
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Leukoplakia of the bladder
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
The genitourinary system is one of the most vulnerable in the human body. In addition to cystitis and other inflammatory diseases, painful structural processes can develop, such as leukoplakia of the bladder. This is a pathological keratinization of the organ's epithelium, that is, the transformation of transitional epithelial tissue into flat tissue. As a result, foci of keratinization appear on the mucous tissues that do not perform the necessary protective function, which soon leads to the development of chronic inflammation of the bladder.
Leukoplakia is often mistaken for common cystitis, which, however, does not respond to conventional treatment. Adequate therapy can only be prescribed after a properly conducted diagnosis confirming the insidious disease. [ 1 ]
Epidemiology
Chronic inflammatory processes in the lower segment of the urinary tract in female patients are very common. They are the most common reason for women to visit a urologist, gynecologist and therapist.
Urination disorders annually "bring" approximately 3 million American women to the doctor. In the post-Soviet space, the incidence is estimated at approximately 15-20 thousand cases per 1 million patients. Every two women out of ten suffer from inflammatory disease of the bladder at least once in their life, of which one woman suffers from a chronic form of inflammation.
Relapses are typical for leukoplakia of the bladder. It has been determined that every second woman experiences a repeated episode of the disease after the inflammatory process subsides during the year, and 50% of cystitis exacerbations occur more than three times a year.
According to various data, leukoplakia of the bladder is diagnosed during cystoscopy in 64-100% of cases accompanied by persistent urination disorders and chronic pelvic pain. The most common localization of pathological foci is the neck of the organ and the bladder triangle.
Despite the prevalence of the disease, leukoplakia is still considered one of the least studied pathologies of the mucous tissue of the bladder. [ 2 ]
Causes bladder leukoplakia.
Despite numerous studies, the cause of bladder leukoplakia still remains a mystery to scientists. The most common theory is that leukoplakia is a consequence of some intrauterine anomalies. That is, during intrauterine development, certain defective foci are formed in the walls of the urinary system. This theory is supported by the fact that the disease is most often detected in people suffering from developmental disorders of the urinary tract. In addition, risk factors, which we will describe a little later, also have some influence. The most common fact is infectious influence: cellular transformation begins its development after an infectious pathology. [ 3 ]
The development of leukoplakia is provoked by the following infection:
- gonococcus;
- chlamydia;
- trichomonas;
- herpes virus;
- papillomavirus.
Another infection can also enter the bladder through the blood and lymph flow:
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- E. coli, etc.
Risk factors
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing leukoplakia of the bladder:
- endocrine pathologies affecting the function of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, as well as paired female sex glands - the ovaries. With an increase in estrogen levels, the epithelium becomes vulnerable and prone to transformation. In some patients, leukoplakia begins to develop after prolonged treatment with hormonal agents;
- inflammatory processes in the bladder or in organs localized in close proximity to it. Leukoplakia often develops against the background of chronic cystitis, urolithiasis, traumatic lesions of the bladder, penetration of foreign objects into its cavity;
- chronic pathological processes in the body – for example, chronic tonsillitis, dental caries, pyelonephritis, etc.;
- prolonged and severe decline in immune defense.
The onset of leukoplakia of the bladder can occur against the background of promiscuous sexual relations without barrier protection, with frequent stress and hypothermia. [ 4 ]
Pathogenesis
If there are no problems with the bladder, its epithelial layer will produce polymeric carbohydrate-protein complexes – mucopolysaccharides. Their purpose is to prevent microbial cells from adhering to the walls of the organ. These complexes also provide cellular protection from destruction under the influence of acids.
In the case of pathological transformation of the epithelium, such cellular protection ceases to be reliable, and pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the cell structures almost unhindered. The patient develops a chronic inflammatory process. A peculiar cyclicity appears: cystitis aggravates the course of leukoplakia, which, in turn, maintains the activity of the inflammatory reaction.
