
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Transvaginal ultrasound: preparation, how to do it
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 03.07.2025
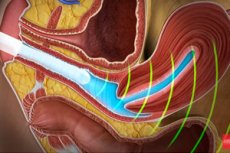
Ultrasound examination is considered one of the most informative and safe methods of studying the condition of human internal organs. This relatively inexpensive diagnostic method has gained particular popularity in connection with pathologies of the pelvic organs, especially since it can be carried out in various ways in order to get closer to the organ being examined. For example, when it comes to women, transvaginal ultrasound has the greatest information content for studying the internal genital organs of the weaker sex. After all, when examining through the vagina, there are the fewest barriers between the sensor and the female organs.
Types of ultrasound: their relevance and safety
Ultrasound diagnostics has recently become increasingly popular in the work of general practitioners and narrow-profile specialists. And this is not surprising, because research using ultrasound, which is generally safe for the human body, helps not only to assess the condition of internal organs if the diagnosis causes difficulties for doctors, but also to determine the main directions of therapeutic intervention and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Ultrasound examination is considered a safer procedure than the popular X-ray examination. Therefore, if there is no need for such deep penetration of rays, as in the examination of the skeletal system, doctors prefer to prescribe ultrasound.
There are three common ways to perform ultrasound diagnostics:
- through the abdominal cavity (transabdominal or abdominal ultrasound) is the most popular and familiar diagnostic method for us, prescribed equally to both women and men in connection with diseases of various organs, including the brain),
- through the vagina (transvaginal or vaginal ultrasound) - a study prescribed only to women to examine organs that are located deep in the body, away from the abdominal wall,
- through the rectum (transrectal ultrasound) - the rarest type of examination that can be performed on patients of both sexes, but it is associated with some discomfort and requires careful preparation.
The first type of ultrasound, which has gained popularity among pregnant women and patients with kidney or liver pathologies, seems to many to be a safer method in terms of the fact that it does not require the introduction of the device into the body. The examination procedure does not cause any discomfort at all, especially when it is not necessary to carry it out with a full bladder, and the harm from ultrasound rays is minimal.
During transvaginal and transrectal examinations, the device's sensor is inserted into the body through a corresponding opening, and this fact alone raises concerns. Is transvaginal (or transrectal) ultrasound dangerous? What is the likelihood of internal damage during the procedure? Will it hurt during the examination?
Such questions are quite understandable and logical, although there is no need to worry about the transvaginal ultrasound procedure. In fact, despite the apparent danger of damage to internal organs, with careful and professional examination, the risk of any damage is minimal. In addition, the examination is not carried out blindly, the doctor controls the movement of the sensor on the monitor and controls it so as not to harm the patient and at the same time get the maximum information about the organ of interest.
The reader may ask, why are such types of ultrasound needed at all, which require penetration into the body, if previously it was quite possible to get by with the usual safe transabdominal ultrasound? The need for transvaginal ultrasound did not arise by chance. The emergence of this type of diagnostics is associated with the growth of various female diseases and the hidden location of the internal genital organs of the weaker sex, access to which through the vagina provides more accurate information about their size and the condition of the mucous membrane.
Another reason for the prevalence of transvaginal and transrectal ultrasound is the increased percentage of people who are overweight. A thick layer of fat on the abdomen can somewhat distort the results of transabdominal ultrasound, especially when it comes to deep-lying organs.
In such situations, when examining women, the doctor rarely has any doubts about which examination is better: abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound? It is clear that the choice will be for the procedure that will give more complete and accurate results. For example, the same common erosion of small sizes can be detected only with the help of transvaginal ultrasound.
Transabdominal ultrasound is performed mainly if the hospital does not have equipment for specialized examinations through the vagina or rectum, as well as in cases where examination through the vagina is impossible.
Indications for the procedure
Transvaginal ultrasound is a procedure that can be prescribed to a woman for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes and for preventive purposes. The fact is that ultrasound diagnostics allows detecting pathological changes in internal organs at the earliest stages, when other research methods are not very effective.
For preventive purposes, this procedure is recommended for adult women at least once every 2 years. And after a woman turns 40 (and in adulthood, the risk of oncological and gynecological pathologies increases significantly), doctors recommend being examined with ultrasound every year.
