
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome.
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 05.07.2025
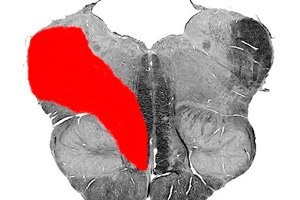
In medicine, there are a number of diseases called alternating medullary syndromes of the brainstem. Among them, one of the most common is Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome. The disease was described back in 1895 by psychotherapist Adolf Wallenberg. Subsequently, 16 years later, another neuropathologist M. A. Zakharchenko supplemented the description of the pathology.
Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is characterized by damage to the posterolateral region of the medullary part of the tegmentum, localized at the level of the medulla oblongata. The affected structures are represented by the double nucleus (9, 10 nerves), the nucleus of the spinal cord pathway (5 nerve), the sympathetic fibers of the Budge center, the rope-like body, the medial loop, the vestibular nuclei (8 nerve), etc.
Below we offer you a description of the classic development of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome.
Alternating Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome
Such pathologies, which are collectively called alternating syndromes, received this name from the term "alternance", which is translated from Latin as "opposite". They include Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, as well as other syndromes accompanied by damage to the cranial nerves against the background of central motor paresis and hypesthesia in the opposite half of the body. Since paresis affects both the body and limbs, it is called hemiparesis, and sensory disorders occurring by analogy are called hemihypesthesia. Due to the specificity of clinical features, alternating syndromes in neuropathology are also called "cross symptom complexes".
Neurologists distinguish a number of such cross-symptom complexes. Among them are bulbar (associated with damage to the medulla oblongata), pontine (associated with damage to the pons) and peduncular (associated with a defect in the cerebral peduncle) disorders. Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome in this perspective is related to bulbar diseases.
Epidemiology
Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome develops especially often as a result of ischemic stroke. When the intracranial zone of the vertebral artery is blocked, persistent alternating signs of damage to the medulla oblongata and transient signs of ischemia of the oral areas of the brainstem, temporal and occipital lobes are combined. Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome develops in approximately 75% of such cases.
The syndrome is diagnosed mainly in patients over 50 years of age, regardless of gender.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Causes Wallenberg-Zaharchenko syndrome.
The most common cause of the development of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is considered to be thrombosis of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (a branch of the vertebral artery), as well as a deficiency of blood flow in the vertebrobasilar basin.
The basis for painful processes may be the following conditions:
- Stroke is the most common cause that provokes the development of the syndrome. Thus, the etiological factor in ischemic stroke is thromboembolism, a spastic state of the arterial vascular system (in particular, the vertebral, cerebral, basilar artery). Hemorrhagic stroke is said to occur when there is bleeding from the named arteries.
- The tumor process in the brain can directly affect the brainstem or be located next to it, putting pressure on the brainstem structures.
- Inflammatory reactions in the brain – encephalitis, abscess, meningitis, spreading to the stem tissue.
- Head injuries, traumatic brain damage - in particular, fractures of the cranial bones that participate in the formation of the posterior cranial fossa.
- Poliomyelitis, syphilis.
Risk factors
There are external and internal factors that can influence the development of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome:
- age over 50 years;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- high blood cholesterol;
- bad habits – smoking and drinking alcohol;
- head injuries;
- hereditary pathologies;
- obesity, diabetes;
- septic complications;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives, hormonal therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- difficult postoperative recovery stage;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- forced prolonged uncomfortable position of the body and limbs;
- strong temperature changes, prolonged hypothermia, heat stroke;
- malignant neoplasms;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- stress, instability of the nervous system.
Pathogenesis
The medulla oblongata is small in size, has a complex anatomical structure, and carries numerous functional loads. Even minor painful foci in it lead to the appearance of various clinical signs - unilateral or bilateral. In pathologies of the medulla oblongata, functional impairments of the 9-12 pairs of cranial nerves are detected. The disease is also characterized by pyramidal motor disorders, changes in sensitivity in the face and body, malfunctions of the cerebellum, vasomotor system, and other disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
Damage to the medulla oblongata is often observed against the background of vascular, inflammatory or tumor pathologies affecting the nervous system. Direct bleeding into the medulla oblongata is rare: Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is more often caused by softening of the brain structures - for example, in poliomyelitis. This type of damage is the most dangerous, due to the high risk of developing respiratory paralysis.
 [ 2 ]
[ 2 ]
Symptoms Wallenberg-Zaharchenko syndrome.