Microbial infection penetrates the urinary system mainly by the ascending route, namely from the surface of the external genital area. The infection can also be transmitted with blood or lymphatic fluid, but this option is relatively rare. In this situation, bacteria can penetrate from organs such as the kidneys, lower digestive tract, uterus, etc. [ 5 ]
Epithelial transformation in the area of the bladder triangle is within the normal range. This condition develops in women under the influence of estrogens. If these changes are not subject to
Symptoms bladder leukoplakia.
The basic symptoms of leukoplakia of the bladder are very similar to those of acute cystitis. Patients report pain in the pubic area, frequent urge to urinate, cutting and burning sensations at the final stage of urination, discomfort during sexual intercourse. Light flakes and even blood threads can be visually detected in the urine.
First signs of a problem:
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- interruptions in the flow of urine during urination;
- discomfort, pain, and other unpleasant sensations during the urination process;
- an uncomfortable feeling in the lower abdomen, a pulling sensation in the lumbar spine;
- deterioration of general well-being, apathy, impaired ability to work;
- a feeling of insufficient emptying of the bladder.
Urinary incontinence is a symptom that does not occur in all patients. It is characteristic of the so-called cervical leukoplakia (when the lesion is located in the neck of the bladder), or is detected in advanced forms of this disease. Incontinence can have varying degrees: in some patients it occurs against the background of a relatively full bladder, while in others leakage can be observed as early as 15-20 minutes after complete emptying of the organ. [ 6 ]
The symptoms indicated are non-specific and may indicate not only the presence of leukoplakia, but also an exacerbation of cystitis or other problems with the urinary system. The final diagnosis will never be established only by the description of the clinical picture. A thorough diagnosis with cystoscopy and biopsy is necessary.
Leukoplakia of the bladder in women
Leukoplakia of the bladder can affect both male and female patients. However, women are more likely to encounter this disease, primarily due to certain anatomical features.
A short urethral canal allows the infectious agent to easily enter the bladder of patients. And weakened immunity, stress in combination with other factors allow the rapid development of pathological processes.
Most often, the infection enters the urinary tract in an ascending manner from the external genital area.
In leukoplakia of the bladder, the normal epithelial layer is transformed into a flat one, with the formation of keratinized foci. The disease is diagnosed either by chance or during long-term and ineffective treatment of cystitis. In this case, the basis for correct diagnosis is a biopsy with subsequent histology of the selected materials.
In women, leukoplakia can affect not only the bladder, but also the cervix. This pathology occurs in many patients of childbearing age. The disease is usually characterized by a chronic course.
Leukoplakia of the bladder and pregnancy
With leukoplakia of the bladder, pregnancy can be significantly complicated - primarily due to the high probability of relapse of the disease. If the disease worsens in the first trimester of pregnancy, there is a risk of spontaneous termination of pregnancy or the appearance of developmental defects in the future baby.
An exacerbation in the third trimester creates a risk of premature placental abruption, intrauterine infection of the fetus, and premature birth.
In case of exacerbation of leukoplakia during pregnancy, antibiotic therapy is postponed. However, antibiotics are still prescribed in case of significant and intense symptoms. The full course of treatment is carried out after the birth of the child.
Patients suffering from leukoplakia should take measures to eliminate the disease before pregnancy. Even if a woman suffers from frequent cystitis, chronic cystitis, she needs to undergo a course of preventive treatment in advance. [ 7 ]
Stages
Leukoplakia of the bladder goes through several stages or phases in its course:
- Squamous cell transformation. This stage is characterized by the reorganization of the transitional epithelial tissue layer into multilayered squamous epithelial tissue. As for the cells themselves, they do not change.
- Squamous cell replacement. This stage is the first step towards cell death as they gradually undergo pathological changes in the degenerated multilayered tissue.