As for treatment and diagnostic measures, transvaginal ultrasound is most often prescribed for pathologies of the genitourinary system, inflammatory and dysplastic gynecological diseases, suspected oncology in the pelvic organs, and diagnosis of pregnancy in the first 10-12 weeks. Transvaginal ultrasound can also be prescribed in emergency situations, for example, if it is impossible to determine the source of bleeding from the female genital organs.
Let's consider in which situations transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs provides the greatest benefit:
- if you experience pain in the lower abdomen for an unknown reason,
- if there are complaints of pain during sexual intercourse,
- in case of menstrual cycle disorders (a woman may complain of delayed periods, their absence for a long period of time, bloody discharge between periods, too long or, conversely, too short a duration of menstrual bleeding),
- if suspicious discharge from the female genital organs appears (bloody streaks, spotting, purulent discharge with a smell, etc.),
- if there is a suspicion of inflammation developing in the internal genital organs,
- if there is a suspicion of benign and malignant neoplasms in the uterus and ovaries, among which the most common are myoma, endometriosis and uterine dysplasia, ovarian cysts and cancer, etc.,
- if female infertility is suspected, if a woman cannot become a mother for six months or more, despite regular sexual activity (determination of the shape and features of the functioning of the ovaries, the patency of the fallopian tubes using contrast agents),
- if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected,
- in case of bleeding from the genital tract of unknown etiology (helps to determine the cause of blood loss),
- if varicose veins of the pelvis are suspected (the pathology affects the functioning of the female reproductive organs, since circulatory disorders in the uterus and ovaries provoke menstrual irregularities, regular pain in the lower abdomen and even problems with conceiving a child),
- if there is a suspicion of pathologies of the urinary system (for example, with urination disorders: pain, urinary retention or incontinence, the appearance of mucus in the urine), in this case a transvaginal ultrasound of the bladder is prescribed.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the intestine is performed less frequently due to bowel movement disorders. Transrectal ultrasound examination provides more information in this regard. But if it is complicated, for example, due to intestinal obstruction or in the presence of neoplasms (polyps, hemorrhoidal cones) that can be damaged by the ultrasound tube inserted into the rectum, transvaginal examination comes to the rescue. In this case, it is more effective than abdominal examination due to the fact that the large intestine is located near the thin walls of the vagina. Examination of the intestine through the abdominal wall cannot provide such accurate results as examination from the vagina.
Transvaginal ultrasound is also used to monitor the in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure. After the fertilized egg is implanted into the female body, all processes occur hidden from the human eye and can only be safely monitored using ultrasound.
Transvaginal ultrasound in gynecology
Transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed both to clarify the suspected diagnosis and for informational purposes to determine the boundaries, size and condition of specific organs. For example, it can be used to obtain information about the structure and health of a woman's main reproductive organ - the uterus. Vaginal ultrasound can be used to measure the length of the cervix, the size and shape of the uterus, the thickness of the mucous layer (endometrium), which constantly changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
The smallest thickness of the endometrium (about 1 mm) is observed on the 1st and 2nd day of the menstrual cycle. On the 3rd and 4th day, it increases to 3-4 mm. Research on these days is of little information. From the 5th to the 7th day, the thickness of the uterine mucosa can reach 6 mm, and before menstruation - 10-20 mm. In this case, the endometrium should have a uniform structure without any compactions or bulges, which may indicate inflammatory (endometritis) or tumor processes.
Endometritis (inflammation of the uterus) is visible on the screen as an enlargement of the organ cavity, a decrease in the thickness of the mucous membrane with pronounced heterogeneity of its composition, and gas accumulation inside the uterus. Comparative characteristics of the thickness of the endometrial wall are carried out depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, otherwise the results will be inaccurate.
Measuring the length of the cervix is relevant if there is a risk of miscarriage. Normally, the length of the cervix is about 3.5 - 4 cm.
The diameter of the cervical canal of the cervix is between 2 and 3 mm. The cervical canal contains a uniform mucous secretion. Changes in the size of the cervix and heterogeneity of the mucous secretion may also indicate inflammatory or malignant processes, or pathological proliferation of the uterine endometrium (endometriosis).
