
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Pachyonychia nail
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
In dermatology, there is a little-known term "pachyonychia", which means a violation of the structure, density and shape of the nail plate. This condition can accompany various diseases, or occur independently - for example, with a hereditary variant of the pathology.
In dermatology, there is a little-known term "pachyonychia", which means a violation of the structure, density and shape of the nail plate. This condition can accompany various diseases, or occur independently - for example, with a hereditary variant of the pathology.
Epidemiology
Pachyonychia is more common in men and boys. The approximate ratio of affected men to women is 7:4.
Pachyonychia, as an independent pathology, is detected relatively rarely. More often, this symptom accompanies other diseases - of dermatological or endocrinological etiology.
Causes pachyonychiae
The main reason for the appearance of such a pathology as pachyonychia is a disorder of trophism or structuring of the nail. Externally, such a disorder manifests itself in the form of a change in the thickness and shape of the nail plate.
If pachyonychia is not congenital, it can be caused by candidiasis, chemical exposure, or inflammatory processes at the base of the nail.
The following risk factors play a special role in the development of pachyonychia:
- psoriasis;
- bullous dermatosis;
- lichen planus;
- ichthyosis;
- alopecia;
- pyoderma;
- eczema.
In old age, pachyonychia may be a consequence of deterioration of capillary circulation of blood and lymph, which can cause a disruption in the process of nail formation in its bed.
In young people, impaired capillary circulation can be caused by diabetes mellitus, metabolic and endocrine disorders.
When talking about the congenital form of the disease, they usually mean Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome. This is a genetic pathology with several inheritance patterns, which occurs with a change in the process of formation of the stratum corneum of the skin and nails. In this situation, pachyonychia is the main symptom, which is caused by improper formation of collagen and impaired absorption of some vitamin substances.
Pathogenesis
Pachyonychia is considered a type of onychodystrophic disease. It can be acquired or congenital, associated with certain genetic changes.
The hereditary form of pachyonychia was discovered by dermatologists Jadassohn and Lewandowsky a hundred years ago. Acquired pachyonychia is much more common and can accompany various dermatological diseases.
Sometimes pachyonychia is detected as an age-related feature in elderly patients.
Since pachyonychia in the vast majority of cases is associated with other diseases or age-related tissue changes, many specialists do not distinguish it as a separate pathology, considering it as just a symptom or a painful sign.
Symptoms pachyonychiae
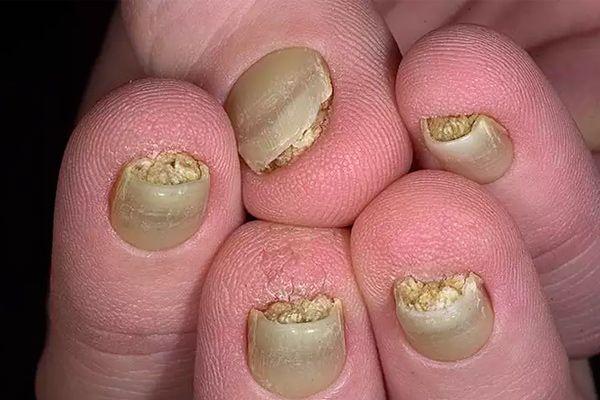
The main distinguishing feature of pachyonychia is the coarsening and thickening of the nail. In this case, not all nails are necessarily affected - one or two nails can be affected. Additionally, hyperkeratosis of the skin at the base of the nail plate, a violation of its shape and a change in color are possible.
If pachyonychia of the nail is one of the symptoms of dermatological diseases, then other signs may also be present - for example, a rash, scales on the skin, papules, vesicles, plaques. As a rule, the lesion spreads to the base of the nail, and then turns into full-fledged pachyonychia.
If the disease is caused by chronic exposure of the skin and appendages to alkaline chemicals, then this condition manifests itself as a loose structure of the nail, and over time, its thickening. Nail development can also be disrupted as a result of an inflammatory reaction, which is a consequence of professional regular adverse effects.
Age-related pachyonychia develops progressively over many years. The first signs of age-related damage are clouding and change in the color of the nail. If a person smokes for many years, the nail may change color to yellow or even brown.
Congenital pachyonychia has the most pronounced clinical picture. Due to the genetic nature of the disease, specialists have divided it into the following types:
- Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome (there is obvious thickening of the nails on the extremities, pain in the feet, there are signs of hyperkeratosis on the inner part of the hands and feet);
- Jackson-Lawler syndrome (in addition to thickening of the nails, early appearance of teeth, mental retardation, and focal alopecia are observed).
