
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Iron in pregnancy
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 08.07.2025
Iron during pregnancy ensures the normal functioning of the mother and baby. It promotes the production of blood, which ensures the connection between the woman and her child. Let's consider the most pressing issues regarding the norm, level, deficiency and excess of iron in the body of a pregnant woman.
During pregnancy, the female body works with double the load. That is why the main task of the woman is to help the body cope with it. Iron (Fe) is the element that is required by pregnant women in large quantities. It is responsible for the production of blood and the formation of red blood cells, which are responsible for supplying the body with oxygen.
A lack of Fe in the body of a pregnant woman is a lack of red blood cells. In this case, the woman develops anemia, which is accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms. Excess iron causes problems in the functioning of the body. Therefore, it is very important to maintain its level at a normal level and take care of the condition of the body, which works for two.
How to take iron during pregnancy?
How to take iron during pregnancy - a gynecologist and attending physician who monitors the condition of the woman's body can answer this question. Most often, Fe is prescribed in syrup, tablets or drops. Much less often, they resort to using iron-containing injections. Since injections contribute to the appearance of abscesses and can worsen the blood clotting process. Iron in tablets is the most convenient form for taking. Let's consider how to take iron during pregnancy.
- Iron-containing preparations should not be taken with other tablets or medications.
- Iron must be washed down with water (tea, juice, milk, etc. are not suitable).
- After taking Fe, it is not recommended to consume calcium-containing products, i.e. antacids, for two hours. Since they impair bowel function.
- If you forgot to take the drug at the appointed time, then the next dose should go according to the schedule, you cannot change the dosage of the drug on your own. Excess Fe in the body is much worse than deficiency.
Iron injections during pregnancy
Iron injections during pregnancy are prescribed if a woman has Fe absorption disorders, diseases of the digestive organs and gastrointestinal tract, duodenal ulcer, intolerance to iron preparations and side effects (dizziness, vomiting, nausea). The only side effect after injections during pregnancy is a feeling of fullness in the stomach. The most commonly used Fe injections are Ferlatum, Ferrum Lek and Maltofer. The peculiarity of these injections is that they do not cause side effects and do not have a negative impact on the body of the mother and child.
Iron during pregnancy is one of the most important microelements. Fe is responsible for the normal course of pregnancy. Iron deficiency is the cause of serious diseases, both in the mother and in the baby. Excess iron in the body of a pregnant woman causes pathologies and can cause a miscarriage. That is why every pregnant woman should regularly take a blood test to determine the level of Fe in the body and, if necessary, adjust the results. Since normal iron levels during pregnancy are the key to the birth of a healthy baby.
Overdose
An iron overdose during pregnancy has a negative effect on the female body and the development of the child, just like a deficiency of this microelement. Excess Fe can cause gestational diabetes, lead to miscarriage and infertility. That is why any iron-containing drugs must be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
The main symptoms of iron overdose during pregnancy are diarrhea, vomiting, headaches, and abdominal pain. The daily dose of Fe for pregnant women should be 27-30 mg per day, but this figure varies depending on the individual characteristics of the female body. Any iron-containing drugs should not be taken for a long time, as this can cause excess iron in the body and lead to serious consequences that pose a risk to the normal course of pregnancy and the development of the child.
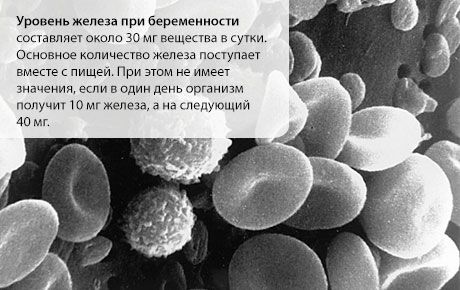
Iron levels during pregnancy
The iron level during pregnancy is about 30 mg of the substance per day. Its main amount comes with food. It does not matter if one day the body receives 10 mg of Fe and the next 40 mg. On average, in two days you will receive the required norm and will not experience symptoms of deficiency.
Significant iron expenditure during pregnancy requires constant replenishment of reserves. For example, a child needs at least 400 mg of Fe during pregnancy. The growing uterus takes about 50 mg of the substance, the construction of the placenta and its normal functioning - 100 mg, and so on. In addition, the female body accelerates the metabolism process, which requires an additional 500 mg of the microelement. During childbirth, a woman loses about 200 mg of iron. Many women during pregnancy are additionally prescribed drugs that replenish the deficiency of this macroelement: injections (the drug "Ferrum Lek"), "Sorbifer" tablets and vitamin complexes.