With uterine myoma, an enlargement of the organ, a change in its contours and the detection of a neoplasm (nodule) in the muscular layer are observed. The echogenicity of the myoma nodule varies: sound waves are reflected from the near contour, and the distant contour may not even be visible depending on what is hidden inside it (these can be cystic formations or seals formed from calcium compounds). With endometriosis, bubble formations are detected both in the fallopian tubes and in different parts of the uterus.
Polyposis of the uterus (as well as the intestine) is characterized by volumetric formations inside the organ caused by a viral infection, which, depending on the size and location, can somewhat affect its contours. But in most cases, they are determined as round, relatively small formations inside the uterus, they are clearly visible with contrast.
When examined using an ultrasound sensor, cancerous tumors have some similarity to polyps, but inflammatory edema is visible on the tissues near them. A biopsy can confirm or refute the diagnosis. In this case, a piece of tissue for testing for malignancy is taken directly during the diagnostic procedure, because at the end of the device there is a special channel with a needle for taking a biopsy.
According to the ultrasound results, a cancerous tumor of the cervix is defined as a highly echogenic neoplasm with uneven contours. Doctors also note a narrowing of the cervix and an increase in regional lymph nodes. In addition to the exact location of the tumor, it is also possible to determine the depth of penetration of the cancerous tumor into the tissues of the uterus and nearby organs.
Uterine cancer is suspected in the presence of the following symptoms: bloody discharge outside of menstruation, pain in the lower abdomen, blood during intercourse, profuse watery discharge, swelling of the lower extremities in the absence of heart and kidney pathologies, difficulty urinating.
The possibilities of conducting a vaginal ultrasound examination during pregnancy are somewhat limited. Transvaginal ultrasound is performed only in the early stages of pregnancy, until the procedure can cause contractions of the uterus and miscarriage. The sonologist (the doctor conducting the ultrasound diagnostics) sees increased uterine tone as a local increase in the thickness of the wall of the reproductive organ. But such a study allows for a high-precision diagnosis of pregnancy already in the first weeks after conception and to track the development of the child in the very important first trimester of pregnancy.
Determining the size of the uterus plays a role in diagnosing pregnancy at a period of 3 weeks or more. Normally, the uterus measures 4.5-6.7 cm (length) by 4.6-6.4 cm (width) and is about 3-4 cm in diameter, and if transvaginal ultrasound reveals deviations from generally accepted indicators, this is already a reason for reflection.
A small uterus creates problems with bearing a fetus, while an enlarged size may indicate the onset of pregnancy. A more thorough examination in the latter case helps to confirm or refute other possible, but less pleasant diagnoses, such as uterine fibroids or malignant neoplasms in it.
Starting from the 5th week of pregnancy, transvaginal ultrasound can determine the baby’s heartbeat, which is an important indicator of fetal development.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and appendages plays a major role in diagnosing infertility. It can be used to assess both the functioning of the ovaries and the ability of the egg to enter the uterus through the fallopian tubes.
The size of the ovaries is within the range of (3-4) x (2-3) x (1.5 -2.2) cm (length, width, thickness). In the middle of the menstrual cycle, the ovaries should contain several small follicles (egg embryos) up to 6 mm in size and one large one up to 2 cm. The presence of larger follicles may indicate a follicular cyst.
Larger than normal ovarian sizes indicate an inflammatory process in them or the presence of neoplasms in the organ.
As for the fallopian tubes, ideally they are practically invisible. This organ can only be seen by contrasting. If the fallopian tubes can be seen without the use of contrast agents, this indicates an inflammatory process. Which is always associated with an increase in the size of the organs. Transvaginal ultrasound can detect the presence of liquid secretion in the fallopian tubes (this can be inflammatory exudate, pus, blood).
Another reason for the "growth" of the fallopian tubes may be an ectopic pregnancy, which is associated with obstruction of the organ due to the presence of adhesions, inflammation or congenital defects (kinks, small diameter of some sections of the tube, etc.). Such a study is carried out using contrast agents.
