
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Frontal bone
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 06.07.2025
Frontal bone(os frontale) participates in the formation of the anterior part of the vault (roof) of the skull, the anterior cranial fossa and the eye sockets. The frontal bone is composed of the frontal squama, orbital and nasal parts.
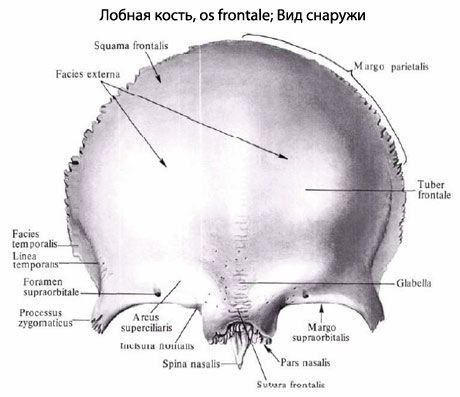
The frontal squama (squama frontalis) has a convex anterior surface, on which the frontal tubercles are visible. From the inside, the frontal squama is concave, forming the inner surface facing the brain. In front, the frontal squama passes into the orbital parts, forming the paired supraorbital margin (margo supraorbitalis). On the supraorbital margin, closer to the nasal part, there is a supraorbital notch (incisura supraorbitalis). Sometimes it closes, forming the supraorbital opening. In the medial part of the supraorbital margin there is usually an insignificant frontal notch (opening) (incisura frontalis, s. foramen frontale). Laterally, the supraorbital margin ends in a thick at the base and narrowed at the end zygomatic process (processus zygomatics). From this process the temporal line (linea temporalis) goes back and up. Above the supraorbital edge on each side there is a ridge-like elevation - the superciliary arch (arcus superciliaris). Between the two superciliary arches there is a flattened area - the glabella, or bridge of the nose.
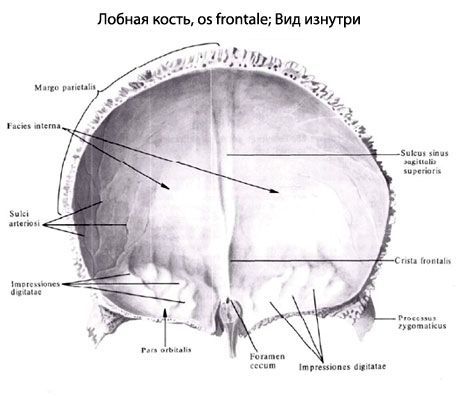
On the inner (cerebral) surface of the squama, along the midline, there is a groove of the superior sagittal sinus (sulcus sinus sagittalis superior). This groove passes in front and below into the frontal crest, at the base of which is located the blind opening (foramen caecum) - the place of attachment of the process of the dura mater of the brain.
The orbital parts (partes orbitales) are thin horizontal plates that participate in the formation of the upper wall of the orbits. Between these plates is a deep ethmoidal notch (incisure ethmoidalis). In the area of the lateral angle of the orbital part there is a depression - the fossa of the lacrimal gland (fossa glandulae lacrimalis). In the medial part of the orbital part there is a trochlear fossa (fovea trochlearis) and next to it - a bony protrusion - the trochlear spine. On top of the orbital part, the so-called finger-shaped impressions and cerebral protrusions are clearly visible - a trace of the adjacency of the frontal lobe of the brain.
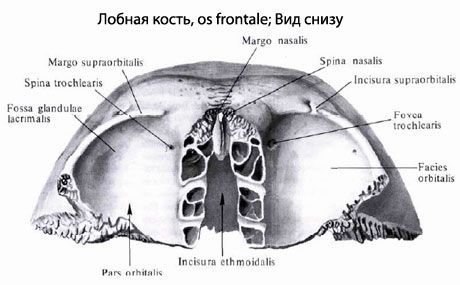
The nasal part (pars nasalis) of the frontal bone is located between the orbital parts, bordering the ethmoid notch in front and on the sides. On the sides of the pointed protrusion - the nasal spine (spina nasalis) are visible openings - the apertures of the frontal sinus, leading into the frontal sinus. The frontal sinus (sinus frontalis) can have different configurations and sizes. The sinus communicates with the nasal cavity, it is lined with a mucous membrane and filled with air.
Where does it hurt?
What do need to examine?
How to examine?


 [
[