
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Open tibia fracture
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
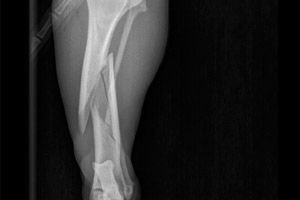
An open fracture of the tibia is a dangerous, pathological injury. Let's consider its causes, main symptoms, types, methods of diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation.
The part of the leg from the knee to the ankle joint is the shin. It consists of two bones: the tibia and the fibula. Violation of their integrity is a fracture. Most often, damage to the tibia is recorded with preservation of the integrity of the fibula, but damage to both is possible. Injuries to the fibula are extremely rare.
The violation has different levels of complexity, which depend on the following factors:
- Localization of damage
- How the fragments are arranged
- Severity of rupture of soft tissues, joints and vessels
- Presence of complications
That is, this kind of pathology is quite complex, but its severity is assessed individually for each patient. The treatment is carried out by a surgeon and a traumatologist. The patient will undergo an operation that will allow the bones to be folded and fixed with pins, bolts or plaster. After a long period of immobilization, the patient will have a difficult period of rehabilitation aimed at full restoration of leg functions.
Epidemiology
The pattern and frequency of open fractures of the tibia are largely related to age and gender factors. Epidemiology is based on the general condition of the body and type of activity. Very often, injuries occur in athletes and people with pathological diseases that cause bone fragility.
According to the conducted research, men suffer from shin fractures more often than women. At risk are people whose work is connected with motor transport, as there is a risk of accidents, athletes, workers. But you can’t be 100% sure that the injury will not occur in people who are not included in this category. That is, no one is insured against open shin injuries.
Causes open tibia fracture
The main cause of an open fracture of the tibia is a directed impact of great force. The bones cannot withstand strong pressure and break. Most often, this occurs when falling on a leg that is fixed or bent in an awkward position. Blows, falling heavy objects, traffic accidents, sports injuries, pathological and chronic processes (tumor, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis) provoke bone damage.
There is a certain classification of open injuries, which is based on the location of the injury, the location and number of bone fragments, the nature and extent of damage to soft tissues and joints. Let's consider the main types of injuries:
- Single and multiple - with a single fracture, the bone is broken in one place and there are two fragments, and with multiple fractures, in several places, which results in more than two fragments.
- Straight, spiral, oblique – depends on the line of the defect. If the bone cracked across, then it is straight, diagonally – oblique. If the line is uneven, then it is a spiral injury.
- With and without displacement - depends on the localization of bone fragments. If the injury is without displacement, then the normal position of the fragments to each other is observed. With displacement, there are changes in the position of the bones and if they are compared, they will not form a normal bone.
- Splintered and smooth - smooth ones have the same fracture line, splintered ones have uneven edges, teeth of different shapes and sizes.
- Intra-articular and extra-articular - if the joint tissues are involved in the pathological process, then this is a severe intra-articular injury. If only the shin is hit and the joints are intact, then this is an intra-articular injury.
In addition, injuries to one or both bones, the upper, middle or lower third are distinguished:
- Proximal part of the tibia or upper third of the tibia and fibula - this category includes injuries to the condyles, head and neck of the fibula, and tibial tuberosity.
- Middle part or middle third of the tibia - damage to the diaphysis.
- The distal part or lower third of the tibia are ankle fractures. As a rule, injuries of this group are accompanied by ankle or knee joint injuries, which significantly complicates the overall picture.
The most complex injuries are most often caused by accidents and falls from heights. But regardless of the cause of the pathology, the more areas of the bone are damaged, the longer the treatment and rehabilitation process.
 [ 10 ]
[ 10 ]
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of fracture development is based on the direct impact of a force that is perpendicular to the bone axis. Pathogenesis is associated with strong impacts. In medical practice, this pathology is called a "bumper fracture" because a blow from a car bumper almost always causes an open injury to both limbs. A characteristic feature of the injury is the direction of the impact wave. As a rule, the injury has a wedge shape with many fragments in the wound area.
Athletes are more often diagnosed with injuries to the right shin, since for many it is the supporting and pushing leg. If the force was directed along the axis of the bone, then damage to the ankle, condyles of the tibia, and ruptures of the cruciate ligaments develop.
