
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Simple leukoplakia
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
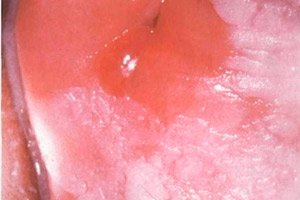
Simple leukoplakia is a dyskeratotic disease, that is, one that is accompanied by impaired keratinization. The pathology affects multilayered flat epithelial tissue and can be found in the oral cavity, respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and anal area. Due to the increased risk of malignant degeneration, the disease requires careful diagnostics with histology and cytological analysis of the biomaterial taken. [ 1 ] Treatment is mandatory and is prescribed immediately after all diagnostic manipulations.
Epidemiology
The incidence of simple leukoplakia is 48% of all cases of this disease. The most common localization is the inner surface of the cheeks, corners of the mouth, tongue, bladder, cervix, vulva, clitoris. Less often, the head of the penis, prepuce, and anal area are affected. Leukoplakia of the oral mucosa is most often diagnosed in India and the southern part of the United States: this is due to the widespread use of smoking and other tobacco products.
Malignancy of the pathological process occurs within 12 months to five years from the onset of the disease. More dangerous forms are considered to be warty and erosive-ulcerative leukoplakia. Malignancy occurs in approximately 2-21% of cases. [ 2 ]
The average age of those affected is 30 years. Leukoplakia of the cervix is most often detected at the age of 20-30 years. The onset of the disease in childhood or old age is almost never registered.
Information on the epidemiology of simple leukoplakia is contradictory, which is due to differences in the selection criteria (age category, gender and race, presence of bad habits, eating habits, etc.). There are also differences in the diagnosis of the disease: for example, epidemiological data should include the frequency of repeated examinations, characteristics of the treatment, and also provide for uniform diagnostic criteria.
Patients with leukoplakia are more often men. Idiopathic leukoplakia is diagnosed in 10% of cases.
Causes simple leukoplakia
The exact causes that precede the development of simple leukoplakia are still unknown to scientists. It is assumed that the main role is played by external irritants, such as mechanical, chemical and temperature irritation of the mucous tissue. For example, as gynecological practice shows, every third patient diagnosed with cervical leukoplakia has previously undergone a diathermocoagulation procedure. Cases of the disease associated with the specifics of the profession (work in chemical plants, oil and coal mining) are no less often recorded.
On the oral mucosa, the disease often develops as a result of damage to the mucosa by unsuitable dentures, or by galvanic current, which is formed as a result of the heterogeneity of denture materials. Smokers often suffer from leukoplakia of the lips, which is explained by the negative influence of tobacco components and the effect of temperature. [ 3 ]
Other causes may include chronic inflammation and neurodystrophy processes in the mucous tissue. For example, leukoplakia may be a consequence of stomatitis or gingivitis, vulvovaginitis, cystitis, etc.
The genetic factor cannot be denied, since the disease is often detected against the background of congenital dyskeratosis.
Many experts point to the existence of a connection between the development of leukoplakia and chronic candidiasis.
Risk factors
Additional risk factors for the development of simple leukoplakia include:
- hypovitaminosis of vitamins A, E, B 12; [ 4 ]
- frequent and deep stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- occupational hazards – work in chemical plants, in hot shops;
- endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus);
- age-related changes (age over 50 years);
- HPV.