Stages
Congenital pachyonychia can progress differently, depending on the stage and the presence of individual symptom complexes:
- Pachyonychia, which is characterized by a symmetrical arrangement of keratoderma and follicular hyperkeratosis.
- Pachyonychia with symmetrical keratoderma, hyperkeratosis and leukokeratosis of the mucous tissues.
- Pachyonychia with keratoderma, hyperkeratosis, leukokeratosis of the mucous tissues and cornea.
- Pachyonychia with keratodermia, hyperkeratosis and pachydermia, against the background of congenital defects of the mesoderm (eg, osteopathy).
Complications and consequences
Pachyonychia is a disease that is almost impossible to cure completely. It is characterized by a periodically worsening course, with frequent relapses.
Pachyonychia does not pose a threat to the patient's life, but this condition can negatively affect a person's self-perception and socialization. Therefore, sometimes such indirect complications as neuroses, depression, and alcohol addiction are observed.
In cases of congenital pachyonychia, complete loss of the affected nails is possible in the future.
Diagnostics pachyonychiae
It is not difficult for an experienced doctor to correctly diagnose pachyonychia. Even during the preliminary examination, he will pay attention to the change in the nail plates. However, in order to prescribe the most optimal treatment, it is often necessary to conduct a number of additional diagnostic procedures - first of all, to determine the initial cause of the disease.
The examination allows us to detect such pathologies as eczema, psoriasis, and lichen. And to diagnose other diseases that can cause pachyonychia, other diagnostic procedures are almost always required - this applies, for example, to diabetes mellitus or other endocrine and microcirculatory diseases.
Additional tests for pachyonychia:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- urine analysis for hydroxyproline content;
- biochemical blood test;
- blood sugar test;
- Blood test for thyroid hormone levels.
Instrumental diagnostics for pachyonychia:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Thyroid ultrasound;
- computed tomography;
- angiography.
How to examine?
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of pachyonychia is carried out with the following diseases:
- anonychia is a congenital anomaly that is accompanied by the absence of nail plates;
- hapalonychia – excessive softness of the nails, which is accompanied by their splitting, change in shape and the appearance of cracks;
- onycholysis – separation of the nail from the nail base;
- onychorrhexis – changes and splitting of the nail plates along longitudinal lines;
- onychoschisis – transverse splitting of the nails;
- trachyonychia is a type of onychodystrophic condition in which the nail becomes dull, flaky and rough;
- dyschromia – change in the color of the nails;
- candidiasis – fungal infections of the nail plates;
- bullous dermatoses, pyococcal paronychia, psoriasis of the nail plates, nail lesions in syphilis or gonorrhea.
Congenital pachyonychia or Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome should be distinguished from Siemens multiforme keratosis and Schaefer syndrome. In Siemens keratosis, children often have a rash near the lips, leukoplakia of the mucous tissues, and mental retardation. In Schaefer syndrome, cataracts and follicular keratosis with atrophy are usually present.
Who to contact?
Treatment pachyonychiae
Treatment should be comprehensive: it is necessary to influence the cause of pachyonychia and all pathogenetic components, not only by ensuring the intake of necessary medications, but also by changing nutrition and lifestyle.
In case of pachyonychia, vitamins are prescribed: retinol 100 thousand IU daily for 4-6 weeks, as well as complex agents with sufficient iron and calcium content.
If indicated, thiamine, cyanocobalamin, nicotinic acid, vitamins C and E, and aloe extract are prescribed.
Food gelatin has a positive effect on pachyonychia:
- 1 tbsp of gelatin is poured into 0.5 l of cold water and left for 2.5 hours to swell;
- heat until dissolved;
- drink the prepared volume throughout the day.
The course of treatment with gelatin usually lasts from 1 to 4 months.
It is recommended to take hot baths with water temperature of about 45°C, with the addition of baking soda, pine extract, starch, bran. Duration of taking a bath is from 20 to 40 minutes.
You can do contrast dousing of your hands, as well as rubbing in melted wax.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of pachyonychia involves applications of paraffin or ozokerite, the use of therapeutic mud. Such procedures as paravertebral diathermy on the affected areas, subcutaneous oxygen insufflations, and limb massage are recommended.
