
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Cervical leukoplakia
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
Among the many gynecological pathologies, cervical leukoplakia occupies a special position. The factors causing this disease have not yet been fully clarified.
What is dangerous about cervical leukoplakia? Why does this pathology occur and how to get rid of it? We will talk about this and much more in this article.
Causes cervical leukoplakia
According to scientific research, there can be many causes of leukoplakia. These include previously present infections in the body, immune disorders, hormonal disorders, unqualified treatment of cervical diseases, trauma to the cervix during labor or artificial abortions, and other factors.
It is believed that the risk of developing leukoplakia in a woman with a menstrual cycle disorder or with an inflammatory pathology of the reproductive organs is several times higher than in others.
The development of the disease can be triggered by genital infections, viral lesions (including herpes), promiscuous sex life. Risk factors also include various medical procedures: the procedure of diathermocoagulation of erosions, curettage, installation of a spiral contraceptive.
Symptoms cervical leukoplakia
Simple leukoplakia of the cervix does not have any characteristic symptoms: the pathology is usually detected during a gynecological medical examination. However, some types of leukoplakia do have some signs, which, if detected, can be used to suspect the development of the disease.
A healthy cervix has an epithelial covering, like all skin. However, this covering is not capable of keratinization, due to which the cervix can stretch during labor. If the tissues do keratinize, this is a pathology and is called leukoplakia.
Focal leukoplakia of the cervix is a pathology in which a flat lesion appears, level with the mucous membrane. Such an area can only be detected during a colposcopy procedure. This is the most favorable form of leukoplakia, since structural abnormalities are observed only in the superficial layer of tissue. The lesion may appear isolated or in a group.
Extensive leukoplakia of the cervix can spread to other parts of the genitals: such spread is often observed on the vaginal vaults. Extensive pathology is close to malignancy, it can be combined with cicatricial changes and hypertrophy of the cervix. This form of leukoplakia can be accompanied by severe itching (especially at night during sleep), pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, the appearance of microcracks on the skin and a feeling of tightness.
Thin leukoplakia of the cervix is characterized by the appearance of the thinnest scales on the surface of the epithelium (a kind of thin films), which may not be noticed even during a preventive examination. To diagnose this form of pathology, additional laboratory tests may be required.
It is also possible to develop a warty form of the disease, which occurs as a consequence of simple leukoplakia. This complication manifests itself in the form of clear flaky areas of keratinization, resembling warts in appearance.
Cervical leukoplakia and pregnancy
Leukoplakia detected during pregnancy does not directly affect the process of gestation, embryo development and does not provoke the formation of pathologies in the fetus. However, some danger still exists for the woman herself: the disease can worsen, causing the development of more complex conditions, including degeneration into a malignant process. This is facilitated by a decrease in immunity, a change in the balance of hormones during pregnancy, as well as labor, during which the tissues of the cervix are subjected to serious mechanical impact, stretching and damaging.
Of course, if cervical leukoplakia was detected before pregnancy or during the planning process, it is necessary to get rid of the disease before pregnancy, although the pathology does not affect the conception process itself. Before IVF, leukoplakia is subject to mandatory preliminary treatment.
If the disease is not treated, the consequences of cervical leukoplakia can be serious: first of all, this is the appearance of atypical cells, which is the beginning of the malignant transformation of the process.
Where does it hurt?
What's bothering you?
Diagnostics cervical leukoplakia
Comprehensive diagnostics of cervical leukoplakia may include clinical, cytological and colposcopic examination. On an individual basis, the doctor may prescribe morphological, bacteriological and bacterioscopic analysis. The most indicative in this case are considered to be morphological studies and colposcopy.
The colposcopy method provides an opportunity to assess the nature and extent of the lesion, examine the general condition of the epithelial tissues in the vagina and cervix. A colposcope is the same microscope, but with a greater magnification, capable of examining the smallest changes in tissue structure.
During colposcopy, it is possible to perform the so-called Schiller test - a painless test that can help in adequate diagnosis. The essence of the method is to stain the surface of the cervix with 3% Lugol's solution (the solution consists of potassium iodide, pure iodine and distilled water). This method allows you to determine the absence of glycogen in the integumentary epithelium, which indicates atypical and non-standard areas of epithelial tissue. As a result of staining, healthy tissue becomes brown-dark, and the affected areas do not change their color.
