a mixture of grated chalk and hemp oil (proportion 1:4). The prepared mixture is applied to the mole several times a day for 7-110 days.
- Prepare a tincture with two cloves of garlic per 200 ml of apple cider vinegar (infuse for 14 days). The resulting medicine is used for compresses at night.
- Mix equal parts of honey and castor oil. Apply the resulting mass to the birthmark for 10 minutes twice a day, then rinse with water.
It is also recommended to undergo liver cleansing treatment: this helps to improve the pigmentation process.
Prevention
There are no specific methods for preventing the occurrence and malignancy of white moles. However, people who are prone to pigment metabolism disorders are advised to adhere to the following rules:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially at midday, when solar radiation is most active;
- do not use a solarium;
- do not rely on cosmetics to protect your skin: such products protect against sunburn, but do not prevent melanoma;
- If new moles appear, or if the appearance of birthmarks changes, you should consult a specialist.
Also, you should not touch the mole without need, especially not press on it or intentionally damage it with chemicals. If the formation is frequently injured by clothing or accessories, you should visit a doctor and discuss with him the possibility of removing the mole.
Forecast
The prognosis can be favorable if the patient regularly pays attention to the condition, color, shape of moles, records possible changes and consults a doctor in a timely manner. In most cases, a white mole exists on the skin for a long time without bothering its owner.
 [ 16 ]
[ 16 ]