Damage is differentiated depending on the direction of the force of impact on the bone: spiral, transverse, helical, oblique. Longitudinal tend to have the worst tendency. This is due to poor blood supply to the tibia. Another severe injury is helical fractures. They occur with rotational movements of the shin when fixing the foot. They are accompanied by bone fragments, severe ruptures of muscles and skin.
Symptoms open tibia fracture
Like any injury, bone damage has characteristic signs. Symptoms of an open fracture of the tibia depend on the location of the defect, its cause and a number of other factors. The first thing the victim experiences is severe pain, bleeding and swelling. When trying to move the limb or palpate it, there is a crunch of bone fragments rubbing against each other. It is impossible to lean on the leg, as well as to make an active movement of the shin. Bone fragments protruding from the wound are visible, and an elongation or shortening of the leg is also observed.
Shin injuries have a number of similar symptoms to other lower limb injuries:
- Anatomical and functional disorders.
- In the area of the fracture, excessive mobility of the leg appears.
- At the site of injury there is severe pain and swelling, and a rupture or sprain of the ankle ligaments is possible.
- If the injury is displaced, hematomas and bruises appear.
If the bone has damaged the peroneal nerve, the foot hangs down and cannot be bent. If the injury is caused by blood vessel fragments, the skin turns blue.
The main symptoms of an open fracture of the tibia:
- Heavy bleeding
- An open wound with bones breaking through soft tissue and skin
- Sharp pain
- Limitation of mobility
- Traumatic shock state
- Dizziness, weakness, loss of consciousness
To diagnose the extent of damage and its localization, the victim undergoes an X-ray, MRI or CT scan. If the injury falls on the diaphysis, then swelling and cyanosis with severe pain develop. The shin is severely deformed, the crunch of bones is heard in the tissues, the foot is turned outward. With injuries to the tibia, it is impossible to lean on the leg, while with fractures of the fibula, support is possible. Distal injuries are characterized by severe pain and swelling, the foot is turned outward or inward, support on the limb is impossible.
First signs
Pathological damage to the fibula or tibia can be suspected by knowing the first signs of a fracture. The victim has a shortened shin and a deformed limb. The shortening is due to the fact that the muscle tissues surrounding the broken bone are trying to connect it, so the limb is pulled up. Another characteristic sign is pain and bleeding, which intensify when trying to move the leg or touch it.
The first signs include swelling in the area of injury. It is associated with bleeding into the joint. Crepitation of bone fragments and increased mobility of the leg are observed. It is impossible to lean on the injured limb, and pain shock can cause loss of consciousness.
Open fracture of the fibula
The fibula consists of two epiphyses, it is thin, long and tubular. The main components of the ankle are the lower end of the bone (the outer, lateral malleolus), which acts as a stabilizer of the joint. There are several types of open fractures of the fibula, which can form at different levels. But in most cases, the damage occurs in the area of the lateral malleolus, accompanied by dislocation and shortening of the foot, rupture of the distal syndesmosis.
The bone body has a triangular shape and three surfaces: lateral, medial, posterior. They are separated from each other by ridges. Damage can be transverse, fragmentary, spiral and oblique. Diagnosing the pathology is not particularly difficult, since the injury has a clear clinical picture:
- Severe pain and bleeding from tissue torn by bone.
- Swelling and limited range of motion.
- Damage to the peroneal nerve (possible with a fracture of the neck and head of the bone).
- Drooping of the foot and the inability to bend it (occurs with a complete rupture of the nerve).
The most common injury is the diaphysis, which is possible with a direct blow to the outer part of the shin, due to a twisted foot, or a fall from a height. Various pathological diseases of the bones provoke their fragility, which can also cause injury. A fracture of the diaphysis increases the risk of injury to the fibular nerve.
The diagnosis of damage is based on symptoms. To identify the injured area, the victim is sent for an X-ray (the images are taken in two projections). If there is a need for a more thorough examination, then CT or MRI is performed.
Treatment is long and depends on the severity of the injury. The main danger of open injuries is the possibility of infection of the wound, which will significantly complicate the recovery process. The risk of infection increases in the postoperative period, when the victim's body is weakened. Without timely medical care, an open fracture of the fibula can lead to amputation of the injured limb or part of it.
