
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Gastroscopy of the stomach and colonoscopy under anesthesia
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 03.07.2025
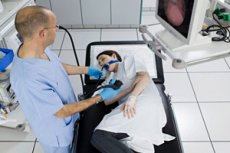
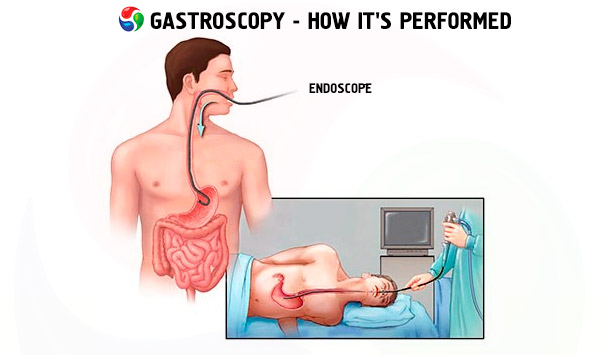
Gastroscopy is one of the methods of examining the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which consists of an endoscopic examination of the stomach, esophagus or duodenum.
The procedure is prescribed when it is necessary to diagnose gastrointestinal diseases, perform a biopsy or during surgery. Indications for the procedure may include complaints of stomach or intestinal upset, increased acidity in the form of heartburn, frequent belching, pain in the stomach and intestines, which may indicate an ulcer, gastritis and duodenitis, the appearance of tumors of various etiologies.
To conduct this examination, a gastroscope is required, with which the endoscopist performs the appropriate manipulations. The gastroscope is a tube that penetrates from the mouth through the esophagus into the stomach due to its flexibility and long size. Inside the gastroscope is an optical fiber, at the end of the device is a camera that transmits video or photo images to the screen.
Endoscopic examination of the stomach is performed using several methods:
- traditional (with pain relief or preliminary administration of sedatives);
- endosonography (traditional gastroscopy using ultrasound to detect tumors);
- capsule (involves swallowing a capsule with a video camera by the patient, which then exits through the intestines; this procedure is expensive);
- with sedation (the patient is put to sleep, during which the necessary manipulations are carried out);
- Gastroscopy under anesthesia (endoscopy using anesthesia).
Indications for the procedure
The main indications for the use of gastroscopy under anesthesia are:
- the need to diagnose the patient;
- performing a biopsy;
- surgical treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies;
- performing the procedure on small children;
- performing it on people who find it painful to undergo the traditional version of the procedure, for example, when the gag reflex is triggered or the patient moves abruptly due to painful sensations, which prevents the doctor from performing the manipulations.
Preparation
When preparing for gastric endoscopy, you should prepare yourself first and foremost mentally. You need a psychological attitude and confidence in the need for the procedure.
First of all, the patient should undergo the following examinations:
- on tolerance to anesthesia;
- for allergic reactions to anesthesia;
- general blood test;
- coagulation analysis;
- electrocardiogram (for people over 55 years old).
Based on the test results, the possibility of performing an endoscopy is determined.
The day before the procedure, you should stop taking any medications, except for sedatives, which a specialist may prescribe before gastroscopy to avoid anxiety. Sedatives may also be prescribed if the patient cannot sleep due to anxiety before the upcoming gastric endoscopy.
The last meal should be about 12 hours before the procedure. Smoking is prohibited 3 hours before gastroscopy. Immediately before the procedure, it is recommended to remove glasses and lenses, if the patient uses them, jewelry and precious items, dentures. The bladder should also be emptied.
It is advisable to bring wipes (wet and paper) to the clinic. A personal towel may be required, but in this case the patient will be warned before the procedure.
Preparing children for gastroscopy under anesthesia is no different from preparing adults.
For more information on how to prepare for a gastric endoscopy, read this article.
Technique gastroscopies under anesthesia
Endoscopic procedures such as colonoscopy and gastroscopy under anesthesia are indicated mainly in cases where there is a need for surgical manipulations. Such a procedure is very painful for the patient, so anesthesia should be used. Also, thanks to anesthesia, the patient will not interfere with the doctor with the natural reflexes of his body.
Gastroscopy under anesthesia for a child is mandatory at the age of up to 6 years; later, anesthesia may not be used. Due to the delicacy of handling the child's mucous membranes, specialists use endoscopes with small tubes (up to 9 mm).
Gastroscopy is performed by an endoscopist in a special room with the necessary equipment. The total time of manipulations often does not exceed 20 minutes.
First, anesthesia is used. This can be done:
- gastroscopy under general anesthesia;
- sedation (putting the patient to sleep);
- local anesthesia (performed by irrigating the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue with an anesthetic).
The first two methods require the use of special equipment and can cause the development of many complications. Local anesthesia is the most acceptable for gastric endoscopy, since it has the lowest potential for complications.
After local or general anesthesia, the patient should lie down (or be placed) on the left side. The legs should be bent at the knees and the back should be straight.
The patient is given a mouthpiece, which he clamps with his teeth. This is necessary both to protect the teeth and to protect the endoscope itself, which the patient can damage with his teeth. Then the endoscope tube is inserted inside, and the patient should constantly swallow so that the tube moves down the esophagus. After that, the doctor begins to blow air through the gastroscope. This happens when it has already reached the stomach and is necessary to smooth out all the folds that may be on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. At this point, swallowing is prohibited; the nurse collects saliva using a saliva ejector.
Thanks to anesthesia, all procedures will be painless for the patient, and it will be convenient for the doctor to perform manipulations.
Contraindications to the procedure
Contraindications to gastroscopy under anesthesia include conditions such as:
- gestation period;
- asthma;
- lack of blood clotting;
- post-infarction or post-stroke condition of the patient;
- mental illness;
- intolerance to drugs used for anesthesia.
It is worth noting that most of these contraindications can be waived if the patient is in a condition where a fatal outcome is possible. In order to save a person's life, the procedure is allowed to be performed even with some contraindications.
 [ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
[ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
Consequences after a gastroscopy procedure under anesthesia
The first two days after gastric endoscopy, a person may experience:
- nausea;
- frequent belching;
- bloating.
During this period, these symptoms are not a cause for concern. Dizziness may also occur periodically.
If these symptoms do not go away within two days, you should consult a specialist.
Complications after the procedure
If the gastroscopy procedure under anesthesia is performed by a qualified doctor, the likelihood of complications is minimal. However, there are a number of complications, in the presence of which you should urgently contact a doctor. Among them:
- very painful sensations in the stomach area;
- high temperature;
- vomiting blood;
- very dark and liquid feces;
- severe aspiration.
Complications occur in 0.001% of all cases.
Care after the procedure
Until the anesthesia wears off (1-2 hours depending on the type of anesthesia), the patient is under the supervision of a doctor.
You can return to your normal diet after local anesthesia once the numbness of your tongue and throat has passed.
The patient must be accompanied home by a close person. About 12 hours after gastric endoscopy with anesthesia, it is forbidden to drive a car and drink alcohol. The doctor should indicate more precise conditions of life after the procedure.
Reviews of gastroscopy under anesthesia
Most patients are satisfied with the gastroscopy procedure under anesthesia and consider it a worthy replacement for the traditional one. Since the probability of complications is extremely low, if there are no contraindications, endoscopic examination of the stomach with anesthesia is a convenient procedure, which satisfies both the specialist and the patient in terms of technique.