Pathogenesis
Medicine still cannot give an exact answer to the question of the origin and mechanism of development of simple leukoplakia. Some specialists of the last century spoke of the disease as a sign of syphilitic or parasyphilitic lesions. Today, scientists more often point to the viral theory of pathology. At the same time, the most obvious provoking factors are considered to be smoking [ 5 ] and irritation of mucous tissues (mechanical, chemical, etc.). [ 6 ]
Another factor is the neurotrophic process in tissues, complicated by a chronic inflammatory reaction. Some specialists refer to leukoplakia as a syndrome that occurs as a result of prolonged inflammation in the mucous tissue. Such inflammation, in turn, can be provoked by various infectious processes, traumatic, chemical or thermal irritants. [ 7 ], [ 8 ]
It is important to understand that not every area of hyperkeratosis combined with inflammation should be considered leukoplakia. Many erosive and ulcerative processes are similar to this disease, since they look like foci of localized redness covered by light epithelium that can be scraped off. In acute trauma with destruction of mucous tissue, epithelial turbidity may be associated with hyperkeratosis, which manifests itself as a reaction to prolonged and regular irritation. Such “fake” leukoplakia disappears immediately after the disappearance of its underlying cause. [ 9 ]
Taking into account the above, the following forms of leukoplakia are distinguished:
- A symptom such as leukoplakia is not a full-fledged pathology, but only a sign caused by an inflammatory reaction in the mucous tissues.
- True leukoplakia is a direct pathology without a clear cause.
- “False” leukoplakia is a painful condition that develops as a consequence of other diseases affecting the mucous tissue.
During pathological diagnostics, simple leukoplakia reveals itself as a focus of chronic inflammatory reaction in mucous tissues, sometimes near the vascular network. Connective tissue fibers in the damaged area have pronounced signs of rarefaction and destruction. The epithelium of the mucous tissue is particularly affected: the granular and horny layers, which are usually absent, are determined. Acanthosis, devoid of atypical cellular structure, is clearly manifested. During tissue analysis, in case of damage to the bladder, the transformation of transitional epithelial tissue into multilayered squamous epithelium is detected. [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ]
Symptoms simple leukoplakia
Simple leukoplakia is most often found on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity (on the inner buccal surface), in the corners of the lips, on the lower lip, less often on the tongue and alveolar processes. Urogenital leukoplakia is diagnosed in the area of the clitoris, vagina, vulva, cervix, head of the penis, urethra and bladder. Respiratory leukoplakia often affects the vocal cords, epiglottis.
Leukoplakia lesions appear as single or multiple light spots with clearly defined outlines, but with different sizes and shapes. Most often, the first signs remain unnoticed, since the pathology does not cause any noticeable discomfort. That is why leukoplakia is often discovered by chance - for example, during a visit to the dentist, during a colposcopy, etc. Negative sensations can only occur with damage to the scaphoid fossa of the urethra (difficulty urinating) and larynx (cough, hoarseness, voice change). [ 13 ]
The mechanism of leukoplakia development is step-by-step. At first, a small area of low-intensity inflammation appears on the mucous tissue. Then the epithelium of the inflamed area begins to keratinize, a typical light lesion is formed, similar to a film coating, which cannot be removed with a spatula.
Simple leukoplakia can exist for years or transform into warty leukoplakia: the affected area becomes denser and convex. Along with areas of keratinization, cracks and ulcers may appear, which is typical for the erosive course of the disease. [ 14 ]
Stages
The term "leukoplakia" is considered to be purely clinical, and is practically not used for morphological description. In pathology, one of four types of changes is usually detected:
- focal epithelial hyperplasia;
- squamous cell intraepithelial neoplasia stage 1; (SIN)
- PIN 2 tbsp.;
- PIN 3 tbsp.
As a rule, the disease begins clinically with a preleukoplakic stage, characterized by an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane. Then keratinization is observed with the development of flat, or simple leukoplakia.
Forms
Typically, specialists divide leukoplakia into several varieties:
- Focal simple leukoplakia, or flat, is expressed by a sharply limited opacity of the mucous membrane. Sometimes such a lesion resembles a superficial dense film with a dry and rough surface. Its color shade fluctuates from grayish to almost white, which depends on the degree of keratinization. The outlines are tooth-like. In the oral cavity, leukoplakia can look like a wrinkled film or light folds.
- Verrucous leukoplakia has the appearance of a raised white smooth growth, but sometimes appears as dense tubercles, raised by about 2.5 mm. Verrucous and simple leukoplakia are often found in the background of each other.
- Erosive leukoplakia is characterized by the appearance of erosive lesions and cracks in the area of a simple or warty leukoplakia lesion.
