
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
inguinal epidermophytosis
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
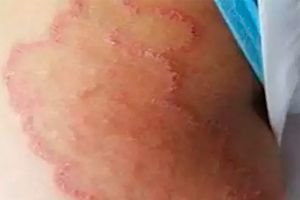
Causes inguinal epidermophytosis
The causative agent of this fungal infection is Epidermophyton floccosum, less often - Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagraphytes.
Infection of the groin area occurs in patients with athlete's foot, as well as through household items used by the patient (oilcloths, washcloths, underwear). Risk factors include hot, humid climate, tight trousers, obesity, and long-term treatment with topical corticosteroids.
Symptoms inguinal epidermophytosis
The process is usually localized in the inguinal folds, but can also occur in other areas of the skin (intergluteal fold, under the mammary glands). The disease is characterized by acute inflammatory symmetrical rashes, prone to peripheral growth. The lesions are rounded spots of red-brown color, polycyclic outlines. The marginal zone of the lesion, covered with vesicles, pustules, erosions, scales and crusts, in the form of a continuous ridge stands above the surrounding skin. The process is usually accompanied by severe itching, sometimes excruciating.
Inguinal epidermophytosis is chronic, becoming aggravated by irritating factors (for example, sweating) in hot weather.
 [ 4 ]
[ 4 ]
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
Who to contact?
Treatment inguinal epidermophytosis
In the acute period, lotions of 0.25% silver citrate solution, 1% resorcinol solution are used, hyposensitizing and antihistamine drugs are prescribed.
Of the local antifungal agents, zalain, lamisil, clotrimazole, pizoral, etc. are used. If external agents are ineffective, lamisil (250 mg/day for 14 days) and itraconazole (200 mg/day for 7 days) are prescribed.

