
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Staphylococcus aureus in a swab from the pharynx, nose: causes, treatment
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
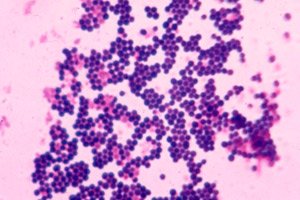
Staphylococci are one of the most common groups of microorganisms that include saprophytes and pathogens of humans and animals. Despite the relative ease of detecting staphylococci in biological material from patients and environmental objects, in practice there are numerous difficulties. This is due to the fact that staphylococci are representatives of normal microflora, therefore staphylococci in a smear are not always objective evidence of their etiological role in the development of the disease. It is also necessary to take into account the variety of their manifestations, the degree of pathogenicity, wide variability under the influence of antibacterial agents, and the extreme diversity of clinical forms.
That is why the scheme of diagnostics and treatment of this infection cannot be universal, but should be developed taking into account the specifics of a particular nosological form of the disease. In addition, an important measure is the combined determination of qualitative and quantitative indicators of the content of pathogenic staphylococci in the studied material.
Food toxic infections of staphylococcal etiology occupy one of the leading places among bacterial poisonings in terms of the number of cases.
Staphylococcus norm in smear
Normally, staphylococcus must be present in the smear, since it is a representative of the normal microflora. Its absence or low level has the same negative effect on health as high levels. The norm is considered to be up to 103 (10 in 3). Any deviation, both in the direction of increasing the concentration and in the direction of its decrease, is considered a violation. An increase above this level is a pathological condition in which staphylococcus is released into the environment, even with calm breathing.
Staphylococcus in smear 10 in 3 - 10 in 5
The unit of measurement for quantitative analysis is CFU/ml – the number of colony-forming units in 1 ml of the biological material being studied.
To perform calculations and determine the degree of contamination, first count the number of homogeneous colonies that grew in the Petri dish after sowing. They should be identical in color and pigmentation. Then recalculate the number of colonies into the degree of contamination.
Let's look at a specific example. For example, if 20 CFU grew in a dish, this means that 0.1 ml of the test material contained 20 colonies of microorganisms. The total number of microorganisms can be calculated as follows: 20 x 10 x 5 = 1000, or 103 (10 in 3). In this case, we proceed from the fact that 20 is the number of colonies that grew on the Petri dish, 10 is the number of colony-forming units in 1 ml, taking into account that only one tenth of the microorganisms were seeded, 5 is the volume of physiological solution in which the sample was diluted.
The concentration of 104 (10 in 4) is determined in a similar way, which many specialists consider as a borderline state between the relative norm and pronounced pathology, in which bacteremia and acute inflammatory process develop. The indicator 105 (10 in 5) is considered as an absolute pathology.
Causes staphylococcus aureus in the smear.
Staphylococcus aureus will always be detected in a smear within the normal range, since it is a representative of normal microflora. Therefore, from the point of view of bacteriology, it makes sense to discuss the reasons for the increase in the quantitative indicators of staphylococcus. Thus, the concentration of staphylococcus aureus increases primarily with reduced immunity. Normally, the immune system produces protective factors (histocompatibility complex, interferons, immunoglobulins, etc.), which stimulate the normal state of the mucous membranes, prevent uncontrolled reproduction of bacterial flora, and suppress active growth.
Another reason is dysbacteriosis. For various reasons, the number of normal microflora representatives decreases. As a result, "free space" appears, which is immediately occupied by other microorganisms, including staphylococcus. It is one of the first microorganisms that colonize free space and firmly attach to it. As a result, quantitative indicators increase sharply.
There are many causes of dysbacteriosis. Perhaps the most important is taking antibiotics, since there are practically no targeted antibiotics that affect only the pathogen. All of them are broad-spectrum drugs. They affect not only a specific pathogen, but also the accompanying flora. Chemotherapy and antitumor treatment have a similar effect.
Reduced immunity and disruption of normal microflora are facilitated by hypothermia, overwork, constant nervous and mental strain, stress, failure to comply with the daily routine. Inadequate and inadequate nutrition, lack of vitamins, microelements, bad habits, unfavorable living and working conditions have a negative effect.
