Skin biopsy
Last reviewed: 24.06.2018

All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
A skin biopsy is a procedure in which a specific area of skin is removed and processed for detailed examination under a microscope. Let's consider the features of the method, the technology of implementation and other nuances.
Several methods are used in the examination process, the choice of which depends on the size and location of the atypical area to be removed as a sample. The biopsy is placed in a sterile container or special solution for further examination under a microscope. The main feature of the diagnostics is that no special preparation is required. In some cases, local anesthesia may be used for pain relief.
After the procedure, which lasts 5-25 minutes, a bandage or plaster is applied to the affected area to prevent infection. Pain may occur at the site of skin sampling, which goes away after 1-2 days. If swelling, bleeding, severe pain, discharge and other painful symptoms appear at the wound site, you should seek medical help. This is due to the fact that biopsy is accompanied by certain risks. First of all, this is poor wound healing, bleeding, infection, scarring and nerve damage. The risk group includes patients with blood clotting disorders and circulatory problems, smokers and those suffering from immunosuppression.
Indications for skin biopsy
Skin examination refers to diagnostic methods that are used to establish a specific diagnosis. It can be used to remove and examine an area of abnormal skin. For this purpose, razor, puncture and excisional biopsy are used.
Main indications for the procedure:
- Diagnosis of bacterial, fungal or viral infections.
- Detection of inflammatory lesions.
- Suspected benign neoplasms.
- Checking the condition of the skin at the site of tumor removal.
- Red lupus.
- Tuberculosis of the skin.
- Cancer.
- Psoriasis.
- Scleroderma.
- Amyloidosis.
- Deep mycosis.
- Nodular periarteritis.
- Darier's disease.
- Reticulosis.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
When taking material for examination, pay attention to the localization of the affected area. The required sample is placed in a solution, and if there is a suspicion of infection, in a sterile container. The tissues are processed and examined under a microscope for pathologies.
Most often, diagnostics are carried out to detect cancer, which is accompanied by changes in pigmentation and poor wound healing. Timely detection of the disease allows for early treatment, preventing possible consequences.
Skin biopsy instrument
A skin biopsy is performed using a special instrument. There are many diagnostic techniques, so the equipment used varies. Typically, this is a disposable set of instruments that contains a cannula with a hole, a probe, and a movable tube that is installed in the cannula. At the end of the tube, there is a special ring-shaped protrusion used to insert into the hole in the wall and hold the tissue sample. The probe is installed in the cannula, at the ends of which there are tubes with heads. If necessary, the heads are connected. This reduces trauma during the sample collection process and preserves its macroscopic and microscopic properties.
During a puncture biopsy, tissue is extracted with a special needle. It is several centimeters long, and the syringe barrel has a diameter equal to a regular paper clip. The needle is hollow inside, which allows for the extraction and capture of tissue. The peculiarity of the instruments is that they have a wide range of sizes for taking samples from any area of the skin. The ribbed handle allows you to hold them securely in your hand and control the procedure. All instruments are absolutely sterile (eliminates infection), have a steel sharp razor for minimal tissue trauma.
Skin biopsy needles
Several types of needles are used to perform a biopsy:
- A thin needle with a syringe (thinner than needles for drawing blood from a vein).
- Automatic, cutting with a spring mechanism. Consists of a thick needle that is inserted into a cell with a shell attached to the mechanism.
- Vacuum for aspiration biopsy – allows you to take large tissue samples.
