
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Types and complications of polyps in the sinuses
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 07.07.2025
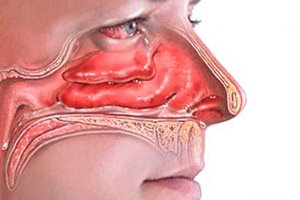
Today, one of the main otolaryngological diseases is polyposis, in which polyps are formed in the nose. Sometimes people go to the doctor with complaints of nasal congestion, nasal voice and night snoring. The doctor conducts an examination, as a result of which polyps are diagnosed. But quite often a person does not even suspect that he has polyps, and they are discovered completely by accident during an examination.
In both cases, treatment is required, and the sooner it is started, the greater the chances of recovery. If you do not take any measures, refuse treatment, you can only worsen the situation, getting numerous complications. The most dangerous thing about polyps is that they can become inflamed, block the nasal passages. This can cause a lack of oxygen, night apnea (stopping breathing). Local and then general immunity is significantly impaired, the body's defenses are reduced. This leads to even greater proliferation of polypous tissue, further hyperplasia.
There may be many reasons and all of them must be taken into account when developing a treatment strategy and tactics. This means that qualified medical care is needed; self-medication should not be relied upon. The pathogenesis may be based on an inflammatory process, allergic reaction, infection, decreased protective abilities of the immune system, or a violation of the microflora. Other concomitant pathologies also often contribute to the development of polyps. For example, frequent colds, sinusitis, rhinitis, in which the mucous membrane is subject to inflammation and further hypertrophy, can provoke increased growth of polyps.
Many of these causes are interconnected and support each other's existence. Accordingly, the treatment will be based on the cause of the pathology: antiallergic, antiviral, immunocorrective, anti-inflammatory therapy. Conservative therapy is tried first. If it is ineffective, surgical intervention will be required.
Large polyp in the nose
A large nasal polyp definitely requires careful attention. It is important to conduct the necessary diagnostics, identify the reasons for its development. Often, such a polyp develops as a result of an oncological process, in which cells undergo malignant transformation. As a result, the polyp becomes a cancerous tumor. Also, large polyps can develop with a strong inflammatory process, hormonal imbalance.
White polyp in the nose
White polyp in most cases is formed by fibrous tissue. It can be of different sizes: from small to large. The main complaint of patients with such pathology is frequent nosebleeds, nasal congestion, constant nasal breathing problems, in which drops and other symptomatic medications are ineffective.
The doctor conducts an examination and often a tumor is found in the indicated place. The appearance can be used to guess the type and nature of the tumor, as well as the stage of its development. Bleeding sometimes occurs during palpation.
Often it is necessary to resort to lubrication with an adrenaline solution for a more detailed examination. It does not lead to a decrease in the size of the polyp, but helps to eliminate the edema. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in more detail.
Paranasal sinus polyp
Polyps are such structural organizations in which the main pathological process is often localized not in the nasal passage itself, but in the paranasal sinuses. In this case, various symptoms develop. Sometimes a sinus polyp can grow so much that it comes out of the sinuses and fills part of the new passage, or it completely.
Choanal polyp in the nose
Choanal polyps differ somewhat from ordinary polyps in size, morphological features, and mechanisms of their development. Therefore, they are often considered as separate forms of polyps, or even an independent disease. This pathology is quite rare and accounts for approximately 5% of all polypous formations in the nose. They can be located in the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. Treatment and diagnostics are determined by the location of the polyp, its size, and structure.
They can be divided into 3 groups: antrochoanal, sphenochoanal and ethmoid-choanal. The first two types develop mainly from the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth, frontal sinus, nasal septum and nasal conchae. This type of pathology is extremely rare.
Antrochoanal polyp in the nose
In total, only three cases of polyps developing from the nasal turbinates are found in medical literature. Two of them developed from the inferior nasal turbinate, and in one case – from the middle nasal turbinate.
