
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Otitis externa: acute, chronic, purulent, diffuse otitis media
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 12.07.2025
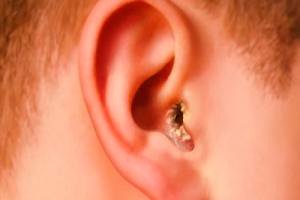
Causes otitis externa
The reason for the onset of inflammation of the outer ear is an infection.
In addition, any small wounds, scratches and cuts that may occur during ear wax cleaning with unsuitable objects (matches, toothpicks, hairpins, pens, etc.) can become open gates for infection.
Most often, the causative agent of external ear inflammation is staphylococcus.
In addition to it, the following can become provocateurs of this pathology: Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Moraxella, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Candida fungi.
Risk factors
The occurrence of damage to the outer ear is facilitated by:
- Childhood (in this case, eczema contributes to this, which is characterized by peeling and the occurrence of erosions);
- A plug of sulfur (as this increases the likelihood of cleaning it yourself);
- Narrow ear canals;
- Chronic inflammation of the middle ear (as a result of this, pus is consistently found in the ear canal);
- Reduced immunity (for example, in diabetes).
Pathogenesis
Most often, external otitis becomes a complication of acute respiratory infections (viral or bacterial). The pathogens of acute respiratory infections penetrate the ear cavity and contribute to the development of inflammation. But this is not always the case. Sometimes the pathogens of ear inflammation and at the same time ongoing inflammation of the nose and nasal sinuses, pharyngeal tonsil and pharynx are completely different. This can happen because against the background of a weakened acute respiratory infection of the body, a person becomes sensitive to various microorganisms (cocci, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ), which in a healthy person will not cause absolutely any symptoms.
Symptoms otitis externa
The occurrence of the following symptoms is a reason to immediately contact a doctor:
- Ear pain of varying intensity. It may increase if you press on the tragus (a cartilaginous process that limits the entrance to the acoustic canal) or pull the patient's ear;
- Feeling of congestion;
- Decreased hearing acuity. Feeling of "water in the ear";
- Discharge from the ear canal. Sometimes it can be purulent, or even with streaks of blood;
- The swelling of the ear is quite pronounced, making it impossible to use earplugs.
- Unpleasant odor coming from the ear;
- Poor general health, elevated body temperature (can reach up to 39C);
- The ear is inflamed and significantly enlarged in size;
- The ear may be covered with small red pimples, scratches or boils.
Ear pain with otitis externa
Pain is the main symptom of ear damage. Its severity can vary: from slight, almost imperceptible to very strong, almost unbearable. Manifestation is pulsation or "shooting". It is almost impossible to distinguish pain during inflammation of the outer ear from the middle ear without consulting medical personnel. The only difference may be the information that with external otitis, pain sensations should appear upon contact with the skin at the entrance to the acoustic canal.
Temperature in otitis externa
It cannot be said that the inflammatory process that affects the outer ear occurs without fever. After all, it is precisely with this pathological state of health that a “rise” in body temperature is very often detected, becoming a symptom indicating a deterioration in a person’s condition.
If a furuncle is detected, which is a characteristic sign of a limited form in the external auditory canal, then most likely there will also be an increase in temperature to 38-38.5 C. In children, the febrile reaction will be more acute.
In the case of the diffuse form of external otitis, the temperature is mostly at a subfebrile level (up to 37.9C). The general condition of the patient is practically not disturbed. And the temperature is not the main (predominant) complaint.
Swelling with inflammation of the outer ear
The inflammation that occurs as a result of infection contributes to the appearance of edema of the outer tissues of the external acoustic canal, and this serves as the source of the occurrence of other characteristic symptoms.
Ear congestion
People say that with this pathology they have a feeling of ear congestion and decreased functionality. They complain that their hearing is declining. This is explained by the fact that due to the damaging process, there is swelling of the auditory process, as well as an increase in the lymph nodes located in the ear area.
Otitis externa during pregnancy
If there is a possibility of an inflammatory process of the outer ear in a woman who is in the gestational period, she needs to immediately consult a doctor.
