
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Why ingrown hair on the skin of the face, legs, groin and what to do?
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
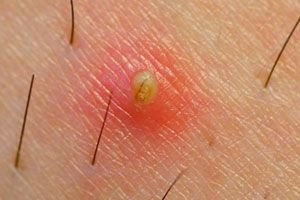
A common cosmetic problem that occurs in both men and women is an ingrown hair. Let's look at its causes, types, complications and treatment methods.
Pseudofolliculitis is a small formation. The tubercle is reddish in color with serous or purulent contents inside, in which ingrown vegetation can be seen.
- The pathological condition occurs on any skin (regardless of phototype) that is subject to regular shaving.
- The defect is accompanied by inflammation and irritation.
- Ingrown hairs occur because after shaving, hair strands grow deeper into the epidermis.
- Dead skin clogs the hair follicle and causes the appearance of a defect.
From a medical point of view, ingrown hairs are not life-threatening. But in cosmetology, this is one of the most common problems. Without proper treatment, it can cause a number of serious consequences. A reddish formation can turn into a lump that will fester and become inflamed or into an abscess. After such a complication, scars often remain on the skin.
Most often, this pathology is encountered by people with an African type of appearance, as well as with coarse or curly/wavy locks and dark skin. The softer and lighter a person's hair, the less susceptible he is to ingrowth. In women, pseudofolliculitis occurs in the bikini area (pubis) and in the armpit area, in men more often on the face. The appearance of the disorder indicates that epilation was performed incorrectly, and it is necessary to consult a dermatologist or a professional cosmetologist.
Epidemiology
According to medical statistics, pseudofolliculitis affects every third person who regularly removes hair from their body. The epidemiology of ingrown hairs indicates that this problem is most often encountered by representatives of the African-American race. The defect occurs with regular shaving. Men and women are equally susceptible to the pathology.
The defect can occur on any part of the body that is subject to the removal of unwanted hair. As a rule, ingrowth sites appear where the strands are the toughest and have a curly structure: legs, armpits, beard growth zone in men.
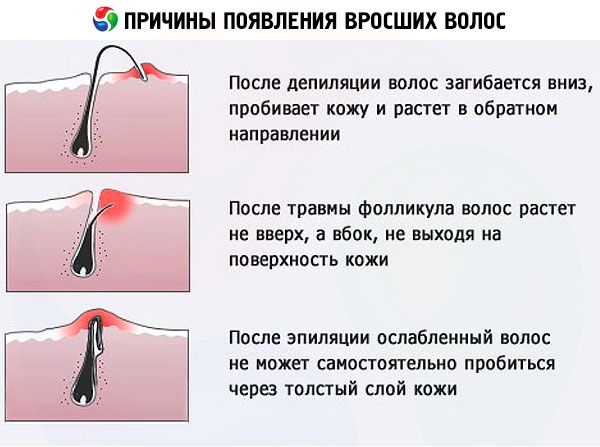
Causes ingrown hair
After shaving or epilation, many people face the problem of ingrown hairs. Owners of coarse and curly locks are more prone to this pathology. Pseudofolliculitis can occur with an imbalance of sex hormones, that is, with excess hair on the body and a number of other factors.
There are several reasons why hairs become ingrown:
- Dense epidermis layer - because of the dense skin, it is difficult for a new growing curl to break through to the outside, so it grows bent along the path of least resistance.
- Peculiarity of structure and structure – owners of dark, curly, curly and hard strands are more prone to ingrown hairs. As a rule, these are Africans and African Americans.
- Hormonal background – increased estrogen production, adolescence, pregnancy, endocrine diseases or hirsutism.
- Preparing the skin for epilation – to prevent ingrowth, peeling must be performed before the removal procedure. With its help, the dead layer of the dermis will be removed, which will improve skin respiration and normalize the growth of the hair shaft.
- Tools – if you are removing hair with a razor, you need to make sure that the blades are sharp. An old razor can injure the skin, leave scratches or cuts. In addition, a dull razor does not remove hair the first time, which is why you have to run it over the skin several times, causing irritation. When using an electric razor, strong friction of the epidermis is created, which very often provokes pseudofolliculitis.
- Cosmetics – regular use of depilatory creams leads to irritation of the root (bulb) of the hair. Its structure becomes weaker, normal growth is disrupted.
- Skin care – after shaving or other hair removal methods, a disinfectant and moisturizer should be applied to the skin. Immediately after the procedure, the epidermis is vulnerable to bacteria. This can cause inflammation or abnormal hair growth. For care, use lotions, creams and gels designed for treating skin after shaving.