Serum iron during pregnancy
Serum iron during pregnancy is a test that allows you to determine its concentration in the woman's blood. The concentration of this macroelement depends on the resorption and accumulation in the intestines, spleen, stomach and bone marrow. The level of serum iron changes throughout the day, the highest values are observed in the morning. During pregnancy, the level of serum iron decreases, especially in the second trimester. This is due to the formation of internal organs and glands in the child.
Serum iron analysis during pregnancy allows you to determine the deficiency or excess of this microelement in the blood. With a lack of Fe, anemia begins, which is accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms. Excess serum iron also causes diseases that negatively affect both the health of the mother and the development of the child. You can diagnose the iron level in detail using complex laboratory diagnostics, which will determine the process of metabolism of this macroelement in the body and the level of distribution.
Iron norm during pregnancy
The iron norm during pregnancy is at least 30 mg of the substance per day. If the body lacks Fe, then anemia begins. In order to determine its amount in the blood, it is recommended to take a blood test to determine the level of serum iron. In a normal state, that is, in a healthy body, this indicator is from 13-30 μmol per liter of blood. If the test results show a value below 13, then we are talking about Fe deficiency.
Pregnant women need this macronutrient twice as much as men and non-pregnant women. That is why a pregnant woman's diet should include foods rich in Fe. This will help maintain its level at a normal level, ensure the normal course of pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Iron deficiency during pregnancy
Iron deficiency during pregnancy occurs due to a lack of this microelement in the body of the expectant mother. If a pregnant woman does not receive enough Fe, this lowers the hemoglobin level and causes anemia. There are certain factors that increase the risk of developing Fe deficiency during pregnancy. First of all, these are problems with iron deficiency before pregnancy and chronic diseases. Multiple pregnancy and early toxicosis also cause Fe deficiency. If a woman had long and heavy menstruation before pregnancy, this is another factor in the development of iron deficiency during pregnancy.
There are certain symptoms and signs that allow you to determine Fe deficiency in the body of a pregnant woman. First of all, this is increased fatigue, irritability, general weakness. Many pregnant women complain of dizziness and severe headaches in the morning. Fe deficiency makes the skin pale and the mucous membranes dry, which very often causes inflammatory processes. A pregnant woman may develop stomatitis, brittle nails and hair, shortness of breath, digestive problems, problems with smell and taste. You can accurately diagnose iron deficiency during pregnancy using a blood test for Fe levels.
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency during pregnancy is very common and causes anemia. This disease has two forms: hidden, that is, latent and pronounced or clinical. Iron deficiency during pregnancy is caused by low hemoglobin levels. Due to Fe deficiency, a pregnant woman may experience symptoms such as: tinnitus, weakness, headache, and others. Symptoms of iron deficiency are very similar to early signs of pregnancy. It is necessary to treat Fe deficiency carefully, since a deficiency of this microelement can cause oxygen starvation for the baby.
Many pregnant women begin to experience iron deficiency in the second trimester of pregnancy. The deficiency worsens in winter and spring, when food is not enriched with iron-containing substances. Fe deficiency is diagnosed by blood tests and the hemoglobin content in it. Iron deficiency during pregnancy has a negative impact on the health of the child. Babies who experienced Fe deficiency in the womb are susceptible to infectious diseases and allergies. Treatment of iron deficiency in the blood during pregnancy is carried out by taking special iron-containing drugs and following a diet with the use of foods that are rich in this microelement.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency
Symptoms of iron deficiency during pregnancy can appear in the first trimester, but most often in the middle of the second. Symptoms of Fe deficiency are visible to the naked eye. A woman experiences deformation and brittleness of nails, physical weakness occurs, the skin becomes dry and rough to the touch, painful cracks appear in the corners of the lips, the woman often suffers from colds. In addition, a woman may experience a perversion of taste, which indicates the development of sideropenic syndrome. In this case, the pregnant woman begins to eat very strange things - paper, sand, chalk.
A blood test is the only way to accurately diagnose iron deficiency during pregnancy. A doctor studies the symptoms of Fe deficiency and, based on the tests, prescribes treatment and gives recommendations for restoring iron levels in the blood. Fe deficiency during pregnancy has serious consequences that are dangerous for both the mother and the baby.
Excess Iron During Pregnancy
Excess iron during pregnancy is as dangerous as its deficiency. Thus, excess Fe can cause the development of intestinal and liver cancer, worsening of Alzheimer's disease and the appearance of rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms of excess Fe are similar to the early signs of hepatitis. The skin becomes yellow, the liver enlarges and severe itching appears. In addition, strange pigmentation in the armpits and palms can be observed. Excess iron during pregnancy can be confirmed using a biochemical blood test.