Staphylococcus aureus in throat swab
A throat swab is taken during preventive examinations for workers in the catering and child care sectors, as well as for the diagnosis of infectious diseases (only if indicated). The main indication is the presence of inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and pharynx.
The development of staphylococcal infection, food poisoning begins with the oral cavity and pharynx. Often, the microorganism persists in the pharynx, nasopharynx, and the person does not even suspect this, since in the early stages the pathological process can be asymptomatic. However, its number increases, which can subsequently result in chronic pathology, severe inflammation, tonsillitis, enlarged lymph nodes. In addition, with an increased concentration of the microorganism, it is released into the environment. As a result, the person becomes a carrier of bacteria. At the same time, the person himself may not be sick, but he infects others.
If staphylococcus is detected in a throat swab, people are not allowed to work in food enterprises, culinary workshops, canteens, which helps to avoid food poisoning. Also, carriers of bacteria are not allowed to work with children, especially children of early, preschool, and younger age. Mandatory sanitation is carried out
Determining the exact concentration of staphylococcus in a smear makes it possible to accurately determine the pathogen and diagnose the pathological process, and select the optimal treatment.
The material for the study is collected using a sterile swab, by passing it over the surface of the tonsils. The material must be collected on an empty stomach, or no earlier than 2-3 hours after eating. It is necessary to collect the material before antibiotic therapy, otherwise the results will be distorted.
Then, in laboratory conditions, the material being studied is seeded on nutrient media. The material must be seeded within 2 hours after collection. The optimal medium for seeding staphylococcus is considered to be milk-salt agar, yolk agar.
 [ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ]
[ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ], [ 7 ]
Staphylococcus aureus in nasal swab
A nasal swab is taken when examining certain categories of workers (working with children, in the catering industry). The sample is taken with a sterile swab from the nasal mucosa. A separate swab is used for each nostril. The nasal cavity should not be treated with anything, and rinsing should not be done the day before. The sample is taken before antibiotic therapy, otherwise the result will be invalid.
The analysis takes an average of 5-7 days. After collecting the material, it is sown directly onto the surface of the nutrient medium. 0.1 ml of the wash is used for sowing. It is convenient to use the Baird-Parker medium, on which staphylococcus colonies are very easy to recognize by their opalescent shine and black colonies. In general, the choice of medium is determined by the laboratory technician, depending on the laboratory equipment and individual research goals, specialization and level of qualification. The ratio of the seed material and nutrient medium is 1:10. Then incubate in a thermostat.
Then, on the 2-3 day, the culture is transferred to slanted agar, a pure culture is isolated. Further studies (biochemical, immunological) are carried out with it, the main properties are determined, the culture is identified, the concentration is determined, and, if necessary, the sensitivity to antibiotics.
Microscopy is carried out separately, which makes it possible to determine an approximate preliminary assessment of the smear, to identify the species of the microorganism based on characteristic morphological and anatomical features. Other signs of pathology can also be detected: signs of inflammation, neoplasms.
A person is given only the finished result indicating the type of microorganism, the degree of contamination, and sometimes sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Staphylococcus aureus in vaginal smear
They are detected because they are permanent inhabitants of the skin and mucous membranes. Diseases caused by staphylococci are autoinfections, i.e. they develop when the main parameters of the human biochemical cycle change, the hormonal background, microflora, damage to the mucous membranes, pregnancy. Less often, they are a consequence of exogenous penetration of infection (from the external environment).
Staphylococcus aureus in a smear from the cervical canal
They can be detected against the background of dysbacteriosis, which develops during pregnancy, decreased microflora, and hormonal cycle disorders. Since staphylococcus is characterized by a wide range of infection sources and polyorganism, they can easily be transported with blood and cause inflammation beyond the main source. Often, the development of staphylococcal infection is a consequence of antibiotic therapy, physiotherapy, and surgical interventions.
Risk factors
The risk group includes people with a pathological source of infection in the body. For example, staphylococcal infection can develop in the presence of caries in the oral cavity, inflammation of the tonsils, chronic and not fully cured diseases of the respiratory tract, genitourinary organs, in the presence of purulent-septic wounds, burns, damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Catheters, implants, transplants, prostheses pose a great danger, since they can be colonized by staphylococcal infection.