- Tight-fitting clothing – tight or cramped clothing causes mechanical friction of the skin. Because of this, its upper layers become denser, the pores of the hair follicles become clogged, and a defect appears.
By minimizing the above-described causes, you can prevent abnormal hair growth and the complications associated with it.
 [ 6 ]
[ 6 ]
Risk factors
Inflammatory processes on the skin after shaving occur for many reasons. Risk factors are associated with improper hair removal. Due to injury to the hair follicle, abnormal growth of curls begins, which leads to their ingrown hairs.
Let's look at the main risk factors for pseudofolliculitis:
- Dry skin.
- Acute angle of inclination of the follicle in relation to the skin.
- Coarse and curly strands.
- Frequent shaving using dull razors.
- Incorrect preparation for hair removal and lack of skin care after the procedure.
- Waxing, sugaring.
- Blockage of hair follicles.
In men, lesions are localized in the beard and neck area. In women, most often in the armpits and bikini area. There are many prerequisites for the appearance of inflammatory pathology. To eliminate risk factors, it is necessary to properly care for the epidermis or entrust this matter to a cosmetologist.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of pseudofolliculitis development is based on its cause. Pathogenesis is most often associated with shaving. Due to such hair removal, curls growing spirally become sharp, which allows them to penetrate the skin. The free end of the hair grows into the skin, forming an arch above its surface. If the ingrowth occurs immediately after the strand leaves the bulb, it passes the skin in the stratum corneum, forming a black stripe.
Ingrowth into the dermis causes an inflammatory reaction. The pathological process may be accompanied by the appearance of microabscesses and inflammatory infiltrate, as a reaction to a foreign body. On the body, this manifests itself as small nodules that hurt and itch.
In some cases, the disorder develops into fibrosis of the dermis. Follicular papules and pustules appear, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected area. Papules can later degenerate into cysts. Very often, after removal of advanced ingrowth, scars remain.
Symptoms ingrown hair
Disruption of normal hair growth is possible on any part of the body that is often subjected to shaving, epilation and other hair removal procedures. Symptoms of ingrown hair are divided into early and late. Their manifestations largely depend on the location of the defect. At first, pseudofolliculitis is characterized by the following signs:
- Irritation and redness of the epidermis.
- Local inflammation and swelling.
- At the site of ingrowth, a rash appears: papules (inflamed nodules) and pustules (abscesses).
- Small but hard, round-shaped bumps form that are painful to the touch.
- Hyperpigmentation.
- Scarring of inflamed tissues.
At the initial stages, the pathological condition manifests itself as local hyperemia and swelling of the skin where depilation was performed. After a couple of days, inflammation, dense itchy and painful nodules are observed at the site of the lesion. The dark tip of the hair can be seen through the epidermis. After the inflammation subsides, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and scars remain. In rare cases, ingrown hairs come out on their own.
First signs
Pseudofolliculitis, like any other dermatological disease, has a number of symptoms characteristic of it. The first signs of the disorder:
- Local hyperemia and swelling.
- After 2-3 days, painful sensations and itching appear. The place of ingrowth becomes denser, and papules form.
- If there was an infection, the bump will become infected and the pus will often show through the skin.
- A hair may be visible through the upper layers of the dermis: a loop or its tip.
- The appearance of milia - whitish nodules, dense to the touch. They form a couple of weeks after shaving or epilation.
- If the defect becomes complicated, abscesses and pustules form due to the infectious process (staphylococci, pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Further symptoms depend on the nature of the pathological process. The hair can break through on its own. If this happens, the inflammation gradually subsides. When trying to open the nodule and pull out the hair on your own, infectious complications are possible. A purulent pustule forms at the site of ingrowth, which leaves a scar. If treatment is carried out in a medical institution or by a cosmetologist, then a small wound and hyperpigmentation remain at the site of the ingrown lock.
 [ 14 ]
[ 14 ]
Ingrown hairs in the bikini area
Many girls who do hair removal and regularly take care of their skin face such a problem as ingrown hairs in the bikini area. This defect causes irritation, pain and inflammation. Sometimes the place of ingrowth begins to fester, turning into a lump or furuncle. In this case, the help of a dermatologist or cosmetologist is needed, who will remove the defect and its consequences. To prevent pseudofolliculitis, you should regularly peel the epilated areas of the body and use special cosmetics.
