
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Teniarynchiasis
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025

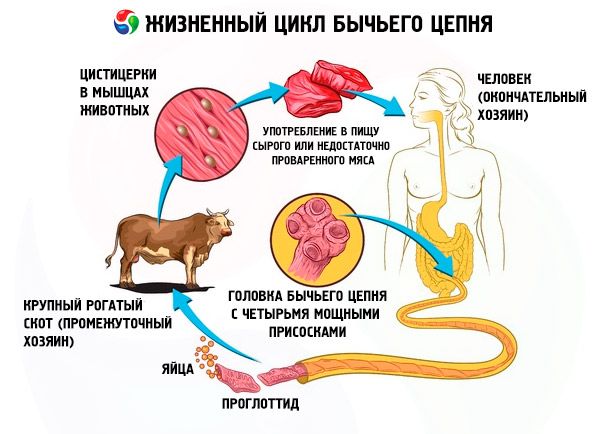
Taeniarhynchosis (Latin: taeniarhynchosis) is a helminthiasis from the group of cestodiasis caused by Taeniarhynchus saginatus (beef tapeworm) or Taeniarhynchus confusum and characterized by the development of dyspeptic symptoms. A person becomes infected by eating beef containing the larvae of the pathogen and not having undergone sufficient heat treatment.
Epidemiology
The source of contamination of the environment by bovine tapeworm oncospheres is man, the only definitive host. The greatest danger is posed by people caring for animals (shepherds, milkmaids, etc.)
Animals are most often infected in pastures. Helminth eggs enter the intestines of the intermediate host with food. 16 weeks after the animal is infected, its meat becomes infectious to humans. Cysticerci in animal muscles remain viable for 1-3 years.
The mechanism of human infection is oral - when eating raw or undercooked finnose meat of animals, intermediate hosts of the helminth. The meat of young animals is most affected. Helminthiasis is common in areas where pasture and distant-pasture keeping of cattle is common.
Causes tenyrhinchosis
Taeniasis is caused by Taeniarhynchus saginatus (the unarmed tapeworm, the beef tapeworm), which belongs to the phylum Plathelminthes, class Cestoda, family Taeniidae. Its body is flat, ribbon-shaped and consists of a head with four powerful suckers and many (1000 or more) segments (proglottids). The length of a mature segment is 20 mm, the width is 5 mm. The uterus has a median trunk and 18-30 lateral branches. The helminth reaches a length of 4-12 m. Mature hermaphroditic proglottids contain more than 140,000 eggs.
The eggs are almost spherical in shape, with an embryo (oncosphere) inside. The bovine tapeworm is a biohelminth, and changes two hosts during development. Man is the final host, and the intermediate hosts are cattle, buffalo, yak, and zebu.
In the human body, adult helminths parasitize in the small intestine for a long time (up to 20 years). Mature segments, breaking away from the strobila, enter the environment with feces, passively or actively crawl out of the anus. In the body of the intermediate host, the larvae develop in muscle and connective tissue, where they turn into oval-shaped larvae - cysticerci (Finns). Larvae that enter the human intestine reach the stage of an adult helminth after 2.5-3 months.
Pathogenesis
The beef tapeworm in the human intestine, as a rule, parasitizes in the singular (the old name of the helminth is tapeworm). The parasite, reaching a size of several meters, attaches with suckers to the mucous membrane of the small intestine, causes damage, irritates the receptors of the intestine, affecting the motor and secretory functions of the intestine. Additional mechanical impact can be caused by separated proglottids, which provoke pain syndrome, especially when passing through the ileocecal valve.
There are cases of parasites penetrating the appendix, common bile duct and pancreatic duct, which led to obstruction and inflammatory changes. It is possible to develop taeniasis intestinal obstruction. Intensive consumption of nutrients by the parasite during growth and development (a young individual grows 7-10 cm in a day) creates a deficit of the most biologically valuable components in the patient's diet. Of certain importance in the pathogenesis of taeniasis are the blocking effect of substances secreted by the helminth on the enzyme system of the human intestine, as well as sensitization by the metabolic products of the bovine tapeworm.
Symptoms tenyrhinchosis
There are no symptoms of taeniasis in case of invasion by bovine tapeworm. Taeniasis is manifested only by the release of segments from the anus with feces and/or outside the act of defecation as a result of their active crawling out of the anus. Heartburn, nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium appear on the 2nd-3rd week, and stool is disturbed on the 8th week. With prolonged invasion, patients note general weakness, abdominal pain, sometimes weight loss, diarrhea, increased appetite, asthenoneurotic manifestations occur: dizziness, headache, sleep disturbance. fainting, epileptiform convulsions. In some cases, eosinophilia in the blood and anemia are recorded.
Complications and consequences
Teniarinhoz may have the following complications: mechanical intestinal obstruction, appendicitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis - occur very rarely.
Diagnostics tenyrhinchosis
The symptoms of taeniasis are not very specific. A combination of dyspeptic syndrome and weight loss with increased appetite may cause suspicion of invasion.
Faeces are examined to detect strobila fragments (proglottids) and helminth eggs using enrichment methods.
Indications for consultation with other specialists
In case of intestinal obstruction and acute inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, a consultation with a surgeon is indicated.
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
What tests are needed?
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics of taeniasis is carried out with other intestinal cestodiasis - taeniasis and diphyllobothriasis, in which, unlike taeniasis, there is no independent active departure of helminth segments from the anus.
Who to contact?
Treatment tenyrhinchosis
Treatment of taeniasis consists of a single administration of praziquantel at a dose of 15 mg/kg. Niclosamide can also be used for deworming: 2 g taken at night, thoroughly chewed and washed down with water. It is recommended to drink 1-2 g of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) 15 minutes before taking it. The drug causes the death of the scolex and immature segments. If the release of segments resumes, a repeated course of treatment with the same anthelmintic drugs is carried out. If the release of segments stops within 2-3 months after antiparasitic treatment, this indicates effective treatment. In such cases, a control study of feces is carried out for the presence of helminth oncospheres.
Approximate periods of incapacity for work
Working capacity is not impaired during the illness.
Clinical examination
Teniarinhoz does not require medical examination. A control helminthological examination is carried out 2-3 months after treatment. If oncospheres are detected in feces, the course of treatment is repeated.
More information of the treatment
Prevention
Prevention of taeniasis is carried out using a set of medical and veterinary measures aimed at identifying sources of invasion during mass examination of the population. Measures are taken to protect the environment (pastures) from faecal contamination. Personal prevention consists of excluding raw and insufficiently thermally processed cattle meat from the diet.
Forecast
Taeniasis usually has a favorable prognosis.


 [
[