- Nicotine leukoplakia is found in smokers. It looks like a keratinized hard palate of a light shade, against the background of which reddish inclusions (outlet ducts of the salivary glands) are visible.
There is another classification of the disease depending on the localization of the painful process:
- Simple leukoplakia of the cervix often occurs without specific symptoms, and the areas of keratinization of the mucous membrane are discovered accidentally during a gynecological examination. Some patients may complain of the presence of leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor and color, itching of the genitals. Sometimes there is an increase in pain during menstrual bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse. Leukoplakia of the cervix and pregnancy
- Simple vulvar leukoplakia is a dystrophic transformation of the vulvar cellular structures, which is accompanied by keratinization processes. This problem is most often found in women who have crossed the threshold of menopause or climacteric.
- Simple leukoplakia of the oral cavity most often occurs in areas subject to frequent damage to the mucous membrane - for example, with close contact or uneven placement of teeth, in the presence of incorrectly installed fillings or dentures.
What does the term "simple leukoplakia without atypia" mean?
Leukoplakia without cellular atypia refers to the processes of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis. When examining smears-imprints, keratin lumps, accumulations of superficial cellular structures (devoid of a nucleus) are detected. The cytoplasm of the cells is stained yellow or orange according to Papanicolaou. Layers of polygonal keratinizing cells - dyskeratocytes - may be encountered. [ 15 ]
The diagnosis of simple leukoplakia without atypia means that the risk of transformation of the disease into a malignant form is practically absent.
Complications and consequences
The most undesirable complication of simple leukoplakia can be considered a malignant transformation of the disease - that is, its degeneration into a cancerous process. However, warty and erosive leukoplakia most often become malignant.
If the painful process affects the cervix, there is a risk of developing infertility.
If laryngeal lesions are treated incorrectly or untimely, some irreversible tissue changes may develop, which may result in the patient developing frequent ENT diseases.
When the bladder is affected, there is a possibility of various chronic disorders of the urination process. They, in turn, negatively affect the patient's quality of life. [ 16 ]
Diagnostics simple leukoplakia
In the vast majority of cases, simple leukoplakia is diagnosed without any particular problems if we are talking about areas accessible for examination by a doctor (for example, if the lesions are located in the oral cavity, on the external genitalia). To clarify the diagnosis, cytology with histological examination is mandatory.
Cytology helps to detect atypical cells, which is typical for a precancerous condition. During cytological diagnostics, many multilayered epithelial cells with signs of keratinization are identified. It is important to consider that a smear cannot cover the underlying tissue layers, which may have signs of atypia. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, it is better to take a biopsy rather than a smear.
Histological examination reveals keratinization of the epithelium without the upper functional layer, since the upper epithelial layer is at the parakeratotic or hyperkeratotic stage. Hyperactivity and atypicality of basal cells are possible, indicating an increased probability of malignancy. [ 17 ]
Leukoplakia of the cervix is determined during a gynecological examination or colposcopy.
Auxiliary analyses are carried out:
- smear for the presence of antibodies to sexually transmitted diseases;
- bacterial analysis;
- CBC and blood for STDs, HPV, HIV;
- immunogram;
- study of hormonal status.
Instrumental diagnostics are appropriate if leukoplakia of the larynx is suspected: laryngoscopy is performed in combination with biopsy. In case of bladder leukoplakia or damage to the urethra, urethroscopy, cystoscopy with mandatory simultaneous biopsy are appropriate.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out with oral and genital thrush, secondary syphilis, Bowen's disease and Queyrat's disease, keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma, and lichen planus. [ 18 ]
Cervical leukoplakia and cancer are easily identified using the Schiller test. The affected area in the cervix is treated with Lugol's solution: if atypical cells are present, they will not change their shade. Additionally, a biopsy and histology of the material removed from the cervix and cervical canal are taken.
Who to contact?