Ingrown pubic hair
Anyone who removes unwanted hair in the intimate area faces such a problem as an ingrown pubic hair. Moreover, women suffer from this much more often than men. The cause of ingrown hair is associated with a pathological change in the direction of hair growth. During the removal process, the bulb is injured, due to which the strand does not break through to the outside, but grows under the skin. In most cases, everything ends with redness and mild inflammation, but there are cases of infection and more serious complications.
There are a number of symptoms characteristic of pseudofolliculitis in the pubic area:
- Local inflammation and swelling.
- Itching.
- Painful sensations.
- Pus.
If the above symptoms are ignored, discomfort and further progression of the pathology occur. As a rule, the acute onset of the disorder is observed within a few days. In some cases, the symptoms can be confused with acne, STDs, genital herpes and other diseases. The dermatological problem requires treatment. For this, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, surgeon or cosmetologist. If the inflammatory reaction occurs without significant complications, then you can try to eliminate the defect yourself.
Methods for removing ingrown pubic hair:
- Treat the affected area with a scrub and apply a warm compress. This will help soften the skin, which will make the procedure much easier. Treat the tweezers with alcohol and take a sterile syringe needle. Use the needle to pull the hair out of the follicle and remove it with tweezers. This method can be used if the ingrowth is visible under the skin. In other cases, it is better to consult a surgeon, since the curl may be deep in the skin, and attempts to remove it on your own will lead to injury to the epidermis and infection.
- Another option for combating cosmetic defects after shaving is chemical depilation. A special cream is applied to the pubic area, which weakens the hair, making it easier to remove. Tretinoin cream can be used for the procedure. It affects the follicle, due to which the hair sits loosely inside and its removal is painless.
- If the defect is accompanied by a secondary infection, you should see a doctor who will prescribe antibiotics, both internally and externally. Without proper treatment, abscesses and purulent papules may form. After the risk of infection is minimized, the doctor will remove the neoplasm.
Do not forget about pseudofolliculitis prevention methods. First of all, pay attention to the method you use to remove hair. If you shave, it is better to treat the skin with a special gel or cream, not soap. This will allow the razor to glide better over the skin and not leave irritation. After the procedure, the depilated area should be disinfected and moisturized. When waxing, it is necessary to exfoliate and soften the skin. This will allow you to completely remove the hairs without damaging the follicles or disrupting their growth.
Ingrown hair after epilation
In the fight against excess hair on the body, many women resort to such a procedure as epilation. It is a method of removing hair along with the root. After such a procedure, smooth and velvety skin remains, which pleases for several weeks. But in some cases, complications may arise - this is an ingrown hair after epilation. This happens due to the lack of preparation for epilation or due to improper body care immediately after the procedure. To treat pseudofolliculitis, you must contact a cosmetologist who will select the best method of hair removal without disrupting their growth.
Ingrown hairs on legs
A side effect of many hair removal methods is ingrown hairs. They appear on the legs more often than on other parts of the body. This is due to the fact that the legs are often shaved, especially in the summer. The defect is accompanied by an inflammatory process, irritation, itching, burning, hyperemia develop. In particularly severe cases, folliculitis or secondary infection may develop.
In addition to painful sensations, the defect also causes cosmetic problems. Ingrown hairs look like black dots, they can turn into compacted nodules and bumps with pus, which require medical treatment.
The main reason for the development of the disorder is that during the removal of hair from the legs, only the epidermal part of the hair is affected, and not its bulb. After the procedure, the hair begins to grow and tries to break through the rough skin. If it does not succeed, then it bends towards the bulb, that is, inside the root.
For the treatment and prevention of pseudofolliculitis on the legs, the following methods are recommended:
- Exfoliate and exfoliate regularly to help remove dead skin cells.
- Use moisturizing lotions and creams. When shaving, it is better to use special gels rather than soap. This will allow the razor to glide easily over the skin without damaging it.
- Shave with the grain of your hair, not against it. This will minimize the risk of damaging the follicle.
If an ingrown hair does appear, it must be removed. To do this, steam the skin or apply a warm compress to the affected area, which will soften the epidermis. Prepare a sterile needle, a disinfectant, and tweezers. Using a needle, carefully lift the lock of hair and remove it with tweezers. To avoid a wound at the site of ingrowth, wipe the skin with alcohol or chlorhexidine solution. But this method is only suitable if the lock is under the surface of the skin and is visible.
Hairs that have grown in deep enough, turned into a lump or are festering should be treated by a surgeon or dermatologist. The doctor will open the growth, clean it from pus, remove the root, preventing further complications.
Ingrown hair after sugaring
Hair removal using thick sugar syrup is sugaring. Sugar epilation has a number of advantages over other methods of hair removal from the body:
- Cost-effective and easy to use – the hair removal paste consists of water and sugar. It is very easy to use, just roll it into a ball and rub it over the skin with unwanted hair.
