
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Schmorl's hernia of the lumbar, thoracic spine: what it is, how to treat it
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
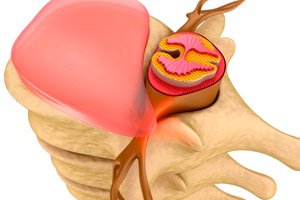
Schmorl's node of the spine or Schmorl's cartilaginous node is a radiological concept, it was first described by the German scientist and physician Christian Schmorl.
Schmorl's node of the spine is a collapse or pressing of the cartilage tissue of the endplates into the spongy bone, inside the body of the lower or upper vertebra. Very often it has a genetic nature or is formed in early childhood as a result of rapid growth of the human body.
As the child grows, the soft tissues can quickly stretch, but the bone tissues cannot respond so quickly to rapid growth and begin to lag behind in development. The result of this process is the formation of voids inside the vertebrae (in their spongy body). Over time, the endplates of the vertebrae fall into these voids.
A Schmorl's node differs from a regular intervertebral hernia in the following ways:
- Localization (location).
- The pathological reaction does not involve vascular-nerve bundles.
- Schmorl's node does not compress the spinal roots and spinal cord.
- Clinical manifestations may be absent or very scanty, since only the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs participate in the formation of Schmorl's nodes.
- Almost always occurs in childhood and adolescence.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Why is Schmorl's node dangerous?
- Over time, Schmorl's nodes contribute to the thinning of the vertebrae, making them vulnerable to physical stress and impacts, and as a result, a compression fracture may occur (a very severe pathology).
- Involvement of the intervertebral disc in the pathological process, its pushing through or falling into a hernia, significantly disrupts the function of the spine, which can cause disability.
- Also, Schmorl's nodes contribute to increased load on the intervertebral joints, which is one of the reasons for the development of early arthrosis of these joints.
- A Schmorl's node detected on an X-ray may be a harbinger of the future formation of an intervertebral hernia.
This is what makes Schmorl's hernia dangerous, i.e. its complications. Therefore, even in the absence of clinical manifestations of this hernia, but there are accidentally detected radiological signs, it is necessary to begin therapy immediately to prevent the occurrence of complications.
Causes of Schmorl's nodes
The following causes of Schmorl's nodes are distinguished:
- Hereditary predisposition (individual features of the structure of the endplates of the vertebrae).
- Rapid growth of a child in early or adolescence, accompanied by a lag in bone growth with normal growth of cartilage. And as a result, voids form in the vertebrae and are filled with cartilage tissue.
- Microtraumas of the spinal column or excessive physical stress on it (for example, in sports: diving, dancing - shaping, aerobics or during pregnancy).
- An injury resulting from a sudden lifting of something heavy or from a fall from top to bottom.
- Deformation of bone and cartilage tissue due to osteoporosis, especially in old age.
- Deterioration of blood supply to the vertebrae, as a result of which they become less durable and are simply pressed through by the intervertebral discs (reasons for deterioration of blood supply to the spine are stooping, kyphosis, Scheuermann-Mau disease, a sedentary lifestyle, often found in astronauts).
- Lack of calcium in bone tissue.
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc.
Symptoms of Schmorl's nodes
Clinical symptoms of Schmorl's nodes are usually absent or very scanty. Since Schmorl's nodes:
- does not compress nerve roots and blood vessels,
- does not cause aseptic inflammation,
- does not cause muscle spasm.
Schmorl's node, as mentioned earlier, is a radiographic sign and is very often detected accidentally, during diagnostic examinations related to other problems of the spine. Sometimes pain of a local (local) nature may appear. Such pain often appears during physical exercise and decreases or disappears during rest. In this regard, the main complaints are the inability to perform exercises to the full extent during sports.
By palpation (feeling) in the area of the affected vertebra, slight pain may appear and muscle spasm may be determined. Neurological and vascular changes are not observed.
Schmorl's node of the lumbar spine
Schmorl's node of the lumbar spine usually does not manifest itself in any way. But it can be accompanied by increased fatigue in the lumbar region, a feeling of discomfort and reduced flexibility of the back. It is detected accidentally during a diagnostic X-ray examination of the spine for other diseases. Very rarely, Schmorl's node can cause pain in the lumbar region and lower extremities, which occurs under the influence of physical activity or is an initial sign of a complication of the hernia. As the pathological process progresses, the intervertebral disc can completely fall into the hernia, which will disrupt the function of the lumbar vertebrae. In addition, Schmorl's node of the lumbar spine is a weak spot where a compression fracture of the vertebra can occur. This happens:
- with significant lateral load on the spinal column,
- during a strong blow,
- in case of compression of the spinal column along the axis.