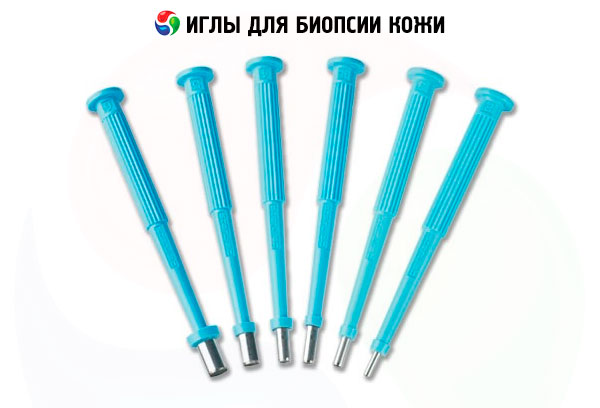

The diameter of the needle can be from 2 to 8 mm. If whole tissue segments are taken for histological examination, a hollow needle is used. It contains a cannula with an edge or a special probe for cutting the tissue and inserting it into the selected part of the body. The biopsy is placed in a cylindrical channel and held there by suction or mechanical means. The resulting sample has an elongated cylindrical shape. Samples should reflect the structure of living tissue as accurately as possible.
There are special automated devices used for puncture biopsy. This technology is called "correct cut needle". It contains a cannula with a sharp edge and an internal probe with a semi-cylindrical recess near the tip. A significant disadvantage of this tool is that it allows you to take tissues whose volume is equal to half the volume of the cannula. In addition, the quality of the sample deteriorates, since the probe passes through the area being examined.
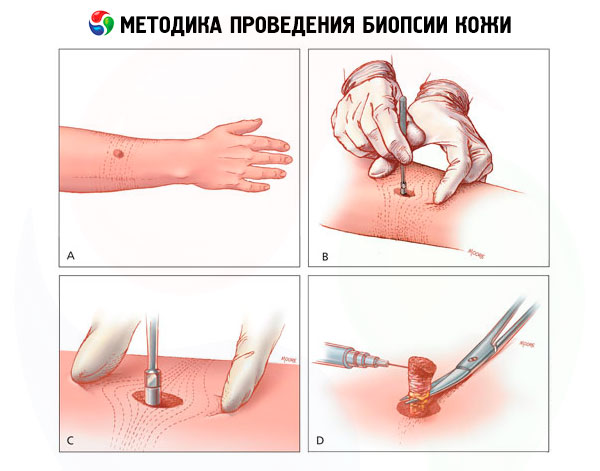
Skin biopsy technique
The research method involves excising a small area of skin or taking tissue samples under local anesthesia for further study. Three methods are currently used:
- Shaving
Using a scalpel or a special blade, take a superficial cut of the lesion. That is, the protruding part of the pathological element is cut off and placed in a formalin solution. The cut site is treated with a sterile napkin to prevent bleeding.
- Trephine biopsy
Using this method, a tissue column with skin and subcutaneous fat is taken from the central part of the affected area. In the area of the procedure, the skin is stretched and pierced with a trepanation needle, gradually rotating it around its axis. The needle is removed, and the resulting tissue column is pulled up with tweezers and cut at the level of the fat. If the wound surface does not exceed 3 mm in diameter, a sterile plaster is applied to it. If the diameter is larger, a suture is applied.
- Excisional
The lesion and the adjacent healthy area are excised with a special instrument. The method is used when there is a suspicion of malignant tumors. A biopsy with pronounced changes (discolored skin, on which wounds heal poorly) is selected for examination. The wound surface is treated with a sterile napkin to prevent infection and bleeding. The wound is sutured; if the defect is large, a skin graft is used to close it.
The results of the study are influenced by factors such as:
- Collection of a sample without pathological changes or with minimal deviations.
- Use of a non-sterile container or improper fixation of the material and its damage.
The main goal of the above methods is differential diagnostics of benign and malignant lesions, detection of chronic fungal and bacterial infections. The obtained material is immediately sent to the laboratory.
Scalp biopsy
The scalp examination involves taking tissue for histological analysis. Using a special needle, the doctor cuts out a 2-4 mm piece, which is then examined under a microscope after special treatment. The entire procedure is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not experience discomfort or pain.
The wound surface is sutured and removed after 3-7 days. It is not recommended to wash your hair for the first two days to prevent infection or suppuration of the wound. Such excision is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing skin and dermatological diseases.
The operation is performed to clarify the diagnosis when a rash appears on the head or when there is cicatricial alopecia. The analysis allows us to identify infectious, fungal, viral or bacterial lesions, as well as various autoimmune diseases. The procedure is performed for wounds and burns of varying degrees.