- Formation of focal thickenings against the background of cellular keratinization processes. [ 8 ]
With leukoplakia of the bladder, a number of sclerotic processes occur, affecting the internal walls of the cavity. Over time, the organ can no longer contract adequately, which, in turn, leads to incontinence of urinary fluid. Such a complication is characteristic of leukoplakia: with cystitis, such a symptom is not observed. [ 9 ]
Forms
There are three types of leukoplakia of the bladder:
- flat leukoplakia;
- warty leukoplakia with pronounced areas of keratinization;
- erosive leukoplakia with the presence of ulcerative lesions of the mucous tissue.
The flat type of leukoplakia often proceeds almost asymptomatically, and only with large lesions is a characteristic clinical picture observed.
The warty and erosive varieties of pathology are accompanied by pronounced painful symptoms. Leukoplakia of the bladder neck is characterized by particularly intense symptoms: as the pathological process spreads, the patient's condition worsens sharply, and symptoms of acute cystitis appear. Drug therapy often does not bring visible relief.
Complications and consequences
Even after a full course of treatment for leukoplakia of the bladder, the patient will have to undergo systematic preventive diagnostics to prevent the recurrence of the disease, as well as to prevent complications such as:
- malignancy, development of a malignant process in the walls of the bladder;
- disruption of the normal function of the urinary system, loss of contractility of the bladder, urinary leakage and incontinence;
- renal failure with subsequent disruption of water, electrolyte, nitrogen and other types of metabolic processes;
- bleeding, hematuria.
Relapse of leukoplakia of the bladder after drug treatment is quite common, since conservative treatment does not eliminate the disease forever. After more radical surgical intervention, the disease recurs in approximately 7-12% of cases. It is possible that relapse may be due to incomplete excision of the pathological zone, since in some areas a deeper impact may be required. If such features are not taken into account, prerequisites for incomplete removal of the pathology arise, which becomes the basis for the re-development of leukoplakia. The smallest number of relapses is noted after the radiofrequency excision procedure. [ 10 ]
Diagnostics bladder leukoplakia.
The diagnosis of leukoplakia of the bladder cannot be established only on the basis of patient complaints and the results of an objective examination. A comprehensive diagnosis with mandatory histological examination of tissue particles of the cavity organ is required.
The full range of examinations is approximately as follows:
- Collection of anamnestic data (frequency and intensity of attacks, presence of other pathologies and predisposing factors).
- Vaginal examination of women (necessary both for differential diagnosis and for assessing the general health of the patient’s reproductive system).
- Laboratory tests: complete blood count, urine analysis, vaginal and urethral smear examination, blood biochemistry, creatinine and urea levels assessment, urine culture.
- PCR and ELISA diagnostics for detection of latent infection.
- Instrumental diagnostics: ultrasound examination of the kidneys and organs located in the pelvis, urodynamic diagnostic procedures (urometry, cystoscopy), endoscopy. [ 11 ]
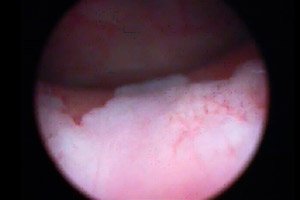
Cystoscopy of the bladder is necessarily accompanied by a biopsy - a procedure for pinching tissue material for further histological examination. For leukoplakia, this method is considered the most informative, as it provides an opportunity to assess the nature of the disease, its form and the degree of damage. During cystoscopy, leukoplakia foci look like flattened whitish zones, or small erosions, or yellowish plaques. [ 12 ]
To clarify the diagnosis of leukoplakia of the bladder, ultrasound is performed for all pelvic organs, as well as for the kidneys. Such a study demonstrates the location, shape, structural features, and size of the organs in question. During the diagnosis, echo-positive formations can also be detected - for example, stones or tumors that can reflect the ultrasound flow.
To confirm the diagnosis of leukoplakia of the bladder, histological detection of metaplastic transformations in cellular structures is important, even in cases where there is a clear endoscopic picture of the disease.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics include squamous cell papilloma and, in some cases, a malignant process in the bladder. Bladder leukoplakia and cancer may have similar symptoms, but proper diagnostics in the form of urine cytology and cystoscopy with biopsy usually clarify the situation. The probability of detecting carcinoma is facilitated by the procedure of cystoscopy with blue light, after intracavitary instillation of hexylaminolevulinate. Sometimes there is a need for additional biopsy, with muscle tissue sampling.
