
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Gastroscopy of the stomach: sensations, what shows, results
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 06.07.2025
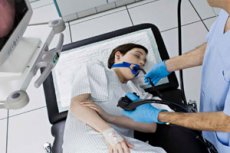
Gastroscopy is a procedure that examines the membranes and cavity of the esophagus and stomach. The duodenum is also affected. In some cases, gastroscopy allows you to visualize the image and display it on the screen. A gastroscope is used for the examination, which is inserted through the oral cavity into the esophagus, then into the stomach. The gastroscope can be imagined as a flexible tube of small diameter, which the patient swallows. At the end or inside there is a special optical system that allows you to examine the internal cavity.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health, since 2010 all gastroenterologists' offices must be equipped with two gastroscopes with the ability to take a biopsy. This requirement is explained by the importance and diagnostic significance of the procedure, which makes it possible to identify pathologies at an early stage and promptly take the necessary measures, prescribe treatment. Many specialists recommend regularly undergoing such examinations for preventive purposes. At least, you should not ignore the study if it is prescribed by a doctor. This means that there are grounds for this.
Is it painful to have a gastroscopy?
The examination is not without discomfort and painful sensations. However, today there are many methods that make it less unpleasant and painless. For example, the use of anesthesia, the latest probe-free examination methods.
Indications for the procedure
The procedure is used for the purpose of a detailed examination of the stomach walls. Most often it is used when there is a suspicion of a tumor process or possible bleeding, ulcers. The method allows for a visual demonstration of the nature of the pathological process, to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Based on the exact diagnosis, further examination is carried out. It is often used to establish the clinical picture of other diseases of the stomach and esophagus. It can be used as an additional method of examination for diseases not directly related to the digestive system.
It is also performed when pain of various nature occurs in the stomach and esophagus. It allows to determine the nature of pain, to detect the pathological process in a timely manner. With such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, heartburn, gastroscopy is mandatory. If there is bleeding, vomiting with blood, stool disorders - gastroscopy is a mandatory procedure. It is often performed for diagnostic purposes when there is a suspicion of an oncological process, for example, anemia, sudden weight loss, lack of appetite. It is performed for other diseases when it is necessary to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus, when food does not pass. It can be performed for therapeutic purposes.
Gastroscopy for gastritis
Gastroscopy can be a very informative procedure used for gastritis and suspected gastritis. It allows visualizing the internal space and getting a full clinical picture of the pathology. It is performed for sharp pains in the epigastrium, nausea, vomiting. It can be performed for both therapeutic and preventive purposes. For examination, a gastroscope is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus, the walls are viewed, then advanced into the stomach, the condition of the walls and mucous membranes is assessed. If necessary, a biopsy is taken. Based on the results, it is possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis, as well as identify other possible pathologies.
Preparation
In order to prepare for the examination, you need to consult a doctor, tell him your complaints, and provide information about all the medications you are taking. If you have allergies and diabetes, you should also tell your doctor about this. A few days before the examination, you should eat only dietary food and exclude alcohol. The last meal is allowed 10 hours before the procedure, that is, you can only eat in the evening. In the morning, before the procedure, you cannot eat or drink water.
Who to contact?
The device for carrying out the procedure
To examine the stomach cavity, special devices called gastroscopes or endoscopes are used. The difference between them is in the structure of the optical system at the end, which allows for visualization of the image. The device can also be located on any side: on the side, at the end of the tube.
Technique gastroscopies
Gastroscopy is performed in a special room. The patient must lie on his side. The throat is pre-treated with local anesthetics. A lidocaine solution is often used as a spray. The throat is irrigated, which reduces the gag reflex and eliminates pain. This also allows the muscles to relax, so that the probe can be swallowed freely without damaging the walls of the organs. Sedation is often used. This is a procedure in which the patient is given various sedatives and painkillers, which significantly facilitate the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia is used. In this case, an injection is given, most often intravenously.
After the preliminary preparation is completed, the patient is laid down, the patient is given a mouthpiece, which must be clamped in the teeth. It prevents damage to the teeth and lips, prevents biting the gastroscope. The gastroscope is slowly inserted into the throat, then advanced into the esophagus. At this time, a gag reflex inevitably occurs, the patient should breathe deeply and calmly. Then air is supplied through the device, which makes it possible to straighten the walls. An examination of the mucous membranes, walls, cavity is carried out. The esophagus, stomach, upper part of the duodenum are examined. If necessary, a biopsy and therapeutic effects are performed. Many modern gastroscopes make it possible to visualize the image on the screen, take photos and videos. After the examination and necessary manipulations, the gastroscope is removed.