 [ 5 ]
[ 5 ]
Facial skin biopsy
If malignant diseases or other lesions of the facial skin are suspected, an operation is performed, during which a small piece of tissue is taken for examination. Before excision, it is necessary to stop taking medications that promote bleeding, anti-inflammatory drugs and anticoagulants.
The procedure may be prescribed if there is a suspicion of cancer, psoriasis, amyloidosis, periarteritis nodosa, lupus erythematosus and other diseases. The area to be examined is thoroughly washed and treated with an alcohol solution of iodine or ether.
- Typically, the procedure is performed using the thin-cut method, i.e. a thin layer of skin is removed using a scalpel. A sterile plaster is applied to the wound for self-healing.
- In some cases, a puncture biopsy is performed using a special needle. This method allows taking deeper layers of skin and subcutaneous tissue. A cosmetic suture is applied to the wound.
The obtained material is examined under a microscope to identify differences in cells (cytology) and tissues (histology). To avoid pain, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. As a rule, this is superficial anesthesia, that is, spraying the drug and freezing the area through which the needle passes. The analysis can cause a number of complications: inflammation, keloid scars. You have to wait 1-6 weeks for the results.
Skin biopsy for psoriasis
If psoriasis is suspected, the patient will undergo a number of tests and diagnostic procedures, including skin excision for histology and cytology. As a rule, it is not difficult to detect psoriasis, since the disease is indicated by the characteristic appearance of tissues. If the disease is active, progressive or severe, then standard blood tests reveal endocrine and biochemical disorders.
In this case, the patient is prescribed a diagnostic excision to exclude other diseases and histological confirmation of psoriasis. During the study of the affected tissues, clusters of Reet bodies are detected, that is, histological immaturity and thickening of the keratinocyte layer, increased proliferation and accelerated angiogenesis in the tissues under the plaques.
Another characteristic sign of the disease, which is revealed during the analysis, is pinpoint bleeding under the skin with a plaque when trying to scrape it off. This is due to pathological increased permeability, lightness of vessels in the affected areas and accelerated angiogenesis.
Biopsy of skin lesions
The examination of skin neoplasms is performed by means of an operation, during which tissues are taken for examination. Subcutaneous and cutaneous tumors are common, so they require careful examination and early diagnosis. There are several ways to take a tumor sample. The doctor chooses the most appropriate one, taking into account a number of factors, i.e. localization, possible diagnosis and cosmetic effect. All samples obtained are sent not only for cytology and histology, but also for morphological examination.
Methods of taking a biopsy:
- A scalpel is used to make a thin cut of the epidermis and the upper layer of the dermis. This procedure does not require stitches on the wound. This method can completely remove a small tumor and take material for research from a large sample.
- For a puncture biopsy, special needles with a diameter of 1-6 mm are used. During the operation, a column of underlying tissue is obtained. The method is excellent for examining large tumors. It can be used to completely remove a tumor if its diameter is smaller than the diameter of the needle. The wound is sutured. The technique is not used for diagnosis or removal of neoplasms in fatty tissue.
- Incisional examination involves excision of a portion of the tumor, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. This allows for histological analysis. The wound is sutured.
- Total examination is the complete removal of the neoplasm and histology. All layers of skin are taken for analysis. If there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration, the edge of the excised tissue is marked by stitching with a thread. In the future, this facilitates a repeat operation, since the doctor will be able to recognize the malignant area.
Before the operation, the wound surface is treated with an anesthetic. For these purposes, 1% lidocaine or a mixture of adrenaline and lidocaine is used.
Skin biopsy with histological examination
Histological examination is one of the main methods for detecting skin diseases. Histology is performed by taking tissue from the affected area. This allows differentiating between different lesions, which significantly simplifies the process of determining the disease. The main rule for taking a biopsy is choosing a place to take it. The material should contain subcutaneous fat.
