
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Diagnosis of cervical dysplasia
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 06.07.2025
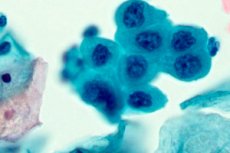
What methods are used to diagnose cervical dysplasia:
- Examination in the doctor's office, on the gynecological chair. Visible signs of dysplastic changes are determined using mirrors. Criteria are the color of the vaginal walls, mucous membrane, the presence of shine in the pharynx area, the uniformity of the epithelium, the presence of small whitish foci, etc.
- Pap test, a cytological examination of epithelial tissue using a microscope. Samples of material are taken from different sectors of the cervix to obtain a complete clinical picture. In addition, cytology allows you to determine markers of the infection that provokes dysplasia (most often HPV).
- Colposcopy (extended) may be prescribed as an additional method if cervical dysplasia is not accurately diagnosed by cytology. Optical examination in combination with samples provides a clearer clinical picture.
- Biopsy is a targeted biopsy. The histological method of examining tissue material is needed as important information about the nature and degree of dysplasia (exclusion or confirmation of malignancy, degeneration into cancer). Such a revision is needed for almost all patients over 40 years of age to prevent the development of cervical cancer.
- PCR diagnostics is an immunological method aimed at specifying the type of HPV (papillomavirus), as well as choosing the tactics of drug or surgical treatment
- Based on the indications, a comprehensive blood test and hormonal balance study may be prescribed.
Diagnosis of cervical dysplasia requires differentiation from the following pathological processes:
- Leukoplakia without signs of atypical changes.
- Erosive processes in the cervix.
- Dystrophic processes typical for the older age group of patients.
- Cervicitis.
- Pseudoerosion during pregnancy.
If dysplasia (CIN) is defined as a stage III disease, the patient is referred to an oncogynecologist. An immunologist, endocrinologist and surgeon may also be involved in the diagnostics.
Tests for cervical dysplasia
The gold, generally accepted standard for diagnosing cervical dysplasia (CIN) is the Pap test. The analysis was named after the doctor who first used it. Cytological analysis is accepted as mandatory in all developed countries of the world. Its reliability is extremely high (up to 80%), especially if cervical dysplasia is determined as a first-degree disease during the initial examination.
In cytological material, the Pap test shows intraepithelial changes in the layers lining the cervix. Deviations from the norm are usually designated by Latin letters, let's take a closer look at how this is deciphered:
- SIL(Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions) or squamous intraepithelial changes.
- LSIL (Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions) – epithelial lesions are not clearly expressed, low degree.
- HSIL (High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions) changes, atypia of epithelial tissue cells are clearly expressed. Here, the analysis is differentiated - moderate degree CIN II, carcinoma in the initial stage, CIN III is diagnosed less often.
- AGUS – lesion of the glandular cell layer, cervical adenocarcinoma.
Tests and procedures that are suggested if cervical dysplasia is detected:
- Examination ( bimanual examination in the gynecologist's office).
- Cytology.
- PCR.
- Examination with a colposcope.
- Histology (cervical tissue biopsy).
- Conization (cone biopsy).
 [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ]
[ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ]
Cytology
Cytology is mandatory for cervical dysplasia. This is a standard test that identifies and reveals abnormalities in the structure of epithelial tissue cells. Timely diagnostics helps reduce the incidence of women with such a formidable pathology as cervical cancer. All over the world, practicing gynecologists use the PAP test (Papanicolaou test), a smear is supposed to be taken from women starting from 18-20 years old. Cytology is especially relevant for the following categories of patients:
- Age over 40-45 years.
- If a woman is diagnosed with chronic viral diseases.
- Cancer in the family.
- Early or late birth, including frequent births.
- Frequent miscarriage.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Frequent or, on the contrary, irregular sexual intercourse (changing partners).
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs, including contraceptives.
How is cytology performed?
- A smear allows for a fairly accurate study of the cellular structure of the cervical epithelium.