The doctor will carefully study the patient's medical history, as well as clarify the pregnancy period and examine the patient. The doctor will check for ear deformation, the degree of its pain and the presence of discharge. In addition, the doctor will evaluate the woman's lymph nodes.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a woman will need to take an ear sample for subsequent culture and determination of sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. If this pathology (severe course) occurs not for the first time, it is also worth taking a blood test for sugar and HIV.
Otitis externa in childhood
The appearance of otitis externa in a child can be determined by the following signs:
- he complains of pain in his ear;
- capricious;
- cries for no reason;
- he has a high temperature;
- the lymph nodes on the affected side may be enlarged;
- If you press on the child's tragus or pull on the auricle, the pain will intensify.
The doctor makes a diagnosis based on the child’s complaints and questioning.
The symptoms of this pathology are quite specific, so the doctor (especially after an otolaryngological examination) will not have any difficulty making a diagnosis.
But it is worth keeping in mind that to exclude complications and determine the cause of the pathology, smears from the ear, urine and blood tests can be taken. This will allow the most accurate diagnosis of the child. If the examination reveals an allergy as the cause of external otitis, a doctor with a specialization in allergology will be involved in the treatment.
A breastfed baby with this pathology will also become restless, will suckle poorly, or may refuse to eat altogether.
Forms
In adults, in most cases of the disease, unilateral otitis is detected on the right or left side. Symptoms and treatment regimen do not depend on the affected side.
 [ 23 ]
[ 23 ]
Bilateral otitis externa
Adults mostly suffer from unilateral damage to the outer ear. Bilateral damage is most often detected in children under three years of age. This is explained by the fact that the child's ear is still developing before this age and has not acquired the protective functions that are inherent in an adult ear.
External otitis has quite a few types. This helps to better differentiate this pathology and apply effective therapy. There are such types of the disease:
- Diffuse - characterized by global damage to the tissues of the auditory canal, sometimes involving the eardrum in the inflammatory process.
- Fungal - a rare pathology (about ten percent of all types of this pathology). A distinctive feature of this pathology is the normal state of health of the patient, who only feels itching or mild pain in the ear. During the examination, the doctor will find fungal contents of white or black color.
- Limited - the characteristic form of pathology in this case will be a carbuncle or furuncle. This occurs due to damage to the sebaceous glands or infection of hair follicles or abscesses (local), which can occur due to damage. The causative agent in this case is Staphylococcus aureus.
- Malignant - another name for this type is necrotizing. This is a very serious disease that affects not only the skin, but also the cartilage tissue of the outer part of the ear.
- Purulent - characterized by the appearance of discharge from the ear. At the beginning of the disease there is little pus, but as the disease progresses, its amount increases significantly.
 [ 24 ], [ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ]
[ 24 ], [ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ]
Acute otitis externa
The acute period of inflammation of the outer ear is characterized by severe pain. The patient may have a fever and blocked ears.
 [ 28 ]
[ 28 ]
Chronic otitis externa
Such a diagnosis may be given to a patient if the duration of the pathology is more than a month or there have been more than four relapses during the year.
The pathology can develop into a chronic stage if adequate treatment was not carried out in the acute form. Sometimes this can be facilitated by excessive cleaning of the ears with cotton swabs, as this contributes to the destruction of the protective layer of sulfur and damage to the tissues of the acoustic canal.
External otitis of diffuse type
External diffuse otitis is a purulent inflammation that spreads throughout the entire auditory canal, affecting the subcutaneous layer and the eardrum.
Symptoms:
- itching inside the ear;
- increased pain when pressing;
- reduction of the external opening of the acoustic channel;
- purulent discharge;
- increase in body temperature;
- general painful condition.
These symptoms will be weakly expressed or almost absent if the diffuse lesion becomes chronic. In this case, the patient may feel only slight discomfort in the ear area.
The hearing function is not impaired in this type of pathology. This distinguishes it from inflammation of the middle ear, in which the tympanic cavity is affected.
 [ 31 ]
[ 31 ]
External bacterial otitis
This type of pathology of the outer ear is a purulent lesion, the location of which is in the area of the external acoustic canal. It, like fungal with allergic otitis, refers to the diffuse type of pathology. But its cause in this case will be bacterial.
Bacterial otitis externa can occur in two stages: acute and chronic.