Treatment simple leukoplakia
Simple leukoplakia, regardless of the location of the painful focus, requires the appointment of complex therapy. Treatment should be aimed at neutralizing the causes that caused the problem, as well as correcting associated problems. Therapeutic measures include:
- elimination of damaging factors that traumatize the mucous membrane;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- combating hypovitaminosis;
- treatment of existing diseases of the digestive, endocrine, genitourinary systems, somatic diseases, infectious and inflammatory pathologies.
Radical procedures for simple leukoplakia are rarely used. Such measures are relevant only when atypical cells are detected. Usually the patient is carefully examined, and the pathological process is monitored. Drug treatment may include taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, hormonal and immunomodulatory agents. [ 19 ]
Medicines that a doctor may prescribe
Hyposensitizing drugs |
Prescribed to suppress the pathogenetic mechanism of allergic process development. Example: Astemizole is taken 10 mg once a day. Possible side effects: paresthesia, myalgia, sleep disorders. |
Keratoplastic means |
Prescribed to normalize metabolic processes in the epithelium of the mucous tissue. Example: Carotolin is an oil extract from the pulp of rose hips, used for applications to the affected mucous tissues of the oral cavity. Possible side effects: allergy. |
Immunomodulators |
Prescribed to improve the body's immune response. Example: Immunal is taken 1 tablet 4 times a day for 10 days. Possible side effects: allergic reactions, dizziness, arterial hypotension. |
Antiseptics |
Used to speed up tissue healing. Example: Tantum Verde is used to irrigate the affected areas of the oral cavity 4 times a day. Possible side effects: dry mouth, allergies. |
Vitamin products |
To normalize metabolism in epithelial tissue, a long course (about 2 months) of vitamin A is prescribed, 10 drops 3 times a day, or Aevit, 1 capsule three times a day after meals. This treatment is repeated 2-3 times a year. It is recommended to apply an oil solution of vitamin A to the oral mucosa three times a day for 20 minutes. |
Vitamins
For the treatment and prevention of leukoplakia, a long course of vitamin A is prescribed. There is evidence of the positive use of a combination of retinol acetate with thiamine. In general, specialists recommend prescribing the following vitamin preparations to patients:
- coenzyme Q10 – a source of cellular energy, eliminates vulnerability and accelerates the healing of mucous tissue;
- vitamins B 3 and B 6 – normalize the sensitivity of mucous membranes;
- Vitamin A – increases tissue resistance to infectious and inflammatory processes, takes part in metabolic processes.
In case of oral leukoplakia, it is especially recommended to use green tea extract, which helps strengthen the gums, has bactericidal activity and antioxidant properties.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy methods for leukoplakia are not of decisive importance, but can be used at some stages of recovery:
- photodynamic treatment;
- immunostimulation;
- X-ray therapy;
- ozone therapy;
- hydrotherapy (irrigation, baths, showers);
- mud therapy;
- UFO of the lumbosacral region;
- acupuncture;
- ultrasound.
The essence of photodynamic therapy is the use of light-sensitive components. We are talking about photosensitizers: they are introduced into the patient's body, after which they are activated using laser radiation. This method is successfully used to treat many malignant processes, dermatological diseases, and to eliminate inflammation foci. The procedure involves the application of sensitizers, which selectively accumulate in the affected tissue areas. Then, irradiation is carried out with a low-intensity laser with a power of 1-2 W. With such power, it is possible to control the temperature threshold of sensitivity.
The use of ozone-oxygen mixtures during ozone therapy procedures allows optimizing the intracellular microcirculation of vitamins and minerals. In addition, ozone is a good disinfectant and affects the oxygen release in tissues, stimulating all biological processes.
Folk remedies
The vast majority of medical professionals do not recommend treating leukoplakia with folk remedies. There are many known cases where such treatment led to the transformation of the disease into a malignant form. However, some patients still ignore warnings and practice folk methods. In their opinion, available means allow keeping the pathology under control and eliminating painful symptoms.