Let's look at the options for treating the injury:
- If the injury occurred in the middle third of the bone, then a plaster cast is applied to the leg from the middle of the thigh. In addition, the knee and ankle are immobilized for 2-3 weeks.
- If the fracture is in the upper half without damage to the peroneal nerve, then a plaster cast is applied for a month. But on the 2-3 day, the victim can walk, leaning on a crutch.
- Trauma to the fibular head with nerve damage is accompanied by severe bleeding and bruises. The patient is given a plaster cast up to the middle of the thigh and the foot is fixed at a right angle.
Medicines, physiotherapy procedures, a course of massage and therapeutic exercises are prescribed without fail. After 3-4 weeks, the plaster cast is replaced with a removable knee splint. If the therapy method does not give the desired results (incorrect therapy regimen, presence of serious concomitant diseases), then full recovery and restoration may not occur. In this case, the victim loses the ability to move normally.
 [ 17 ]
[ 17 ]
Open fracture of the tibia
The tibia is a long tubular bone that is most often the subject of shin injuries. As a rule, when it is fractured, the fibula is also deformed. An open fracture of the tibia is possible with high-energy injuries, i.e. accidents, falls from a height, or sports injuries. Very often, the pathology is combined with fractures of the pelvis, ribs, other limbs, abdominal and chest injuries.
Symptoms:
- Sharp pain
- Bleeding from the site of injury
- Swelling and deformity of the leg
- Crepitus and pathological mobility of the limb
- Bruises on the skin
- Bone fragments can be seen through the wound.
To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray of the shin is performed. Based on the images, the doctor determines the number of fragments, the presence of displacement and damage to the fibula, ankle or knee joints. If there is damage to the joints, then a CT scan is additionally performed. In case of damage to nerves or blood vessels, a consultation with a neurosurgeon, neurologist and vascular surgeon is required.
First aid consists of taking a painkiller and immobilizing the limb. The skin around the wound must be cleared of foreign bodies and dirt, covered with a sterile bandage. If there is severe bleeding, a tourniquet is applied to the thigh. Anti-shock measures are indicated in case of traumatic shock.
Inpatient treatment can be surgical or conservative, depending on the complexity of the injury. If the fracture is without displacement, then immobilization of the limb and wound treatment are indicated. In other cases, skeletal traction is performed. A pin is inserted through the heel bone and a splint is applied. The leg is kept in this position for a month, after which a control X-ray is taken. If the image shows signs of bone callus, then the traction is removed and a plaster cast is applied for 2-3 months. Drug therapy is mandatory, which consists of analgesics and drugs to stop infection from an open wound.
In particularly severe cases and in case of comminuted fractures, surgical intervention is performed. Treatment is aimed at restoring the normal position of bone fragments. Prevention of post-traumatic contractures is also carried out. The operation is performed 7-10 days after the patient is admitted to the hospital. During this time, the swelling decreases and the general condition normalizes. The patient spends the entire preoperative period on skeletal traction.
During the operation, the doctor selects the method of osteosynthesis, focusing on the nature and level of the fracture. For these purposes, various metal structures are used: blocking rods, pins, plates. Extrafocal osteosynthesis with Ilizarov devices is very often used. The period of fusion of the tibia with an uncomplicated fracture takes 3-4 months. In case of comminuted injuries, treatment can last six months or more. Physiotherapy and exercise therapy are carried out during the entire period of therapy. After the bone has fused, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation course.
Open fracture of the tibia with displacement
A direct blow in the transverse direction is the main cause of fractures with displacement. The injury causes bone fragments to form, which shift in different directions. Their displacement can be peripheral, angular, lateral, fragments can wedge and go behind each other.
An open fracture of the tibia with displacement is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain and crunching when injured.
- At the site of the lesion, a bruise and swelling form with pronounced impairments of the motor function of the leg.
- Due to the displacement of the fragments, the soft tissues and skin are torn.
- At the site of the fragments' movement, a depression or indentation is formed.
- The damaged limb is shorter than the healthy one.
- The movement of the lower leg is carried out in an unnatural direction.