The biopsy is treated with a formalin solution, which can preserve tissue for months without causing damage. Excisional excision is usually used. The material is taken with a special needle or scalpel. The resulting tissue is examined using light, electron microscopy, or immunofluorescence staining.
Wound care after skin biopsy
After taking the skin for examination, the wound surface requires special care. Depending on the size of the wound, a sterile dressing may be used for several days. In some cases, immediately after the procedure or the next day, the site from which the biopsy was taken bleeds. In this case, you must seek medical help.
After a puncture and excisional biopsy, a small scar remains on the body. If it is on the neck, back or chest, it causes discomfort, including cosmetic. Healing takes several weeks, but the wound heals in 1-2 months. If tissue from the upper or lower extremities was taken for the study, they heal much more slowly than in other areas.
While the skin is healing, it needs to be properly cared for:
- Before touching the wound, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- The surface must be treated with an antiseptic and covered with a sterile bandage or adhesive tape.
- The wound should be dry and clean.
- Do not immerse the affected area in water until the tissues have healed well.
- Continue care until tissue is completely healed or until the stitches are removed.
If signs of infection appear after the operation, i.e. fever and chills, swelling, bleeding, discharge or increased pain, then you should seek medical help. In this case, the patient is prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. When stitches are applied, they remain for 3-14 days, depending on the location of the wound.
 [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ]
[ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ]
Can you wash after a skin biopsy?
Many patients who have been prescribed diagnostic excision of the skin have the same question: is it possible to wash and wet the affected area immediately after the procedure.
- If the study involved excision of the upper layer of the epidermis and dermis and the patient does not feel severe pain, the wound can be wetted. After water procedures, an antiseptic should be applied to prevent infection.
- When taking a puncture sample, the wound is stitched, so it is not recommended to get the affected area wet for 1-2 days.
- The skin should not be stretched, as this may cause bleeding, enlargement of the wound, which will subsequently lead to the appearance of a scar.
Complete healing occurs within 1-2 weeks.
How to treat a wound on the face after taking a skin biopsy?
If the biopsy was taken from the face for the study, then it is necessary to know how to speed up the healing. To treat the wound, it must be treated with an antiseptic, for example, brilliant green. During the recovery period, it is better to spend a couple of days at home, so as not to feel discomfort from the constant glances of others. Of course, if we are talking about a large wound surface and the problem is of an aesthetic nature.
After a skin biopsy, wound-healing ointments (Panthenol, Actovegin, Bepanten) or creams are used to care for the damaged surface. Such medications accelerate healing and provide a good cosmetic effect. Local agents have an anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect, relieve redness and irritation.
Patient consent for skin biopsy
If there are indications for a biopsy, the patient's consent is taken before it is performed and they are warned about possible risks and complications. The doctor's task is to explain that the study is an examination of a piece of flesh for various infections. The patient is explained the essence of the method and all questions of interest are answered. The procedure does not require special preparation or diet.
Since local anesthesia may be used to prevent pain, it is necessary to determine whether the patient has an intolerance to the anesthetic.
Before diagnosis, the patient must warn the doctor about the following cases:
- Taking medications, especially anti-inflammatory drugs, as they affect the results of the study.
- The presence of allergies to certain drugs.
- Bleeding problems and taking blood thinning medications (Warfarin, Aspirin, Coumadin).
- Pregnancy.
As for the risks and complications, these are bleeding, infection, painful sensations, long-term wound healing. After this, the patient must sign a consent form.
Skin biopsy cost
The cost of diagnostic skin excision depends on the histological examination used. The procedure is expensive and costs 300-5000 UAH, depending on the place of material collection and the diagnosis of the suspected disease.
- Punch examination of the skin of the trunk and limbs - from 600 UAH.
- Collection of material from the face, neck, hands, feet or genitals - from 700 UAH.
- Excisional surgical excision – from 800 UAH.
- Pathological examination of biopsy – from 500 UAH.
Samples are collected in specialized clinics. Tissue samples are examined both in Ukrainian laboratories and sent to diagnostic centers outside the country. Analysis results are provided within 1-6 weeks.