Traditional medicine is based on the use of various means available in ordinary household conditions. These can be food products, plants, etc. For example, 4-6% natural apple cider vinegar is often used to treat painful areas, which has anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, antifungal, healing and softening properties. But: in no case should you use undiluted vinegar or concentrate, since it will lead to burn damage to the mucous tissues. For the same reason, leukoplakia lesions are not treated with alcohol solutions, brilliant green, iodine, etc.
It is recommended to add pumpkin to the diet of patients suffering from leukoplakia. Pumpkin juice and pulp contain many useful substances necessary for the body, help cleanse tissues and remove toxic components.
It is also useful to drink a glass of fresh carrot and celery juice in the morning. To enhance the effect and if there are no contraindications, add a pinch of baking soda to the juice. [ 20 ]
Herbal treatment
According to traditional healers, the most pronounced effect on leukoplakia is provided by:
- rinsing with an aqueous infusion of saffron;
- chewing propolis;
- rinsing with meadowsweet infusion.
Calendula, basil, birch buds, viburnum fruits, motherwort, bay leaf, eucalyptus, dandelion rhizome have a similar positive effect. Plants considered poisonous are not recommended for the treatment of leukoplakia. Such undesirable herbal preparations include celandine, potato blossom, wormwood, hemlock, etc.
To rinse the mucous membrane, an infusion of St. John's wort (1 tbsp. of the plant per 500 ml of water), sage (1 tsp. per 200 ml of water), and also fresh white cabbage juice are successfully used.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic treatment for leukoplakia of various localizations is carried out against the background of traditional therapy, since they effectively complement each other. A homeopathic specialist will be able to offer the most suitable drug, maintain the correct proportions and frequency of use. As a rule, there are no side effects from such treatment: it is easily perceived by patients of any age.
Homeopathic suppositories have proven effective in treating leukoplakia:
- Calendula;
- Propolis;
- Chaga;
- Thuja;
- Femican.
- Ointment preparations are no less effective:
- Calendula;
- Propolis;
- Arnica;
- Thuja;
- Witch hazel.
Homeopathic remedies often help prevent complications of leukoplakia, such as slow-healing wounds, cracks, ulcers, and erosions. However, the use of homeopathy alone, without the main traditional treatment, is not welcomed by specialists.
Surgical treatment
The use of surgical treatment in most cases allows to neutralize all painful foci of leukoplakia and get rid of them completely. The following technologies are most often used:
- The radio wave method involves removing the affected areas of mucous tissue using a radio wave knife. This method is effective, painless and bloodless, does not require anesthesia, and completely eliminates postoperative bleeding and infectious complications.
- The cryodestruction method involves treating the affected tissues with liquid nitrogen, which causes them to die. The procedure is painless, lasts no more than fifteen minutes, and the degree of effectiveness (absence of relapses) is estimated at more than 95%. The only drawback is that after healing, a rough scar may form at the site of the leukoplakia focus.
- The chemical coagulation method involves treating lesions with a special chemical composition, which is considered quite effective and virtually painless.
- The argon plasma coagulation method involves cauterization of pathologically altered tissues using radio waves of varying power. The method is painless, bloodless, and does not leave behind gross cicatricial changes. Cauterization leaves virtually no chance for the development of microbial infection.
Some situations require surgical excision of the affected area. After such intervention, reconstructive plastic surgery is usually performed.
If the leukoplakia area is localized on the laryngeal mucosa, then microlaryngological surgery is prescribed. The bladder mucosa is subjected to coagulation during cystoscopy. [ 21 ]
Should simple leukoplakia be removed?
Simple leukoplakia, of course, cannot remain without treatment, which should include the eradication of factors that led to the development of the disease. It is important to get rid of mechanical damaging agents (for example, dentures or dental crowns), give up smoking and drinking alcohol, establish the supply of necessary vitamins to the body, cure existing pathologies of the digestive and endocrine systems, as well as all somatic disorders, infectious and inflammatory processes.