Risk factors include decreased immunity, endocrine system disorders, dysbacteriosis, and gastrointestinal diseases. People who have recently undergone surgery, after serious illnesses, after antibiotic therapy, and chemotherapy are also at risk.
A separate group consists of people with immunodeficiencies, AIDS, other infectious diseases, autoimmune pathologies. Newborns (due to the immaturity of the microflora and immune system), pregnant women (due to hormonal changes) are at risk. Women in labor and those who have given birth, since currently in hospitals and maternity homes, hospital-acquired strains of staphylococcus, which live in the external environment, have acquired multiple resistance and increased pathogenicity, pose a serious danger. They are quite easy to get infected.
The risk group includes people who do not follow a daily routine, do not eat enough, and are subject to nervous and physical stress and overexertion.
A special group is represented by medical workers, biologists, researchers who work with various cultures of microorganisms, including staphylococcus, have contact with biological fluids, tissue samples, feces, and are in constant contact with both infectious and non-infectious patients.
This also includes laboratory technicians, nurses, orderlies, employees of sanitary inspection agencies, pharmacists, developers of vaccines and anatoxins, and their testers. Agricultural workers who deal with animals, products of slaughter of cattle and poultry, which are also a source of infection, are also at risk.
Symptoms staphylococcus aureus in the smear.
Symptoms directly depend on the localization of the infection. Thus, when a respiratory infection develops, colonization of the oral mucosa and nasopharynx occurs first. This manifests itself as inflammation, swelling, hyperemia. There is pain when swallowing, a sore throat, a burning sensation in the throat, nasal congestion, a runny nose with the release of yellow-green mucus, depending on the severity of the pathology.
As the infectious process progresses, signs of intoxication develop, the temperature rises, weakness appears, the body's overall resistance decreases, immunity decreases, as a result of which the pathological process only worsens.
Signs of systemic organ damage may develop. The infection moves down the descending respiratory tract, causing bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy with a strong cough and copious sputum production.
When an infection develops in the genitourinary tract and reproductive organs, irritation of the mucous membranes develops first, itching, burning, hyperemia appear. Gradually, the pathological process progresses, inflammation, pain, white discharge with a specific odor appear. Pain during urination, burning appear. The progression of the disease leads to the development of an intense infectious process that spreads to the rectum, perineum, and internal organs.
When the inflammatory process is localized on the skin and wound surface, the wound becomes infected, a specific odor appears, the local and then local and general body temperature may increase. The source of infection is constantly spreading, the wound is "weeping", does not heal, and is constantly growing.
With the development of staphylococcal infection in the intestinal area, signs of food poisoning appear: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion, stool, loss of appetite. Pain and inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract appear: gastritis, enteritis, enterocolitis, proctitis. With the generalization of the inflammatory process and the increase in signs of intoxication, body temperature rises, chills and fever develop.
First signs
There are early symptoms that are precursors to the disease. They develop as the concentration of staphylococcus in the blood increases and appear long before the actual symptoms appear.
Thus, the development of staphylococcal infection is accompanied by increased heart rate and breathing, trembling in the body, chills, fever. When walking, increased load, the load on the heart, lungs can be felt, slight shortness of breath appears. Headache, migraine, nasal congestion, ear congestion, less often - lacrimation, sore throat and dryness of the throat, dry skin and mucous membranes can appear.
Often there is a feeling of elevated temperature, but when measured it remains normal. The person quickly gets tired, work capacity decreases sharply, irritation, tearfulness, drowsiness appear. Concentration of attention and ability to concentrate may decrease.
 [ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ]
[ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ]
Staphylococcus aureus in smear
Staphylococcus aureus, S. aureus, is a common causative agent of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the internal organs of humans and animals. More than 100 nosological forms of diseases caused by this pathogen are known. The pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus is based on a whole complex of toxic substances and aggressive factors, enzymes that are produced by microorganisms. In addition, it has been established that the pathogenicity of the microorganism is due to genetic factors and environmental influences.
