
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Transverse septal cyst of the brain
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
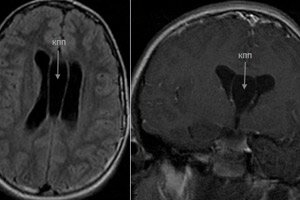
The number of abnormal cerebral formations of a benign nature – congenital or acquired – includes a cyst of the septum pellucidum of the brain.
In most cases, it is asymptomatic and is detected completely by chance during visualization of brain structures. [ 1 ]
Epidemiology
There are no clinical data regarding the incidence of diagnosable septum pellucidum cysts, and septum pellucidum cysts are found in 0.04% of patients with cerebral cystic lesions.
Causes transparent septal cysts in the brain.
The general causes of most cerebral cysts, including intracerebral cysts of the septum pellucidum, are most often congenital. That is, their formation is caused by deviations in the ontogenesis of the brain - the process of its formation by neural stem and glial cells - in the prenatal period (in the first two months of pregnancy).
Read also – Variants and anomalies of the brain
A cyst of the septum pellucidum in adults may be associated with a neuroinfection (meningitis), traumatic brain injury, tumor encephalopathy, or brain surgery.
More details in the publication - Complications and consequences after traumatic brain injury
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of abnormal formations in the form of brain cysts are considered to be:
- diseases of the pregnant woman (acute viral, chronic and systemic);
- teratogenic effects of alcohol or drugs on the embryo and fetus;
- various pregnancy pathologies, including placental insufficiency and fetal hypoxia;
- prematurity of the child (birth before 35-37 weeks of gestation);
- complicated childbirth, often resulting in birth trauma;
- cerebral edema in newborns.
Pathogenesis
The transparent septum (septum pellucidum), located below the corpus callosum, is a vertical triangular membrane that separates the anterior horns (cornu frontale) of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain (ventriculi laterales) located in the frontal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres and forms their middle walls. This septum has two layers in the form of plates consisting of white matter (substantia alba), nerve cells (neurons) and fibrin fibers.
A cyst (from the Greek "sac") is a delimited closed cavity with clear contours, often with liquid contents. The pathogenesis of congenital neuroepithelial cysts has not been fully studied. Although among the hypotheses of the mechanism of formation of a cyst of the transparent septum, there is a version of its connection with the functions of the ventricular (ventricular) system and the movement of cerebrospinal fluid - the cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus cerebri).
If the cystic formation of the septum pellucidum is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (liquor cerebrospinalis), which is produced by the lateral ventricles, then a cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the septum pellucidum is determined.
In addition, a cyst of the cavity of the septum pellucidum may be detected. A slit-like closed space - a cavity between the plates of the septum pellucidum - is formed in the third month of intrauterine development of the fetus and is considered a marker of the development of its nervous system. During the fifth month of the prenatal period, the plates begin to merge, and three to six months after birth, the closure of this cavity is complete.
But in 12-15% of cases the cavity does not close, especially in premature babies. And when it is found in adults, it is considered an anatomical variant of the norm.
If cerebrospinal fluid remains in the closed cavum septum pellucidum, then this is a cyst of the septum pellucidum in a child. [ 2 ]
Symptoms transparent septal cysts in the brain.
Often, a cyst of this localization does not manifest itself in any way. But it can press on the brain tissue and cause symptoms such as headaches accompanied by dizziness, vomiting and epileptic seizures, problems with vision and hearing (patients often complain of tinnitus).
The first signs of the presence of a cyst of the septum pellucidum also manifest as periodic headaches. In addition, patient complaints include dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and visual impairment. [ 3 ]
Complications and consequences
The consequences and complications associated with this cerebral cyst arise due to its significant size. It can exert pressure on the occipital and temporal horns of the lateral ventricles of the brain and part of the aqueductus cerebri - with the development of obstructive hydrocephalus. In such cases, morning headaches in the frontal region, difficulty concentrating, and other symptoms of increased intracranial pressure appear.
In addition, compression of the cyst may disrupt venous blood outflow from the brain or affect hypothalamic structures and areas of the midbrain, causing autonomic or sensorimotor symptoms.
It is also possible that a cystic formation may rupture, which can lead to quite serious problems with the central nervous system.
Diagnostics transparent septal cysts in the brain.
Symptoms and patient history are not enough for diagnosis. Instrumental diagnostics are necessary:
- echoencephaloscopy or neurosonography;
- color duplex ultrasound of brain structures;
- CT – computed tomography of the brain;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics are performed with an arachnoid cyst of the interhemispheric fissure, a pineal gland cyst of the brain, and an arteriovenous malformation (aneurysm) of the vein of Galen.
Who to contact?
Treatment transparent septal cysts in the brain.
Only when a septum pellucidum cyst causes symptoms does it require treatment.
Although there is no cure for this cystic formation,
Empirically, drugs are prescribed to improve metabolic processes in brain tissue - nootropics (Piracetam, Pyriditol, Cerebrolysin ).
Thus, Piracetam (Nootropil), used for memory impairment, decreased cognitive abilities and myoclonus, is taken at 1.24-4.8 mg per day (the dosage is determined by the doctor). In this case, the side effects of this drug are nausea and vomiting, weight gain, nervousness and depression, increased excitability and hyperkinesis, insomnia or drowsiness.
Diuretics - osmotic diuretics Diacarb (Acetazolamide), Mannitol - are prescribed for increased intracranial pressure. Diacarb tablets are taken 0.125-0.25 g twice a day, but it is contraindicated in liver and kidney failure, closed-angle glaucoma and children under 12 years of age. Possible side effects include electrolyte imbalance in the body, thrombocytopenia, suicidal thoughts, and growth retardation in children.
Mannitol is administered intravenously (with a dose calculated based on body weight); its side effects include headache, nausea and vomiting, poor circulation, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalance.
If the cyst increases in size, surgical treatment may be required, which includes shunting of the cyst cavity or its endoscopic fenestration. [ 4 ]
Prevention
The possibilities of preventing the formation of a congenital cyst of the septum pellucidum of the brain are limited by the fact that not all risk factors for the development of anomalies in the intrauterine period can be avoided. Therefore, prevention, in fact, concerns only a complete refusal of alcohol before and during pregnancy, as well as extreme caution in the use of drugs.
Forecast
In the treatment of symptomatic septum pellucidum cysts and the absence of neurological complications, the prognosis is considered favorable.