- Hypoallergenic and painless - sugaring paste does not cause allergic reactions. In addition, the product sticks less to the skin, which does not cause such discomfort as when using wax.
- Long-lasting effect and minimum complications – sugar caramel envelops both the hair and its bulb, allowing it to be completely removed. During the procedure, the hairs do not break and their growth is not disturbed. The effect can last up to 20 days.
Ingrown hairs after sugaring occur much less frequently than after waxing or shaving. Pseudofolliculitis may develop if the removal procedure was performed in violation of technology. Therefore, it is better to have sugaring done by a professional cosmetologist.
Treatment of pseudofolliculitis after sugaring is the same as after other methods of hair removal. If the curl is not deep, the skin should be steamed and pulled out with a sterile needle. If there is inflammation with signs of suppuration, it is better to consult a dermatologist or surgeon who will clean the wound and remove its contents.
Ingrown hair on face
Many men are familiar with such a problem as ingrown hair on the face. Most often, its appearance is associated with the following reasons:
- No preparation for shaving – although many razors have a soap strip, it cannot replace a normal shaving product. Before the procedure, the depilation area must be treated with a special foam or gel and the skin must be steamed for 3-5 minutes.
- Incorrect hair removal – very often facial hair grows in different directions, so before shaving it, you need to determine the direction of stubble growth. You need to shave in the direction, not against it.
- Bad tool - if you have a tendency to pseudofolliculitis, then you should refuse razors with several blades. This is due to the fact that the first blade catches the bulb and lifts it above the skin, the second removes the hair, and the third injures the root. Because of this, irritation occurs, pustules appear on the skin and other cosmetic troubles.
- Improper skin care after the procedure - to prevent pseudofolliculitis, moisturize and disinfect the skin. There are many lotions, balms and creams after shaving for this purpose.
If an ingrown hair appears on the face, it should be removed. To do this, you need to steam the skin. You can prepare a herbal decoction with an anti-inflammatory effect, for example, from chamomile or parsley. After this, pick up the hair with a sterile needle and remove it with tweezers. The damaged area should be wiped with a disinfectant.
If the curl is deep in the skin, do not try to squeeze it out or pick at the skin and pull it out. In most cases, such actions lead to infection of the wound. Contact a cosmetologist or surgeon, the doctor will remove the defect and tell you about prevention methods. Also, do not forget that following the rules of shaving and proper facial care minimize the problem of ingrown hairs.
Ingrown hairs become inflamed
Very often, shaving unwanted hair is complicated by the fact that ingrown hairs become inflamed. A small bump appears on the skin, inside which you can see a hair. Any touch to the lump causes painful sensations. If you leave this defect unattended, it can lead to serious complications. Since in some cases, ingrown locks reach the subcutaneous fat and cause more problems than any abscess.
The risk of complications depends on the localization of the inflammation. The most dangerous is the lesion near the lymphatic system, for example, in the armpits. Therefore, as soon as you notice inflammation after shaving, you should consult a doctor. A dermatologist or surgeon will open the seal, clean it from pus, and prescribe a course of antibiotics. Attempts to independently cope with pseudofolliculitis in the acute stage are contraindicated.
Ingrown hair on the labia
Almost all women who remove hair in this area face such a problem as ingrown hair on the labia. Ingrown hair is possible after any method of removal: sugaring, waxing, shaving. The pathological condition is characterized by an inflammatory process. Purulent bumps-pimples appear on the skin, in which a hair can be seen.
If you leave this problem unattended, the inflammation will become chronic. This can lead to the appearance of a boil or abscess. Attempts to independently remove the defect in such an intimate area are unacceptable. Since there is a risk of infection and injury to the skin. It is enough to contact a gynecologist or cosmetologist who will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and painlessly remove the neoplasm.
Ingrown hairs under the arms
The most unpleasant and painful complication after depilation is ingrown hairs under the armpits. The skin in the armpits is very thin, so it is easily irritated. The presence of sweat glands and regular use of deodorants aggravate pseudofolliculitis, causing discomfort, pain, and infection.
It is quite difficult to eliminate ingrown hairs in this area on your own. But if the ingrown hair is under the surface of the skin, you can try to remove it.
- The affected area should be treated with an acne treatment that contains salicylic acid.
- After a couple of minutes, wipe off the ointment thoroughly and steam the skin.
- Using a sterile needle, pick up the hair and pull it out with tweezers.
- Treat the skin with an antiseptic.