Very often, such injuries cause traumatic shock. Treatment begins with matching the displaced bones. This is necessary to give the limb the correct shape and its normal fusion. The procedure is carried out manually or with the help of special instruments. In order for the victim not to suffer from pain, he is laid on his back and anesthetized. After this, the patient is taken by the hip, and the second doctor grasps the leg, holding the heel and the back of the foot. In this position, doctors slowly stretch the limb and determine the position of the displaced fragments.
After the reduction, the doctor compares the length of the injured leg with the healthy one. If their parameters match, then the open wound is treated and the shin is immobilized. After 10 days, the patient must undergo a control X-ray. This is necessary to confirm normal fusion. If repositioning is impossible, then metal structures are used to fix the displacements.
Comminuted open fracture of the tibia
A comminuted open fracture of the tibia is a violation of the integrity of the bone with more than three fragments and a rupture of soft tissues. It is considered one of the complex injuries, as it carries the risk of interposition of soft tissues, compression of nerves and vessels. With a large number of fragments, difficulties arise during reposition, since the fragments cannot be aligned.
Signs of a comminuted open injury to the shin:
- Pain and bleeding
- Swelling
- Hematomas
- Deformation of the leg and its pathological mobility
An X-ray is used for diagnosis. Treatment begins with creating conditions for the fusion of fragments and subsequent restoration of limb function. At the first stage, bone fragments are displaced and fixed to prevent repeated shifts. The method of therapy depends on the nature and location of the injury, its severity, the general health of the victim, the presence of concomitant injuries and diseases.
With a large number of fragments, treatment is performed by surgical restoration of the surface. Various methods are used for this: the Ilizarov apparatus, osteosynthesis with screws, plates and pins. In case of complex multi-fragment intra-articular injuries with displacement, surgery is an absolute indication. In some cases, when the tibia and fibula are damaged, surgery is performed only on the former. When it is restored, the second bone will fuse on its own.
The duration of immobilization depends on the severity of the injury, but is usually 3-5 months. Rehabilitation to restore normal functioning of the leg and its motor functions takes 3-4 months. The patient will undergo exercise therapy, massages, and special gymnastics.
Open fracture of the lower third of the tibia
Most often, leg fractures occur in the lower third of the shin. If the injury mechanism is direct (directed blows, car accidents), then a transverse fracture of one or two bones occurs. Indirect injuries (bending, rotation of the shin with a fixed foot) result in a screw-shaped, i.e. oblique, injury.
An open fracture of the lower third of the leg is very dangerous, as it is accompanied by a passive position of the limb. In particularly severe cases, this is so pronounced that the surface of the foot can be placed on any plane. Palpation reveals severe pain, and lateral deviations of the leg are determined. If both bones are broken, there is crepitation and mobility of the fragments.
To accurately determine the location of the defect, X-rays are taken. Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture, the presence of displacement, and the condition of the soft tissues. The open wound is cleaned and disinfected, the fragments are surgically displaced. Knitting needles, bolts, or plates are used to fix them. A V-shaped cast is applied for 1-1.5 months, but before that, a Behler splint and a skeletal tension system are used to allow the wound to heal and the swelling to subside. Damage to the lower third of the leg heals slowly, unlike injuries in the overlying areas. Complete restoration of the limb takes 4-5 months.
Double open fracture of the tibia
In terms of frequency among double injuries of tubular bones, double open fracture of the tibia ranks first. The mechanism of its origin is direct in most cases, but is accompanied by extensive damage to surrounding tissues. The intermediate bone fragment enters the main blood supply, deforming the artery. It must be excluded from the blood flow, as this causes delayed consolidation and frequent cases of nonunion. The duration of immobilization is extended and can reach 4-6 months.
Depending on the characteristics of the displacement, there are four types of double open leg injuries:
- No bias
- With displacement at the level of distal damage
- With displacement at the level of proximal damage
- With displacement of the intermediate fragment
All these types have a typical clinical picture with more or less pronounced signs of soft tissue rupture and bleeding. Diagnosis is made using radiography in different projections. Treatment depends on the nature of the injury:
- In case of displacement, immobilization is performed with a circular plaster cast, covering the knee joint for up to 4-5 months.