Excess iron in the blood during pregnancy causes hemosiderosis. This disease provokes massive destruction of red blood cells. Excess iron in the blood can also lead to diseases such as: thalassemia, acute hepatitis, leukemia, hemolytic anemia, nephritis and others. Excess Fe in the body is especially dangerous during pregnancy, as it can cause miscarriage, premature birth and a number of pathologies in the baby.
Iron taste in mouth during pregnancy
Many women experience a taste of iron in the mouth during pregnancy. Often, unpleasant taste sensations appear in the first trimester and continue until the middle of the second. There are several reasons that can create an unpleasant iron taste in the mouth. The first reason is a lack of nutrients in the diet. In this case, a woman may develop oral diseases and bleeding gums. Another reason for the taste of iron in the mouth during pregnancy is hormonal changes in the body.
You can eliminate the taste of Fe by changing your diet. A pregnant woman's diet should be balanced and rich in vitamins and minerals. Another way to eliminate unpleasant sensations is regular mouth rinsing and using mint candies. If none of the above methods help, it is recommended to seek medical help and take tests that will help find a solution and effective treatment for this problem.
How to increase iron during pregnancy?
How to increase iron during pregnancy is a pressing issue for women who have been diagnosed with a deficiency of this microorganism. The first treatment option is to follow a diet and eat foods that are rich in Fe. The second option for increasing iron during pregnancy is drug therapy, Fe injections, and taking vitamin complexes.
As for nutrition aimed at increasing the level of Fe in the blood, the diet should contain a lot of fruits, vegetables and cereals. It is recommended to pay special attention to buckwheat porridge and apples, as they contain a lot of Fe, which is necessary for the body of a pregnant woman. Regarding drugs to increase iron in the blood, they are divided into two groups: Fe salts (chloride, sulfate, fumarate) and Fe complexes (trivalent) with sugars and proteins. Dietary nutrition, as well as restoring the level of Fe with drugs, must be carried out after consultation with a gynecologist. It is prohibited to take drugs that increase the level of Fe on your own, as this can lead to side effects that are dangerous to the health of the mother and baby.
Iron preparations
Iron supplements during pregnancy help restore iron levels in the body and cure anemia. The peculiarity of iron supplements during pregnancy is that they must be safe for the pregnant woman's body and not harm the child. The supplements are prescribed based on the results of a blood test. Most often, pregnant women are prescribed Sorbifer Durules tablets. This supplement contains vitamin C and 100 mg of iron. Totema is an iron-containing solution. Each ampoule of the supplement contains 50 mg of Fe. Fenuls is a capsule containing 45 mg of Fe. This supplement is used for anemia and to prevent Fe deficiency.
The dosage of iron preparations is prescribed by a doctor (from 30 to 100 mg per day). Taking Fe causes changes in the body's functioning, most often this is expressed in a change in the color of the stool to a darker one. Many packages with preparations say iron sulfate. In order for the body to receive 30 mg of Fe, it is necessary to take 150 mg of iron sulfate. The attending physician will help you accurately calculate the dosage and time of administration.
Iron Rich Foods
Iron-rich foods during pregnancy help to replenish the Fe deficiency in the woman's body and are an excellent preventative measure against anemia. Thus, the diet during pregnancy should contain a lot of vegetables, fruits, cereals and nuts. Particular attention should be paid to buckwheat porridge and lentils, they are rich in iron and help to replenish the deficiency of this microelement in a natural way. Salads from table beets and fresh apples are also rich in Fe and are recommended for consumption during pregnancy.
Walnuts, hazelnuts and almonds contain a lot of Fe. And seaweed is a vitamin storehouse that enriches the body with iron and useful microelements, and also serves as an excellent prevention of thyroid diseases. Animal liver contains a lot of Fe, but you can’t eat a lot of liver during pregnancy. Iron-rich foods are divided into those in which Fe is absorbed well and poorly. The latter products include eggs, white cabbage, spinach. It is very important that the product not only contains Fe, but also allows the body to quickly absorb it. Thus, a 60 mg iron tablet is much more effective than a kilogram of white cabbage and a dozen eggs.
Attention!
To simplify the perception of information, this instruction for use of the drug "Iron in pregnancy" translated and presented in a special form on the basis of the official instructions for medical use of the drug. Before use read the annotation that came directly to medicines.
Description provided for informational purposes and is not a guide to self-healing. The need for this drug, the purpose of the treatment regimen, methods and dose of the drug is determined solely by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous for your health.


 [
[