From the described case it follows that a person with an antrochoanal polyp has complaints of lack of nasal breathing, abundant mucus discharge from the nasal cavity, an unpleasant odor from the nasopharynx and pharynx. Strong snoring is recorded during sleep. The patient was a girl aged 12 years.
The treatment was surgical removal of the polyp using a Lange hook. The resulting material was then subjected to bacteriological and histological examination. As a result, the prevalence of fibrous tissue and severe edema against the background of natural opportunistic microflora was established.
Approximately one month after the operation, the disease relapsed. A repeat operation was performed using a similar method. After 2 months, breathing difficulties were observed. After 3 months, nasal breathing disappeared completely. During the examination, obstruction of the nasopharynx was established against the background of a dirty yellow coating, quite dense in size. Due to the obstruction, it was not possible to fully examine the nasopharynx.
A smear was taken for bacteriological examination. The results showed the presence of a fungal infection, the diagnosis is aspergillosis, which is explained by a sharp decrease in local and general immunity after two surgeries and a disrupted local microbiocenosis. A deviated nasal septum was also established.
During rhinoscopy, the presence of a gray polypous formation was established, which filled the middle and posterior sections of the nasal passage. The polyp is tightly adjacent to the nasal conchae and completely covers the choana. All posterior sections of the nose are filled with a small polyp appendage, which penetrated through the right choana.
Additionally, an otoscopy was performed, which showed that the eardrums were strongly retracted and limited. Audiometry was prescribed, according to the results of which acute catarrhal bilateral tubootitis was diagnosed. Conductive hearing loss was noted.
A CT scan revealed a shadow of a soft tissue formation that was identified as a polyp. It fills the common nasal passage, nasopharynx, and pharynx. Signs of a secondary inflammatory process were recorded, its spread to the maxillary sinus, as well as the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth and sphenoid bone. General urine and blood tests did not show any significant changes.
Despite the rather extensive results of tomography, a complete rhinological examination, it was not possible to fully identify the localization of the polyp stalk. This was due to the presence of obstruction and a strong hyperplastic process.
The nasal polyp was dissected and partially removed (under local anesthesia), which made it possible to fully examine the nasopharynx and pharynx. It was found that with a thin knife, the nasopharyngeal component of the polyp was attached to the lower edge of the turbinate. The polyp was then dissected at the level of the large ethmoid vesicle, which made it possible to see the lower edge of the polyp. Attempts to completely remove the polyp after its stalk was removed were unsuccessful, since the polyp had strongly fused with the anatomical structures of the nose.
Thus, the analysis of the existing practice allows us to conclude that today there is no treatment for antrochoanal polyps. Even surgical methods are powerless.
 [ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
[ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
Polyp in the maxillary sinus
Polyps are often localized in the maxillary or maxillary sinus. This is one of the largest sinuses of the nose. It is located in the cavity of the upper jaw and contributes to the emergence of the main symptoms that force a person to see a doctor. There is an increase and inflammation of the mucous membrane, swelling, hyperemia and nasal congestion appear.
But the main problem with maxillary sinus polyps is their ability to completely block breathing, causing a person to suffocate. The lack of air is especially pronounced at night. Snoring, voice changes, inflammation of the mucous membranes of not only the nose, but also the entire nasopharynx and pharynx occur. This can lead to the accumulation of infection. The nasopharynx is connected to the middle and inner ear and eye by various canals and tubes. The spread of infection through the canals can lead to inflammation of the corresponding parts of the body.
The cause of polyps in the sinus can be allergy hyperplasia of the mucous membrane. The main method of treatment is surgical removal. Conservative methods are not able to provide the desired effect. There are certain difficulties here. It is not so easy to remove the polyp due to its inconvenient location. It is located in the sinus, so it is not easy to get to it. Drug treatment is even more unable to eliminate the pathology. Removal of polyps of this type requires a specialist with the appropriate experience and qualifications. In addition, special high-tech equipment is needed.