An important factor in diagnosing infertility is the location of the uterus. Normally, it should be slightly tilted forward. If there is such a tilt, but in the opposite direction (congenital defect), the probability of a normal pregnancy decreases, but the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy appears.
Using transvaginal ultrasound, it is possible to detect fluid accumulation in the lower abdominal cavity, which is associated with inflammatory processes of internal organs (release of exudate into the pelvic cavity) or rupture of cystic formations filled with liquid secretion.
Within 2-3 days after ovulation (from 13 to 15 days) a small amount of fluid may be detected in the cavity behind the uterus, which is considered quite normal. In other periods, the appearance of fluid near the uterus indicates infectious processes in the organ.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries is prescribed for inflammatory pathologies of the organ in which future eggs mature, and for severe pain in the lower abdomen (if they are not associated with menstruation). The same study will be relevant if there is a suspicion of a cyst or ovarian cancer. In these cases, the doctor conducting the ultrasound procedure notes an increase in the size of the ovary, tissue edema, deformation of the organ contours (in the case of neoplasms), the presence of fluid inside the neoplasms (in the case of an ovarian cyst).
Ultrasound vaginal diagnostics allows to detect pathological changes in the uterus associated with malignant neoplasms in the organ associated with pregnancy. For example, both during and after the resolution of pregnancy, a tumor consisting of epithelial cells can form in the embryonic part of the placenta (chorion) in the uterus. Such a neoplasm is called chorionepithelioma. Less often, the tumor is found not in the body of the uterus, but on its cervix or on the ovaries. It is capable of destroying blood vessels, quickly metastasizing to various vital organs.
The echogram in this case shows an enlargement of the uterus (its cervix or ovary), because the tumor grows quickly, the tone of the organ muscles decreases, they become soft with a non-uniform consistency. The shape of the organ changes, tubercles appear on it, which are not typical for a healthy state.
Another dangerous pathology of early pregnancy is considered to be a hydatidiform mole. The pathology is characterized by pathological proliferation of chorionic villi with the formation of bubbles at their ends, tumor penetration into the deep layers of the myometrium, and destruction of uterine tissue. In this case, fetal death is observed at an early stage of development, both with complete and partial hydatidiform mole. But the uterus still continues to grow, although not the organ itself, but the malignant tumor that has affected it.
Transvaginal ultrasound reveals unevenness of the uterine tissue (a dense mass with inclusions of unusually soft areas), the presence of small cystic formations, large cysts on the ovaries. The size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age, and the fetus may no longer be detectable in it.
It is very important to detect the tumor as early as possible, when there is a suspicion of intrauterine fetal death. After all, a miscarriage in this case does not mean the disappearance of the tumor, and the woman is in serious danger.
Preparation
Transvaginal ultrasound is a very informative method for diagnosing various pathologies of the pelvic organs in women, which allows identifying deviations from the norm at the initial stage of the disease. The procedure itself is not difficult for either the doctor or the patient. It is carried out quickly and, in most cases, painlessly.
Another advantage of this type of diagnostic examination is the lack of special preparation for the procedure. For example, examination of the bladder and other pelvic organs using the abdominal method involves preliminary consumption of a large amount of liquid. Diagnostics is carried out with the bladder as full as possible (based on the principle of echolocation in navigation), which is not very convenient. During the procedure, a person experiences certain inconveniences due to an irresistible desire to empty the bladder when the sensor moves along it and when pressing on the abdomen.
With the transvaginal method of examining the pelvic organs, filling the bladder is not required, because the sensor is in direct contact with the organs being examined, and the ultrasound waves pass through the air and are reflected from the internal organs, creating the desired image on the screen. The patient may even be asked to go to the toilet before the procedure so that the bladder is empty.
Another condition for high-quality transvaginal ultrasound is the absence of gases in the intestines, which distort information about the size of the organs. If a woman suffers from increased gas formation, which often happens with gastrointestinal pathologies, the day before the procedure (a couple of days before it) it is not recommended to eat foods that can cause flatulence (raw vegetables and fruits, pastries, fermented milk products). Some medications, such as "Activated carbon", "Smecta", "Espumisan", etc., will also help cope with excess gases in the intestines.
