
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in blood
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
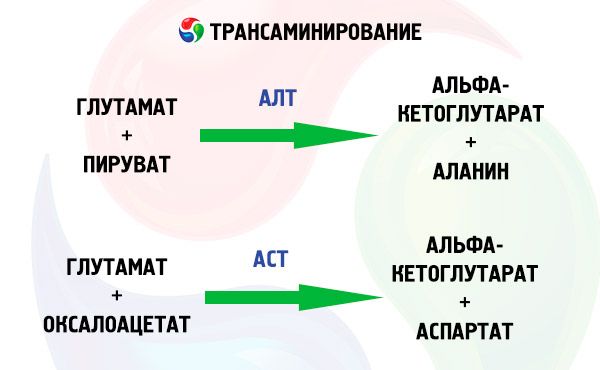
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the blood is a specific enzyme that shows how stable the condition of the tissues of various human organs is.
Alanine aminotransferase is generally a deviation from the norm, but alanine itself is an important enzyme, contained in large quantities in skeletal muscles, liver, heart and kidneys. This substance is actively involved in the metabolism and synthesis of various amino acids. ALT can enter the blood only in case of tissue damage, in a healthy state of the tissues of internal organs, ALT is practically not present, and if observed, then in small quantities. Alanine in tissues is also an amino acid that is quickly converted into glucose, which provides energy for both the central nervous system and the brain. Strengthening the immune system, active participation in the production of lymphocytes, control of the metabolism of sugars and acids - all these are the functions that alanine performs.
The norms within which alanine aminotransferase in the blood should be as follows:
Reference values (norm) for ALT activity in blood serum are 7-40 IU/L.
- For men – no more than 40-41 units/l;
- For women – no more than 30-31 units/l.
Analytical studies of this enzyme require high accuracy, and it is directly related to the intake of certain drugs that can distort the analytical picture. Therefore, before checking the ALT level, you need to consult a doctor who will either temporarily stop taking medications or take into account deviations in the analysis results associated with drug therapy. In addition, ALT in the blood depends on age, for example, in newborn babies, the ALT level does not exceed 17 units. Then the amount of ALT gradually increases, this is explained by the launch of all protective mechanisms in the body. The ambient temperature also affects analytical studies.
Causes of increased ALT in the blood
Alanine aminotransferase is elevated in diseases such as:
- hepatitis, including viral;
- toxic effects of alcohol, including cirrhosis;
- oncological process in the liver;
- drug intoxication;
- cardiac pathology, including failure;
- myocarditis, heart attacks;
- shock conditions due to burns and various serious injuries;
- necrotic lesions of skeletal muscles.
Also, alanine aminotransferase in the blood is usually elevated in all pregnant women. However, an excessive amount of ALT should alert the attending physician, since such an indicator may indicate a serious pathology of internal organs, especially the liver.
An increase in aminotransferase activity (AST and ALT) by 1.5-5 times compared to the upper limit of the norm is considered as moderate hyperfermentemia, by 6-10 times - as moderate hyperfermentemia, more than 10 times - as high. The degree of increase in aminotransferase activity indicates the severity of the cytolytic syndrome, but does not directly indicate the depth of the impairment of the organ function itself.
In myocardial infarction, an increase in ALT activity in the blood serum is detected in 50-70% of cases, more often with extensive necrosis of the cardiac muscle. The greatest increase in ALT activity is detected in the acute phase - on average 130-150% of the norm, which is significantly inferior to that of AST - on average 450-500% of the norm.
In liver diseases, ALT activity changes first and most significantly compared to AST. In acute hepatitis, regardless of its etiology, aminotransferase activity increases in all patients. The activity of ALT contained in the cytoplasm changes especially due to its rapid exit from the cell and entry into the bloodstream, therefore, determining ALT activity is a more sensitive test for the early diagnosis of acute hepatitis than AST. The half-life of ALT is approximately 50 hours. AST is located mainly in the mitochondria, its half-life is 20 hours, therefore, its activity increases with more severe damage to the hepatocyte. ALT and AST activities increase 10-15 days before the onset of jaundice in hepatitis A, and many weeks in hepatitis B (the activity of these enzymes increases simultaneously, but ALT - to a much greater extent). In a typical course of viral hepatitis, ALT activity reaches its maximum in the 2nd-3rd week of the disease. If the course of the disease is favorable, ALT activity normalizes in 30-40 days, AST - in 25-35 days. Repeated or progressive increase in aminotransferase activity indicates new necrosis or relapse of the disease. Prolongation of the period of increased aminotransferase activity is often an unfavorable sign, as it may indicate the transition of the acute process to a chronic one.
In the acute period of viral hepatitis in all forms except severe, the de Ritis coefficient fluctuates from 0.55 to 0.65, in severe cases this coefficient averages 0.83, which reflects a more significant increase in AST activity. In terms of differential diagnostics, it is of some importance that in alcoholic liver damage, as opposed to viral, a predominant increase in AST activity is characteristic (the de Ritis coefficient is more than 2).
Chronic hepatitis is characterized by moderate and average hyperfermentemia.
In latent forms of liver cirrhosis, an increase in enzyme activity is usually not observed. In active forms, a persistent, albeit insignificant, increase in aminotransferase activity is detected in 74-77% of cases.
Noteworthy is bilirubin-aminotransferase dissociation, i.e. cases of pronounced hyperbilirubinemia (mainly due to direct bilirubin) and low aminotransferase activity. This dissociation is observed in subhepatic jaundice with stable biliary hypertension, acute liver failure. The activity of AST and ALT, as well as alkaline phosphatase, increases with the resolution of chronic heart failure (peak usually on day 3-4).
Increased activity of ALT and AST can also be detected in practically healthy carriers of the hepatitis B surface antigen, which indicates the presence of outwardly asymptomatic active processes in the liver.
 [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ]
[ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ]
Reasons for decreased ALT
Alanine aminotransferase may be below normal in very serious pathologies, such as necrotic liver atrophy. Release, release of ALT into the bloodstream is possible only in case of damage to hepatocytes, their cell membranes. In addition, elementary deficiency of vitamin B6 can also affect the decrease in ALT levels.
Alanine aminotransferase in the blood is usually determined together with AST – aspartate aminotransferase, both of these indicators are important for assessing the condition of many internal organs.

