
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Ovarian adhesions
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 12.07.2025
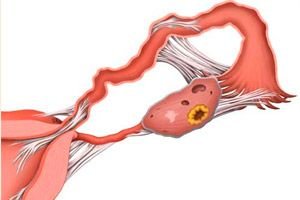
Adhesions on the ovaries are connective tissue formations. This is a common problem that leads to pain syndrome in gynecology, the cause of which is often difficult to determine. Even more often, adhesions can be the cause of infertility, which requires serious treatment and timely diagnosis. This pathology occurs in women of childbearing age and therefore, despite its small prevalence, can be a serious pathology that prevents the onset of normal pregnancy. Therefore, it is necessary to know the main symptoms of the disease and possible ways of correction.
Epidemiology
The epidemiology of this problem is that ovarian adhesions are the most common cause of infertility in women of reproductive age. This is due to the fact that recently the incidence of chronic inflammatory ovarian infections has progressively increased and their recognition has decreased. Speaking about the structure of the causes that are a priority in the development of adhesions, then in the first place are surgical interventions, and in the second place are inflammatory pathologies. The cause of pain syndrome of unknown etiology in 45% of cases are precisely ovarian adhesions, which are difficult to diagnose.
Causes adhesions on the ovaries
Speaking about how important it is to pay attention to your health, it is necessary to know that any disease can be the cause of the development of the following pathologies in the future. Therefore, it is very important to know what reasons can lead to this.
Most often, the cause of adhesions on the ovary is a process that disrupts their integrity, that is, most often it is a surgical intervention. Any operation for a cesarean section or cyst removal always occurs with a violation of normal blood clotting processes and cell regeneration processes. When there is any tissue damage, the body tries to restore the structure of this damaged tissue. And normally, this regeneration process occurs due to the intensive division of cellular structures. If the process of cellular regeneration does not have time to recover, then the body thus replaces the tissue defect due to the intensive synthesis of fibroblasts and the formation of connective tissue. This is how adhesions appear on the ovaries, which are connective tissue by their structure. Therefore, when the peritoneum of the small pelvis and ovarian tissue are damaged, the regeneration process is triggered, and adhesions are formed, which can involve not only the ovary itself in the process, but also form adhesions with the peritoneum of the small pelvis and neighboring organs. Thus, the topic of the ovary itself is disrupted due to its possible tension by these adhesive processes.
Risk factors
First of all, it is necessary to identify the risk group in which adhesions form most often. This group includes:
- women who have had an induced abortion;
- women after cesarean section;
- inflammatory diseases of the ovaries - chronic or past acute adnexitis, oophoritis;
- ovarian cyst, mainly operated;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- ovarian hypoplasia of congenital or acquired etiology;
- ovarian endometritis;
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of the development of adhesions on the ovaries lies in the mechanisms that trigger reactions of active synthesis of connective tissue. In this case, the activation of cellular synthesis and stimulation of regeneration occurs due to the involvement of mediators, which in turn lead to the activation of fibroblasts. As a result of these processes, the synthesis of fibrin increases, which can accumulate on the surface of the ovaries in the places of regeneration and these changes deepen even more.
Chronic inflammatory processes of the ovaries and tubes are the second most common cause of adhesions. This creates very favorable conditions for maintaining a sluggish inflammatory process, which is supported by many cells. Thus, chronic inflammation in the ovary is accompanied by the constant presence of neutrophilic leukocytes, granulocytes, monocytes and fibroblasts - all these cells damage the cellular membrane of the ovarian stroma, which is a condition for the constant process of proliferation and regeneration. Such favorable conditions are the cause of adhesions.
Adhesions on the ovaries after a cesarean section are a very common occurrence, since this operation is very common, and it also leads to the processes described above. Therefore, a risk group can be identified from women who have undergone surgery on the uterus or ovaries, and such women should be monitored for adhesions. This will help reduce not only the problem with ovariomenstrual cycle disorders, but also reduce female infertility, which can still be cured at this stage of fibroplastic changes.