- The material is collected using a medical spatula or brush.
- The obtained material is placed on a special sterile glass, where it is fixed with a fixative.
- The glass is marked and sent to a laboratory for testing.
- Laboratory technicians stain the resulting material and study the reaction results using a microscope.
Indications for cytology:
- The main objective is the prevention of one of the most common diseases in women – cervical cancer.
- Determining the cause of menstrual cycle irregularities.
- Clarification of the condition of the cervix in chronic infectious or viral diseases.
- Persistent infertility.
- Long-term use of oral medications for contraception.
- All endocrine diseases.
- Human papillomavirus in a sexual partner (infection of a woman is almost inevitable).
- Violation of the weight norm - anorexia or obesity.
- Planned procedure for insertion of a contraceptive IUD.
Cytology significantly reduces the development of oncology in women, as well as timely diagnoses the initial stages of various pathologies of the cervix.
 [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
[ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
Smear for cervical dysplasia
A smear is considered a simple and generally accepted procedure that is part of a comprehensive health examination or the determination of cervical pathologies.
Cervical dysplasia is often accompanied or, more precisely, provoked by imbalances in the microflora of the mucous membrane. Bacterial, viral infection can be the primary factor that gives rise to changes in the structure of epithelial tissue cells. A smear for cervical dysplasia shows the amount of certain indicators. Smears are of the following types:
- Smear to determine the state of microflora.
- Determination of microflora sterility.
- Cytological smear (PAP test).
- Smear that detects infections (PCR).
Also, with the help of a smear for dysplasia, a gynecologist can evaluate some criteria of the state of a woman’s hormonal system.
How is a cervical dysplasia smear performed?
- A small amount of mucus and cellular tissue from the surface layer of the cervical mucosa is collected on the gynecological chair. The choice of the type of material for analysis depends on the diagnostic task.
- The smear can be performed several times. The initial one is needed to assess the condition of one or another parameter of the cervix, the next ones are needed to monitor the success of the treatment of diseases. If the therapy is long-term, the smear is performed every three months.
- A smear is considered a painless and quick diagnostic procedure that requires certain preparation from the patient (the doctor gives recommendations on preparatory measures).
If the woman is healthy, the smear usually shows a large number of lactobacilli (up to 95%). They are the ones that can produce protective lactic acid, which serves as a barrier to the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The acidity of the microflora is one of the important indicators of the health of the vaginal microenvironment.
Let us clarify the purposes for which a smear test for cervical dysplasia is performed:
- The absence or presence of infectious agents, including sexually transmitted ones (Trichomonas, chlamydia, gardnerella, etc.).
- Determination of latent chronic infections (PCR).
- Assessment of the condition of cervical epithelial cells as a mandatory procedure for the prevention of cervical cancer.
The smear purity can be as follows:
- Healthy reproductive system, first purity group (pH 4.0–4.5).
- The second group is an indicator of the initial stage of infection, the presence of gram-negative bacterial flora (pH 4.5–5.0).
- Determination of bacterial flora in a smear, third group (pH 5.0–7.0).
- The fourth group is the presence of a critically large number of pathogenic microorganisms (pH 7.0–7.5), a sign of an inflammatory process.
Normally, a smear for cervical dysplasia should not contain the following indicators:
- Presence of atypical cells.
- Cells that are affected by infectious agents, key cells (squamous epithelial cell tissue affected by infectious agents).
- Candida and other types of fungal pathogens.
- Gardnerella.
- Coccal bacterial infection (gonococci, staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci).
- Trichomonas.
If cervical dysplasia is diagnosed as a first or second degree epithelial lesion, the smear shows the presence of pathogenic agents, this does not mean that the woman has cancer. A huge number of infections in modern medicine have already been studied and successfully treated. Timely detection of pathological changes in the cells of the cervical tissue allows preventing cancer in almost 75%, according to some recent data, this percentage has increased, thanks to a program of regular screening activities.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostics is the leading method in a comprehensive examination when cervical dysplasia requires both clarification of the severity and monitoring of the success of treatment of the disease.