Women may also have cervical leukoplakia simultaneously with bladder lesions. However, the combination of these pathologies is rare and requires different diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Who to contact?
Treatment bladder leukoplakia.
The possibility of treating leukoplakia without the help of a surgeon is assessed by a doctor after making an accurate diagnosis and determining the degree of complexity of the pathology. The conservative method involves the use of medicinal effects on the infectious component of the disease.
To do this, it is necessary to use the following medications:
- antimicrobial drugs to destroy pathogenic flora;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- means for strengthening the immune system;
- multivitamin preparations.
To restore the bladder walls damaged by the pathological process, irrigations with special agents are used, which are analogues of natural glycosaminoglycans. Thanks to such procedures, it is possible to restore the damaged tissue.
Physiotherapy and diet therapy are appropriate as a supplement to treatment.
Surgical treatment is resorted to if conservative therapy does not bring the necessary positive result. [ 13 ]
Medicines that a doctor may prescribe
In case of an infectious process, it is necessary to prescribe specific drugs that act directly on the pathogen. A preliminary analysis of urine fluid with bacteriological examination and an assessment of the sensitivity of pathogenic flora to antibiotics is carried out.
Trichomonas cystitis requires the prescription of Macmiror, Metronidazole, Furamag.
For fungal inflammation, Pimafucin, Itraconazole, and Fluconazole are prescribed.
Acyclovir and interferons are used to treat herpes and cytomegalovirus.
A course of immunostimulants is required - for example, tincture of echinacea, Cycloferon.
In the context of antibiotic therapy, Bifidumbacterin and Lactobacterin are used to support the immune system.
The drugs Kanefron or Nefrosten, which are taken over a long period of time, are useful.
Monurel |
Cranberry extract, the so-called natural antimicrobial drug. Take once a day, before going to bed: dissolve 1 packet of granules in 100 ml of water. Possible side effects: diarrhea, heartburn, skin rashes. |
Canephron |
A herbal preparation, an active diuretic with analgesic and antimicrobial effects. Enhances the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. Take 2 tablets (or 50 drops) three times a day, with a sufficient amount of liquid. Nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions may occur during treatment. |
Urolesan |
A herbal remedy with antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial effects. The drug eliminates pain and normalizes urination. Urolesan is taken orally with food, 1 capsule three times a day, for up to one month (the drug can also be taken in the form of drops or syrup). Side effects: dyspepsia, allergic reactions, dizziness, blood pressure changes. |
Nevigramon |
Uroseptic, the action of which is based on the presence of nalidixic acid. The drug is taken 1 g 4 times a day for a week (the dosage can be adjusted by the attending physician). The most likely side effects: dyspepsia, cholestasis, headache, visual impairment, allergy. |
Nolitsin |
A broad-spectrum antibacterial agent, a second-generation fluoroquinolone. Tablets are taken between meals, with plenty of water (to ensure stable diuresis). Dosage and frequency of administration are selected individually. Possible side effects: heartburn, nausea, jaundice, increased anxiety, arrhythmia, hypotension. |
Kanefron for leukoplakia of the bladder
Canephron is most often prescribed for the treatment of cystitis and pyelonephritis, but this drug is also appropriate for leukoplakia of the bladder. What is it for?
Canephron successfully copes with bacterial infection, accelerates the removal of fluid and salts from the body, and protects the tissues of the urinary system from damage. If the patient is to undergo surgical removal of leukoplakia foci, then here too you cannot do without Canephron: the drug will help stop the inflammatory process and prepare the patient for surgery.
Standardly, for leukoplakia of the bladder, Kanefron is taken either in drops (50 drops three times a day) or in tablets (2 tablets three times a day). The duration of administration is 2-3 months, sometimes longer, at the discretion of the doctor.