Therefore, the detected Schmorl's hernia requires timely therapy. Schmorl's hernia can form at any level of the lumbar spine. There are five vertebrae in this section, and they are the largest, since the lumbar spine bears a large load. Depending on the location of the hernia, the X-ray "diagnosis" of Schmorl's hernia L1, L2, L3, L4 or L5 will be made.
Schmorl's node of the thoracic spine
A Schmorl's node of the thoracic spine can form at any level of the thoracic spine and is less common than other types of hernias. Most often, it occurs at the level of th8 - th12. Often, a Schmorl's node is asymptomatic. Since only bone tissue is affected, and nerve endings are not. And the absence of pain syndrome is accompanied by untimely diagnosis of the hernia. As the Schmorl's node grows in the thoracic spine, increased general fatigue and local fatigue in the thoracic spine may occur. Increased general fatigue occurs due to disruption of the internal organs - the heart and lungs (shortness of breath, rapid pulse may occur). Over time, back pain occurs, especially during physical activity, which decreases at rest and can radiate to the arms.
Schmorl's node of the cervical spine
Schmorl's nodes of the cervical spine are most common due to the softness of the cervical vertebrae themselves. At the initial stage and with a small size, the course of Schmorl's nodes in the cervical spine is asymptomatic. As the process progresses, weakness, increased fatigue and pain in the neck occur, especially during physical exercise. The progression of a cervical hernia (its increase or complication) can be accompanied by a violation of cerebral circulation, which is clinically manifested by headache, drowsiness, general weakness, increased fatigue.
Multiple Schmorl's nodes
Multiple Schmorl's nodes affect a significant section of the spinal column, as a result of which their main manifestations are:
- chronic pain that increases in an upright position (when a person stands or sits) and decreases in a lying position.
- Visually, such people have a noticeably increased forward tilt of the spinal column, and the natural curves of the spine - thoracic and lumbar - are smoothed out, as a result of which it forms a very straight shape.
- Stooping and poor posture are noted.
- Increased back fatigue is also noted and, as a result, work capacity decreases.
Multiple Schmorl's nodes may also be asymptomatic, especially in cases where the central part of the vertebrae is affected. As a rule, such nodes are detected by chance in early childhood and adolescence, and can often disappear on their own. The cause of such nodes is genetic predisposition (most often) and possibly calcium deficiency.
If multiple Schmorl's nodes are located on the anterior part of the vertebrae, there is a high risk of intervertebral hernia and compression fracture. Often, such deformations on the anterior part of the vertebrae occur in the lumbar region and can be accompanied by central hernias in adjacent parts of the spinal column. Such pathology requires mandatory specialist observation and timely therapy.
Schmorl's disc herniation
A Schmorl's disc herniation can be single or multiple. A single Schmorl's disc herniation usually does not manifest clinical symptoms. But if there are several such hernias in the spine (especially in one section), this leads to impaired mobility and curvature. Single Schmorl's disc herniations usually form in adulthood and old age and are localized mainly in the lumbosacral region. Multiple Schmorl's disc herniations occur in young people and more often in the thoracic spine. A Schmorl's disc herniation is detected accidentally during radiography for another disease.
Central Schmorl's node
- The central Schmorl's hernia is characterized by a more favorable course and is most often encountered. Usually, the course of this hernia is asymptomatic and it is determined using an X-ray or tomographic examination method. In cases where the central Schmorl's hernia is large, then clinical symptoms characteristic of spinal osteochondrosis appear:
- pain that occurs while walking, standing for a long time, or bending over;
- feeling of fatigue in the back area;
- pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the lower limbs, is possible;
- change (limitation) of mobility of the spinal column in the affected area.
If a central Schmorl's node is accidentally detected, it is better to see a specialist in order to begin timely prevention of possible complications.
Schmorl's nodes and pregnancy
Schmorl's nodes and pregnancy are compatible. Especially if the node did not manifest itself in any way before pregnancy. But in any case, if a Schmorl's node is detected during pregnancy, it is necessary to be under special supervision of a doctor (orthopedist, neurologist, obstetrician-gynecologist) and take great care of yourself. Because during pregnancy, the load on the spine increases significantly. It is possible that during pregnancy there will be a need to wear a support belt, corset or bandage, as well as go to the pool. All these activities will be very useful for both the pregnant woman and the future child. If a Schmorl's node is detected before pregnancy, it is recommended to strengthen the back first before planning it.