Symptoms adhesions on the ovaries
Very often this pathology develops asymptomatically and the changes progress to the extent that there are no treatment measures. Sometimes after surgery on the ovary, there is a compensatory initial synthesis of connective tissue, and over time, this synthesis progresses so much that symptoms appear several years after the surgery.
The first signs of ovarian adhesions may first manifest when a woman tries to get pregnant. In this case, numerous attempts become unsuccessful and after many tests and examinations, the exclusion method leads to a diagnosis of ovarian adhesions. This happens because the connective tissue that forms on the ovary prevents the egg from leaving the follicle, so the ovulation process is incomplete. In this case, the egg simply does not reach the uterine cavity and fertilization does not occur. Therefore, ovarian adhesions can have clinical manifestations in the form of infertility, which is what happens most often.
Also, clinical symptoms of adhesion formation may be pain syndrome. Pain with adhesions on the ovaries has its own characteristics: the pain is dull, constant, localized on one side in the lower abdomen. They can intensify due to menstruation, which may be due to compression of nerve endings when the uterus increases. Such pain syndrome is not intense and responds well to treatment with antispasmodics. The peculiarity of such pain is that they are uniform and do not intensify, do not have a progressive nature. If the nature of the pain has changed or if the localization has changed, then it is worth thinking about it, because this may be a sign of complications.
Also, the symptoms of adhesions can manifest themselves in the form of problems with the patency of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms of a chronic inflammatory process of the tubes or ovaries arise, which occurs due to the maintenance of a chronic source of infection. In this case, symptoms of a chronic intoxication process arise in the form of periodic or constant maintenance of subfebrile body temperature, lethargy and weakness, decreased performance, periodic or constant mild pain syndrome. These symptoms should also be paid attention to, since they may indicate such a pathology.
Sometimes adhesions on the ovaries can disrupt their normal functioning so much that the structure of the stroma and glandular structure of the organ changes and a dysfunction occurs. This is manifested primarily by disorders of the ovariomenstrual cycle. Often these two pathologies are not connected with each other, but it is necessary to remember that such reasons can also exist. In this case, disorders in the form of ovarian insufficiency most often occur and this occurs as amenorrhea. Such delays can be up to two to three months, and then, when the amount of hormones is restored, normal menstruation can resume.
Symptoms of ovarian adhesions may also manifest as pathological discharge. Such discharge may be green or yellow, in small quantities with inflammation of the same ovary. There may also be bloody discharge if adhesions are accompanied by a change in the topic of the fallopian tubes and secondary trauma. Then there may be minor bloody discharge after active physical exertion.
Complications and consequences
What is the danger of ovarian adhesions? This question does not have a clear answer, since all changes depend on the woman's age and the severity of symptoms. The main complication of such adhesions in women of reproductive age is infertility. This happens if the process has spread to the fallopian tubes and caused a change in the topic of the organs. This raises the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with ovarian adhesions? Despite the irreversibility of the changes, nature has provided the woman with two ovaries and two fallopian tubes for this case, therefore, given that the process is mainly one-sided and the changes are asymmetrical, it is possible to get pregnant, in extreme cases, there are alternative methods.
Diagnostics adhesions on the ovaries
It is very important to diagnose the adhesion process in the pelvis before it causes infertility. Therefore, when examining a woman with any pathologies, it is important not to exclude such a process in the ovaries using not only general data, but also to conduct additional research methods if necessary.
First of all, the consultation should begin with finding out the anamnesis data - it is important to establish and detail the complaints, as well as find out the patient's anamnesis. It is necessary to find out about the nature of pain, localization, duration, reaction to analgesics, as well as find out the dynamics of symptoms and whether they have changed recently. Such detailing of complaints is also necessary for further differential diagnostics. From the anamnesis data, it is necessary to find out what surgeries the woman has had, whether there were pregnancies and how the birth went, as well as the presence of ovarian and uterine diseases. It is important to find out the time of the last menstruation, their regularity and nature. Further, during the examination, indirect signs of the adhesion process can be detected. During bimanual palpation of the uterus, its insufficient mobility can be determined, and with large adhesions, a unilateral infiltrate can be determined, non-painful or moderately painful, in the projection of the ovaries. This can be the initial stage for further diagnostics and differential diagnostics of such a process. But also when examining a woman in mirrors there may not be any specific changes, so additional research is necessary.