According to reviews, phonophoresis with Aevit (with preliminary treatment of the nail area with Fukortsin) is especially effective for pachyonychia. It is also useful to use ointments that contain gelatin, vitamin A and/or ichthyol. Phonophoresis is carried out in a course of 12-15 sessions, 15 minutes daily. The phonophoresis mode is continuous, with an intensity of 0.8 to 1 W per cm². After three months, the phonophoresis course can be repeated.
Medicines for pachyonychia
Method of administration and dosage |
Side effects |
Special instructions |
|
Aloe extract |
Prescribed as intramuscular injections, 1 ampoule once a day or every other day. |
Dyspepsia and pain in the injection site are rarely observed. |
The drug should not be used during pregnancy or in children under 12 years of age. |
Calcemin |
Take 1 tablet 2 times a day. |
Sometimes allergies, bloating, and vomiting may occur. |
The drug is not prescribed in the presence of kidney stones. |
Merz |
Take 1 tablet twice a day. |
Allergy to the drug is possible. |
The dosage of the drug should not be exceeded, as this may cause harm to the body. |
Aevit |
Take 1 capsule daily. |
Sometimes allergies appear. |
The drug is not prescribed to children under 14 years of age. |
Folk remedies
- Once or twice a week, repeat the baths using heated vegetable oil, adding an oil solution of vitamin A and lemon juice.
- It is useful to add a little homemade apple cider vinegar to the bath with vegetable oil.
- For pachyonychia, compresses made from a mixture of 5 g of alum, 25 g of glycerin and 70 g of warm water are very helpful. Compresses are applied every evening for two weeks.
- Prepare salt baths using sea salt (without dyes and flavors). Use 1 tbsp. salt per 1 liter of water. Duration of the procedure is 20 minutes.
- Lubricate the affected nails with sea buckthorn or peach oil before going to bed. Put on cotton gloves on top, which are removed only in the morning.
Herbal treatment is also used as a comprehensive approach: herbal infusions are taken internally or used to prepare baths.
Herbal treatment
- At night, it is recommended to apply compresses with chamomile or sage infusion.
- You should regularly rub strong infusions of yarrow, St. John's wort, and grape leaves into your nail plates.
- A good remedy is a compress based on aloe or golden mustache. The cut of the plant is applied to the affected nail and bandaged, leaving it overnight.
- Rub tea tree oil into your nails.
It is equally useful to add celandine or garlic juice and a small amount of honey to regular baby cream. Rub this cream into the affected nails 3-4 times a day, every day.
Homeopathy
Among homeopathic remedies, only a few preparations are particularly popular for pachyonychia. They should be selected as follows: improvement should be observed within two weeks, but if there is none, then another remedy should be tried.
After the condition improves, you should stop taking the selected drug and resume it only when the symptoms of pachyonychia return.
- Silicon (Silica) 6X – 2 granules three times a day;
- Calcarea carbonica – 2 tablets 2-3 times a day;
- Natrium muracicum – at the beginning of treatment, take every 3 hours, then 2-3 times a day;
- Graphite 12 – 3 granules at night, daily.
When choosing a homeopathic remedy, it is necessary to take into account the specific disorder within the body that led to pachyonychia. There are no direct contraindications to the use of homeopathic remedies.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention in many cases is not as effective as expected at first. The appearance of the nail plate after surgical treatment may remain virtually unchanged. As a rule, the nail deformation remains after surgery.
Experts recommend paying more attention to caring for affected fingers, using strengthening preparations and external agents. An experienced dermatologist will individually explain the features of caring for altered and thickened nails.
Prevention
Preventive measures consist of high-quality, timely treatment of any skin and inflammatory diseases.
In addition, it is important to protect your hands and nails from the negative impact of the external environment:
- use protective equipment when working with chemicals;
- use properly selected cosmetics for feet and hands;
- choose high-quality and lightweight shoes that will not deform your feet and nails.
Periodically, you should take complex preparations containing the necessary vitamins and minerals. It is also important to eat right, not allowing a deficiency of certain substances in the body.
Forecast
Prognostic data for pachyonychia are not fully defined: they depend on the underlying cause of the pathology. If the therapy prescribed for pachyonychia is effective, the deformed nail may gradually acquire the appearance of a normal nail plate.
In the case of the congenital variant of pachyonychia, in most cases the prognosis is unfavorable: the majority of patients lose their nails and also develop other disorders in the body.


 [
[