It is worth emphasizing that Staphylococcus aureus has polyorgan tropism, that is, it can become the causative agent of a pathological process in any organ. This is manifested in the ability to cause purulent-inflammatory processes in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, lymph nodes, respiratory tract, urinary system, and even the musculoskeletal system. It is a frequent causative agent of food toxic infections. The special significance of this microorganism is determined by its role in the etiology of hospital infections. Among Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant strains often arise, which are highly resistant to the action of any antibiotics and antiseptics.
It is easy enough to recognize in a smear, since it looks like gram-positive cocci, the diameter of which varies from 0.5 to 1.5 µm, arranged in pairs, short chains or clusters in the form of a bunch of grapes. Immobile, do not form spores. Grow in the presence of 10% sodium chloride. Surface structures are capable of synthesizing a number of toxins and enzymes that play an important role in the metabolism of microorganisms and determine their role in the etiology of staphylococcal infections.
It is also easy to recognize in a smear by such morphological features as the presence of a cell wall, membrane structures, capsule and flocculation factor. An important role in pathogenesis is played by agglutinogen A - a protein that is evenly distributed throughout the thickness of the cell wall and is covalently linked to peptide glycan. The biological activity of this protein is diverse and is an unfavorable factor for the macroorganism. It is capable of reacting with mucous immunoglobulin, forming complexes that are accompanied by damage to platelets and the development of thromboembolic reactions. It is also an obstacle to active phagocytosis, contributes to the development of an allergic reaction.
Staphylococcus epidermidis in smear
For a long time, it was believed that epidermal staphylococcus was not pathogenic. But recent studies have confirmed that this is not the case. It is a representative of the normal microflora of the skin and can cause diseases in some people. This is especially true for people with reduced immunity, after burns, damage to the integrity of the skin, with various wounds. As a result of the development of staphylococcal infection, a purulent-septic inflammatory process develops quite quickly, zones of necrosis, erosion, ulcers, and suppuration appear.
In a smear, it is quite easy to recognize by the formation of pigmented colonies, up to 5 mm in diameter. They form cocci, can be single or combine into polycompounds resembling bunches of grapes. They can grow both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Hemolytic staphylococcus in smear
The hemolytic properties of staphylococcus are its ability to lyse blood. This property is provided by the synthesis of plasmacoagulase and leukocidin - bacterial toxins that break down blood. It is the ability to break down and coagulate plasma that is the leading and constant criterion by which pathogenic staphylococci are fairly easily identified.
The principle of the reaction is that plasma coagulase reacts with plasma co-factor, forming coagulase thrombin, which converts thrombinogen into thrombin with the formation of a blood clot.
Plasmacoagulase is an enzyme that is easily destroyed by proteolytic enzymes, such as trypsin, chymotrypsin, and when heated to a temperature of 100 degrees or higher for 60 minutes. High concentrations of coagulase lead to a decrease in the blood's ability to clot, hemodynamics are disrupted, and tissue oxygen starvation occurs. In addition, the enzyme promotes the formation of fibrin barriers around the microbial cell, thereby reducing the effectiveness of phagocytosis.
Currently, 5 types of hemolysins are known, each of which has its own mechanism of action. Alpha toxin is not active against human erythrocytes, but lyses erythrocytes of sheep, rabbits, pigs, aggregates thrombocytes, has a lethal and dermonecrotic effect.
Beta-toxin causes lysis of human erythrocytes and exhibits a cytotoxic effect on human fibroblasts.
Gamma toxin lyses human erythrocytes. Its lytic effect on leukocytes is also known. It has no toxic effect when administered intradermally. When administered intravenously, it causes death.
Delta toxin differs from all other toxins in its heat lability, broad spectrum of cytotoxic activity, damages erythrocytes, leukocytes, lysosomes and mitochondria.
Epsilon toxin provides the widest possible area of action, lysing all types of blood cells.
Coagulase-negative staphylococcus in smear
The importance of coagulase-negative staphylococci in the development of internal organ pathology is beyond doubt. According to researchers, this group is responsible for the development of urogenital tract pathology in approximately 13-14% of cases. They are the causative agents of skin and wound infections, conjunctivitis, inflammatory processes and sepsis in newborns. The most severe form of infection is endocarditis. The number of such complications has increased especially due to the high prevalence of heart surgery for the installation of artificial valves and bypass of blood vessels.