If simple leukoplakia does not show signs of atypia of cellular structures, the doctor may not insist on radical treatment in the form of removal of problem areas. However, such patients should be monitored with periodic examination. If basal cell hyperactivity and atypia of cells are determined during the diagnostic process, then it is necessary to remove the leukoplakia area as soon as possible. [ 22 ]
The affected mucous tissue is removed using laser technology or radio waves, diathermocoagulation or electroexcision methods. For individual patients, surgical excision of the entire affected area (urethra, vagina, etc.) may be recommended, which requires further reconstructive plastic surgery of the organ.
If signs of malignancy of simple leukoplakia are detected, radical intervention is prescribed followed by radiotherapy.
If simple leukoplakia is detected in the larynx, microlaryngosurgery may be recommended. In case of bladder lesions, coagulation is performed by cystoscopy. If the disease is characterized by a pronounced increase in symptoms and the spread of the disease process, resection of the organ may be required.
Competent and timely therapy even with a rapid course of pathology leads to a positive result. But, unfortunately, there is no guarantee that the patient will be able to avoid relapses. This is especially true for cases where radical removal was not used. Therefore, the patient's health must be monitored by a doctor. It is necessary to be extremely careful with heat treatment and all kinds of folk therapy methods. Such questionable methods of treatment can lead to malignancy and worsening of the pathology. [ 23 ]
Prevention
To prevent the development of simple leukoplakia, it is necessary to eliminate all possible causes and factors of the disease development. For example, it is necessary to limit the likelihood of infection entering the body as much as possible, namely:
- strengthen the immune system;
- avoid contact with infected people;
- observe sanitary and hygienic rules.
It is imperative to devote time to health activities, lead an active lifestyle, eat well and give up all bad habits.
Prevention of the development of oral leukoplakia includes:
- regular oral hygiene (removal of tartar, correct selection of dentures, timely treatment and restoration of teeth and gums, etc.);
- avoiding the consumption of very hot, spicy foods, alcohol, and medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- quitting smoking;
- elimination of occupational hazards that adversely affect the mucous membrane;
- avoid taking medications not prescribed by a doctor;
- regular preventive visits to doctors (dentist, gynecologist, therapist).
It is important to prevent and promptly identify any mechanical and chemical damage to the mucous membrane, avoid occupational hazards, smoking and alcohol consumption, and prevent hypovitaminosis of vitamins A and B 2. Preventive measures include early detection and timely treatment of any diseases.
Patients are recommended to undergo periodic medical examinations with subsequent registration at a dispensary if chronic pathologies of the mucous tissues are detected.
Many patients believe that they are quite competent in terms of sanitation and personal hygiene, and they do not need special explanations on this matter. But practice shows that clear explanations and demonstrations of sanitary and hygienic rules and standards cannot be "superfluous": it is important to instill correct hygiene skills and even monitor the success of their implementation. It has been noted that all the doctor's efforts to cure simple leukoplakia can be in vain if the patient ignores advice on personal hygiene - in particular, the genitals and oral cavity.
Maintaining an adequate hygienic status in the body will ensure the normal course of many physiological processes. For this reason, explanations regarding the rules and methods of self-organization and a healthy lifestyle are an important goal for all representatives of the medical profession.
Forecast
With early detection of simple leukoplakia, complete recovery is achieved in 99 patients out of a hundred. Thus, the prognosis can be considered quite favorable, provided the disease is detected early. However, if the provoking factors are not eradicated, each patient remains at risk of recurrence of the pathology. And in some cases, a simple painful process acquires a malignant course - for example, this happens in 15% of patients diagnosed with cervical leukoplakia.
After the course of treatment, all patients who have had leukoplakia should be registered with a dispensary. Women should visit a gynecologist twice a year to take a cytological smear. Colposcopy and analysis for the human papilloma virus are mandatory. If the disease does not recur within two years, the patient is removed from the register.
Simple leukoplakia, unlike warty and erosive-ulcerative forms, does not often transform into a malignant disease. However, such a development of events cannot be ruled out. The pathology is subject to mandatory treatment - first of all, to prevent the development of complications and to slow down the disease process. The appearance of complications significantly worsens the quality of the prognosis.