The classic course of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is determined by the following symptoms:
- dysfunction of the soft palate muscles with vocal cords;
- unilateral motor coordination disorder of the cerebellar type;
- Horner's (Bernard-Horner's) symptom complex (triad): drooping of the upper eyelid, abnormal constriction of the pupil, sunken eyeball;
- dissociated sensory impairment (primarily the middle and caudal areas of Zelder are affected).
The course of the disease may differ slightly, depending on the type of pathology (we have described them below).
The first signs of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome are quite typical:
- impaired swallowing;
- impaired speech (up to and including complete inability to speak);
- partial loss of functionality of the soft palate;
- immobilization of the vocal cords;
- Horner's triad (ptosis, miosis, enophthalmos);
- vestibular-cerebellar disorders (“empty” motor activity of the limbs, tremors, loss of balance, nystagmus);
- pain in the head or face (partial or complete).
The listed clinical features are explained by the occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar arterial vessel, which entails necrosis of the outer regions of the medulla oblongata, the exit zone of the trigeminal nerve and the fibers of the sympathetic system.
Stages
Classification of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome by stages is not always appropriate, so not many specialists use it. However, it exists and consists of four stages of the pathological process:
- Acute period of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome.
- Early recovery period of the patient, with the formation of necrotic areas and the development of collateral blood flow.
- Late recovery period, with the formation of cicatricial changes in tissues.
- The period of residual effects of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome.
Forms
Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome develops as a result of blockage of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The disease manifests itself from the side of the lesion by paresis or paralysis of the soft palate with the vocal cord, damage to the sympathetic fibers and the trigeminal nerve (segmental type), cerebellar disorders (ataxia, nystagmus). On the opposite side, pain and temperature sensitivity is lost, movements are impaired in the form of paralysis or paresis.
Neurologist M. A. Zakharchenko identified a number of pathology variants:
- The first variant of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome occurs with the development of paralysis of the soft palate with the vocal cord and deviation of the tongue to the side opposite to the affected one. Horner's symptom complex is observed, loss of the palatine and pharyngeal reflex, electrical excitability of the soft palatine muscles worsens, swallowing and speech are impaired, pain and temperature sensitivity of the part of the face on the side of the pathology disappears. There are disturbances in the trophism of the skin of the auricle, herpetic rash, dryness and peeling of the skin in the hair growth zone and on the face, atrophic rhinitis develops. On the healthy side, dissociated disturbances of pain and temperature sensations on the body and limbs are observed.
- The second variant of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is somewhat different from the first variant. When the pathological process spreads to the structures above the bridge, damage to the 6th-7th cranial nerves occurs. Horner's symptom is recorded, coordination and statics are impaired, and paresis of the vocal cord with the soft palate appears. Hemianesthesia is recorded on the opposite side.
- The third variant of the Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is characterized by paralysis of a part of the soft palate with the vocal cord and deviation of the tongue to the opposite side. There is no pharyngeal and palatal reflex, swallowing and speech are impaired, Horner's symptom complex is observed, the sensitivity of one side of the face is impaired, the trophism of the skin and mucous membranes worsens. Atrophic rhinitis, locomotor ataxia develop, statics are impaired. A slowdown in heart rate is detected, taste sensations on one side of the tongue change. The patient is bothered by dizziness (sometimes with vomiting), nystagmus in the direction of the affected area. On the opposite side, a dissociated failure of sensitivity is recorded on the body and limbs.
- The fourth variant of the Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome is observed when the process spreads to the descending sections up to the intersection of the pyramidal tracts. There is paresis of the soft palate with the vocal cord, Horner's symptom complex, limb coordination and statics are impaired, crossed triplegia (or hemiplegia) is detected, as well as alternating sensory disorder (in the affected area on the face, on the opposite side - on the body and limbs).
 [ 3 ]
[ 3 ]
Complications and consequences
With Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, as with all alternating syndromes, serious complications may arise. With spastic hemiparesis, joint contractures develop, which only aggravate motor disorders. With nerve paresis, facial symmetry is disrupted, which becomes a significant aesthetic problem. With unilateral paresis of the oculomotor group, double vision occurs, which negatively affects visual function.
The most dangerous complications develop against the background of the progression of the pathology, when the process spreads to the brain areas responsible for respiratory and cardiovascular functionality.
The quality of recovery of patients depends on many factors, and it is almost impossible to predict in advance the subsequent development of events and the outcome of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome.