Considering the biological properties, it is worth noting that the microorganisms are cocci with a diameter of no more than 5 µm, do not form pigments, and can grow both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. They grow in the presence of 10% sodium chloride. They are capable of hemolysis, nitrate reduction, have urease, and do not produce DNAase. In aerobic conditions, they are capable of producing lactose, sucrose, and mannose. They are not capable of fermenting mannitol and trehalose.
Of greatest importance is Staphylococcus epidermidis, which is one of the leading clinically significant pathogens. It causes septicemia, conjunctivitis, pyoderma, urinary tract infections. Also, among the coagulase-negative strains there are many representatives of hospital infections.
 [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ]
[ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ]
Staphylococcus saprophyticus, saprophytic in smear
Refers to coagulase-negative strains that are capable of existing in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. They actively reproduce in wound surfaces, in damaged areas of the skin, with severe burns, with a foreign body in soft tissues, in the presence of transplants, prostheses, and during invasive procedures.
Often lead to the development of toxic shock. This effect is caused by the action of endotoxins. Often develops when using absorbent tampons in women during menstruation, in the postpartum period, after abortions, miscarriages, gynecological operations, after long-term use of barrier contraception.
The clinical picture is represented by a sharp increase in temperature, nausea, sharp pain in muscles and joints. Later, characteristic spotted rashes appear, most often generalized. Arterial hypotension develops, accompanied by loss of consciousness. Mortality reaches 25%.
Fecal staphylococcus in smear
It is the main causative agent of food poisoning. It is well preserved in the environment. The main route of transmission is feco-oral. It is released into the environment with feces. It enters the body with poorly cooked food, dirty hands, unwashed products.
The mechanism of action is carried out by staphylococcal enterotoxins, which are heat-stable polypeptides formed during the reproduction of enterotoxigenic strains, staphylococci in food products, intestines and artificial nutrient media. They exhibit high resistance to the action of food enzymes.
Enteropathogenicity of toxins is determined by their connection with epithelial cells of the stomach and intestines, the effect on the enzymatic systems of epithelial cells. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the rate of formation of prostaglandins, histamine, and an increase in the secretion of fluids into the lumen of the stomach and intestines. In addition, toxins damage the membranes of epithelial cells, increasing the permeability of the intestinal wall for other toxic products of bacterial origin.
The virulence of fecal enteropathogenic staphylococci is regulated by the genetic apparatus of the bacterial cell in response to environmental factors, which allows the microorganism to quickly adapt to environmental conditions, which allows the microorganism to quickly adapt to changing conditions when moving from one microbiocenosis to another.
Differential diagnosis
When determining the role and significance of various representatives of the genus Staphylococcus in the etiology of purulent-inflammatory diseases of humans, despite the relative simplicity of their detection, they are associated with numerous difficulties. This is due to the fact that staphylococcus is a representative of normal microflora, which inhabits various biotopes of the human body. It is necessary to clearly distinguish between endogenous staphylococcus, developing inside the body, and endogenous, which penetrates the body from the environment. It is also important to understand which of the biotopes of the human body is typical for it, and where it is a representative of transient flora (introduced accidentally).
It is also important to take into account the high variability of the microorganism under the influence of various factors, including antibiotics. A wide variety of clinical manifestations and nosological forms is taken into account. Therefore, there is no universal diagnostic scheme for staphylococcal infection. It is easier to examine those biological environments that are normally sterile (blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid). In this case, the detection of any microorganism, colony is a pathology. The most difficult is the diagnosis of diseases of the nose, throat, intestines, and a study on bacterial carriage.
In the most general form, the diagnostic scheme can be reduced to the correct collection of biological material, its bacteriological primary seeding on an artificial nutrient medium. At this stage, preliminary microscopy can be carried out. By studying the morphological, cytological features of the sample, it is possible to obtain certain information about the microorganism, to carry out at least its generic identification.