- If there is a displacement at the level of the distal fracture, then repositioning with skeletal traction for 1.5-2 months is indicated. This is necessary to eliminate the displacement along the length. After traction, a circular plaster cast is applied to the limb up to the upper third of the thigh for 3.5-4 months.
- In case of displacement of the intermediate fragment or at the level of the proximal fracture, open reduction is performed. Due to the impaired blood supply, the surgical intervention should be with minimal trauma. For this purpose, extrafocal osteosynthesis devices or osteosynthesis with a rod fixator are used. The duration of consolidation of injuries of this nature is 2 times longer than the period of fusion of single fractures. Complete restoration of the limb occurs in 7-10 months.
Where does it hurt?
Complications and consequences
Open fractures are the most difficult to treat. This is due to the risk of possible displacement, fragments, ruptures of blood vessels and nerves. All consequences and complications are divided into three large groups, depending on when they appeared.
- Direct – observed during injury.
- Early ones – appear a couple of days after the fracture.
- Late – appear after a long period of time after the injury.
Straight |
Early |
Late |
Systemic |
||
Hypovolemic shock |
Hypovolemic shock Fat embolism Deep vein thrombosis Sepsis Infection |
Abnormal bone fusion Non-unification Cross fusion |
Local |
||
Damage to large blood vessels Injuries to muscles, tendons, joints |
Infection Traumatic compression syndrome |
Aseptic necrosis Shortening and stiffness of joints Osteomyelitis Ischemic contracture Osteoarthritis Sudeck's dystrophy |
With open fractures of the tibia, victims may experience the following consequences and complications:
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels – deformation of a large artery can cause amputation of the entire limb below the fracture. Gait and foot movement disorders may occur.
- Infection – an open wound causes suppuration, purulent damage to the ends of bone fragments, their shortening and slow healing. Infection is also possible after surgery.
- If surgical treatment is untimely or incorrect, limb deformation occurs.
- Fat embolism – particles of fatty tissue that enter the vessels can migrate with the blood flow, disrupting the blood supply to various organs.
- Formation of a false joint - this is possible if there are pinched tissues between the fragments of the bone that do not grow together, but there is still mobility between them.
- Complications arise after using the Ilizarov apparatus – infection at the sites of the needles, damage to tendons, blood vessels and nerves, curvature of the limb, improper fusion of fragments due to insufficient fixation.
Particularly severe injuries, as well as untimely or incorrect treatment, may cause amputation of the limb. In this case, the decisive factors are: the extent of the damage, the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the shin and foot, the volume of damaged skin. The longer it takes to decide on the method of treatment or amputation, the higher the risk of developing gangrene.
Diagnostics open tibia fracture
If a fracture is suspected, it is very important to make a correct diagnosis, since further treatment and recovery depend on the correctness of its interpretation. Diagnosis of an open fracture of the tibia is based on characteristic signs indicating a pathological injury. The victim is examined by a traumatologist or surgeon using clinical and instrumental methods, let's consider them:
- Examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis
- Comparison of the injured limb with the uninjured one
- Palpation and percussion
- Assessment of the range of motion of joints
- Checking the blood supply
- Determination of sensitivity and muscle strength
During visual examination, an open fracture cannot be confused with other injuries. Since bone fragments protrude from the open wound, there is bleeding, swelling, crepitus. The leg does not perform a supporting function. The mechanism of injury can be direct and indirect, which determines the nature of the fracture: transverse, oblique, comminuted, spiral, with displacement, double. To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are carried out.
Instrumental diagnostics
In determining the degree of traumatic injury, special attention is paid to instrumental diagnostics. If there is a suspicion of shin damage, radiography is indicated. The image is taken in two projections. In order to clarify the severity of the compression fracture, a computed tomography is performed. This is a special X-ray examination that allows you to obtain complete information about the nature of the injury and the presence of additional damage.
In addition to X-rays and CT, magnetic resonance imaging and other methods that visualize the affected area can be used. As a rule, several methods are used simultaneously during diagnostics. This is due to the high frequency of intra-articular injuries in open fractures of the tibia. Destruction of the subchondral plate joints delays the treatment process and worsens the prognosis for full recovery. The data obtained as a result of complex diagnostics allow us to determine the treatment tactics and avoid possible errors.