Diagnostics Wallenberg-Zaharchenko syndrome.
The presence of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome can be determined already during the examination by a neurologist. The visual information obtained allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made, establishing the localization of the problem. Based on the characteristics of the course of the disease, the etiology of the syndrome can be roughly imagined. Therefore, differential diagnostics are often carried out already at the time of the initial medical examination.
Tumor processes are characterized by a steady increase in symptoms over the course of a couple of months (in some cases, even several weeks).
In inflammatory processes, mainly general signs of intoxication are observed: high temperature, weakness, drowsiness, dry mucous membranes, etc.
In strokes, alternating syndrome always develops abruptly, with a rapid increase in symptoms simultaneously with changes in blood pressure.
In hemorrhagic stroke, an atypical picture of alternating syndrome is observed, which can be explained by the unclear limitation of the painful focus due to pronounced perifocal reactions (edema, reactive signs).
To clarify the cause of the development of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics.
Instrumental diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain (helps to examine the inflamed area, the site of hemorrhage, the tumor process, the stroke zone, to distinguish between hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, to assess the severity of pressure on the brainstem structures).
- Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography of cerebral vessels (reveals cerebrovascular accidents, symptoms of thromboembolism, local spasm of cerebral vessels).
- Ultrasound examination of extracranial vessels (helps diagnose occlusion of the vertebral and carotid arteries).
Blood and urine tests are performed in the usual manner, but they are of little use in diagnosing Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome. A lumbar puncture may be performed if an infectious and inflammatory pathology is suspected. In case of infectious inflammation, the cerebrospinal fluid will be cloudy, there will be an increased content of cellular elements due to neutrophils, and bacteria will also be detected. Additional bacteriological and virological tests will help identify the pathogen.
Who to contact?
Treatment Wallenberg-Zaharchenko syndrome.
It is necessary to start treatment of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome as early as possible. The main goal of such treatment is to normalize the function of vital organs and brain areas, as well as to eliminate tissue edema and stabilize blood circulation.
General measures include the use of decongestants and neuroprotectors, as well as agents that correct blood pressure. When a thrombus forms, thrombolytic and vascular therapy are prescribed.
In general, initial therapy for Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome consists of the following stages:
- oxygen inhalations, artificial respiration;
- stabilization of blood pressure (if the readings increase, Magnesium sulfate, Enap, Metoprolol are administered);
- elimination of brain tissue edema (L-lysine, Furosemide, Mannitol);
- correction of nerve cell nutrition (Piracetam, Cavinton, Neurobion, Ceraxon, Neuromax, etc.);
- administration of thrombolytics or anticoagulants (Actilise, Heparin, Clexane);
- symptomatic therapy with the use of analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics.
The rehabilitation period is monitored by a joint team of specialists such as a rehabilitation specialist, a chiropractor, a physical therapy doctor, and a physiotherapist.
Medicines for Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome
Method of administration and dosage |
Side effects |
|
Metoprolol |
In the acute period, the drug is administered intravenously, in individual doses (analog Betaloc). Later, if necessary, it is taken orally at 100-150 mg per day in 1-2 doses. |
Bradycardia, palpitations, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath. |
Furosemide |
It is administered by injection, in an individually selected dose, taking into account the recommended average daily dosage of 1500 mg. |
Electrolyte imbalance, arterial hypotension, nausea, acute pancreatitis, itching, urticaria. |
Neurobion |
It is administered intramuscularly, in the acute period - one ampoule per day, then - one ampoule 1-3 times per week. |
Nervous excitement, dizziness, nausea, abdominal pain. |
Clexane |
It is administered subcutaneously, in an individually selected dosage, under the control of blood clotting properties. |
Hemorrhagic episodes, headache, allergic reactions. |
Heparin |
Administered intravenously or subcutaneously, in individual dosages. Indirect anticoagulants are prescribed 1-3 days before drug withdrawal. |
Thrombocytopenia, headache, increased liver transaminases, osteoporosis, skin rash. |
Vitamins and nutritional features
The diet of patients diagnosed with Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome should be maximally fortified with vitamins. It should consist of fruits, vegetables, cereals, berries, dairy products and vegetable oils. The daily menu includes foods containing dietary fiber - to normalize bowel function and prevent increased cholesterol levels.
It is important to eat foods with a high content of omega-3 fatty acids. They are present in fish (mackerel, tuna, salmon), fish oil, and help prevent thrombosis and stabilize blood circulation.