This treatment is supplemented by the use of medicinal urological collection, drinks based on cranberries and rose hips.
Vitamins
To treat and prevent exacerbations of leukoplakia of the bladder, most doctors advise taking measures to strengthen the body's defenses and increase resistance to infections. For all patients, multivitamin complexes with minerals are a good addition to treatment.
High-quality complex and biologically active preparations can be found in most pharmacies. And the attending physician will help you choose the necessary optimal vitamin option, for example:
- Solgar, Natural Cranberry with Vitamin C;
- Nephrocaps, Elite-Pharm;
- Cystimin, Vivasan;
- Uva Ursi, Natures Way, Bearberry;
- Vitamax, Aloe Cranberry Concentrate, concentrated Aloe and Cranberry juice;
- GoLess, Country Life, Bladder Health;
- D-Formula, Altera Holding;
- Rensept, Art Life.
Taking vitamin preparations is usually long-term. Dosage - according to the instructions for a specific complex product.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy methods are often used to treat leukoplakia of the bladder:
- laser treatment in combination with short-pulse electroanalgesia;
- laser treatment with magnetic therapy;
- short-pulse electroanalgesia with magnetic therapy;
- microwave therapy;
- ultra-high frequency therapy;
- exposure to sinusoidal modulated currents;
- endovesical phonophoresis.
In the process of physiotherapeutic treatment, it is recommended to supplement the use of sinusoidal modulated currents with electrophoresis. Thanks to this combination, it is possible to block the disturbed impulses from the organ damaged by the disease.
The use of warming procedures for leukoplakia of the bladder is inappropriate. Moreover, heat procedures carried out at home (baths, heating pads, etc.) provide the creation of optimal conditions for the rapid reproduction of infection.
Ozone therapy for leukoplakia of the bladder
For some patients with leukoplakia of the bladder, a combination therapy is used with Tamsulosin 0.4 mg in the morning and intravenous ozonized saline with an ozone concentration of 6 mg/liter. The ozone therapy course consists of five daily intravenous injections, after which a one-day break is taken and a five-day course is repeated. The duration of each infusion is from half an hour to fifty minutes.
The criterion for the effectiveness of ozone therapy is considered to be the stabilization of the urinary process, the disappearance of clinical symptoms of the disease, the improvement of laboratory and functional indicators. As a rule, the first signs of improvement are observed after 1-2 procedures.
Ozone therapy is not accompanied by negative side effects and allergic processes. The technique is quite simple and accessible, and can be used both in hospital and outpatient settings.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies, unfortunately, are not able to completely cure a person from leukoplakia of the bladder. However, they can act as an additional factor in the complex treatment prescribed by the doctor.
- Instead of tea, they drink freshly squeezed carrot and beetroot juice.
- Apply gauze pads soaked in rosehip and sea buckthorn oil to the external genitalia.
- Chew propolis several times a day every day.
- In the evenings, treat the external genitalia with goose fat, coconut or palm oil.
- Drink 250 ml of fresh milk with soda dissolved in it (1/2 tsp) daily.
A good effect is also found when adding natural herbal preparations prepared on the basis of medicinal herbs.
Herbal treatment
- Every morning drink a glass of decoction of young fir needles (1 tbsp. raw material per 250 ml of boiling water). If well tolerated, the decoction can be consumed more often - for example, twice or three times a day.
- Take hemlock infusion: pour 100 g of plant inflorescences with 0.5 l of vodka, keep for three weeks in a cool place. Filter and begin treatment. On the first day, drink 1 drop of tincture with 100 ml of water. Every day, increase the number of drops by one, bringing it to 40 drops per day.
- Wash daily with chamomile infusion (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of water).
- Take a pharmacy tincture of ginseng - three times a day, 1 teaspoon, for a couple of weeks.
Remember: any folk treatment must be agreed with your doctor!
