
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Suppurative sore throat without fever
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 05.07.2025
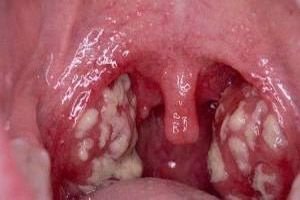
Purulent tonsillitis without fever is much less common than inflammation of the tonsils with a significant increase in body temperature.
In Latin, the palatine tonsils are called tonsillae, and in the practice of ENT doctors this diagnosis sounds like catarrhal tonsillitis.
Let's find out when there is a sore throat that is not accompanied by a rise in temperature, given that this disease has an infectious etiology.
Causes purulent sore throat without fever
The main causes of purulent tonsillitis without fever are associated with the activation of pathogenic bacteria of serological group A that have entered the throat - by airborne droplets or through objects, for example, dishes or cutlery. First of all, this is beta-hemolytic streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes, which is the culprit in almost 80% of cases of acute inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
In addition, purulent tonsillitis without fever can occur due to Staphylococcus aureus. This gram-positive bacterium is present on the skin and mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract in almost 25% of people and coexists with humans according to the principle of commensalism. This is a type of coexistence in which the tenant bacterium does not interfere with the life of the host organism that has “sheltered” it, but at the same time, the responsibility for the relationship with the environment lies entirely with the host. Therefore, as soon as the immune system (usually preventing the bacteria from showing its pathogenic properties) weakens, or the body's non-specific protection against infections fails, one or another disease develops. In this case, purulent tonsillitis without fever.
As otolaryngologists note, purulent tonsillitis without fever may have a mixed etiology, when the tonsils are attacked by both streptococci and staphylococci - against the background of weakened immunity due to hypothermia. In addition, the source of infection does not necessarily have to be external: often the tonsils become inflamed from an infection concentrated in the paranasal sinuses (for example, with chronic sinusitis or sinusitis) or in the cavities of teeth affected by caries.
Causes of purulent tonsillitis without fever can also be chronic tonsillitis, difficulty breathing, infection of the larynx with the fungus Candida albicans, infection of the palatine tonsils with fusiform bacillus and spirochetes (Vincent's angina), stomatitis, syphilis.
Symptoms purulent sore throat without fever
Angina (acute tonsillitis) has several clinical forms: catarrhal, lacunar and follicular, fibrous and phlegmonous. And only catarrhal angina, in which the inflammatory process affects only the upper layer of the mucous membrane of the tonsils, can be purulent angina without fever.
Obvious symptoms of purulent tonsillitis without fever are manifested in the form of:
- irritation, dryness and pain in the throat, which intensifies during swallowing and can radiate to the ears;
- hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the tonsils, as well as hyperemia of the palatine arches and the back wall of the pharynx;
- yellowish-white mucopurulent plaque covering the tonsils entirely or partially;
- slight enlargement of the submandibular or parotid lymph nodes, which may cause pain when palpated.
What's bothering you?
Diagnostics purulent sore throat without fever
Diagnosis of purulent tonsillitis without fever is carried out by an otolaryngologist based on the patient's complaints and through a routine examination of his throat. As a rule, this is quite sufficient to prescribe the necessary therapy.
But if purulent tonsillitis without fever occurs frequently, then to determine the type of pathogenic bacteria, a microbiological examination of a smear from the surface of the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx is prescribed. You will also need to take a general blood test for ESR and leukocytes, as well as a blood test for CRP (C-reactive protein of blood plasma).
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
Who to contact?
Treatment purulent sore throat without fever
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis without fever necessarily includes gargling. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a solution of hydrogen peroxide (3%), a solution of furacilin (1 tablet per 100 ml of warm water), a solution of boric acid (one teaspoon per 200 ml of water), a solution of rivanol (0.1%), solutions of Chlorophyllipt or Benzydamine.
Also, for gargling, which should be done 4-5 times a day after meals, decoctions and water infusions of medicinal plants are used: sage, St. John's wort, chamomile and calendula flowers, oak bark and eucalyptus leaves (a tablespoon of dry herbs per glass of boiling water).
