
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Caseous plugs on the tonsils in the throat
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 12.07.2025
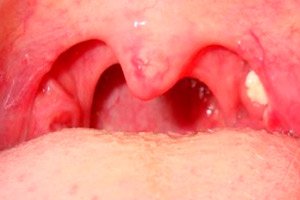
Otolaryngologists observe such a symptom as caseous plugs on the tonsils in the throat quite often - both during inflammatory processes in the throat, and in cases where there are no signs of obvious inflammation of the palatine tonsils.
Causes caseous plugs
Caseous plugs in adults, children, and during pregnancy can appear for one reason - as a result of recurrent, that is, frequently recurring infectious inflammations of the pharynx and tonsils in the throat (glands), as well as a chronic inflammatory process in the nasopharynx or paranasal sinuses. [ 1 ]
Such plugs are an accumulation of caseous (similar to cheese, from the Latin caseum - cheese) amorphous yellowish substance in the lacunae of the palatine tonsils, and risk factors for their formation include bacterial infection-induced tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) and chronic inflammation of the tonsils, follicular and lacunar tonsillitis, herpetic or aphthous tonsillitis, monocytic tonsillitis (occurring when the pharynx is affected by the Epstein-Barr virus), pharyngomycosis - fungal tonsillitis, chronic pharyngitis, chronic nasopharyngitis, etc. [ 2 ]
In fact, if there are such plugs in the lacunae of the palatine tonsils, tonsillitis can be considered caseous. And with an exacerbation of chronic inflammation with the formation of pus, purulent-caseous plugs can form.
Pathogenesis
The tonsils (including the palatine tonsils) are immune organs that form the pharyngeal lymphoid ring and provide adaptive protection against inhaled or swallowed antigens (bacteria and viruses). And the pathogenesis of caseous plug formation is closely related to the immunological functions of the palatine tonsils.
They have a branched network of depressions - lacunae (or crypts), which increase many times the area of the special mesh epithelium, dotted with nodules of lymphoid tissue that produces protective cells (macrophages, neutrophils, B and T-lymphocytes) and attracts immunoglobulins to the site of infection. And caseous plugs are formed in the lacunae, where detritus gradually accumulates - cellular debris, that is, the products of phagocytosis of microorganisms and the remains of lysis of lymphocytes and macrophages.
Chronic caseous plugs can transform into so-called tonsilloliths, which are mineralized (calcified) caseous accumulations in the lacunae.
Symptoms caseous plugs
When caseous plugs form, symptoms are usually absent, but during the active phase of inflammation of the tonsils, general symptoms of chronic tonsillitis are observed.
And the first signs of the presence of such pathological accumulations in the tonsils outside of the inflammatory process can manifest as halitosis - bad breath associated with the release of volatile substances containing sulfur compounds by many anaerobic bacteria.
The presence of tonsilloliths in the lacunae may be the cause of a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, an unpleasant taste in the mouth and halitosis; in addition, symptoms may manifest as pain when swallowing (sometimes radiating to the ears and neck), dysphagia (difficulty swallowing associated with swelling of the tonsil tissue), and frequent coughing.
Complications and consequences
What is the danger of caseous plugs? They prevent the natural cleansing of the lacunae and thus increase the risk of developing an infection in the tonsils - creating favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of both pathogenic microorganisms and opportunistic bacteria and bacteroids of the obligate microflora of the pharynx, for example, the Fusobacteriaceae family, capable of causing necrosis of epithelial cells.
And if Streptococcus pyogenes (beta-hemolytic streptococci), Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilus influenzae are present in the lacunae, consequences and complications characteristic of chronic inflammation of the tonsils are possible, including sleep apnea and cardiological problems.
Read more in the publication – Chronic tonsillitis – Complications.
Diagnostics caseous plugs
The presence of caseous plugs on the tonsils in the throat is detected by otolaryngologists during a standard examination - examination of the pharynx, as well as during a visual examination of the larynx - direct laryngoscopy. [ 3 ]
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics are carried out with purulent plugs, peritonsillar abscess, and keratin cyst of the tonsils. And tonsilloliths - with foreign bodies of the pharynx, granulomatosis, venous calcifications (phleboliths) of the soft tissues of the pharynx, and malignant neoplasms.
Who to contact?
Treatment caseous plugs
Many experts believe that treatment is not required if caseous plugs and formed tonsilloliths do not bother the patient.
However, otherwise, rinsing, or more precisely oral irrigation of the tonsils with a solution of common salt is necessary; it is also recommended to use a solution with the addition of an antiseptic, for example, 0.05% Chlorhexidine Bigluconate (but it cannot be used for children under 12 years of age and pregnant women).
If tonsillitis is caused by a fungal infection, the throat should be rinsed with solutions of Miramistin or Hexoral.
No other medications will help to get rid of caseous plugs. And antibiotics (Azithromycin, Augmentin, Doxycycline, Ceftriaxone, etc.) are prescribed by a doctor during exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis of bacterial etiology. Read more: Antibiotics for tonsillitis.
As a rule, treatment is carried out at home, trying to remove plugs, including calcified ones, by intensively (at least twice a day) gargling with salt (salt water).
Only in cases that do not respond to conservative measures - with worsening symptoms of chronic tonsillitis and significant hypertrophy of the tonsils - surgical treatment is recommended:
- cryptolysis – removal of tonsilloliths formed in the lacunae using a carbon dioxide or diodymium laser or radiofrequency radiation;
- laser ablation of the tonsils;
- tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils). [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
Prevention
The main thing in preventing the formation of caseous plugs on the tonsils in the throat is the treatment of recurrent and chronic tonsillitis and nasopharyngeal infections.
Forecast
The presence of caseous plugs has a good prognosis for the life of patients, but measures not taken in time - taking into account possible complications - can significantly worsen their condition.