Homeopathy
Homeopathic treatment is always prescribed against the background of conservative therapy: the combination of methods is discussed personally with the attending physician. Since leukoplakia of the bladder is a fairly serious pathology, it is very important that the treatment is competent and justified: the choice of homeopathic medicine should be left to an experienced and knowledgeable specialist who is familiar with all the details of a particular disease and has all the necessary information about the patient.
It is necessary to take into account that at the very beginning of homeopathic treatment, depending on the prescription scheme, the onset of the so-called "primary deterioration" is possible. Its duration and severity are always different, and it is impossible to guess them. However, within a few days the condition should normalize.
In the complex therapy of patients suffering from leukoplakia of the bladder, it is possible to use the following homeopathic preparations in individually selected dosages:
- Actea racemosa (black crowfoot);
- Causticum;
- Agaricus muscarius (fly agaric);
- Cocculus indicus (cockle nut);
- Conium maculatum (hemlock);
- Kalium carbonicum;
- Kalium phosphoricum;
- Lachesis (rattlesnake);
- Plantago major (big plantain);
- Rumex crispus (curly dock);
- Staphysagria.
It is also permissible to use combination drugs Berberis Homaccord, Belladonna Homaccord, Populus Compositum, etc.
The remedies are selected both in accordance with the predominant symptoms of leukoplakia of the bladder and taking into account the constitutional characteristics of the patient.
Surgical treatment
If drug treatment does not produce the desired result, the doctor suggests that the patient seek the help of a surgeon. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- persistent inflammatory process, occurring with disturbances in the function of bladder contraction;
- leukoplakia of the second or third degree, confirmed by histology;
- intense pain syndrome that cannot be relieved by medication;
- diagnostically confirmed presence of atypical cellular structures, which is a sign of a precancerous condition.
In case of leukoplakia of the bladder, the doctor may consider the following surgical treatment options:
- TUR is a transurethral resection of the bladder. The intervention involves removing pathologically altered areas of mucous tissue using a special loop instrument. The loop is inserted into the urethral canal using the endoscopy method. This procedure is considered gentle and does not involve any damage to the organ.
- Cauterization of bladder leukoplakia is performed by thermal action of high-frequency current supplied to tissues using directed ionized argon plasma. The device for intervention consists of a source of gaseous argon and a source of high-frequency current. Tissue coagulation occurs by heating them. The depth of action depends on its duration, hardware settings and the set power. The method allows not only to remove pathological foci, but also to neutralize pathogenic flora in the subepithelial layer.
- Laser coagulation of bladder leukoplakia results in the formation of a clearly defined homogeneous area of carbonization: the radiation is completely absorbed, causing point evaporation of the tissue. The depth of the laser "work" is insignificant against the background of a strong hemostatic effect, which is a positive moment when performing surgery on bladder tissues saturated with blood vessels. Laser coagulation is considered one of the highly effective methods of treating leukoplakia. The undoubted advantages are minimal invasiveness, good degree of hemostasis, almost complete absence of surgical complications, the minimum possible stay of the patient in the hospital. The rehabilitation period is short: the bladder mucosa is completely cleared of scab within 3-4 weeks.
- Laser ablation of bladder leukoplakia involves the use of a laser pulse, which ensures high-quality hemostasis, minimal surgical trauma, no postoperative complications, and a short recovery period. Removal of bladder leukoplakia occurs in two main stages:
- penetration into the urethra using special instruments;
- performing an operation by evaporation. [ 14 ]
During the operation, the surgeon can control the entire process by changing the wavelength, duration and frequency of the pulses.
- Plasmakinetic vaporization of bladder leukoplakia helps to achieve complete devitalization of the damaged layer of the bladder, with minimal impact on the surrounding and underlying tissues. The postoperative period, including antibiotic therapy, ensures the eradication of bacteria and inhibits the development of a new wave of the inflammatory process. Inclusion of glycosaminoglycan analogues in the therapeutic scheme helps to create a protective shell over the operated area: this prevents the adhesion of uropathogens and prevents the penetration of urinary particles into the mucosa. This fact significantly accelerates the regeneration process.