To obtain more detailed information, it is necessary to isolate a pure culture and conduct further biochemical, serological and immunological studies with it. This allows us to determine not only the genus but also the species, as well as to determine the biological affiliation, in particular, the serotype, biotype, phage type and other properties.
 [ 24 ], [ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ]
[ 24 ], [ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ]
Who to contact?
Treatment staphylococcus aureus in the smear.
Staphylococcal infection requires antibiotic therapy. The therapy is exclusively etiological, that is, it is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease (the bacteria itself), or more precisely, reducing its degree of contamination to normal levels. Various antibiotics are used.
Some doctors prefer to use broad-spectrum drugs, while others prescribe antibiotics to their patients that are aimed exclusively at eliminating gram-positive infections, including staphylococcus. The choice is determined primarily by the results of an antibiotic sensitivity test, which determines the most effective drug and selects its optimal dosage.
In some mild cases, antibiotic therapy may not be needed to correct the condition. It may simply require normalization of the microflora. This is observed with dysbacteriosis. In this case, probiotics and prebiotics are prescribed, which normalize the state of the microflora by reducing the amount of pathogenic flora and increasing the concentration of representatives of the normal microflora.
Symptomatic therapy is rarely used, as it is usually enough to eliminate the infection, and the accompanying symptoms will disappear on their own. In some cases, additional measures are prescribed, for example: painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines, antiallergic drugs. For skin diseases, external agents are used: ointments, creams. Physiotherapy, folk and homeopathic remedies may be prescribed.
Vitamin therapy is not performed, since vitamins act as growth factors for microorganisms. The exception is vitamin C, which must be taken in a dosage of 1000 mg / day (double dose). This will increase immunity, resistance, and the body's resistance to adverse factors.
Medicines
Treatment of infectious diseases should be taken seriously. Self-medication should not be done, as it often has disastrous consequences. It is necessary to take into account many nuances before starting treatment. Only a doctor can do this best.
It is important to take precautions: do not treat the infection "blindly", even with a pronounced clinical picture. It is necessary to conduct a bacteriological study, isolate the pathogen, select the most optimal antibiotic for it, determine the necessary dosage that will completely suppress the growth of the microorganism.
It is also important to complete the full course, even if the symptoms have disappeared. This is because if you stop treatment, the microorganisms will not be completely killed. The surviving microorganisms will quickly develop resistance to the drug. If used again, it will be ineffective. Moreover, resistance will develop to the entire group of drugs, and to similar drugs (due to the development of a cross-reaction).
Another important precaution is that you cannot lower or increase the dosage on your own. Lowering it may not be effective enough: the bacteria will not be killed. Accordingly, they will mutate in a short time, acquire resistance and a higher degree of pathogenicity.
Some antibiotics can also have side effects. The stomach and intestines are especially sensitive to antibiotics. Gastritis, dyspeptic disorders, bowel disorders, and nausea can develop. Some have a negative effect on the liver, so they should be taken together with hepatoprotectors.
Below are antibiotics that have proven effective in treating staph infections with minimal side effects.
Amoxiclav is effective in treating staphylococcal infections of any localization. It is used in the treatment of diseases of the respiratory tract, genitourinary system, and intestines. Take 500 mg per day for three days. If necessary, repeat the course of treatment.
Ampicillin is prescribed mainly for diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract. The optimal dosage is 50 mg/kg of body weight.
Oxacillin is effective both in local inflammatory processes and in generalized infections. It is a reliable preventative measure against sepsis. Prescribed at 2 grams every 4 hours. Administered intravenously.
For purulent-inflammatory skin diseases, levomycetin ointment is applied externally, applying a thin layer to the damaged surface. Levomycetin is also taken internally, 1 gram three times a day. In case of strong generalization of the infectious process, levomycetin is administered intramuscularly, 1 gram every 4-6 hours.
Suppositories for Staphylococcus aureus
They are used mainly for gynecological diseases, urogenital tract infections, and less often for intestinal dysbacteriosis with inflammation of the rectum. Only a doctor can prescribe suppositories and select the optimal dosage, since if used incorrectly, there is a high risk of complications and further spread of infection. Suppositories are not prescribed without preliminary tests. The indication for their use is exclusively staphylococcus in a smear.