Sensations during gastroscopy
During gastroscopy, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations. Discomfort is felt when swallowing the tube. This is accompanied by a gag reflex. If the patient is too nervous and fearful, the procedure may take even longer. Therefore, you need to behave calmly, try not to be nervous, then the procedure will be quick and will cause minimal inconvenience. Many patients have unpleasant pain in the throat, which lasts from 1 to 3 days.
Gag reflex during gastroscopy
During the procedure, a gag reflex may occur. It occurs in almost everyone, as it is a natural protective reaction. The urge may be quite intense, but, as a rule, the contents can be contained. Thanks to modern pharmacological agents, the gag reflex can be successfully overcome and suppressed. Anesthesia and muscle relaxants make it possible to relax the muscles of the esophagus, calm the nervous system. Local anesthesia is mainly used.
How to breathe during gastroscopy?
During the procedure, you should breathe slowly and calmly, in a normal rhythm. The tube does not affect the airways in any way and does not block the air flow. Moreover, the diameter of the tube is very small, due to which air circulates freely through the airways. The more the patient relaxes and is less nervous, the easier it will be to breathe, since in many ways the lack of air is an imaginary mechanism.
How long does a gastroscopy take?
Usually the procedure itself lasts 2-3 minutes. If it is a medical procedure, or during the examination there is a need for medical measures, it can last up to 15-20 minutes.
Anesthesia for gastroscopy
Many patients dream of a gastroscopy without pain. Today, this is possible thanks to the use of anesthetic solutions and painkillers. This makes it possible not only to eliminate pain, but also suppresses the gag reflex. At the patient's request, even gastroscopy is performed under general anesthesia. The peculiarities of local anesthesia are that it acts in the area of the pharyngeal ring. Local anesthesia and simultaneous relaxation of the larynx muscles occur. But at the same time, the person is fully conscious, can control everything that is happening, sees and is aware.
Types of gastroscopy
There are three main types of research.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or EGDS, allows for an examination of internal organs using an endoscope. In this case, the mucous membranes of the internal organs are examined. It allows for an assessment of the condition of the internal organs, early assessment of possible pathologies, and selection of the optimal treatment.
Fibroesophagogastroduodoscopy, or FEGDS, allows for examination of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum using a conventional gastroscope. This is a traditional gastroscopy.
Video endoscopes are also used, which make it possible to obtain a detailed and clear image from the cavity of internal organs. The image is displayed on the monitor screen, and can then be printed using a printer. It makes it possible to make a correct diagnosis and select treatment. The main advantage of this method is the ability to save the result.
Gastroscopy with sedation under general anesthesia
Some people are too sensitive, with a weak nervous system. They are too afraid, nervous, which does not allow the procedure to be carried out. Therefore, there is gastroscopy under anesthesia, during which a person is put under anesthesia, he is in a state of sleep, and the doctor can calmly carry out the procedure. This method is also used for children, since it is often difficult for them to carry out such a procedure due to their restlessness, fear, excessive activity.
Gastroscopy of the stomach without swallowing a probe
The study can be conducted without traditional swallowing of a probe. For this, the capsule method is used. The essence of the method is to swallow a special capsule that contains an optical system. The capsule is washed down with water, then it begins to move along the digestive tract and transmit the image to the screen. It is excreted after a certain time in a natural way and does not cause harm to the body.
Transnasal gastroscopy through the nose
A very unusual, but nevertheless effective method that allows examining the stomach and esophagus. It is used when there is a fear of suffocation or when it is impossible to insert an endoscope through the oral cavity. During this examination, the tube is first inserted into the nose, then through the throat into the esophagus and stomach. The difference lies in the method of insertion and the size of the endoscope. It is extremely thin - no more than 6 mm. It allows examining the gastrointestinal tract cavity no less effectively than when inserting an endoscope in the traditional way. In this case, there is no urge to vomit, but a cough may occur when the endoscope passes through the throat.
In most cases, coughing occurs only if the throat is tense and something is wrong. When the throat is relaxed and in a calm state, coughing does not occur. At this stage, you just need to relax and trust the specialist, who will carry out all the necessary manipulations as carefully and harmlessly as possible.
Otherwise, the procedure is similar to traditional gastroscopy. If necessary, the doctor can take a piece of tissue for biopsy. This technique can be used to diagnose various pathologies, including gastritis, ulcers, and cancerous tumors.