What do need to examine?
Differential diagnosis
The fracture line is a characteristic radiographic sign, so differential diagnostics are rare and difficult. This is due to the fact that pathological and healthy tissue images in some cases simulate fracture lines, cracks or bone fragments.
- An erroneous diagnosis can be made in the presence of epiphyseal lines. In this case, ossification is possible within many variants, which complicates the interpretation of the nature of the shadow lines. For this purpose, a control radiograph of a healthy limb is performed, which may also contain lines simulating a fracture.
- Pseudoepiphyses are another reason for differential diagnostics. Accessory bones are of great importance. The distinctive feature of pathology is the contours of the tissues. In fractures, they are finely jagged and uneven, the accessory spine is rounded and has smooth contours.
The presence of an open wound with torn tissue and bone fragments protruding from it very rarely causes difficulties with diagnosis or requires differentiation. Therefore, the diagnosis is based on X-ray and CT data.
Who to contact?
Treatment open tibia fracture
Different types of shin fractures require different methods of therapy. Treatment consists of a set of procedures aimed at normal fusion of damaged bones and healing of the open wound.
Treatment algorithm:
- Comparison of bone fragments to give it a normal position. This is necessary for proper fusion. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, manually or with the help of a skeletal traction system during surgery.
- Open wound treatment with mandatory introduction of several drainage systems. The wound is fixed with a rare suture. If the skin rupture does not form immediately, but due to a puncture by a bone fragment and is secondary, then it is treated with antibacterial agents and sutures are applied without drainage. If an open fracture is accompanied by extensive damage to the skin, then their transplantation is required.
- Fixation of bone fragments using pins, bolts, side loops, various devices (Ilizarov, Tkachenko, Kalnberz, Hoffman).
- Immobilization of the shin by applying a splint and installing a compression-distraction device for several weeks to months. This is necessary for the fracture to heal.
Different methods and materials are used for each specific case. If some methods are ineffective, they are replaced by others. The duration of treatment is from 4 months.
First aid for open fracture of the tibia
An open fracture is a serious injury in which the integrity of the bone and surrounding tissues is compromised. It is very important to provide timely assistance, preventing possible complications. The injury may be accompanied by the following dangers:
- Traumatic shock - an open wound causes severe pain, which can cause temporary loss of consciousness.
- Severe bleeding – one of the important tasks is to stop the bleeding. Since severe blood loss is a threat to life.
If you suspect bone damage, you need to call an ambulance, which will take the victim to the emergency department and provide professional medical care. But before the doctors arrive, in order to minimize or completely prevent all sorts of complications, first aid is indicated. In case of an open fracture of the tibia, the following measures are recommended:
- Fix the injured leg. Any available materials (boards, reinforcement, tree branches) will do for this purpose. The limb should be tied to them using a bandage or a long piece of fabric. If possible, it is better to make a G-shaped splint, this will allow you to fix the knee and foot. If there are no materials at hand, then the sore leg will be bandaged to the injured one.
- Be sure to take off your shoes. Pathological trauma causes swelling, so shoes can cause bleeding problems in the limb. Tight shoes will cause even more pain. If the victim is not taken off his shoes, it will be difficult to do so later.
- Give a painkiller. This will help overcome the pain shock. Any drugs that are available will do for this (Analgin, Sedalgin, Nimesulide). If possible, it is better to give an intramuscular injection (Novocaine, Lidocaine), the closer to the fracture the injection is, the better the painkiller effect. Upon arrival of the doctors, you need to report what drugs were used and in what dosage.
- Stop the bleeding. Open fractures are very often accompanied by severe blood loss. In order to assess the extent of the damage, you need to cut the clothes covering the injured leg. When large vessels are ruptured, blood flows out in a strong stream. To stop it, a tampon of cotton wool and bandage should be applied to the wound, and a bandage should be applied over them. It is not recommended to apply a tourniquet, since the muscles underneath will be tense, and if the fracture is comminuted, the fragments will be even more displaced. There is also a risk of damaging other vessels. If the blood flows out slowly, then a tampon is not applied, but an antiseptic treatment of the wound is carried out. As an antiseptic, you can use: iodine, brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide and any alcohol-based liquid. Only the edges of the wound need to be treated; you cannot pour the antiseptic inside.