The tests that need to be done to detect adhesions are not specific and can only be done for the purpose of differential diagnostics. In case of chronic inflammatory process in the ovary and formation of adhesions as a result of it, changes in the general blood test can be determined - leukocytosis with neutrophilic shift of the formula to the left, acceleration of ESR. This should prompt the idea of a chronic inflammatory process. It is also necessary to conduct a study of the vaginal smear for bacterial flora - this will make it possible to identify the causative agent of this chronic infection.
A histological examination of the cervical smear is also mandatory to check for dysplasia.
Instrumental diagnostics of ovarian adhesions is not the most informative method, but it is used at the first stage of examination. There are no specific symptoms, and the nature of the changes depends on the size of the adhesion conglomerates. Adhesions on the ovaries on ultrasound have the appearance of heterogeneous echo signals of varying intensity, but it is difficult to differentiate and confirm these changes. Therefore, preference is given to more informative methods.
Hysterosalpingography is a method in which the uterine cavity and tubes are filled with a contrast agent and an X-ray examination is performed. In this case, any defects in the filling of the tubes in the ampullar part and the degree of filling with contrast can be seen, which can be used as a basis for diagnosing the adhesion process. It is possible to determine the degree of disruption of the topic of the fallopian tube and ovary due to the development of connective tissue and determine the stage of the disease. There are three main stages of this process:
- the adhesion process is limited only to the ovaries without serious processes on the tubes and there are no obstacles to the release of the egg;
- adhesions move from the ovaries to the tubes, and the capture of the egg by the fimbriae is disrupted;
- The adhesion process deforms the fallopian tube, causing it to bend or change its location.
The stage of the process is important for clarifying the diagnosis and choosing treatment tactics.
The "gold standard" for diagnosing ovarian adhesions is laparoscopy. This is a visual diagnostic method, which involves inserting a camera through a special conductor into the pelvic cavity, which allows one to directly see the nature of the changes and their prevalence. The diagnostic value of this method increases due to the fact that it is possible to simultaneously perform surgical intervention, during which the pelvic cavity is revised. This is an accessible and minimally invasive method, which can also be used to diagnose the adhesion process and differential diagnosis of the volumetric process in the pelvis.
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics of ovarian adhesions should be carried out with many pathologies if a woman is infertile for this reason. Then, at the second and third stages of the adhesion process, it is necessary to exclude first of all those pathologies that may be accompanied by ovulation disorders. With insufficiency of the luteal phase, ovulation may not occur, which must be taken into account in the differential diagnostics of adhesions, which may be accompanied by a violation of the release of the egg. Therefore, to exclude hormonal causes of ovulation disorders, it is necessary to conduct hormonal screening, and only then think about mechanical factors.
When a significant conglomerate of adhesive etiology is detected on the ovary during palpation, differential diagnostics with tumor processes should be performed. In this case, the ovarian tumor is often painless, does not move and does not have clear contours. Sometimes, in order to differentiate these two processes, it is necessary to conduct magnetic resonance imaging, which allows us to clarify the nature of the process and its infiltration growth, in the case of a tumor.
It often happens that there is a need to differentiate ovarian adhesions from a cyst. The main thing here is ultrasound, which can accurately determine the changes characteristic of a cyst in the form of a cavity with clear edges and echo-negative contents. Sometimes accurate differentiation can only be done visually, seeing the changes during laparoscopy.
It is very important to conduct a full range of diagnostic studies not only to establish a diagnosis, but also for the purpose of conducting differential diagnostics.
Who to contact?
Treatment adhesions on the ovaries
Treatment of ovarian adhesions must necessarily take into account the etiological, pathogenetic principle and severity of symptoms. If this pathology is asymptomatic and does not affect reproductive function, then the treatment should not be active.