In addition to biopsy, chromoscopy and medical procedures are performed. The procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes. Many patients who underwent this study were satisfied, since they do not have to swallow the probe, and there is no gag reflex. The patient also lies on his side, and the device is inserted into one nostril. The second one remains free. The mouth is also closed and unoccupied. In this regard, there is no panic or feeling of lack of air. Many patients note that anesthesia is not needed for such a procedure, since it is absolutely painless. A special lubricating gel is used to facilitate the insertion of the tube. If necessary, anesthesia can also be used. Discomfort may be felt for a short time when the doctor turns the gastroscope, but it disappears fairly quickly.
It is interesting that even a runny nose is not a contraindication for the procedure. But this procedure can cause nosebleeds if a person has a tendency to bleed, or if there is damage to the mucous membrane.
The procedure itself is much simpler. There are practically no complications, no need for anesthesia. There is also no pain. The person can go about their business immediately after the procedure. The patient does not experience a sore throat, which often accompanies traditional gastroscopy, and is much less nervous. The risk of injury to the mucous membrane is significantly reduced, accordingly, there is practically no risk of developing an infectious and inflammatory process.
Capsule gastroscopy
Capsule gastroscopy is a new method of examination that is performed using a disposable capsule. The patient swallows the capsule and washes it down with water. The capsule is no more than 1.5 cm in size. In the middle of the capsule is a miniature color video camera, light sources, and a mini radio transmitter. The device is designed to operate for 6-8 hours. During this time, it moves along the digestive tract and transmits an image to the doctor's screen. It is also possible to take photos and videos as it moves, and save images. After the examination is completed, the capsule will travel the rest of the way and be excreted from the body with feces.
During the data transfer, they are registered using a special reader. It can be of different types: sometimes the patient is given a device with wires, similar to an armored vest. Sometimes the patient simply has a device similar to a telephone in his pocket. It receives the signal from the capsule. The materials are loaded into a computer with an installed program for their decoding. The received data is processed. A preliminary diagnosis is made by the program automatically. The impulses and all the data on the basis of which this particular diagnosis was determined are also saved. The doctor reviews the results. He can either confirm the diagnosis or prescribe additional studies.
With the help of this method of examination, the doctor determines what problems exist in the stomach and intestines. The peculiarity of this method is that it allows diagnosing the small intestine. No other method has such capabilities, since this area is not reached. The capsule allows identifying numerous gastrointestinal diseases that are practically not amenable to examination by any other methods. This is the most effective method for diagnosing bowel cancer, Crohn's disease, gastrointestinal pathologies and hidden bleeding. Also, with the help of this method, it is possible to diagnose iron deficiency anemia, damage caused by taking hormonal drugs.
The disadvantages of this method include the fact that if any pathology is detected, the capsule will simply transmit a signal about it to the computer. No medical manipulations can be carried out. It is also impossible to take a piece of tissue for histological examination, it is impossible to take smears for microflora and Helicobacter. It should also be taken into account that the capsule moves evenly along the digestive tract, at a certain speed, and the doctor remains just an observer. He cannot either turn, slow down, or speed up its passage. However, researchers are constantly working on improving the technology, and in the near future it will be possible to control the camera from a computer, turn it if necessary, adjust the angle and speed of passage.
 [ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
[ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
Gastroscopy with a thin probe
A thin probe, the diameter of which does not exceed 6 mm, is used for intranasal gastroscopy, in which the probe is inserted into the stomach and intestines through the nose. A thin probe is also used for examination of children.
Gastroscopy of the esophagus
An esophagus examination is performed if there are indications. Most often, the need for such an examination arises if a person suspects any damage to the surface of the esophagus, mucous membranes. The examination can provide a lot of information if there is a suspicion of an oncological process, when diagnosing esophageal cancer. Esophageal obstruction is the main indication for gastroscopy. The procedure is painless. Its duration ranges from 2 to 15 minutes. It can be delayed if there is a need for any additional examinations. Often, when examining the esophagus, there is a need to take a biopsy for further histological examination. Sometimes polyps or other formations are found on the wall of the esophagus. They must be removed immediately.
Esophageal gastroscopy is the main method for early detection of esophageal cancer. Preliminary preparation includes preliminary adherence to a dietary diet, refusal of alcohol. The last meal should be 8 hours before the examination. Drinking water on the day of the examination is also prohibited. A capsule or endoscope is used for the examination. Each of the methods has its advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, the doctor independently decides on the need for this or that examination method.