Consequences of Schmorl's nodes
The consequences of Schmorl's nodes can be varied. It can exist for a long time and not manifest itself in any way, not progress or become complicated. But if it increases, the process progresses, the following consequences arise:
- the formation of an intervertebral hernia, a more serious disease that requires long-term therapy with possible surgical intervention. Since the pathological process already involves the vascular-nerve bundles and even the spinal cord.
- There is a tendency towards compression fractures of the spine, which can occur during physical activity (especially in people involved in sports).
- The increasing load on the intervertebral joints provokes the development of early arthrosis of these joints.
- Posture, flexibility and mobility of the spinal column are impaired.
- A pronounced curvature of the spine develops - kyphosis occurs if the thoracic spine is affected and lordosis occurs if the lumbar spine is affected.
Such consequences not only disrupt movement when walking, bring pain and discomfort, but also make it impossible to play sports, and can even lead to disability. Given the possible consequences of Schmorl's hernia, it is necessary to take timely measures to prevent its progression.
Diagnosis of Schmorl's nodes
Diagnosis of Schmorl's nodes is based on:
- complaints - the presence or absence of pain, its localization, the dependence of pain on the effects of physical activity, whether the pain decreases in a lying position.
- Medical history – whether there is a Schmorl's node in the family, whether there have been any previous spinal injuries, etc.
- Visual examination and palpation along the spinal column - are there any curvatures or swelling of the soft tissues.
- Additional examination methods – radiography (the main method in making a diagnosis), computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
If necessary, a consultation with doctors of the following specialties is carried out: orthopedist, neurologist, vertebrologist.
Who to contact?
Treatment of Schmorl's nodes of the spine
The detection of usurative defects in the spinal column is a reason to begin treatment of Schmorl's hernia. In the absence of clinical symptoms, therapy will be aimed at preventing the progression of the pathological process.
Therapy for Schmorl's hernia (usurative defects) is carried out taking into account a number of factors: gender, age, characteristics of work activity, degree of severity of the process, concomitant diseases. In addition, when treating a hernia, it is necessary to take into account its cause.
The goals of treatment of Schmorl's nodes of the spine:
- If there is pain, eliminate it.
- It is necessary to improve metabolic processes in bone tissue.
- Improve blood circulation in the back muscles.
- Normalize and restore flexibility of the spine.
- Reduce or eliminate muscle spasm (muscle relaxation).
- Prevent the occurrence of complications.
Therapy for Schmorl's nodes of the spine is mainly conservative, aimed at strengthening the musculoskeletal system and consists of the following.
- Balanced and rational nutrition – fermented milk products (cottage cheese, cheese, kefir, milk), fish, caviar, soy products (milk, tofu), protein products – the spine’s “favorite food”. It is necessary to reduce salt intake, as it is deposited on bones and joints.
- Monitor your weight, as this puts additional strain on your spine.
- If there is pain, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs (dicloberl, nimesil, movalis) are prescribed.
- Sometimes, medications that strengthen the skeletal system are used - calcium preparations - calcitonin (alostin, myocalcic), it is possible to take vitamin D, fish oil (in capsules). It should not be forgotten that taking medications that strengthen the skeletal system can have an adverse effect on the excretory system (kidneys) and ligamentous apparatus, so before using them, you should consult a doctor.
- Avoid riding motorcycles, jumping into water, and carrying heavy objects.
- Therapeutic gymnastics is a fairly effective method that strengthens the back muscles and improves the flexibility of the spinal column.
- Swimming is also an excellent method for strengthening the muscles of the back and spine.
- Therapeutic massage – relieves fatigue and back pain, reduces muscle spasms, normalizes blood circulation and strengthens back muscles.
- Manual therapy – improves blood circulation in the affected area of the spinal column and expands the intervertebral space.
- Acupuncture.
- Spinal traction – improves tissue blood circulation and increases the intervertebral space.
- Hirudotherapy is the application of medicinal leeches to the affected area, which release active substances that improve local blood circulation and metabolic processes.
- Apitherapy is a treatment using bee products (the effect of bee stings).
Treatment of Schmorl's nodes using folk methods is not much different from official medicine, where gymnastics and massage are also used. Alcohol tinctures of medicinal plants are used - dandelion, chestnut flowers or a mixture of horseradish with raw potatoes.