As for filling the intestines, it is advisable to empty them in advance in a natural way without using enemas.
It is recommended to drink the day before the examination only for pregnant women, whose ultrasound is performed with a partially filled bladder. To do this, it is enough to drink a couple of glasses of water an hour before the procedure.
In emergency situations, no preparation for the procedure is carried out, even if this negatively affects the accuracy of the studies, which will subsequently have to be repeated when the patient’s condition stabilizes.
What do you need to take with you to the transvaginal ultrasound procedure? Nothing except shoe covers and a diaper or towel, which you will need to put under yourself on the couch.
When is the best time to perform a transvaginal examination? If you just need to examine a woman's internal genital organs, doctors recommend performing the procedure on the 5th, 6th or 7th day of the menstrual cycle (immediately after the end of menstruation on the 2nd or 3rd day), when the thickness of the endometrium has average values, and its secretion is minimal and does not affect the results of the examination. In principle, it is permissible to perform routine diagnostics up until the 10th day of the cycle.
Somewhere around the 12th to 14th day, ovulation occurs, after which the woman’s body actively prepares for conception, which, naturally, leads to various physiological changes in the gynecological sphere.
By the way, if endometriosis of the uterus is suspected, it is recommended to conduct the examinations during this period, i.e. in the second half of the menstrual cycle. Doctors also prefer to conduct the examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes on the 24-28th day of the cycle (in fact, before menstruation).
If a woman is admitted to hospital with bleeding, the examination is carried out urgently, regardless of the phase of the menstrual cycle.
The answer to the question of whether transvaginal ultrasound can be performed during menstruation is affirmative. Moreover, such a study may even be useful, since it helps to identify cystic formations in the ovaries. But, despite the fact that menstruation is not a contraindication to the transvaginal ultrasound procedure, doctors prefer to prescribe a different time for diagnosis, when there is no menstrual flow. After all, blood in the uterus and fallopian tubes can also be a pathological symptom.
When planning pregnancy and treating inflammatory pathologies of the pelvic organs, the examination may be prescribed several times during one menstrual cycle. This makes it possible to track the process of formation and growth of follicles (diagnostics may be prescribed at intervals of 3-4 days, for example, on the 5th, 9th, 12th, 15th day). In inflammatory diseases, such serial examination helps to evaluate the effectiveness of the course of treatment.
Technique transvaginal ultrasound
Diagnostic procedures for ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs using the transvaginal method are carried out in 2 stages. At the first stage, the patient is explained the essence of the examination and the method of its implementation, after which she is asked to remove all clothing below the waist, put on a diaper and lie down on her back on the couch (it is permissible to use a gynecological chair for the procedure). The legs should be spread and bent at the knees, moving the feet closer to the buttocks.
The transvaginal ultrasound machine, which is a sensor connected to a computer monitor, is inserted directly into the vagina to a shallow depth (up to the cervix). Anything further is examined using reflected ultrasound waves.
The transvaginal probe, also known as the transducer, is not a disposable device. It is used to examine many women, but cannot be effectively disinfected. To protect the woman and the device itself, a new condom is put on the probe before use.
A small amount of a special gel is applied to the condom, which facilitates the sliding of the device inside the vagina and ensures better passage of ultrasound waves.
What is a transducer? It is a plastic rod, 12 cm long and no more than 3 cm in diameter. The outer edge of the rod is equipped with a channel for a needle, which is used to perform a biopsy if cancer is suspected.
Inside the vagina, the sensor can move in different directions depending on which organ is the target of the examination. Since the transducer is inserted shallowly, patients do not feel pain, except in cases of severe inflammation or painful neoplasms. If a woman experiences discomfort during the procedure, it is necessary to notify the doctor who performs the ultrasound.
The duration of a vaginal ultrasound examination in different situations can vary from 5 to 20 minutes, so that in most cases patients do not even have time to get properly scared.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows for a more accurate assessment of the size of the uterine body and cervix, ovaries, ovarian follicles, the location and structure of organs, the exit sites of the fallopian tubes and their filling, the quantitative ratio of mature follicles and those in the embryonic stage, the presence of free fluid in the pelvis. In this case, abdominal examination gives more vague results, which does not allow catching the disease in its infancy. But it is for this purpose that preventive diagnostics of gynecological diseases is carried out.