It is also recommended to consume more products that contain vitamin E: wheat sprouts, vegetable oils (linseed, olive), flaxseed, sunflower seeds, avocado. Vitamin E has antioxidant properties. It strengthens blood vessels, improves immunity, and prevents the development of coronary heart disease.
Exclude margarine, fatty meat products, smoked foods, and confectionery from the diet.
The decision on the use of additional vitamins of complex pharmaceutical preparations is made by the attending physician. Additional intake of nicotinic acid, folic acid, vitamins B 6 and B 12 may be recommended.
Physiotherapy treatment
To obtain the most optimal therapeutic result for patients who have suffered from Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, specific types of physical exercise are used, which involve impact on the affected area. With the help of such impact, it is possible to eliminate swelling, restore damaged vessels and brain tissue.
Modern methods allow to influence the area that suffered the most from the syndrome. Stimulation of blood circulation and tissue nutrition are especially necessary for the fastest rehabilitation of the patient.
Physiotherapy in this case pursues the following goals:
- restoration of speech activity;
- regulation of physical activity (restoration of coordination and some lost functions).
- Among the most effective methods of physical influence are:
- Electrophoresis, against the background of parallel treatment with medications. The duration of one session can be 10-30 minutes.
- Electromyostimulation helps restore blood circulation and blood supply to the affected areas. The procedures are carried out over a long course, until the patient's condition is steadily improved.
- Darsonvalization is used to activate basic processes in damaged limbs.
- Magnetic therapy increases the body's resistance to disease, normalizes vascular tone, accelerates vascular blood flow, and expands the capillary system.
In addition, vibration massage, cold and heat treatments, paraffin application to the affected areas, and ozokerite compresses are often prescribed to restore the body after Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome. Excellent reviews have been received from patients who have taken therapeutic baths with pine and salt extracts.
Folk remedies
During the acute period of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, the patient should be treated only in a hospital setting. At the rehabilitation stage, when the functional capacity of the body is restored, home treatment is allowed, using traditional and folk medicine. Thus, folk healers suggest using the following recipes to speed up recovery:
- Grind 1 teaspoon of crushed peony rhizome and infuse in 200 ml of boiling water for an hour. Take 1 tablespoon of the remedy every three hours.
- Take warm baths with the addition of a decoction of the rhizome of cinnamon rose hips. Such procedures are carried out once every two days, the course is supposed to be at least 25 procedures.
- Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 1 tbsp of spruce needles, leave for an hour, filter. Add the juice of half a lemon and take on an empty stomach a little at a time throughout the day. The course of treatment is at least 60 days in a row.
- Take 2 g of mumiyo before bedtime for 28 days. Then take a 10-day break, after which the course can be resumed.
- Mix 5 parts of pine needles with 2 parts of onion peel and 2 parts of rose hips. Pour 2 tbsp of the mixture into 1 liter of water, boil for 10 minutes, then pour into a thermos and keep in it for 10-12 hours. The resulting remedy is prepared daily and drunk throughout the day instead of water or tea.
- Mix 100 g of honey and the same amount of onion juice. Take 1 tbsp of the remedy after each meal. Store in the refrigerator.
Throughout the recovery period, patients are advised to include dates and raw quail eggs in their diet.
Herbal treatment
- Mix 100 g of chamomile flowers, St. John's wort, immortelle and birch buds. Pour 10 g of the mixture into a saucepan, add 500 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, filter. Take 200 ml of the infusion at night, with one teaspoon of honey, and also in the morning 30 minutes before the first meal.
- Make a mixture of lemon balm, heather, hawthorn, oregano, rose hips and milk thistle. Brew 500 ml of boiling water and 40 g of the mixture in a thermos. Drink the infusion throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 months.
- Add 1 tbsp of sage to 200 ml of boiling water and take it internally instead of tea. Also take baths with sage decoction (300 g of plant per 10 l of water).
- Take equal parts of valerian, peony and bluehead roots. Pour 20 g of the mixture with one liter of water, boil for 30 minutes on low heat, filter. Take 100 ml before bed, daily.
- Sorrel rhizomes are cut, poured with vodka (1 part root to 10 parts vodka), infused for 3 weeks. Filter and take 40 drops with water three times a day.