Early diagnosis of the disease can be made on the basis of special smears from cervical epithelial tissue.
The cytological sample is taken using a special spatula or brush. At the same time, smears are taken from the area of the cervix located closer to the vagina, as well as from the lower part of the cervical canal. In the case of flat leukoplakia, such tests reveal keratin, groups of surface epithelial cells, and a large number of dyskeratocytes.
A biopsy of the cervix in leukoplakia involves the removal of a sample of the surface epithelium from the affected area, followed by cytological and histological examination. At the same time, it is possible to assess the extent of the pathology, check for the presence of degeneration and malignancy of tissues. In the case where histological analysis confirms dysplasia of the surface cover, the disease can be diagnosed as a precancerous stage of the process. The biopsy procedure is performed under local anesthesia using an electrocoagulation system.
Recently, the method of microcolpohysteroscopy has been successfully used for a thorough examination of the cervical tissue and cervical canal. This procedure is painless, it provides an opportunity to simultaneously assess the condition of the surface cover, determine the presence of atypical tissues and conduct a targeted biopsy.
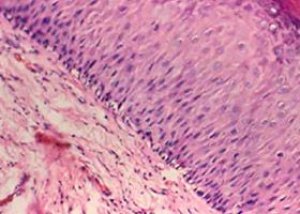
Macroscopically, leukoplakia appears as whitish plaques of various shapes and sizes, located against the background of an unchanged epithelial layer.
Keratinization of squamous epithelium is a consequence of increased functional activity of epithelial cells, which is absent under normal epithelial conditions.
The histological picture of leukoplakia is characterized by:
- proliferation of cells of the stratified squamous epithelium;
- its uneven thickening due to a significant increase in the number of intermediate (subulate) cells);
- acanthosis;
- incomplete keratinization;
- complete keratinization of the epithelium (parakeratosis);
- lymphocytic infiltration of the stroma.
Background processes include leukoplakia without signs of atypia of epithelial cells.
Leukoplakia and papilloma constitute a special form of cervical disease - dyskeratosis.
 [ 13 ]
[ 13 ]
What do need to examine?
What tests are needed?
Differential diagnosis
When differentiating cervical pathologies, it is necessary to pay attention to the type of damaged tissue. This may be epithelial tissue, connective tissue, or muscle tissue. The presence of trophic and innervation disorders also plays a role.
Cervical dysplasia and leukoplakia are similar pathologies that do not have any characteristic clinical picture. The latent course of the process, the absence of pain and external signs of the disease pose a danger of further progression of the pathology, as well as malignant degeneration of cells. Combined course of these diseases is also encountered, which in any case requires complex therapeutic measures.
Leukoplakia and cervical erosion also have some similar signs. However, erosion is a defect most often caused by chemical agents (detergents or medications, aggressive substances), mechanical damage. With this disease, the affected cervical area will be edematous and brightly hyperemic, with signs of bleeding. In addition, there may be complaints about the presence of minor bloody discharge, especially after sexual intercourse.
Who to contact?
Treatment cervical leukoplakia
Nowadays, many methods of treating cervical leukoplakia have been proposed. However, the best effect can only be achieved with a comprehensive approach to treatment, using several methods of therapeutic intervention at the same time. This can be drug and laser therapy, cold treatment and diathermocoagulation, and other methods.
In cases where leukoplakia is detected against the background of inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs, the first step is to eliminate the inflammatory reaction. For this purpose, antibiotics are prescribed (usually broad-spectrum), as well as antitrichomonal, antifungal, antiviral and antichlamydial drugs, according to indications, comparing the prescription of such drugs with the results of bacterioscopy or tests for the presence of viruses and chlamydia.
It is not recommended to prescribe drugs that affect metabolic processes in tissues and stimulate them. Such drugs (aloe, fibs, plasmol, sea buckthorn, rose hips) can increase proliferation and contribute to the development of dysplasia.