Drug treatment should be carried out in the acute period, taking into account the cause that led to adhesions. If the cause of such changes is chronic inflammation of the ovary, then it is necessary to eliminate this inflammation, since it supports the synthesis of connective tissue. Therefore, in the treatment, it is necessary to use a complex of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents. The advantage belongs to the antibiotic to which the flora isolated from the vagina is sensitive.
- Vilprafen is an antibacterial agent that has available forms for the treatment of gynecological pathology, from the macrolide group. The active substance of this drug is josamycin, a drug that is especially effective in intracellular forms of infections. These forms are often the cause of chronic inflammation, since microorganisms inside the cell are difficult to treat. This drug acts by inhibiting the synthesis of protein fragments of the cell wall, which leads to a bacteriostatic effect. The dosage of the drug in the form of vaginal tablets of 500 milligrams. The method of using suppositories for the treatment of chronic inflammation of the ovaries is a course of two vaginal suppositories per day. In this case, suppositories should be placed after hygiene procedures. Side effects are possible in the form of dyspeptic phenomena, dysbacteriosis, as well as an increase in liver transaminases and jaundice. Precautions - do not exceed the course of treatment due to possible local changes in the form of candidiasis. It is necessary to take into account the possible effect on hearing when increasing the dose of the drug.
- Flamax is an anti-inflammatory drug used in combination therapy with an antibacterial drug for severe pain syndrome, as well as to accelerate the resorption of adhesions. This is achieved by activating immune defense cells in the inflammation site and reducing the severity of edema. The active ingredient of this drug is ketoprofen (a non-steroidal non-narcotic anti-inflammatory drug). The drug is available in the form of vaginal tablets, the dosage of the drug is 100 milligrams of the active substance in one tablet. Method of application - one suppository per day should be used vaginally, after hygienic measures, you also need to wait an hour after using other vaginal suppositories. Side effects are possible from the gastrointestinal tract in the form of glossitis, damage to the esophagus, stomach, intestines with dyspepsia, impaired evacuation function of the intestine. Also possible allergic reactions of varying severity. When the drug affects the hematopoietic system, anemia, a decrease in the number of platelets and granulocytic neutrophils may occur. When the drug affects the heart and vascular system, rapid heartbeat, pain in the heart area, heart rhythm disturbances, lability of blood pressure, and edema syndrome may occur. Precautions - should not be used in early pregnancy.
- Longidaza is an enzyme preparation that can be used at the second stage of treatment, when the inflammatory process has been treated. The enzyme preparation has a targeted effect on connective tissue, since it breaks down glycopeptide bonds. Due to this, the targeted action helps to carry out specific proteolytic therapy. The active substance of the preparation is hyaluronidase (a natural proteolytic enzyme). The preparation is available in ampoules for intramuscular administration and the dosage of the preparation is 1500 and 3000 international units. The method of administration of the preparation is intramuscular, 3000 units of the preparation per day, the course of treatment is from ten days to three weeks. The course of treatment can be repeated if necessary. Side effects are possible only in the form of allergic reactions and irritation at the injection site. Precautions - it is undesirable to use the preparation during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is not recommended to combine the intake of this drug with loop diuretics.
- Trypsin is a proteolytic agent that includes the natural enzyme trypsin. This agent has proteolytic activity against connective tissue, so it can be successfully used to improve the dynamics of ovarian adhesion resorption as a combination therapy. The drug is available in ampoules and its dosage is 10 milligrams. The method of administration of the drug can be intramuscular, but local treatment can be used in combination with parenteral treatment. In this case, you need to make a tampon from the trypsin solution from the ampoule and insert it into the vagina for two hours before bedtime. Side effects in the form of burning or discomfort in the vagina are possible. Systemic side effects include increased heartbeat and a feeling of a rush of heat to the face. Precautions - do not use tampons with the agent in case of damage to the uterine cavity or after recent surgeries.