Modern methods of treating polyps include laser therapy. The polyp is quickly evaporated from the cavity, after which the mucous membrane is smoothed out and regenerated. The method is minimally invasive and causes virtually no complications. The operation is painless, and recovery also takes place in a short period.
The endoscopic method is also suitable, with the help of which significant growths are removed. At the same time, the sinuses and nasal passages themselves are cleaned, which allows for timely detection of the polyp when it occurs and removal. The essence is that an endoscope of a sufficiently thin structure penetrates the nasal cavity and removes the polyp.
Due to its thin and mobile structure, the endoscope can penetrate any hard-to-reach area of the body, including the nasal sinuses. The only drawback of the method is that after such manipulation, recovery under the supervision of specialists is required, so hospitalization will be required. Special therapy aimed at restoring the mucous membrane and preventing relapses of the disease is also necessary.
Polyp in the sphenoid sinus
Polyps often form in the sphenoid sinus. Young people are most often susceptible to this pathology. Polyposis can be completely asymptomatic and is most often diagnosed by chance during a CT or MRI scan. It can also be detected during an X-ray examination. Hyperplasia of the nasal mucosa occurs, resulting in the formation of a small cavity. It is filled with fluid. Most often, this is various exudates. This can be pus, mucus, bloody discharge, water, and even air.
The danger is the possibility of infection. In addition, the proximity to the brain determines the likelihood of infection penetrating the brain, inflammation of the meninges. The pain may radiate to the back of the head. Without treatment, vision may decrease, or pain in the eyes may develop. Often the pain radiates to the back of the head, a feeling of distension, pressure in one or more sinuses appears. Later, dizziness, photophobia, darkening in the eyes join. It may be accompanied by dyspeptic phenomena, such as nausea, vomiting. Often the pain is confused with pain of a neurological nature, strong irradiation is observed.
Pain may occur upon palpation. Polyps are similar in consistency to soft plasticine. Only surgical methods are suitable for treatment, since it is impossible to penetrate the sinus cavity by any other methods. They often occur against the background of other concomitant diseases.
Fibrous nasal polyp
It is a polyp, the basis of which is fibrous tissue. It has the ability to grow, sometimes it is in close relationship with the vessels. It is for this reason that the polyp can bleed. It is necessary to conduct a histological examination in order to make sure that the polyp is benign and the risk of its malignant degeneration is minimized.
 [ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ]
[ 6 ], [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ]
Allergic nasal polyp
It develops mainly in the nose or nasal passages. The main cause is an allergic reaction that occurs against the background of increased sensitization and allergization of the body. Any allergen to which the body has developed increased sensitivity can act as an allergen.
It promotes the release of a large amount of histamine and other components that trigger the mechanism of an allergic reaction. As a result, severe swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane develop. With a long-term allergy, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, becomes hypertrophied, as a result of which an existing polyp can develop or increase in size.
Malignant nasal polyps
Nasal polyps can be both malignant and benign. An experienced doctor can determine this even during a routine rhinoscopy. The appearance of these two tumors is very different. Thus, a benign tumor has a dense structure, clearly defined edges. A cancerous tumor can look like a disorganized mass, or a tumor with uneven edges. Its structure is loose.
Despite the rather obvious external signs, an examination alone will not be enough. To ensure the reliability of the data, it is necessary to take a piece of tumor tissue for examination.
Purulent polyps in the nose
Polyps of purulent consistency can occur in the presence of a bacterial infection. Less often, it can be a fungal infection. Such a structure requires urgent treatment, since pus is a rather dangerous discharge from the nasal cavity, which can get into the brain, ear, and other parts of the body along the ascending pathways. Accordingly, an inflammatory and infectious process develops in these areas.
Angiomatous polyp of the nasal cavity
It is mainly a polyp located in the nasal cavity. It can be found in the sinuses very rarely. Histological examination can reveal that it consists of ground tissue (usually fibrous). It is completely permeated with blood vessels. Such polyps often bleed. They are best treated surgically.