Contraindications to the procedure
Transvaginal ultrasound can be called a procedure that requires almost no special preparation. And all because it is extremely simple and safe. Perhaps for this reason, this type of diagnostic examination of internal organs has almost no contraindications.
And yet, despite the fact that the transducer is inserted at a shallow depth, the hymen will be an additional barrier and may be damaged during the procedure. Transvaginal ultrasound is not performed on virgins. As an option, a transrectal examination or even abdominal diagnostics may be prescribed if clarification of the size and structure of the organs is not required.
In cases of obesity of grades 2 and 3, transvaginal ultrasound can also be replaced by diagnostics through the rectum, depending on which organ is being examined.
During pregnancy, transvaginal ultrasound is usually prescribed up to the 14th week. This is a safe examination for both the expectant mother and the fetus in her womb. After all, unlike X-rays, sound waves are not capable of causing gene mutations and leading to various developmental defects in the child.
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, such examination is not used in order not to cause premature labor in the patient due to manipulations near the uterus, which can stimulate its contraction, and not due to the negative impact of ultrasound. Transperitoneal or abdominal ultrasound of pregnant women can be carried out without consequences until labor.
One more thing. If a woman has an allergy to latex, it is necessary to tell the doctor about it before the procedure, so that later you do not have to treat various manifestations of allergic reactions.
 [ 6 ]
[ 6 ]
Complications after the procedure
Transvaginal ultrasound is considered a relatively safe procedure for good reason, since complications after it are possible only in rare cases if contraindications are not taken into account. For example, with an allergy to latex, a woman may subsequently feel itching in the vagina, which will require the use of antipruritic and antihistamines.
During the examination, the patient is asked to relax. Thus, the doctor gets free access to the internal organs through the vagina and can freely move the device inside the patient's body. However, not all women are able to relax, which causes micro-damage to the mucous membrane of the female genital organs outside and inside. Bleeding after transvaginal ultrasound is most often due to this reason.
This symptom is more common in pregnant women. If the expectant mother notices pink or brown discharge on her underwear after a transvaginal ultrasound procedure without any significant pain or discomfort, she has nothing to worry about. This is a common situation for pregnant women who tend to exaggerate the danger. You should see a doctor only if such discharge continues for a long time, becomes more abundant and is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, blood stains appear on the underwear, the back begins to hurt, etc.
As for pain, ideally there should be none after the procedure. Minor discomfort in the lower abdomen in pregnant women may be associated with increased uterine tone, which should return to normal in a short time. If this does not happen, there are nagging pains in the lower abdomen and lower back, indicating the onset of contractions, bloody discharge and other unfavorable symptoms, you must immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital to stop labor.
In principle, the described situation after transvaginal ultrasound is rather an exception, indicating that the examination was carried out at a period of more than 12-14 weeks or there are other deviations in the course of pregnancy not related to the procedure. Theoretically, such a situation may also indicate the incompetence of the doctor who carried out the diagnosis, which is unlikely in this situation.
Pain after transvaginal ultrasound most often occurs against the background of existing inflammatory pathologies. In this case, a woman may experience discomfort both during and after the procedure. Still, the movements of the sensor can disturb the diseased organ, which will subsequently result in pain or pulsation in the lower abdomen.
Due to high blood pressure and anxiety about the procedure, some women begin to experience pain not only in the stomach, but also in the head. In this case, it will be necessary to stabilize the pressure both before the procedure and after the manipulations, if necessary.
Spotting after transvaginal ultrasound in women who do not plan to become a mother happens very rarely and is again associated with microdamage to the mucous membrane or taking a biopsy in an area abundantly supplied with blood vessels. By the way, an earlier onset of menstruation is often observed after such an intervention. There is nothing terrible about this, but it is still worth consulting a doctor, at least in order to differentiate menstrual discharge from bleeding (especially if the discharge of blood is accompanied by pain, which was not observed before).