These are the basic rules that must be followed when providing first aid. In addition, you can apply cold or a towel soaked in water to the site of injury. It is very important to avoid any movements and attempts to stand on your foot. This will lead to even greater trauma, displacement of fragments, damage to nerves and blood vessels. Also, nothing should be set in place; this can be done by a traumatologist and only after an X-ray.
Surgical treatment
The injury to the shin can occur in different places, so a combination of different techniques is used for treatment. Surgical treatment is the most difficult, since the correct fusion of bones and further recovery depend on its results. The main indications for surgery:
- Comparison of bones is impossible without additional opening of the wound.
- Double fracture of the tibia with significant displacement of fragments.
- Compression of nerves and blood vessels by bone fragments.
- Tissue interposition
If both bones are damaged, the operation is performed only on the tibia, since during its recovery, the fibula grows together on its own. Surgical reduction of fragments is possible only with their additional fixation.
There is a certain sequence of operations, let's consider it:
- Comparison of bone fragments. The procedure is performed by a surgeon under local anesthesia. Skeletal traction is used for this.
- Bone fragments are fixed using the most suitable device.
- The operated limb must be immobilized using a special apparatus or plaster cast.
The main types of surgical treatment of the tibia and fibula of the leg:
Type of fixation |
Peculiarities |
Duration of treatment and recovery |
Rods |
A sharpened steel rod is inserted into the spinal canal. An incision is made in the skin to access the bone. The sharp part of the rod goes into the bone, and the blunt part remains under the skin. This will allow it to be removed after the injury has healed. |
After the operation, the leg is allowed to bear no more than 25% of the body weight. After 2 weeks, you can start getting out of bed and moving around with crutches. After 3-4 weeks, you can try to stand on your leg completely. Control X-rays are taken every 2 months. Rods, screws, and plates are removed 1-2 years after the injury. |
Screws |
Using special screws made of surgical steel, the fragments are fixed to each other. |
|
Plates |
Steel plates with holes are fixed to the bones with screws. This method is not used to treat children, as it can cause damage to the periosteum and disruption of bone growth. |
|
Ilizarov apparatus |
The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia (depending on the age of the victim). Metal spokes are pulled through the bones, forming a structure of rods, bolts and nuts. The doctor tightens the nuts, adjusting the degree of tension for fusion. |
Loading the leg is allowed in the early stages, as the device holds the bone securely. Full recovery is possible in 3-4 months. |
During surgical treatment, preference is given to a less traumatic method. This will allow the bones to heal normally and will have a positive effect on the recovery process. In order for the leg to function normally and bear weight in the future, the shin bones must heal correctly. If the treatment process was incorrect or disrupted, this will cause the victim to become disabled and lose his ability to work.
Two-stage treatment of open fractures of the tibia bones
A comprehensive therapeutic approach is required to eliminate limb damage. Two-stage treatment of open fractures of the shin bones consists of osteosynthesis with rod devices for external fixation, followed by plastering and treatment of the open wound, which in most cases requires autoplasty.
- Osteosynthesis is a surgical operation, the essence of which is the fixation of bone fragments with various structures. This procedure allows you to combine all the fragments in the correct position, preserving the functioning and mobility of the damaged area after healing.
There are several types of osteosynthesis:
- External (transosseous) - I fix the site of injury with pins without applying plaster.
- Immersion – the fixator is inserted into the affected area, no plaster cast is required.
- Transosseous - rods or other fixators are pulled through the bone, that is, across the damage.
- Intraosseous – a fixator or a pointed rod is inserted into the bone and remains there until complete fusion. Requires complete immobilization of the limb.
- External - internal surgical intervention, fixators are placed around or near the injury.
Osteosynthesis is the main indication for open fractures. The entire procedure is performed under anesthesia, so the victim does not feel pain. If the operation is performed correctly, healing occurs within 3-4 months.
- Autoplasty of damaged skin is the transplantation or transposition of one's own tissues. The flaps used during the operation are divided into simple and complex. The type of transplantation depends on the presence or absence of blood supply at the site of the lesion. Simple flaps are distinguished by their tissue type: skin, fascial, muscle, tendon, bone, fat, vascular, and others. They are non-vascular grafts. Their engraftment depends on the diffusion of nutrients.