- Atsilakt is a drug from the probiotic group, the main active ingredient of which is lactobacilli. This drug is recommended for use at the final stage of treatment of ovarian adhesions, when the normal microflora of the vagina is restored. After treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and proteolytic enzymes, this drug will help to quickly restore the endometrium and normalize the bacterial composition. The drug is available in the form of vaginal tablets and the dosage is one tablet per day. Method of application - vaginally, you need to insert the suppository not too deeply into the vagina after all hygiene measures and without taking other local remedies. Side effects are rare, allergic reactions to the components of the drug are possible. Precautions - the tablets must be used for the entire course and that's it, long-term storage and an incomplete course reduces the effectiveness of the drug.
These are the main medications that should be used only according to the plan, because the complex of drugs is aimed at different links in the process and it is necessary to carry out treatment in turn.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of ovarian adhesions is very important, since it is a targeted effect on the pathological process using physical methods. A prerequisite for physiotherapy is the absence of acute and chronic inflammation in the ovary, so it is better to use such treatment in remission. The most common method of physiotherapeutic treatment is electrophoresis with enzymes - lidase, trypsin, chymotrypsin. These enzymes, with the help of ions, are able to penetrate deep into adhesions and better break down their bonds. A course of seven to ten electrophoresis sessions is recommended. Magnetic therapy also has a good effect, which enhances cell ionization and also reduces the severity of the process.
Vitamins do not have a specific effect in the treatment of adhesions, but as part of complex therapy they improve blood circulation and normalize the immune status, including local.
Surgical treatment of ovarian adhesions is used in the second and third stages of the disease, when the follicle is drawn into the process and ovulation is disrupted. In this case, surgical intervention is recommended for women who are planning a pregnancy. Treatment can be minimally invasive, when alternative methods to the scalpel are used. Very often, during diagnostic laparoscopy, when adhesions can be visually seen and the extent of the process can be assessed, surgical treatment is immediately performed. The most accessible method is dissection of adhesions with a scalpel. But such surgical intervention has a drawback, since adhesions often form again after this. There are also alternative methods - this is the use of an electric knife or laser excision. In this case, in addition to removing adhesions, there is a parallel "cauterization" of connective tissue cells, so the process of further synthesis is not so significant. This is the advantage of laser surgery - adhesions form again very slowly, but this method is not available everywhere. During such surgery, special absorbable agents can be applied to the ovaries, which can prevent further changes for a long time.
When talking about drug and surgical treatment, it is necessary to take into account the main symptom in this case - the stage of the disease, as well as age and individual characteristics.
Traditional treatment of ovarian adhesions
Priority in the use of folk treatment methods belongs only to the first stage of the disease, when the process is not yet widespread. Herbs and folk methods are used that enhance blood and lymph circulation and thus restore normal blood flow, which reduces the severity of dysplastic processes and connective tissue synthesis. The main folk methods are as follows:
- Flax is a natural remedy that has good anti-inflammatory properties and has proteolytic properties. To prepare the medicine, flax seeds should be boiled in hot water for three minutes, then the solution should be strained and allowed to cool. A gauze swab should be soaked in this solution and inserted into the vagina overnight. Such procedures should be carried out daily for at least a week, then it is recommended to switch to sitz baths from the same solution - this will improve the effect of the treatment.
- St. John's wort reveals its effect by increasing the outflow of lymph, which improves the ovarian trophism and reduces the severity of the adhesion process. For a medicinal solution, you need to take a liter of hot water and pour five tablespoons of dried St. John's wort leaves with this water. This solution is infused for three hours, and then you need to douche. It is better to do this at night with a small pear. The course of treatment is three weeks.
- Compresses from medicinal herbs are very useful and effective in the treatment of adhesions of the pelvic organs. For such compresses, you need to take yarrow and morinda leaves, pour hot water over them and make a compress from gauze. Such a compress should be placed on the lower abdomen and covered with a warm woolen cloth on top. The duration of such a compress should be at least two days. The course of treatment is ten days.
- Aloe contains natural proteolytic enzymes in its composition, so aloe juice has a good effect on the resorption of adhesions. For treatment, the juice of a young aloe plant should be squeezed into a glass jar about twenty milliliters, then add a teaspoon of honey and five drops of vitamin A. Such a solution enhances the proteolysis of adhesions after a few days of treatment. You need to take a teaspoon on an empty stomach once a day, the course of treatment is five days.