But even after a properly performed procedure, there is a risk of complications. This is due to the fact that a damaged follicle may remain in the skin, which will fester. Therefore, at the first signs of dermatological inflammation, you should consult a doctor.
Ingrown hair during pregnancy
The problem of ingrown hairs causes a lot of inconvenience, especially if the hair grows during pregnancy. It is better to treat this defect with a doctor. Since complications from pseudofolliculitis are dangerous.
In order to prevent the development of a dermatological disorder, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Use a good shaving and post-waxing product that won't clog your pores.
- Use only a high-quality razor, preferably a disposable one, or change the blades more often.
- Exfoliate your skin regularly, use scrubs and special lotions with salicylic acid.
- Remove hair in the direction of its growth. If possible, perform the procedure as infrequently as possible.
Following these simple rules will help you avoid unpleasant complications during pregnancy.
Stages
Pseudofolliculitis develops gradually. The stages of the pathology are characterized by increasing symptoms. At first, mild hyperemia and swelling appear, which are replaced by a pronounced inflammatory process and suppuration. Further development depends on the following factors:
- Damage to the shape of the hair follicle - due to improper removal, hair begins to grow under the surface of the skin, it can curl into a spiral or grow in an arch above the surface of the epidermis. Rarely causes severe inflammation and is easily removed at home.
- Overgrowth of the hair root mouth with keratinized epidermis - a weakened curl does not grow to the surface, therefore it begins to go inside the dermis. This process is aggravated by severe inflammation, the appearance of an abscess or furuncle.
Depending on the stage of the ingrown hair and its location, different treatment methods are used. This may include scrubbing and regular peeling, local antiseptics and skin softening agents, or surgery to open the growth.
Forms
Ingrown hair, like many dermatological pathologies, has several types, each of which has its own characteristic signs. The following types of pseudofolliculitis are distinguished:
- Superficial – the ingrown stubble is located under the skin surface and does not penetrate into the deep layers of the dermis. A small suppuration appears, which goes away after 2-3 days. You can see a hair in the abscess. As soon as the abscess dries, the hair will remain on the surface, which will allow you to easily remove it. After the ingrown stubble is removed and the wound heals, pigment spots may remain on the skin.
- Deep – occurs when the hair has penetrated into the deep layers of the dermis. A dense, painful, red nodule forms on the affected area. The size of the seal does not exceed 2 cm. After 5-7 days, the pustule gradually dries up, a crust remains on the skin, but the curl does not come out. After removing the ingrowth, scars remain on the skin.
Regardless of the type and stage, pseudofolliculitis causes a lot of inconvenience. To prevent the development of this pathology, it is necessary to properly remove unwanted hair, having previously prepared the skin for this.
 [ 17 ]
[ 17 ]
Complications and consequences
Ingrown hairs anywhere on the body can cause serious consequences and complications. The most common problems include:
- Bacterial infection
- Hyperpigmentation
- Inflammation of the hair follicle
- Scars and keloids
- Furuncle
- Abscess
If the pathological process is accompanied by a secondary infection, then even blood poisoning is possible.
Why is an ingrown hair dangerous?
At first glance, the problem of ingrown hairs does not pose a danger. But in some cases, an advanced pathological process leads to serious consequences. Let's consider in more detail why an ingrown hair is dangerous:
- Hairs should grow outward, if they remain under the skin, inflammation begins. The body fights a foreign body, which is why pus accumulates in the affected area. After opening a purulent neoplasm, scars may remain on the skin.
- Long-term inflammation of ingrown hair leads to the formation of seals. Small but painful bumps on the skin are a common cosmetic problem, the main cause of which is improper depilation.
- Attempts to remove the defect on your own can lead to serious skin trauma and infection. Against this background, several complications are observed: abscess, furuncle, scars, hyperpigmentation, blood poisoning.
At the first painful symptoms of pseudofolliculitis, you should consult a cosmetologist or surgeon.
Ingrown hair suppuration
One of the most common complications of improper depilation/epilation is suppuration of an ingrown hair. The pathological process is characterized by purulent inflammation of the upper parts of the hair follicle.
An inflamed papule surrounded by reddened skin forms at the mouth of the follicle. A pustule appears on the body, with bristles inside. After 3-5 days, the pustule resolves and a crust or small erosion with an ingrown hair remains. In most cases, after the purulent-inflammatory process has resolved, the curl comes out on its own.
Ingrown hair wounds
An incorrectly performed procedure for removing unwanted hair leads to serious consequences. Ingrown hair wounds most often occur due to attempts to independently remove a hair that is deep in the skin. Wound damage to the epidermis is possible due to complications of pseudofolliculitis, that is, abscesses, boils or furuncles.