Homeopathy
During the recovery period after Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, a homeopathic physician may recommend treatment with one or more homeopathic remedies. The main goal of such treatment is to restore lost functions and improve the patient's quality of life. For example, the patient may be offered the following homeopathic remedies:
- Lycopodium clavatum – restores motor capabilities of the limbs;
- Calcarea fluorica – stabilizes metabolic processes, improves the condition of blood vessels;
- Arnica – accelerates tissue regeneration, especially suitable for left-sided lesions;
- Lachesis is a “left-sided” drug that improves microcirculation in the affected areas of the brain;
- Botrops is a “right-sided” drug that improves tissue blood supply and accelerates thrombus resorption;
- Bufo rana – helps to restore impaired speech function, has calming properties;
- Lathyrus sativus – restores motor capabilities of the lower limbs;
- Helleborus niger – clears the patient’s consciousness, relieves lethargy;
- Nux vomica – improves the functioning of the nervous system, restores the functionality of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
Among the complex homeopathic remedies for Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome, the following are often used:
- Ubiquinone compositum (Heel) – helps restore trophism and nerve conductivity. The drug is administered intramuscularly, 2.2 ml 1-3 times a week, for 2-5 weeks;
- Cerebrum compositum – prevents cerebrovascular accidents, accelerates brain tissue regeneration. The drug is administered intramuscularly, 2.2 ml up to three times a week, for 3-6 weeks;
- Aesculus compositum – normalizes vascular blood circulation, stimulates the restoration of nerve structures. The drug is taken 10 drops three times a day, approximately 15 minutes before meals, for 4-6 weeks.
The medications are selected by a specialist based not only on the existing symptoms, but also on the general well-being of the patient and his constitutional characteristics.
Surgical treatment
- Carotenoid endarterectomy.
This operation involves removing the inner lining of the affected arterial vessel along with the thrombus formed inside it. This intervention helps to minimize the risk of repeated brain damage: most often, it is indicated if the narrowing of the artery lumen exceeds 70%, or if chronic cerebral circulatory deficiency is diagnosed. Surgical access to the site of intervention is in the neck. One of the risks of this operation is the detachment of the thrombus from the arterial wall with the subsequent development of ischemic stroke. To avoid such a complication, the surgeon inserts a kind of "filter" into the lumen of the artery.
- Angioplasty and stenting surgery.
Both of the above methods are usually combined with each other. The essence of angioplasty is as follows: a special catheter is inserted into the lumen of the affected section of the arterial vessel (usually through the supply vessel, with mandatory X-ray observation). Then a balloon is inflated at the end of the catheter, which helps to expand the lumen of the vessel. Angioplasty of the affected arteries is performed. Then stenting begins: a special structure in the form of a frame is installed, which fixes the lumen of the vessel and prevents the formation of blood clots in it.
Prevention
Prevention of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome should be carried out comprehensively and in several directions. First of all, it is desirable to determine the probability of hereditary predisposition, conduct a gene-molecular and biochemical blood test. It is especially important to conduct a thorough diagnosis for those people who have factors that suggest the risk of increased thrombus formation. For example, a high degree of risk is definitely present in patients who have previously had episodes of causeless or repeated thrombosis that appeared after minor provoking factors: minor traumatic injuries, pregnancy, etc.
The main measures that will help avoid the development of Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome are the following:
- ensuring moderate physical activity, excluding excessive activity and physical inactivity (walking in green areas - in a park, square, forest - is considered optimal);
- drinking enough fluids daily, wearing comfortable clothing;
- prevention of infectious pathologies, hardening procedures, strengthening the immune system, a complete vitamin-rich diet;
- cessation of smoking and alcohol abuse;
- avoiding prolonged exposure to scorching sunlight, hot or cold conditions;
- periodic preventive vitamin therapy, taking anticoagulants (if indicated).
Forecast
The outcome of the disease largely depends on how timely medical care is provided to the patient. Delay in hospitalization leads to the patient becoming disabled - less than 20% of such people will be able to live longer than five years.
Emergency care for a patient with Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome should be provided in the first 2-3 hours, starting from the moment the first sign of pathology appears. Only in such a situation can a person's life be saved and further relative restoration of lost functions be achieved. The probability of complete recovery is no more than 2-3%.
The following signs indicate a possible unfavorable prognosis:
- development of locked-in syndrome (de-efferentation syndrome), in which the patient loses an adequate response to any external stimuli due to tetraplegia and paralysis of the bulbar, facial and masticatory muscles;
- disorders of respiratory, cardiovascular and thermoregulatory functions;
- presence of neurological disorders for 12 months or more.
As a rule, Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome results in the patient becoming disabled.