Most often, however, they resort to traditional gastroscopy using an endoscope, since this method makes it possible to immediately perform therapeutic manipulations, if such a need arises. Also, using an endoscope, you can take a biopsy, scraping or smear for examination. During gastroscopy, all the walls of the esophagus are examined. Additionally, with the help of an endoscope, air and water are supplied, which make it possible to examine the walls more thoroughly, which will straighten out. With the help of a camera built into the endoscope.
Gastroscopy of the intestine
The intestine can only be fully examined using capsule gastroscopy. Colonoscopy is used to examine the lower sections of the intestine. But it only allows examining the rectum and part of the large intestine. When examining the upper sections using gastroscopy, only the upper sections can be reached. The examination ends at the duodenum. With the help of a capsule, absolutely all sections can be examined, since it moves along the entire digestive tract and is subsequently excreted through the rectum with feces.
The essence of the procedure is that the patient swallows a capsule containing a built-in sensor. The capsule moves along the digestive tract and transmits a signal to the doctor's computer. Then, using a special program, the data is processed. The procedure is absolutely harmless, the patient does not experience any painful sensations or discomfort.
Determination of Helicobacter during gastroscopy
If a person is suspected of having a stomach ulcer or gastritis, a scraping is taken from the mucous membrane of the esophagus for further testing for the presence of Helicobacter bacteria. They live in the stomach and are the causative agents of gastritis and peptic ulcer disease.
 [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
[ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
Gastroscopy with biopsy
During the procedure, it may be necessary to take a biopsy for further examination. The material is taken for further histological examination if there is a suspicion of an oncological process. After taking the material, it is examined under a microscope, characteristic cells are found that may indicate the development of a malignant neoplasm. If such cells are found, they are seeded on special nutrient media. The cells are incubated for several weeks, then the nature and rate of growth confirm or refute the oncological process. This study is the main method for diagnosing bowel cancer, esophageal cancer. If cancer cells are detected at an early stage, the tumor can be removed without any consequences, and the development of a malignant tumor with further metastases can be prevented.
Also, a fragment of the mucous membrane can be taken for histological examination in order to detect the depth and extent of damage to internal organs by bacteria. Such a need often arises in case of peptic ulcer disease. Using this method, it is possible to determine the pathogen, its quantitative and qualitative characteristics. Also, a great advantage of this method is the ability to select the optimal drug in the required dosage and conduct antibiotic therapy as accurately as possible.
Gastroscopy in sleep
It is performed if a person is extremely afraid of the procedure. Sometimes, due to fear or previous unsuccessful experience, the procedure cannot be performed. There is a way out of this situation: gastroscopy can be performed in a dream. The patient is given special medications that act like anesthesia. The person is in a state of drug-induced sleep. The doctor conducts the examination at this time.
The advantage is that no anesthesia or anaesthesia is used, which have a negative effect on the heart and blood. Special short-acting sleeping pills are used, during which the person calms down and falls asleep. Sleep lasts about 20-30 minutes. During this time, the doctor has time to conduct an examination. After that, the patient wakes up, remembering nothing. Such sleep is absolutely harmless to the body, does not put any stress on vital organs. Can be used repeatedly. Often used when it is necessary to track changes in the dynamics of ulcer treatment. With such a diagnosis, procedures are carried out 2-3 times a week.
The disadvantage of this method is that the doctor performs all manipulations practically "blindly". In a normal state, the doctor monitors the patient's condition, depth and strength of movement, focusing on reactions and reflexes. During sleep, such indicators are absent. In this regard, the likelihood of damage increases. Also, after the procedure, you cannot drive for a long time, since concentration and reaction speed decrease. Heavy physical activity is also contraindicated during the day.
Diagnostic gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is used primarily for diagnostic purposes. It allows diagnosing various diseases of the esophagus and stomach. It is used to confirm inflammatory and infectious processes, such as gastritis, colitis, and ulcerative diseases. It is the main method that allows detecting cancerous tumors at early stages. This method can be used to perform a biopsy and take a scraping from the mucous membrane. It determines the degree of contamination with Helicobacter bacteria, which are the causative agents of gastritis and ulcerative diseases.