A very good treatment is provided by combining different methods of traditional medicine, for example douching and compresses - this enhances the effect of these substances.
The use of herbs is also widely used:
- The use of peony root, as a perennial plant, has a very good effect on the female reproductive system, especially when it comes to adhesions. For treatment, an alcohol tincture is used - for 300 grams of vodka, you need to take two small roots of this plant and insist for at least a week, then take a teaspoon of this medicine twice a day after meals.
- Orthilia secunda is a plant that is widely used in gynecology, as it has many properties - antitumor, resorption, anti-inflammatory. For treatment, use a water infusion of this herb, which is prepared according to standard rules - for three tablespoons of dry herb you need to take a liter of boiled water. You need to use half a glass of this tea twice a day, the course of treatment is seven days.
- Birch buds are also a very effective remedy for treating adhesions of any etiology, and as for adhesions on the ovary, in this case, a local form is used. To do this, you need to make a decoction of birch buds, pouring them with a glass of water. Half an hour after the decoction has infused, you need to make a gauze tampon and insert it into the vagina for two hours. The course of treatment is two weeks.
Homeopathic methods of treating ovarian adhesions are also widely used:
- Acidum fluoricum is a homeopathic remedy of inorganic origin (phosphoric acid). This remedy improves the metabolism of connective tissue cells and promotes their resorption with a pronounced affinity for the ovaries. This remedy is available in the pharmacological form of homeopathic granules and is dosed seven granules twice a day. This is a very strong remedy in its action, which promotes proteolysis of adhesions, even the most pronounced. Precautions - when treating pregnant women, you need to consult a doctor. Side effects of the drug are possible in the form of grinding teeth and a metallic taste in the mouth.
- Silicea is a homeopathic preparation of natural inorganic origin, which is recommended to be taken in combination with Acidum fluoricum, which increases the effectiveness of both preparations. The dosage of the preparation is seven granules three times a day. Method of application - you need to dissolve the granules until they are completely dissolved. Precautions - do not violate the time of administration, this affects the effect of treatment. Side effects were not detected.
- Thuja is a homeopathic remedy of plant origin, which is effective in concomitant inflammatory diseases of the ovary. Dosage and method of administration of the drug - seven granules three times a day, keep in the mouth until completely dissolved. Side effects are possible in the form of a cough, which has a dry character. Precautions - patients with bronchial asthma should use the drug with caution.
- Graphite is a homeopathic remedy based on inorganic material. It is used to treat adhesions in patients with a pronounced exudative component. Method of application - under the tongue, dosage - ten drops of solution three times a day. Side effects are rare, allergic reactions are possible.
Homeopathic remedies should be used for a long time - in case of treatment for at least six months, positive dynamics are possible, up to complete recovery.
Prevention
Prevention of ovarian adhesions is non-specific:
- regular check-ups with your doctor;
- diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cysts, inflammatory processes;
- hygiene of sexual life with the avoidance of promiscuous relationships and a reduction in the level of infection with intracellular organisms;
- family planning and regular sexual intercourse;
- avoidance of unscheduled surgical interventions and artificial termination of pregnancy.
 [ 39 ], [ 40 ], [ 41 ], [ 42 ], [ 43 ], [ 44 ], [ 45 ], [ 46 ]
[ 39 ], [ 40 ], [ 41 ], [ 42 ], [ 43 ], [ 44 ], [ 45 ], [ 46 ]
Forecast
The prognosis for ovarian adhesions in terms of life is favorable, but if such a problem occurs in a young woman and in the case of untimely treatment, complications can be expected, given that this process is irreversible. Therefore, it is necessary to engage in not only primary prevention, but also secondary - it is better to treat adhesions at the initial first stage.
Adhesions on the ovaries are a common problem among women who want to have children. This is due to the fact that the incidence rate increases and clinical manifestations and timely diagnostics of chronic ovarian diseases, as the main element in the formation of adhesions, decrease. Postoperative adhesions have a more difficult treatment and are less treatable, especially conservative. Given this, it is necessary to take care of your health from an early age to fulfill your role as a mother.