If there is serous-fibrous or purulent exudate in the open wound, the patient is cleaned of the wound area and prescribed a number of local remedies that accelerate healing. In particularly severe cases, sterile dressings and regular treatment with antiseptics are used.
To speed up healing, the following medications are prescribed:
- Salicylic ointment is an antibacterial agent that disinfects the skin and accelerates regeneration processes. Before applying the ointment, the skin should be treated with an antiseptic, then apply a thin layer of medicine and cover everything with a sterile bandage. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day until the wound condition improves.
- Rescuer Balm - after application to the skin forms a thin film. Before using the product, the wound must be washed with hydrogen peroxide.
- Eplan cream is an antibacterial agent with disinfectant properties. Reduces the risk of infection of open wounds, accelerates healing.
A doctor should treat wounds with pseudofolliculitis. Attempts to cope with the damage on your own can lead to negative consequences.
Ingrown hair lumps
Very often, injury to hair follicles during shaving or epilation leads to various complications. Seals from ingrown hairs are one of them. The appearance of a lump or a large but painful pimple indicates that there is an inflammatory process under the skin. In this case, regular peelings are recommended to eliminate the defect. Gradually softening the seal will allow painless removal of the hair.
If the growth is large and painful, you should see a surgeon. The doctor will open the growth, remove the ingrowth, and if there is pus, clean the wound. In some cases, the thickening indicates a maturing furuncle. Special ointments and medicinal compresses are prescribed for its treatment.
Scars from ingrown hairs
A third of people suffering from pseudofolliculitis face such a problem as scars after ingrown hairs. The nature of the scar depends on whether there was an infection and how much damage was done to the surrounding tissue.
As a rule, after the defect is removed, keloid scars remain on the skin. They can be star-shaped or fan-shaped, painful, rough to the touch. Since they are small in size, no specific treatment is required. Gradually, they become lighter and less noticeable. But if the scar is on the face or causes discomfort, the following methods are used to remove it:
- Mesotherapy – special injections with active components are introduced into the affected tissues, which accelerate the process of regeneration and restoration of the skin.
- Cryodestruction – the essence of this method is the use of liquid nitrogen. A special attachment is fixed to the scar, which is gradually cooled. The procedure is painless, dead tissue is rejected within a month. In about six months, new healthy skin is formed.
- Laser resurfacing – the scar is exposed to a laser beam, which evaporates connective tissue. The procedure does not take much time and is absolutely painless.
- Vacuum massage – with the help of dermotonia, you can restore lymph flow and tissue blood circulation. This will help reduce the size of the scar and smooth it out.
In addition to the above methods, hardware and chemical peels or drug therapy can be used for treatment. If the scars are fresh, alternative medicine methods can help: beeswax, marshmallow root tincture, Kalanchoe juice and calendula flowers, milkweed, etc.
Hairs constantly grow in
If you are faced with the problem that after shaving hairs constantly grow in, then it is worth taking a number of preventive measures that will help restore the normal condition of the skin.
To combat pseudofolliculitis, it is necessary:
- Regularly exfoliate your skin, especially in areas that will be epilated. This will minimize the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Use special products before and after shaving. They slow down hair growth, moisturize the skin and disinfect it.
- Additionally, use antiseptics before and after depilation/epilation, especially in the intimate area.
- Perform epilation before bedtime and avoid contact with water immediately after the procedure.
- Avoid wearing tight and synthetic underwear.
- Keep hair removal procedures to a minimum.
It is also necessary to choose the ideal method for removing unwanted hair. The best method is considered to be laser hair removal and photoepilation. The problem of ingrown hairs can be minimized with the help of sugaring, that is, hair removal with sugar paste.
Ingrown hair scars
Very often after depilation, there are strands of hair that have grown into the skin. Traces of ingrown hairs occur due to trauma to the epidermis during the process of removing the defect or its complications. The following methods are used to combat hyperpigmentation:
- Peeling – exfoliation of the skin removes the upper layer of cells with altered pigmentation and promotes epidermis renewal. Scrubbing can be used as a preventive measure against pseudofolliculitis.
- Vitamin therapy – to quickly restore healthy skin color and discolor traces of ingrown hairs, you can use an oil solution of vitamin E. The product should be applied to the lesions immediately after showering and peeling, preferably at night.
- Castor oil – it has bleaching properties, like vitamin E. It should be used in the same way.