A woman (pregnant or not) should be wary if, in addition to pain and brown (red, pink) discharge, she also has a fever. This most likely indicates an infection. But we are not talking so much about sexually transmitted infections as about the familiar staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli and other representatives of opportunistic microflora. A condom should protect against more serious infections. But in any case, a visit to the doctor is mandatory.
By the way, it is very important to ensure that the doctor puts a new condom on the sensor before the examination, and does not simply wipe it with a disinfectant solution. This is considered a violation of the established standards for conducting transvaginal ultrasound. In addition, in addition to opportunistic microflora, more serious infections can remain on the sensor, such as HIV or hepatitis viruses, especially if there was no preliminary preparation for the examination in previous patients, and transvaginal ultrasound without a condom exposes women to the risk of infection with dangerous, difficult-to-treat pathologies. This is the opinion of specialists in the field of epidemiology, and not of ordinary patients sowing panic.
Ideally, a smear of microflora should be taken before a vaginal examination so that the doctor knows what he is dealing with. This can help in the future and in clarifying the diagnosis, which is made based on the results of transvaginal ultrasound, printed on a special form.
Care after the procedure
Many women after a gynecological examination or transvaginal ultrasound, fearing infection, rush to carry out serious hygienic procedures called douching. The effectiveness of such procedures in these situations has not been proven. Moreover, in some cases douching can even cause harm, especially since it is not carried out in sterile conditions.
The internal female genital organs are designed in such a way that they are able to cleanse themselves of infection and dirt. This is also facilitated by the beneficial microflora of the vagina, which is roughly washed out by douching, thus giving the opportunity to pathogenic microorganisms and pathogenic fungi that were in an inactive state to develop. In the end, it may turn out that the cause of infection of the internal female genital organs was not the transvaginal ultrasound procedure itself, but the preventive measures that the patient took without a doctor's prescription.
What hygienic and medical procedures to perform after ultrasound diagnostics and diagnosis should be prescribed by the attending physician. The same applies to taking medications.
Reviews
The opinions of patients who have undergone transvaginal ultrasound agree that this examination for gynecological diseases is more informative than the usual abdominal diagnostics. It is the vaginal examination that allows you to see the pathology from the inside and assess the degree of organ damage, which means that the diagnosis will be more accurate.
It is clear that much depends on the professionalism of the doctor and his skills in working with special equipment. Only an unqualified doctor can make a mistake in conditions of full visibility and no time limits. True, an incorrectly appointed time of the study can also play a certain role. It is not for nothing that certain phases of the menstrual cycle are designated when it is necessary to conduct a study specifically for each pathology.
Women consider the procedure's advantages to be its painlessness. Of course, some discomfort may still be present, but here the psychological factor plays an even greater role than objective sensations.
Those who have already encountered the procedure of abdominal ultrasound on a full bladder will be able to appreciate the absence of the need to endure a small need during a transvaginal examination. And slippery cold gel on the body can hardly attract anyone, and with a vaginal ultrasound there is no need to apply it.
As for the safety of ultrasound diagnostics using a vaginal sensor, opinions differ. Most of all, such a study worries pregnant women who are afraid of the threat of miscarriage. However, practice shows that in the early stages, transvaginal ultrasound does not pose a danger if it is carried out very carefully and professionally.
As for the threat of infection through a vaginal sensor, it is completely excluded when using disposable condoms. It is another matter if doctors do not comply with the requirements for the procedure and save on protective equipment, relying on disinfection with antiseptics. Here, women are right to be worried, the risk of catching a dangerous infection when refusing to use condoms always remains.
In principle, there are not so many reviews about the absence of a condom on the sensor and the appearance of suspicious symptoms (pulling pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal itching) and discharge after the procedure. It is important to be careful, because you can always refuse the examination due to the lack of necessary materials (in this case, a condom), go to another clinic where patient care will be at its best.
Regarding the cost of the procedure, it can be said that most patients consider it inexpensive and quite affordable. Moreover, the results that transvaginal ultrasound gives allow you to immediately begin effective treatment without doubting the diagnosis. And if you consider that someone can also be pleased with such diagnostics with the good news of a long-awaited pregnancy at the earliest stage, then its value doubles.