In the acute stage, the patient will complain of:
- Itchy skin;
- Purulent discharge;
- Sensitivity to touch, especially near the tragus;
- Narrowing of the ear canal due to swelling.
During the examination, the doctor will be able to see a mushy mass deep in the canal. But due to the pain, it is almost impossible to examine the patient.
In the chronic course of the pathology, the symptoms will be less pronounced. Here, first of all, the cutaneous thickening of the acoustic canal and the eardrum will be noticeable.
The diagnosis of external bacterial otitis is made on the basis of:
- Patient complaints;
- Anamnesis;
- Inspection.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may conduct a microbiological study.
 [ 32 ]
[ 32 ]
Fungal otitis externa
When the outer ear is affected by mold yeast-like fungi, fungal otitis occurs. Most often, this type affects the walls of the auditory canal, the skin lining the auricle, the eardrum and the middle ear. The causative agents are fungi of a certain type, mainly mold fungi.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must perform a visual examination. After performing it, he will see infiltration, inflamed skin and pathological discharge.
The main symptom of purulent lesions of the outer ear is various types of discharge from the ear. They may differ from each other:
- by color (for example, yellow, brown, gray);
- by quantity;
- by type (depending on the type of pathogen that caused this pathology).
In this case, unlike a purulent lesion, the discharge will not have a specific odor.
Limited otitis externa
This type of otitis externa is characterized by the presence of inflammation of the hair follicle in the form of a furuncle. It is noteworthy that if you look, the furuncle is not visible from the outside. The patient may only experience discomfort due to its presence. The person will feel pain, which will increase when chewing or biting. After a few days, the abscess fully matures and bursts, and the pain gradually goes away.
Eczematous otitis externa
This type of disease occurs as a result of dermatological damage to the skin of the outer ear. Most often, this type of eczema occurs in people who suffer from various skin diseases (for example, psoriasis or seborrhea ).
Symptoms of damage will be:
- The appearance of erythema;
- Exfoliation of the skin;
- Weeping skin segments;
- Cracks in the skin of the auricle and inside the external acoustic canal.
If the patient does not consult a doctor and does not begin treatment, the risk of infection and worsening of the disease increases significantly.
To treat this type of disease, Burow's solution (a solution of basic lead acetate) and hormonal drugs are usually used.
Malignant form of otitis externa
The malignant form of the disease is an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of infection or damage to the bones of the ear canal and the base of the skull.
Symptoms of malignant lesions of the outer ear will be:
- The presence of discharge from the ear, from yellow to yellow-green in color, persistent with an unpleasant odor;
- pain that the patient feels deep in the ears, which intensifies when moving the head;
- loss of hearing function;
- the presence of itching in the ear canal or in the ear;
- temperature rise;
- difficulty swallowing;
- loss of voice.
In this case, the doctor will examine the ear to detect symptoms of infection. A neurological consultation may also reveal that the cranial nerves are not affected.
If a drainage tube is inserted and the doctor sees discharge from the ear with blood or pus, he or she can send it to the lab for analysis. This is necessary to identify bacteria or fungi (most often pseudomonas).
The following procedures can also be used to diagnose this disease:
- CT, MRI of the head;
- radionuclide scanning.
Complications and consequences
Severe consequences of damage to the outer ear can be encountered quite rarely. If the disease has been neglected, or the patient has concomitant chronic diseases, the following pathologies may arise:
- Temporary hearing loss: The patient may complain of ear congestion, and as a result, a decrease in its function. This condition usually goes away after recovery;
- Re-infection of the outer ear (transition of the disease to a chronic stage): this can happen due to failure to follow all the recommendations given by the doctor and as a result of ineffective treatment. Also, this pathology is facilitated by the patient's reduced immunity;
- Destruction of the bones and cartilage of the ear (necrotizing form of otitis externa) - may occur as a result of the spread of infection, due to reduced immunity or special resistance of the pathogen that contributed to the occurrence of the disease. Most often occurs in the elderly category of patients or those suffering from diabetes mellitus.
- Infection of other tissues. In the necrotizing form of the disease, the infection can spread to neighboring areas, including the brain.