 [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
[ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
Therapeutic gastroscopy
Gastroscopy can also be used for therapeutic purposes, for example, to remove polyps, which are growths on the mucous membrane of the esophagus or in the submucosal layer. Manipulations related to the need to stop bleeding from ulcers can also be performed. Gastroscopy is used to apply ligatures to damaged vessels of the esophagus or veins that have undergone varicose expansion. It can be used to remove foreign bodies from the esophagus and stomach.
The gastroscope also makes it possible to make injections directly into the tissues of the stomach and esophagus, inject medications and irrigate the mucous membranes with them. Treatment of the vascular and lymphatic system is also carried out using a gastroscope. The procedure makes it possible to solve the problem of a narrowed lumen in the esophagus. If necessary, a special probe is inserted, with the help of which a nutrient mixture is supplied to the stomach. The therapeutic effect is achieved by introducing various auxiliary instruments into the cavity of the endoscope.
Virtual gastroscopy
There is a procedure known as virtual gastroscopy. The essence of the procedure is that special X-rays are used to conduct the examination. The image of the esophagus and intestines is displayed on the monitor screen. Usually the image is two-dimensional or three-dimensional. Virtual examination is no less informative, gives a clearer image than a regular X-ray examination, takes less time. The patient does not need assistance after the procedure and can go home immediately.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy and gastroscopy
EGDS is a method of visual examination of the walls of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It allows diagnosing most diseases at early stages and allows visualizing the clinical picture of diseases. It is also possible to conduct a histological and cytological study, the results of which become known in about 5-7 minutes. During the procedure, material is collected for this study.
The procedure lasts 10-20 minutes, standard preparation is required, which is to follow the diet and drinking regime. You cannot eat or drink for 8 hours before the examination. It is important to remember that the procedure has its contraindications, so you need to tell the doctor about the presence of concomitant diseases and taking medications.
The procedure involves inserting a tiny device containing a sensor into the esophagus. The signals from it are converted into an image on the monitor screen.
A big plus is the ability to diagnose cancer at an early stage, which allows for timely treatment. According to statistics, approximately 80% of cancer patients learn about their disease only at a later stage. With the help of EGDS and gastroscopy, it is possible to diagnose cancer at an early stage or at the stage of the origin of a cancerous tumor in 99% of cases. Also, with the help of this study, it is possible to conduct an analysis for lactase deficiency, to determine Helicobacter pylori.
Gastroscopy during menstruation
It is better to postpone the procedure for a few days, because during menstruation a woman's sensitivity increases. This can increase pain and the gag reflex. Also during this period, blood clotting decreases, and the risk of bleeding increases accordingly, even with minimal tissue damage. If it becomes necessary to take a biopsy or remove polyps, there is a risk of bleeding.
Gastroscopy protocols
First, the patient's age and medical history are indicated. Subjective complaints and the results of the objective examination of the patient are noted. The gastroscopy protocol displays the condition of the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The presence or absence of erosion, ulcers, foci of cellular transformation are noted. It is noted whether there is leukoplakia, Barrett's esophagus, or tumor formations. A biopsy is taken, information about this should also be indicated in the protocol. If there is a need for therapeutic measures, their essence is also reflected in the protocols.
The condition of the esophagus, stomach, their mucous membrane, pylorus, duodenal bulb, and postbulbar region is described separately.
Ultrasound after gastroscopy
Sometimes, an ultrasound may be required after a gastroscopy. These studies reveal completely different pathological pictures to the doctor and provide an opportunity to comprehensively assess the situation. Each procedure has its own disadvantages and advantages. The doctor makes a choice in favor of one or another method based on the expected results and what exactly needs to be examined.
Ultrasound examination allows to study the structure of the stomach from different angles, allows to study the features of blood circulation in the vessels of the stomach. Allows to study the condition of neighboring organs that are located nearby, in the ultrasound zone. It is possible to study the main processes in dynamics. In addition, this method eliminates the possibility of damage to the walls and mucous membranes. Allows not to involve the patient in a state of stress, since the method is quite comfortable and natural for a person. There are no contraindications. It can be carried out even on people with a weak heart and psyche.
The disadvantages of ultrasound include the impossibility of taking biopsy and physiological fluids for examination. This method can only evaluate the external picture of the organ. The method is ineffective in diagnosing tumors, since it does not allow detecting a tumor at an early stage. It is not always possible to diagnose gastritis.
Thus, each method has its pros and cons. To obtain a more accurate picture, it is better to undergo 2 studies. Therefore, they are often prescribed together. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the external side, structure and functional activity of organs. With the help of gastroscopy, you can detail the image and examine the organs from the inside. Traditionally, ultrasound is prescribed first, then gastroscopy, which is justified by logic: from the general to the specific. First, the picture as a whole is studied, then you can move on to specific cases.