- Baked onion – take a baked onion, cut it and apply the cut side to the skin. Fix it with a sterile bandage, plaster or bandage and change it for a new one after 4 hours. The procedure must be carried out until there are no traces of the ingrown hair.
- Aloe - mix equal parts of aloe juice, olive and almond oil, and flax seed decoction. Soak a cotton swab in the resulting liquid and apply it under the bandage to the pigmented area. Continue treatment until the desired results are achieved.
- Bodyaga – this remedy is used not only to remove hyperpigmentation, but also to eliminate ingrown hairs. Mix bodyaga and hydrogen peroxide in equal proportions. Apply the remedy to the affected area for 10-15 minutes. As soon as you feel a burning sensation, wash it off immediately. The procedure should be carried out for 5-7 days.
If no treatment is carried out, the hair marks will disappear on their own, but this will take a long time.
Red spots from ingrown hairs
Many women face such a problem as red spots from ingrown hairs. As a rule, their appearance indicates inflammation of the hair canal. But the main danger is that the purulent-inflammatory process can recur, which will significantly worsen the condition of the epidermis. In order to get rid of spots and speed up the process of skin regeneration, the following means are used: peeling, laser treatment, photorejuvenation or topical preparations.
The most accessible and simple way to eliminate age spots is to use medicinal masks:
- Aspirin - helps in the treatment of hyperpigmentation in the bikini area. Take three aspirin tablets, a spoonful of honey and water. Melt the honey until liquid, crush the tablets, and mix all the ingredients. Apply the resulting gruel to the reddened area immediately after a shower. The duration of treatment depends on the speed of skin recovery.
- Hydrogen peroxide mask – prepare a bottle of hydrogen peroxide and two bags of badyagi (can be purchased at a pharmacy). Mix the ingredients until a homogeneous gruel is formed. Apply the mask to the body for no more than 30 minutes, wash off with warm water. The product has a drying effect, so after using it, the skin should be moisturized. You can use this mask no more than 2 times a week, the course of treatment is a month.
The use of means for restoring normal pigmentation of the epidermis is possible only after stopping inflammatory and purulent processes. There should be no wounds or other damage on the body.
Abscess from ingrown hair
Purulent inflammation of tissues with the formation of a purulent cavity is an abscess. It can develop from an ingrown hair due to the neglect of the pathological process and the addition of a secondary infection. The disease occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the skin and the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body. This is possible when trying to independently remove an ingrown hair, picking at the skin with a non-sterile needle, or due to non-compliance with disinfection rules.
Due to the rapid proliferation of pyogenic bacteria, a purulent capsule is formed and the skin melts. In pseudofolliculitis, the causative agent of the infection is staphylococcus or pseudomonas aeruginosa. An abscess has a number of characteristic clinical signs:
- Redness of the skin.
- Localized painful sensations.
- Local increase in temperature.
- Swelling.
- General malaise.
If the above symptoms occur, you should consult a surgeon. Without medical assistance, the abscess can break through on its own, either under the skin or outward. To prevent the abscess from self-liquidating, the doctor opens the purulent cavity and drains it. The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, immunostimulants, and local medications. After the abscess cavity is completely emptied, a scar is formed.
Without timely medical care or when trying to treat the abscess on your own, the following complications are possible: bacteria entering the blood, erosive bleeding, and the spread of infection. Prevention of complications is based on compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis and following all medical recommendations.
Furuncle from ingrown hair
One of the complications of pseudofolliculitis is a furuncle. It develops from an ingrown hair if the lock grows into the deep layers of the dermis. Without timely treatment, the pathological process can become chronic. In most cases, a furuncle develops with a staphylococcal infection, that is, due to secondary infection of the wound. It is characterized by purulent-inflammatory processes in the hair follicle and surrounding tissues.
A furuncle from an ingrown hair can appear on any part of the body. Most often, it occurs in the armpits or areas of friction (face, neck, groin, thighs). In its development, it goes through three stages:
- Infiltration – a bright red infiltration appears around the mouth of the hair follicle, which quickly increases in size and becomes denser. The surrounding tissues are edematous and painful.
- Suppuration and necrosis – this stage occurs 3-4 days after the first. A purulent-necrotic core forms in the inflammation site, which comes out on the skin surface as a pustule. The patient’s temperature rises, and there is severe pain in the area of the furuncle. After 3-5 days, the abscess opens and pus and a necrotic core come out through the hole in the skin.
- Healing – granulation tissue forms in the crater of the boil. After 3-4 days, a red-blue scar forms, which fades over time.