Diagnostics otitis externa
When a patient comes to a medical institution complaining of symptoms of inflammation of the outer ear, the doctor, in order to make a diagnosis, necessarily performs an otoscopy. It is done with the help of a special funnel, which is inserted into the lumen of the auditory canal. To do this, the doctor pulls the auricle up and back, thereby straightening the course of the auditory canal, and, having aimed a light, examines it.
The doctor will be able to see redness and swelling of the acoustic canal. Also, if the pathology is accompanied by a furuncle, you can see the pus that is released.
If otitis externa has become chronic, the doctor will notice a perforation of the eardrum, releasing pus.
Next, the doctor will take a sample of pus for examination and analysis of susceptibility to antibacterial agents.
 [ 41 ]
[ 41 ]
Survey
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional tests, for example:
- Urine analysis;
- Blood glucose test;
- Sowing of discharge from the external auditory canal.
Instrumental diagnostics
In this case, the following instrumental diagnostics can be used:
- Ear X-ray;
- CT;
- Radioisotope scanning;
- Scintigraphy;
- MRI.
Differential diagnosis
It is necessary to distinguish external otitis from diseases such as:
- Cranial neuralgia;
- Herpes zoster. Since this disease can be localized in the geniculate ganglion and show symptoms similar to otitis externa. With this pathology, a typical sign will be vesicular eruption, which can appear only one or two days after consulting a doctor. The name of this rather exclusive pathology of herpes zoster is Ramsay-Hunt syndrome. Facial nerve paralysis can also develop.
- Otomycosis may have the following characteristic features: a more intense itching in the ear than pain (with bacterial invasion - everything will be exactly the opposite), a large layer of plaque on the surface of the acoustic canal (white or gray), in which, upon detailed examination, there is a chance of detecting hyphae or fungal spores. To differentiate this type of pathology, a microbiological study of the discharge will be required.
- Purulent otitis media with a ruptured eardrum or an installed tympanostomy tube may be accompanied by discharge from the external acoustic canal. But in this case, the distinctive feature will be the absence of swelling and less pronounced pain. In this case, pneumatic otoscopy will be required to differentiate these diseases.
- In the necrotic type of pathology, the characteristic symptom will be a pronounced, disproportionate ear pain. In addition, granulation can be seen on the wall of the external acoustic canal, and sometimes on the eardrum. The patient will have an elevated temperature and symptoms of general malaise.
For diagnostics the following is mandatory:
- laboratory tests of blood and urine (to determine diabetes);
- X-ray radiological diagnostics;
- CT scan of the temporal and mastoid parts of the skull;
- MRI.
Differences between otitis externa and otitis media
To differentiate inflammation of the outer ear from the middle ear, you need to pay attention to hearing loss. If the patient has otitis externa, hearing may decrease, but will not disappear.
Otitis externa and furuncle
Due to infection (mainly staphylococcal), inflammation of the hair follicle or glandulae sebacea may develop in the bone-cartilaginous area of the ear, which manifests itself as a furuncle. In this case, surgical intervention will be required. The use of local antibacterial agents will not be effective.
Treatment otitis externa
Read about treatment of external otitis in this article.
Prevention
Most often, otitis externa passes without complications. The pain goes away in two to five days, and the person fully recovers in seven to ten days. In some cases, for complete recovery and to reduce the likelihood of relapse, a doctor may need to clean the outer part of the ear.
Improvement occurs after two or three days of taking antibacterial drugs. If this does not happen, the patient should see a doctor again to clarify the diagnosis.
In case of an abscess or chronic form of the disease, surgical treatment may be required. A consultation with a dermatologist is required for the eczematous form of otitis.
The likelihood of complications of external otitis is quite low. Cellulitis or lymphadenitis may appear, the treatment of which will require a course of systemic antibiotic therapy. The acute form of the disease can spread to the entire auricle and turn into chondritis, especially if the patient has recently had a piercing.
The development of malignant otitis externa is the only significant complication that occurs in diabetics, most often in combination with diabetic ketoacidosis, and people with reduced immunity.
Basically, this type of pathology is characterized by the spread of bacterial infection to the cartilage tissue of the auricle, with the occurrence of pain of great intensity and swelling, which are accompanied by a "rise" in temperature and other characteristic symptoms. This category of patients requires treatment in a hospital setting using not only local therapeutic agents, but also antibacterial ones.
 [ 47 ]
[ 47 ]

