
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Scoliosis of the 4th degree: what to do, treatment, disability
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 07.06.2024
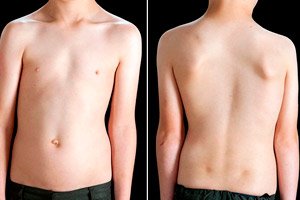
In scoliotic deformity of the spine, the degree of curvature is crucial for choosing treatment tactics and predicting its success, and the most difficult case is scoliosis of the 4th degree.
This degree means that the lateral deviation of the spine (Cobb angle, measured on an X-ray) is 50° or more. [1]
Epidemiology
The prevalence of scoliosis of various degrees is estimated at 4-8% of the general population. And the prevalence of idiopathic scoliosis, according to foreign sources, ranges from 0.5% to 4.5%. At the same time, approximately 30% of patients with idiopathic scoliosis have a family history of the disease.
According to the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons, idiopathic scoliosis is ten times more common in girls over the age of 10 (in whom the ossification process is somewhat faster) than in boys.
And specialists of Scoliosis Research Society note that scoliosis of the 4th degree is diagnosed in 0.04-0.3% of cases with the ratio of female and male patients - 7:1.
80% of idiopathic scoliosis occurs in adolescents (11 to 18 years of age), while infantile scoliosis (under three years of age) accounts for 1% of cases and juvenile scoliosis (in children 4-10 years of age) accounts for 10-15% of cases.
Scoliosis that develops in adults (in the absence of its adolescence) has a prevalence of more than 8% in those over 25 years of age, and in people 60 years and older rises to 68%, but the statistics of the fourth degree of this type of pathology are unknown.
Causes of the fourth-degree scoliosis
In most patients - about 8 out of 10 cases - the causes of scoliosis cannot be identified, although, as is known, this disease is often present in the family: in first-line relatives the incidence is 11%, in second-line relatives - 2.4%.
So, the version of genetic predisposition in cases of familial idiopathic scoliosis is considered, but so far has not yet been accurately identified specific genes, polymorphisms, duplications or mutations of which cause abnormalities in the development of the spine and the process of its deformation. Gene linkage studies show that loci on at least half a dozen chromosomes may be related to the development of this pathology. For example, the involvement of the GPR126 gene on chromosome 6, which encodes cartilage development and is associated with trunk growth, has been identified. [2]
While idiopathic scoliosis of the 4th degree (i.e., of unclear etiology) is most often diagnosed, the possible causes of lateral spinal deformity may be related:
- With intrauterine anomalies or traumas sustained during childbirth. For example, grade 4 thoracolumbar scoliosis in children may be due to a phylogenesis pathology - a defect in the embryonic neural tube leading to incomplete closure of the vertebral arch, i.e. cleft spine, or transverse extension of the vertebrae (plastinospondylia), or a spinal cord anomaly such as diastematomyelia;
- With deformity of facet joints of the spine in spinal gliomatosis (syringomyelia);
- With spinal muscular atrophy or muscular dystrophy (such scoliosis is called neuromuscular or myopathic scoliosis);
- With neurofibromatosis (hereditary Recklinghausen's disease);
- With spinal dysraphia involving the musculoskeletal structures and ligaments of the spine;
- With spinal tumors;
- With hereditary disorder of methionine metabolism (homocystinuria) and mucopolysaccharidosis;
- With mesenchymal disorders such as Marfan syndrome, ehlers-Danlo syndrome, Klippel-Feil, etc., is diagnosed as mesenchymal or syndromal scoliosis;
- In older patients with degenerative spondylosis (osteophyte formation due to bone overgrowth in the spinal joints).
See also -
Grade 4 scoliosis of adults with a mature skeleton differs from scoliosis in childhood. In addition to the fact that adults can have it since adolescence - after surgical treatment or without it (as a neglected case), lateral curvature can develop as a new pathology (scoliosis de novo) - with degenerative changes in the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. [3]
Degenerative lumbar or lumbar scoliosis of the 4th degree in the elderly (aged 65 years and older) may be the result of instability or displacement of the lumbar vertebrae (spondylolisthesis), as well as a consequence of surgical intervention (laminectomy) performed in case of spinal nerve compression of various etiologies. However, in most of these cases, the curvature of the spine does not exceed 2 degrees.
Risk factors
As a rule, scoliotic disease begins in periods of growth spurts before or during puberty (from 10 to 16 years of age), as well as increased growth of the thorax (which begins at the age of 11-12 years). Therefore, when listing the risk factors for this type of spinal deformity, vertebrologists name the age factor first.
It is followed by being female (girls develop scoliosis much more often than boys) and having a family history of scoliosis.
The risk of spinal curvature is increased in case of persistent posture disorders in childhood and adolescence; vertebral and rib-vertebral joint injuries; myofascial pain syndrome (with compensatory pathologic changes in posture); congenital deformity of the anterior chest wall (pectus excavatum); presence in adults of arthrosis of intervertebral joints (spondyloarthrosis) and other degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine; in hyperestrogenia in adolescent girls and hypoestrogenia in women (especially in postmenopause); deficiency of magnesium, vitamins D and K in the body, as well as insufficient body weight.