Gastroscopy for children
The principle of the method is no different from that for adults. The difference is in the size of the swallowing probe: for children, the probe is shorter and thinner. The diameter is 5-6 mm. Preparation is the same as for adults. Gastroscopy is much more difficult for children, as they are active and restless. Many refuse to swallow the tube, throw tantrums. Psychological preparation and support from a loved one, especially the mother, are important for the child. The study must be carried out with special care, since the mucous and muscle layers are underdeveloped and can be easily damaged. Gastroscopy is performed under general anesthesia for children under 6 years of age.
Gastroscopy during pregnancy
In various gastrointestinal diseases, it is often necessary to conduct a study on a woman, despite pregnancy. The procedure begins with the application of a special anesthetic to the larynx and the back of the throat. After numbness occurs, a sedative is given. The woman falls asleep, is half asleep, but fully conscious, which makes it possible to maintain constant contact. To increase the effectiveness of the procedure, air is introduced into the stomach cavity. This straightens the walls and improves visibility. The duration of the procedure ranges from 10 to 25 minutes.
During pregnancy, it is used if other diagnostic methods are ineffective. It allows to clearly determine the location of the inflammatory and infectious process, to detect possible pathologies, in particular, cancerous tumors. The procedure is considered safe in the first and early second trimester. The main condition for safety is the correct choice of anesthetic. Lidocaine is most often used. Pregnant women should not eat food for 10-12 hours before the start of the examination. For half an hour after the end of the procedure, neither food nor drink is allowed. If a biopsy was performed, food should only be warm and soft for the next 24 hours to avoid complications.
Many are also inclined to believe that it is advisable to perform the procedure during sleep. The drugs themselves that provide drug-induced sleep do not harm the woman's body. But the benefit from them is noticeable - the pregnant woman is not nervous, is in an absolutely calm state, and, accordingly, anxiety is not transmitted to the fetus.
Contraindications to the procedure
Contraindications are determined by the urgency of the case. In emergency cases, for example, if severe bleeding occurs, there are no contraindications, and gastroscopy can be performed even on patients with acute myocardial infarction.
There are contraindications when conducting a routine examination. For example, it cannot be performed by people with a heart attack, in a post-stroke state, with an aortic aneurysm, heart rhythm disorders, hypertension and in case of severe mental disorders.
Normal performance
The doctor makes preliminary conclusions directly during the procedure. By assessing the condition of the mucous membrane, he can diagnose gastritis, peptic ulcer, colitis with absolute accuracy. The presence of tumor diseases can be assumed by the change in the color of the mucous membrane, the presence of edema and hyperemia. Based on this data, a preliminary conclusion is made. If a biopsy was performed or a scraping was taken for bacteriological examination, the results will be ready in 5-7 days. Based on the preliminary conclusion and the results of the tests, a conclusion is made for the gastroenterologist.
What does a gastroscopy show?
Gastroscopy makes it possible to detect inflammatory and infectious processes, ulcers, mucous membrane burns, polyps, hernias, and scars. Of particular importance is the ability to detect malignant neoplasms at early stages of their development. Gastroscopy can detect areas of ruptures that will later become a source of hemorrhage. In addition, intestinal parasites and foreign bodies can be detected.
 [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ]
[ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ]
Polyps
During the diagnostic procedure, there may be a need to remove polyps. They are excessive growths of the mucous membrane, which can later develop into a cancerous tumor. Polyps are removed during the procedure, the total duration of diagnostics and removal does not exceed 15-20 minutes. There is no pain. Blood may be released in small quantities, but it stops very quickly without the need to take any measures.
Stomach cancer
The stomach is one of the organs where cancerous tumors are most often detected. Usually, it is quite difficult to identify a tumor in the gastrointestinal tract by symptoms. Gastroscopy can detect the shape, size, and location of the tumor. It is also possible to determine the tumor shape: icteric, cachectic, or painful. In approximately 65% of patients, cancerous tumors occur in the antral part of the stomach. In the vault of the stomach, a tumor occurs in 1.2-2.6% of cases. Adenocarcinoma is most often diagnosed by histological type. Tumors are usually diagnosed at late stages, when they reach large sizes. But with the help of gastroscopy, they can be detected at early stages, and appropriate measures can be taken.