The choice of instrumental assessment is explained by the fact that dysplasia most often develops and proceeds as a process without clinically noticeable manifestations. Laboratory diagnostics is in second place in importance. Visual primary examination in a gynecological chair is mandatory, but is considered only the first step in diagnostics.
What is included in the list of the concept "instrumental diagnostics"?
- Examination with gynecological speculums. This is a special vaginal instrument that helps the doctor assess the condition of the cervical epithelium. The most obvious changes in the tissue will be visible to the naked eye if speculums are used. Instrumental diagnostics in the format of examination with speculums shows the shape, size of the cervix, as well as possible damage to the external os, ruptures. Speculums can assess the criteria for the condition of the lower part (third) of the cervix and the mucous membrane of the cervix. The initial stage of leukoplakia, adnexitis, erosive processes, dysplasia of the cervix - this is far from a complete list of pathologies that can be detected by bimanual examination with vaginal speculums.
- Colposcope. Examination with this instrument is intended to clarify the degree of damage to a specific area of the cervix (magnification 10 times). Also, colposcopy is performed simultaneously with tissue sampling for diagnostic samples (cytological samples, biopsy). The colposcope also helps to take PCR samples (molecular biological, immunological analysis for HIV, viral load assessment, strain clarification).
- Extended colposcopy, which may be required for cervical dysplasia, is divided into several stages. The epithelial tissue is treated with a special acid solution, then another solution is applied again - Lugol's solution. Only after this is an examination and a special sample is taken (Schiller's test). Such procedures are needed to provoke swelling of the mucous membrane (acid), the swelling in turn causes increased blood circulation for better permeability of Lugol's solution. This agent acts as a marker paint. Normally, the epithelial tissue should acquire a reddish tint due to glycogen granules. Any affected area of the cervix will not show a change in color.
- Ultrasound examination also belongs to a number of instrumental examinations. To specify the diagnosis, a woman may be prescribed an ultrasound of the genitourinary organs to exclude or determine cysts, benign tumors, etc. This method is suitable for young nulliparous women as an alternative to scrapings and curettage.
- Cytology (Papanicolaou test).
- Standard and cone biopsy - targeted, cone, curettage - depending on the direction of the diagnostic complex of cervical dysplasia.
Thus, instrumental diagnostics are methods of assessing epithelial tissue, the state of the cervix using medical instruments. In case of cervical dysplasia in gynecological practice, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are one of the mandatory conditions for accurately determining the severity of the pathology.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan may also be prescribed to a patient if a dysplastic process in the cervix is suspected. Cervical dysplasia develops and proceeds without obvious clinical manifestations in 75-85% of cases. It is often accompanied by inflammatory processes in the genital organs, primarily the ovaries and uterus, and the kidneys may also be affected. This is explained mainly by the viral, infectious nature of the factors provoking the pathology. The first complaints of a woman, as a rule, are symptoms of inflammation, and not dysplasia as such. Every time gynecologists meet patients, they tirelessly repeat recommendations for regular preventive examinations. Unfortunately, it happens that a woman consults a doctor only when pain occurs, discharge is atypical for a healthy state, or when pregnancy occurs. Such situations require more detailed diagnostic actions, including not only standard methods - examination on the chair, but also cytology, collection of material for histology and ultrasound examination.
An ultrasound scan to clarify the diagnosis is performed in a special way - vaginally, in combination with an ultrasound scan of the genital organs (pelvis).
What can an ultrasound examination of organs show in case of cervical dysplasia?
- Cysts of various etiologies, sizes and types (require clarification and treatment).
- Myomas, fibroids.
- Benign tumor process.
- Changes in the size and shape of the uterus.
- The position of the ovaries in relation to the uterus (normal or shift towards pathology).
If ultrasound examination of organs does not show obvious changes or pathological deviations from the norm, young patients, especially those who have not given birth, may be spared a more invasive examination – curettage and even biopsy.