Chemical coagulation is very popular and effective. This method involves the use of a drug such as solkovagin - a chemical compound of acids of organic and inorganic origin, which serves as a coagulant of purely cylindrical epithelium, without affecting healthy tissues. This type of therapy is painless and effectively destroys altered tissues. According to statistics, the recovery of patients as a result of using such treatment is about 75%.
Cauterization of cervical leukoplakia is used quite often, but this method has several negative side effects. These include the development of implantation endometriosis, the risk of bleeding during rejection of coagulated tissues, the possibility of relapse or exacerbation of chronic ovarian inflammation, menstrual cycle disorders, a long healing period, and the risk of repeated tissue damage.
The most effective methods currently used to combat leukoplakia include cryotherapy and laser therapy.
Cold therapy (cryotherapy) promotes necrosis of affected tissues by exposure to low temperatures. The procedure is carried out by contact, usually once, for two to five minutes. The method is painless, the effect of such treatment is up to 95%. The only disadvantage of this method is the possibility of recurrence of the disease, most often it affects patients with various menstrual disorders.
Laser treatment of cervical leukoplakia is a more modern and successfully used method. The huge advantages of this procedure include contactlessness, painlessness, and asepticity of such therapy. Laser treatment allows for quick and bleeding-free coagulation of damaged tissues, creating sufficient wound protection from bacterial flora penetration. Laser treatment is usually performed in an outpatient setting, without anesthesia, on the 5th-6th day of the menstrual cycle. Immediately before the procedure, the cervix is treated with Lugol's solution, which allows for accurate determination of the altered tissues subject to laser treatment.
If the pathology is widespread, laser therapy may be prescribed in several stages, with gradual coagulation of the affected areas. Final healing usually occurs within three to five weeks, depending on the extent of the pathological lesion.
Surgical removal of cervical leukoplakia is performed at a late stage of the process, accompanied by hypertrophic and deformative changes in the cervix. The operation may include knife or laser conization, amputation of the cervix with subsequent plastic surgery and reconstruction of the organ. This is a radical operation that is used only in extreme cases.
Radio wave treatment of cervical leukoplakia may be recommended to young nulliparous girls with large-scale manifestations of the disease. This is a relatively new procedure that is performed contactlessly, using radio waves that act as a kind of scalpel. The essence of the method is as follows: a special electrode is inserted into the cervical canal, which produces high-frequency discharges. Under the influence of these discharges, the tissues affected by the pathology seem to evaporate due to the high temperature. The method is considered quite gentle, recovery after treatment is relatively quick and painless.
Medical experts strongly advise against using folk remedies for cervical leukoplakia. Leukoplakia is a disease that can degenerate into a malignant pathology, and delaying qualified treatment with such a diagnosis is extremely unwise. Attempts to independently cure the disease can not only cause harm, but also allow you to miss the time during which you could get rid of the pathology. In addition, the use of tissue-irritating infusions, the use of tampons and douching, which can cause mechanical damage to tissues, usually aggravate the situation and lead to complications of the disease. Cervical leukoplakia is not a case when the use of folk methods is appropriate.
During the entire treatment period and up to 45 days after it, sexual intercourse and the use of chemical contraceptives are not recommended.
Prevention
Preventive measures consist primarily of timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, as well as hormonal imbalance and menstrual cycle disorders. Women who have previously undergone diathermocoagulation or cryotherapy procedures in the cervix for any reason should periodically visit a doctor for a colposcopic preventive examination.
Preventive measures include a stable sex life, the use of contraception if you do not want to become pregnant, and periodic visits to the doctor for a medical examination.
If you are prone to inflammatory pathologies of the reproductive organs, you should follow these rules:
- avoid stressful situations, hypothermia, overwork;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- use high-quality underwear made from natural fabrics;
- review your diet, eliminating alcohol, spicy foods, pickles and sweets;
- no smoking.
Include more vitamins in your diet: this will support your immunity and prevent the disease from progressing.
Forecast
Provided that you contact your doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for the disease may be favorable. If pregnancy develops after recent treatment for leukoplakia, it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the cervix.
Cervical leukoplakia is a disease that is difficult to diagnose. However, timely detection of the pathology allows the disease to be cured without dangerous consequences for the life and health of the woman.