Recurrence of nasal polyp
A polyp can recur after its removal, i.e. appear again. This is due to the high regenerative activity of the cells that form the mucous membrane of the nose. In addition, a polyp can develop again if the cells are not completely removed. If at least a few polyp cells remain, it will recover again.
A polyp can only be completely removed using modern high-tech equipment, such as laser technology. But not all clinics have this option. Often, special treatment is prescribed to prevent relapses, preventing their recurrence.
Polyp in the nose is bleeding
A bleeding polyp is an angiofibromatous tumor, in which fibrous tissue grows and an independent circulatory system is formed in it. It is located on one side of the nasal septum. The main location is the venous-arterial plexus.
It has been established that in most cases polyps bleed in women. The exact cause of this pathological phenomenon has not yet been determined. Many experts are inclined to believe that hormonal imbalances may be the cause. They also often occur as a result of various injuries, damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane. Quite often, increased hyperplasia with damage to blood vessels, the development of an oncological process are considered as causes.
Microscopic examination can reveal the fibrous part and vessels. The degree of bleeding and consistency, size, density, and other properties of the tumor are determined by the composition, or more precisely, the ratio of fibrous tissue and vessels. Quite often, the tumor contains various inflammatory components, which causes bleeding.
This type of tumor requires immediate treatment, as it is dangerous due to its complications, in particular, anemia. This is explained by frequent and severe bleeding, which leads to changes in the composition and function of the blood. An equally dangerous complication is tumor malignancy, which poses a risk of malignant degeneration of the tumor. In order to confirm or refute the oncological process, they resort to conducting a histological study. Differential diagnostics is important, during which the polyp is differentiated from lupus, tuberculosis, scleroma and cancer.
Diagnosis may require x-ray examination, nasal endoscopy, examination of the paranasal sinuses. Various tests may be required, such as nasal mucus analysis, blood tests, virological and immunological studies. Functional tests, such as respiratory function testing, may be required.
It is treated in only one way - radically. The tumor is extirpated together with the underlying perichondrium and cartilage. If the tumor is localized on the nasal concha, it is removed together with part of the underlying concha.
The method of removing a bleeding polyp with a loop followed by diathermocoagulation is considered ineffective, since numerous relapses occur.
Nosebleeds with polyps
With polyps, nosebleeds can occur quite often. Angiofibrous polyps, which contain fibrous and vascular tissue, bleed especially heavily. The degree of bleeding depends on how many vessels the polyp contains.
A polyp can be detected during rhinoscopy. It looks like a round tumor on a stalk. It can have different configurations, and its size can vary significantly. Some people have a polyp the size of a grain of millet, while others have a pathology that reaches the size of a large cherry. The color also varies greatly: from dark red, cherry to blue. Blood is released when blowing your nose, coughing, lightly touching, making sudden movements, sneezing. Sometimes they begin to bleed spontaneously, for no apparent reason.
Runny nose and nasal polyps
With polyps in the nose, a long-term, persistent runny nose often develops, which does not respond to treatment with conventional methods. This is explained by the fact that the cause is a strong inflammatory process that covers the mucous membrane. An infection often joins in. Sometimes an allergic reaction leads to the formation of a runny nose.
Treatment is mainly etiological, that is, aimed at eliminating the main cause - the polyp. Radical methods are often used. Inflamed and hypertrophied tissue is removed surgically. After the mucous membrane is restored, the condition of the nose is normalized, you can resort to treating the runny nose with conservative methods. Often, treatment is not even required: the runny nose goes away on its own after eliminating the cause of its occurrence.
Nasal polyp and fever
Temperature is always a sign of an inflammatory process. Probably, inflammation of the polyp itself or surrounding tissues has occurred. Temperature can also be caused by the addition of an infection, activation of a persistent or sluggish viral infection, dysbacteriosis. Treatment is etiological, that is, it should be aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, the cause of the temperature.