The postoperative period after surgical treatment is usually relatively short: a course of antibiotics and other supportive and restorative drugs is prescribed:
- The drug Vesicare is prescribed after TUR of leukoplakia of the bladder to prevent the development of bladder hyperactivity syndrome. Vesicare is an m-anticholinergic drug, it is taken at 5 mg daily for 2-3 months. Additionally, it is possible to connect the drug Tamsulosin, as well as physical therapy.
- Oral contraceptives, including drugs with antiandrogenic action, are not recommended for histologically confirmed leukoplakia. However, the same drugs - for example, Jess after leukoplakia of the bladder can be taken after 3-4 months, in the absence of relapse of the disease. Hormonal replacement therapy is appropriate during menopause - to improve the condition of the mucous tissue.
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed both to prevent the development of the inflammatory process and to accelerate tissue recovery. For example, acute uncomplicated microbial cystitis is most often provoked by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, enterococci, Klebsiella, Proteus. Sometimes the same Klebsiella is detected after leukoplakia of the bladder, which may require a repeated course of antimicrobial drugs.
Diet for leukoplakia of the bladder
To get rid of leukoplakia of the bladder in the shortest possible time, in addition to treatment, it is necessary to adjust your diet. Dishes and products included in them should be chosen based on the principle of their gentle effect on the digestive organs. It is preferable to cook in a steamer, boil or bake food.
Products recommended for patients with bladder leukoplakia:
- fresh fruit;
- fresh and boiled vegetables (except cabbage, tomatoes, onions and garlic, radishes);
- not too fatty fish, white meat;
- fermented milk products;
- cereals.
It is necessary to drink about two liters of water per day. This is necessary for natural flushing of the bladder and reducing the concentration of uric acid, which has an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the organ. In addition to regular clean water, it is recommended to drink herbal infusions, unsweetened green tea, berry-based compotes, cranberry jelly.
The following products are prohibited:
- spices, seasonings, hot peppers, mustard, horseradish;
- alcoholic beverages;
- marinades, salt;
- fish, meat broths;
- smoked and fried products;
- strong coffee, strong black tea, carbonated drinks;
- chips, snacks, croutons, etc.
The diet is based on the following principle: food should be as natural as possible, without chemical additives, without spices, with the minimum possible amount of salt (and better yet, without it at all). The fewer irritants present in food, the sooner the long-awaited recovery will come.
Prevention
Preventive measures include prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, hormonal disorders, infectious processes throughout the body. It is important to treat metabolic disorders, infectious and inflammatory diseases in a timely manner.
It is advisable to completely quit smoking, limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages, hot spices and seasonings.
All the above measures must be combined with careful observance of personal and intimate hygiene rules. Vitamin therapy, including B vitamins, vitamin A, calcium, and coenzymes, must be carried out over a long period of time.
Particular attention should be paid to the condition and strengthening of the immune defense. To maintain the required level of immunity, it is necessary to eat properly and fully, lead an active lifestyle, often be in the fresh air, and avoid stress.
The bladder area should be protected from injury, and if any suspicious symptoms occur, it is best to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Forecast
The prognosis for bladder leukoplakia can be favorable if timely and competent treatment is provided, which should be carried out before irreversible damage begins to occur in the walls of the organ. The most favorable outcome is expected if the patient underwent endoscopic intervention with resection of the affected epithelial areas. However, no doctor can guarantee one hundred percent that the disease will never remind of itself with a relapse. Recurrent developments of leukoplakia are often noted, which requires a new course of treatment.
With intensive progression of the disease, which is accompanied by shrinkage of the urinary organ, loss of elasticity, the quality of the prognosis becomes difficult to determine. The patient is prescribed long-term maintenance treatment to normalize well-being. If such treatment is not carried out, then there are high risks that leukoplakia of the bladder will be complicated by renal insufficiency. And this can already lead to death.