Warming the neck with a scarf and warming compresses (ethyl alcohol with water in a 1:1 ratio) improves the condition of the throat and lymph nodes.
To treat purulent tonsillitis without fever, antibacterial pharmaceuticals are used - antibiotics of the penicillin or cephalosporin series (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Oxacillin, Rovamycin, Cephalexin, etc.) in the form of tablets for oral administration.
Thus, Ampicillin, which has a broad spectrum of action, is prescribed to adults at 0.5 g 4-6 times a day, the maximum daily dose is no more than 3 g. For children, the daily dosage is determined at the rate of 100 mg per kilogram of body weight, and the daily dose is divided into equal parts into six doses. The semi-synthetic antibiotic Amoxicillin (trade names Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Flemoxin Solutab) adults and children over 10 years old take one tablet (0.5 g) three times a day - before or after meals. The duration of treatment is 5-12 days. Rovamycin is a macrolide antibiotic with a bacteriostatically active substance spiramycin (in tablets of 1.5 million IU) - adults are recommended to take 3 million IU 2-3 times a day, and children - 150 thousand IU per kilogram of body weight per day (in three doses).
The cephalosporin antibiotic Cephalexin (in capsules of 0.25 g) is used: for adults - 0.25-0.5 g 4 times a day (regardless of food intake); the daily dose for children is 25-50 mg per kilogram of body weight, also in four doses. The duration of the course of treatment is 7-14. Daily doses of Cephalexin in the form of a suspension: 2.5 ml for children under one year of age; 5 ml - from 1 year to 3 years (in 4 doses); 7.5 ml - 3-6 years; 10 ml - over 6 years. The minimum duration of taking this drug is 2-5 days.
It should be remembered that all antibiotics have side effects in the form of dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, allergic reactions and changes in the blood, so if purulent tonsillitis without fever occurs during pregnancy or lactation, it is better to do without antibiotics.
Antiseptic lozenges, pastilles and tablets for resorption, such as Strepsils, Faringosept, Astrasept, Hexoral, Falimint, etc., are good for relieving inflammation and sore throat.
For example, Strepsils contains the local antiseptic amylmetacresol and the anesthetic lidocaine. Adults and children over 12 years of age can dissolve these tablets in acute tonsillitis no more than 5 times a day and no longer than three days. The active component of Faringosept is the strong bacteriostatic ambazon; these tablets are used half an hour after eating, and after the tablet has completely dissolved, you should not eat for at least three hours.
In case of purulent tonsillitis without fever, aerosols Tantum Verde, Hexasprey, Anginovag, Bioparox and others are used locally. Spray Tantum Verde relieves inflammation and acts as an analgesic due to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug benzydamine contained in it. Antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect is also provided by Hexasprey, which is allowed to be used for no more than 5 days.
More information of the treatment
Prevention
As trivial as it may sound, the key point in preventing purulent tonsillitis without fever is strengthening the immune system so that bacteria “lodging” in our body or attacking it from the outside cannot display their pathogenic properties.
It is imperative to avoid hypothermia, consume enough vitamins, cure chronic tonsillitis and promptly treat a runny nose, monitor dental health and follow hygiene rules.
The prognosis for purulent tonsillitis without fever is positive if it is treated. But if it is not treated or treated with inadequate methods, then from catarrhal tonsillitis to lacunar or follicular tonsillitis, as they say, it is a stone's throw. And if the "activity" of beta-hemolytic streptococcus on the palatine tonsils is not stopped, it is capable of attacking the ears and paranasal sinuses, and also leading to the development of pharyngeal phlegmon.
In addition, as doctors say, the prognosis for purulent tonsillitis without fever looks much less optimistic if we remember the antibodies that the body produces to fight this streptococcus. However, these antibodies often attack the connective tissues of the heart and the myocardium, causing problems in its functioning. And the waste products of these streptococci - toxins - enter the lymph and systemic bloodstream. And this can result in intoxication, joint inflammation and damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys (glomerulonephritis) for the body.
In general, purulent tonsillitis without fever is also a serious disease. Therefore, its treatment should be taken seriously.


 [
[