Autoplasty using simple fascial flaps is characterized by a small thickness with preservation of the skin at the donor site. This type of transplantation is limited by a small volume of tissue. Dermatome plastic surgery is then performed to close the transplanted fascia. This method is excellent for treating open shin fractures with skin defects.
Rehabilitation
During the treatment of an open fracture of the tibia, as well as after its fusion, the patient will undergo a long course of recovery. Rehabilitation consists of a set of measures aimed at restoring the functions of the injured limb. Its main goals are:
- Elimination of muscle atrophy, swelling and other congestion in soft tissues
- Restoring elasticity and tone of the calf muscles
- Normalization of blood supply
- Development of ankle and knee joint mobility
Rehabilitation consists of the following stages:
- At the first stage, the victim is prescribed massages and rubbing of the shin with hands using creams and ointments, which contain substances that accelerate tissue recovery (Chondroxide, Collagen Plus). In addition to massage, magnetic therapy sessions are indicated. During this period, the affected limb cannot be loaded with exercises, as this provokes severe pain. You can try to move the foot, bend the leg at the knee joint, strain and relax the calf muscles. This rehabilitation stage lasts until the removal of the apparatus holding the bones together or the plaster cast.
- The second stage is aimed at restoring the functions of the limb. For this, massages, rubbing, special baths and exercises are used. The complex consists of the following exercises:
- Leg swings from a standing position to the sides, forwards and backwards
- Walking at the fastest pace possible
- Seated and standing calf raises
- Rotational movements of the foot in different directions
Exercises are performed in different variations, but on a regular basis, that is, every day. The second stage begins immediately after the first and its duration is 2-3 months.
- At this stage, the patient is prescribed a course of therapeutic exercise to strengthen the muscles. The success of rehabilitation also depends on proper nutrition. The diet should include foods containing a large amount of calcium and silicon (milk, cottage cheese, nuts, beans, cabbage, currants, bran bread), vitamins C, D, E. This will speed up healing and improve overall well-being. This stage lasts for 1-2 months after the completion of the previous one.
Special attention should be paid to physiotherapy. In the first week after the injury, the following procedures are recommended:
- UV irradiation – prevents infection of an open wound by destroying pathogenic bacteria.
- Interference currents – dissolve hematomas, relieve swelling and pain.
- Bromine electrophoresis – used for severe pain.
Subsequently, the following physiotherapy procedures are carried out over the course of a month:
- Massage and ultraviolet irradiation.
- UHF – strengthens local immunity, improves blood flow, restores normal bone structure.
- Interference currents are used to normalize metabolism and accelerate bone fusion.
The above-described rehabilitation methods are used until the limb is completely restored under the supervision of a surgeon or traumatologist.
Prevention
Prevention of shin bone fractures is based on preventing injuries that can provoke it. Prevention consists of the following measures:
- Therapeutic gymnastics – a series of physical exercises with a selected load should be performed daily. This helps to restore and maintain muscle structure, normalize blood circulation, relieve inflammation and prevent muscle atrophy.
- Physiotherapy – necessary to reduce inflammation, accelerate healing and restore tissue structure. Helps improve blood circulation and metabolism.
- Massage – daily rubbing and massage procedures help prevent joint stiffness, muscle dystrophy of the lower leg, and the appearance of scars in soft tissues.
- Diet – therapeutic and preventive nutrition should consist of foods rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium, iron, magnesium.
Prevention is aimed at preventing complications after injuries. After the bones have completely healed, the doctor prescribes recommendations for the patient to develop the mobility of the leg and restore its normal functioning.
Forecast
An open fracture of the tibia is rightfully considered the most serious injury. The prognosis for recovery largely depends on the timeliness and correctness of the medical care provided. The quality of the primary antiseptic and antibacterial treatment is of great importance. Since its absence can provoke infection of the wound. Also important is the correct immobilization of the injured leg, the method of fixing bone fragments and healing the open wound. Delay at any stage of therapy can cause amputation of the limb, which makes the prognosis for full recovery impossible.