Inflammation of nasal polyps
Polyps tend to become inflamed when there is an infectious or inflammatory process in the body. The inflammatory process can affect only the polyp, or the surrounding tissues and the sinus itself in which it is located.
If the inflammation affects the sphenoid sinus and the polyp located in it, sphenoiditis develops. If the maxillary sinuses are affected, sinusitis develops. If it occurs with the involvement of the frontal sinuses, frontal sinusitis develops; if the inflammation is localized in the ethmoid labyrinth, ethmoiditis develops.
One or more sinuses may be subject to the inflammatory process. Various forms of the pathological process are also possible. In the acute form, the symptoms are clearly expressed. In the recurrent form, there is a recurrence of signs of acute inflammation after certain periods of time, most often some time after the end of the course of treatment or surgery. There may be a chronic form, in which an exacerbation is observed after the acute form has subsided for some time.
Most often, chronic forms of inflammation are characteristic of polyps localized in the maxillary sinuses. Exacerbation usually lasts at least 2-3 months, even with good treatment.
Signs of inflammation of polyps are nasal discharge, which is purulent and mucous. Sometimes there are mixed discharges. Since the ducts and nasal passages are blocked, it becomes difficult to breathe, there is a sore throat, a reflex cough, sneezing, and a runny nose may occur. Usually these are accompanying symptoms that only indirectly indicate inflammation of the polyp. They do not require special treatment. Usually it is necessary to treat the polyps, and then, after the inflammatory process subsides, both the cough and the runny nose go away.
With a strong inflammatory process, especially if it continues for a long period of time, a persistent headache may develop, the source of which is localized in the area of the nose, forehead, eyes. Olfactory function is impaired. Without treatment, the polyp begins to grow into the nasal passages. Often, the cause of inflammation is a virus. Viral inflammations are especially common in adults. They can also be a consequence of blood and dental diseases (the so-called odontogenic factor). It is especially pronounced in the case of inflammation of polyps in the maxillary sinuses.
In children, inflammation often develops against the background of reduced immunity, which activates a bacterial infection. Often, inflammations have staphylococcal etiology.
Inflammation develops as a result of disruption of the main processes in the nasal sinuses, which occur when polyps are present. Under normal conditions, microorganisms, together with dust particles, air through the nasal passages, enter the sinus caves. Usually they are neutralized there by the ciliated epithelium. Visible mucus is formed on the outside, which is removed to the outside. Warmed and purified air passes further along the nasal passages, into the lungs. In the presence of polyps, the passage of air and the removal of accumulated mucus to the outside presents certain difficulties. It can accumulate in the nasal sinuses and passages, clogging them and preventing normal functioning.
Treatment of polyp inflammation is carried out conservatively. Vasoconstrictors, local antibiotics are used, especially in the development of a purulent inflammatory process. For washing, less often - rinsing the oral cavity, pharynx and nasopharynx. In the case of severe development of the inflammatory process, washing through a puncture of the wall is used. When crusts appear, or the mucous membrane and skin become excessively dry, oil preparations are used. To relieve inflammation, eliminate edema, saline solutions are used for washing, moisturizing the mucous membrane.
A polyp in my nose came off
Cases when a polyp breaks off are known to modern medicine. The cause is most often trauma, mechanical damage. Heavy bleeding occurs, since the polyp is a relatively independent, localized neoplasm. It has a stalk through which its own blood vessel passes. Most often, the injury occurs in this place: the polyp breaks off from the stalk.
In this case, mandatory diagnostics are required, since a polyp can never come off perfectly straight. It always leaves residual effects on the mucous membrane. These then develop into recurrent polyps, which grow from the remains of tissue as a result of their regeneration. The danger lies not so much in the relapse itself (repeated growth), but in the possibility of its malignant degeneration, that is, transformation into a cancerous tumor.