The duration of all stages is 10-14 days. UHF therapy and various local remedies are used to treat the pathological condition. The patient is prescribed ichthyol dressings on the affected area, turundas with Levomekol ointment, and rinsing with antiseptic solutions. Antibacterial therapy is carried out at the healing stage.
Despite the simplicity of this purulent-inflammatory complication of an ingrown hair, a furuncle can also cause a number of complications. Its consequences depend on the location, these can be abscesses, phlegmon, phlebitis, furunculosis and even sepsis.
Lump after ingrown hair
Pseudofolliculitis is very often accompanied by various complications. A lump after an ingrown hair indicates a long-standing inflammatory process. The lump may be reddish in color, hurt and itch. The size of the lump depends on the severity of the defect.
Regardless of the location of the neoplasm, it must be treated. The best solution in this case would be to contact a dermatologist. Using a scalpel or a sterile needle, the doctor will hide the lump, clean it from pus and wash it. A sterile bandage will be applied to the wound and regular washings with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine solution will be prescribed.
There are a number of methods that can prevent the appearance of seals after hair removal:
- If inflammation already exists, then for 2-3 days it is necessary to apply an anti-inflammatory ointment (Dalacin, Baziron, Proderm) to the skin, which will relieve redness and swelling.
- Once the inflammation subsides, the bump should be treated with a scrub. This will remove dead skin particles.
- There are special creams and impregnated wipes that prevent ingrown hairs. Using them on a regular basis is the best prevention of compactions after an ingrown hair.
It is very difficult to remove a lump at home on your own. The main difficulties are associated with the risk of infection, especially if the defect is on the face. The lump has many blood vessels and if removed incorrectly, there is a risk of blood poisoning.
Diagnostics ingrown hair
Based on the expressed clinical picture, an ingrown hair is diagnosed. The doctor collects anamnesis, based on the results of which he makes a treatment plan for pseudofolliculitis or prescribes additional diagnostic procedures.
In the center of inflammation, dense, close, hyperpigmented or erythematous papules are formed, which appear immediately after hair removal. The severity of the disorder depends on the number of pustules and papules. In particularly severe cases, up to a hundred foci of inflammation may occur.
If the seals contain purulent contents, then an analysis is made for infectious flora. As a rule, a secondary staphylococcal infection or other pathogenic microorganisms are found at the site of ingrown hair.
Differential diagnosis
In its symptoms, pseudofolliculitis is similar to many other dermatological diseases. Differential diagnostics are carried out with the following pathologies:
- Pyoderma.
- Folliculitis (bacterial, fungal).
- Acne.
- Acne vulgaris.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis.
- Ostiofolliculitis.
- Impetigo.
Diagnostic methods depend on the localization of the inflammatory process. In the presence of purulent papules, a culture and scraping for infectious flora are done. In particularly severe cases, a biopsy is performed. Since the pathological condition is associated with shaving and other hair removal methods, differential diagnostics is not difficult.
Who to contact?
Treatment ingrown hair
Regardless of the location, it is better to treat an ingrown hair with a dermatologist or cosmetologist. For this purpose, the following medications may be prescribed: retinoids, corticosteroids, antibiotics. In advanced cases, surgery is performed, that is, opening an abscess, furuncle or a lump with a defect. Attempts to independently cure pseudofolliculitis, as well as the lack of timely medical care, can lead to serious complications, one of which is blood poisoning.
Prevention
There are many methods of prevention to prevent ingrown hairs. Let's look at the main preventive recommendations:
- Regular skin peeling to remove the upper keratinized layer of skin. Scrubbing should be done the day before depilation.
- If a razor is used to remove hair, the razor must have a sharp and clean blade. If you are prone to ingrown hairs, shaving should be done no more than 2-3 times a week.
- Before and after hair removal, the skin should be disinfected. Since infection causes an acute inflammatory process with suppuration.
- Waxing and sugaring should only be performed by a specialist. Very often, attempts to carry out such a procedure independently lead to pseudofolliculitis.
- Wear underwear and clothing made from natural fabrics. Clothing should not rub against the skin or be tight-fitting.
If you are prone to frequent ingrown hairs and their complications, epilation and depilation should be done as infrequently as possible. This will allow the hairs to grow a little and become stronger. If possible, shaving and other methods of removing unwanted hair should be replaced with laser hair removal.
Forecast
An ingrown hair, regardless of its location, has a favorable prognosis. In case of serious damage to the skin, scars, bumps and pigmentation foci may remain. If pseudofolliculitis is accompanied by various complications, the prognosis worsens, since without timely medical care it negatively affects the functioning of the entire body.