What is a transvaginal ultrasound?
- This is one of the important examinations in gynecological practice.
- Transvaginal scanning helps to assess the condition of the uterine cavity and its cervix in order to determine the further vector of diagnostic measures.
- Unlike standard ultrasound, which requires fluid in the body to conduct the sound wave, the transvaginal method does not require a full bladder.
- With the help of such technology, a gynecologist can evaluate not only the shape and size of the uterus or ovaries, but also more accurately identify the presence of a particular pathology.
Ultrasound and uterine dysplasia, how is the examination performed?
- The patient does not require any special preparation. The rules are practically the same as for the Pap test (abstaining from sexual intercourse, refraining from using suppositories, tampons, douching).
- With transvaginal diagnostics, a woman does not need to fill her bladder and endure for a long time.
- A special sensor is lubricated and inserted into the vagina. Since it is located quite close to the organs being examined, the examination itself is considered very reliable and is quick.
- The doctor performing the ultrasound has the opportunity, as they say, to see with his own eyes a clear clinical picture and assess the condition of the cavities.
- The procedure does not cause discomfort or pain.
- The scan result is known to the doctor and, in principle, to the patient literally immediately after the procedure.
It should be noted that ultrasound is most often prescribed to assess the condition of the ovaries when dysplasia is suspected. This is necessary to exclude a tumor process and the presence of cysts. Also, ultrasound, both classical and vaginal, helps to monitor the success of treatment, especially in cases of persistent infertility.
Colposcopy
The colposcope is one of the most widely used instruments in gynecological diagnostics. It is an optical medical device that helps to detect the smallest defects in the mucous tissue that are invisible during a simple visual examination. Erosive lesions, point or extensive, microtumors, hemorrhages, and other pathological changes in the cervix are often found during colposcopy. Colposcopy as a method is developing and today there are two types of research:
- Standard colposcopy. Cervical dysplasia requires such examination in 55-60% of cases.
- Videocolposcopy is a more modern technology that requires equipment (probe, monitor, processor).
Why is colposcopy prescribed?
- Definition of erosive processes.
- Identify polyps of different types (shape, quantity, size).
- To assess the severity of dysplastic changes in the epithelial tissue of the cervix.
- Clarify the preliminary diagnosis of leukoplakia.
- Detect oncological processes at early stages.
- Detect erythroplakia.
- To exclude or confirm epithelial hyperplasia.
- Differentiate such pathologies as cervical dysplasia, ectopia, adnexitis, leukoplakia and benign tumor diseases.
A more detailed description of the types of colposcopy that may be prescribed when diagnosing cervical dysplasia:
- Standard colposcopy, when the patient is examined in the doctor's office on a gynecological chair. The colposcope is inserted after dilation with special medical mirrors.
- Colposcopy by the extended method. The initial stages are identical to the simple colposcopic procedure. Then the mucous membrane of the cervix is treated with acid and Lugol's solution. This is how the Schiller test is performed, when cervical dysplasia can be excluded by normal coloring (redness and brownish tint). The test can also show no reaction - this is already a pathology. Damaged areas of the epithelium do not react to provocation with acid and solution, remaining pale, whitish.
- A variant of extended colposcopy is the color method (color colposcopy). The examination is practically the same as the extended one, but Lugol's solution is replaced by methylene blue and classic brilliant green. In this way, it is possible to see areas of damaged vascular network.
- To detect oncological changes in the cervix, fluorescent colposcopy is used. The mucous membrane of the cervix is exposed to fluorochrome. The examination is carried out using ultraviolet light, which reacts with the applied solution. All pathological foci under such "illumination" are visible as pinkish areas.
Pregnant women diagnosed with cervical dysplasia can safely undergo a colposcopy procedure, it is safe for the expectant mother and the fetus as well. The choice of the type of optical examination depends on the patient's health and how the pregnancy is progressing. But in general, such procedures are considered safe and only help to exclude unwanted diseases and pathologies.