Surgical treatment
Surgery for Schmorl's hernia is not indicated. When it is detected, conservative therapy with a set of physiotherapeutic measures is carried out. Surgery may be indicated in case of complications of the hernia, when an intervertebral hernia has formed or a fracture has occurred, as a result of which the person's condition has significantly worsened and conservative therapy does not give results (muscle weakness, back pain, internal organ disorders, etc.)
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for Schmorl's hernia or therapeutic physical training is a concept of using various methods of physical exercise - running, walking, swimming, gymnastics, etc. The method of therapeutic physical training is used for prevention, treatment of Schmorl's hernia, in the rehabilitation period and as a maintenance therapy. Therapeutic physical training is indicated at any age. Therapeutic physical training classes:
- improve metabolic processes throughout the body,
- increase immunity and the body's resistance to various infections,
- improve blood circulation and tissue trophism in the body,
- strengthen the musculoskeletal system,
- have a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state.
The load during therapeutic exercise should correspond to the body's capabilities and is selected individually for each person.
Exercises
Exercises for Schmorl's nodes are done in combination with stretching and massage.
- Pull-ups – strengthen the muscles of the arms, back and chest.
- Barbell presses from a lying position, without arching the back.
- Side swings with dumbbells. Starting position: sit down and lower your arms down. Then smoothly raise your arms with dumbbells above your shoulders, hold for a couple of seconds and lower.
- Training of the abs, back and gluteal muscles.
- Shrugs – exercises to strengthen the trapezius muscle (back of the neck and upper back) – raising and lowering the shoulders with a load. Can be done lying down, standing or sitting.
- Hyperextension – overextension, overstretching. Strengthens the straight back muscles, gluteal muscles and hip flexors. This exercise is especially recommended for those with a weak back. To perform it, you need to lie on your stomach in the simulator, your heels should be under a special roller. Then, lift your torso up and back – ten times, two to three approaches.
 [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
[ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
Gymnastics
Therapeutic gymnastics for Schmorl's hernia is one of the main methods of therapeutic exercise. Therapeutic gymnastics is prescribed and performed under strict supervision of a doctor. A type of therapeutic gymnastics is corrective. With its help, the muscular system (especially the back), ligamentous apparatus, joints (including intervertebral) are strengthened, the flexibility of the spine is increased, as a result of which defects of the musculoskeletal system are eliminated (such as poor posture, curved spine, etc.). Therapeutic gymnastics for Schmorl's hernia is usually prescribed in combination with breathing exercises.
Massage
Massage for Schmorl's nodes is a very effective and efficient method of its therapy. It is important that the therapeutic massage is performed by a competent specialist, since the manipulation should be gentle, soft and, most importantly, not aggravate the pathology. Acupressure has proven itself very well. Thanks to massage:
- improves blood circulation,
- strengthens the back muscles,
- relieves fatigue and tension in the back muscles,
- reduces and eliminates back pain,
- the trophism of musculoskeletal tissues improves.
Massage for Schmorl's nodes is performed in combination with other methods of treatment.
Prevention of Schmorl's nodes
Prevention of Schmorl's nodes is non-specific and consists of the following measures.
- Lead an active lifestyle at all stages of life – do gymnastics, swimming, running, race walking.
- Conduct physiotherapy procedures – various types of relaxing massages.
- People with special work needs – long-term work in a vertical position, professional sports (diving, speed skating, etc.) should pay special attention to the health of their back, and at the slightest pain or discomfort in the spine, seek help from a specialist.
- Monitor your weight, as excess weight is an additional burden on the spinal column.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle - avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, which impair blood circulation and, as a consequence, disrupt tissue trophism (nutrition).
Schmorl's node prognosis
The prognosis for health of Schmorl's node is favorable if it is detected in time, and for professional activity it is relatively favorable, especially for athletes. The danger of such a hernia is its asymptomatic nature, since the absence of clinical manifestations contributes to the progression of the disease and the occurrence of its complications (compression fractures, arthrosis, intervertebral hernias, etc.). But by performing all the necessary preventive measures, an active lifestyle, and careful attention to your health will ensure general health and the health of the spine.
Schmorl's nodes and the army
Schmorl's hernia and the army is a two-sided issue. On the one hand, Schmorl's hernia, which is asymptomatic, is not a contraindication for a conscript, and he can even enroll and study in military educational institutions. On the other hand, when Schmorl's hernia becomes complicated (which is especially typical for multiple Schmorl's hernias) and manifests itself in a violation of sensory and motor functions, then, of course, such a conscript is unfit for military service. But the question of the suitability of a conscript with a detected Schmorl's hernia will be decided by a council of doctors after his additional examination.