Pathogenesis
Attempts to explain potential mechanisms of development - the pathogenesis of scoliosis - have led researchers to recognize the polygenicity of this disease with a certain impact on the structures of the musculoskeletal system of genetic factors, neurocirculatory disorders, hormonal shifts (including sex steroids and melatonin stimulating division of osteoblasts) and peculiarities of general metabolism. [4]
Most of the proposed versions are reduced to the leading pathogenetic role of anomalies of growth plates (epiphyseal plates) of vertebral bodies - secondary centers (points) of their ossification, as well as asymmetric growth of the spine. The mechanism of vertebral growth in height is similar to that in long bones: endochondral ossification (ossification) in the growth plates. And the increase in their diameter occurs by appositional growth in the ossification points adjacent to the intervertebral discs.
How can scoliosis of the 4th degree develop in children? Longitudinal growth of the vertebral body from the primary ossification points occurs throughout childhood (especially rapidly in the first three years of a child's life), adolescence and young adulthood. But during puberty, growth intensifies with the appearance and activation of five secondary ossification centers on the body of each vertebra. [5]
Disruption of the ossification process when the growth plates are overloaded on the concave side of the vertebral bodies results in their wedge-shaped deformation, which causes lateral bending of the spinal segment in the frontal plane and axial twisting of the vertebrae - torsion. This is when the vertebrae are rotated relative to their own axis in the transverse plane: their bodies are turned toward the convexity of the scoliotic arch, while the spinous processes that branch from the vertebral arch are turned toward the concave part of the arch.
Muscular dystrophy or atrophy of the muscles of the spine can develop scoliosis or kyphosis, or both curvatures at the same time. As the spinal column grows, the strength that maintains the vertical position of the spinal column weakens and eventually curves to the right or left in the upper or middle part of the spine to form C-shaped scoliosis, which can progress to grade 4 (with a Cobb angle of 80° or more). [6]
Symptoms of the fourth-degree scoliosis
Patients with grade 4 scoliosis have symptoms due to the fact that the spine is not only curved, but also twisted. As a result, the thorax loses symmetry and becomes deformed, which leads to displacement of thoracic organs.
So, scoliosis 4 degree thoracic scoliosis or thoracic scoliosis, in which the arc of curvature is formed by several vertebrae of the thoracic region - between the third and ninth, is manifested by deformation of the thorax, skewing of the supra-scapular region, protrusion of the scapula, the formation of a rib hump (front or back), back pain and shortness of breath.
Just below the middle of the thoracic spine, a second curvature can be formed in the opposite direction, and then thoracolumbar (thoracolumbar) S-shaped scoliosis of the 4th degree is determined. Due to the torsion of the vertebral bodies, the thorax and pelvis turn in different planes, with a skewed pelvic region (obliquity), different lengths of the lower limbs and limping when walking.
Lumbar or lumbar scoliosis of the 4th degree in 75% of cases is accompanied by spinal pain associated with pelvic misalignment and protrusion of the upper edge of the iliac bone, degenerative changes in the facet joints and displaced intervertebral discs, as well as overload of paravertebral muscles that resist progressive deformity.
Scoliosis of the lumbosacral spine of the 4th degree develops in rare cases, because all five vertebrae of the sacrum gradually fuse at the age of 18-25 years, forming a solid bone - sacrum. But if there is a lateral curvature of this localization, its symptomatology is similar to lumbar scoliosis.
Pregnancy and 4th degree scoliosis
Scoliosis of such a high degree, experts refer to factors that increase the risk of disorders during pregnancy - both for the woman and the future child.
First, as the gestational age increases, the load on the spine increases, especially in the lumbar region (where hyperlordosis is formed), and a pregnant woman with grade 4 lumbar scoliosis will have significantly increased pain. [7]
Secondly, the uterus grows with an increase in the standing height of its bottom, and in thoracic or thoracolumbar scoliosis of the 4th degree, this will lead to serious problems related to the displacement of the uterus, because the thorax is deformed, the internal organs are displaced, and the pelvis is asymmetrical. Therefore, there is also placental insufficiency, and disturbances in the mechanisms of uteroplacental circulation. In addition, the reduction in lung volume in such a spinal disease is fraught with insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus, that is, perinatal hypoxia.
Pregnancy with scoliosis 3 and 4 degrees can at any time interrupt due to detachment of the placenta (even when it is located normally); in some women with this diagnosis, the progression of scoliosis deformity of the spine is noted both during childbearing and after birth.
Natural childbirth with scoliosis of the 4th degree of the thoracic spine is possible if the patient has undergone surgical treatment of scoliosis several years before. But even in such cases, according to some data, almost half of women have a caesarean section. [8]
Complications and consequences
What is the danger of scoliosis of the 4th degree? At this degree of deformation of the spinal column is an uncorrected change in the center of gravity of the body, which, in turn, leads to an imbalance in the load on the muscles, spinal joints and ligaments, which is due to the limitation of mobility and pain of varying intensity.
The normal anatomical position and functions of the organs located in the thorax are disturbed. In particular, due to the reduction of lung volume in thoracic and thoracolumbar scoliosis, pulmonary hypertension, dyspnea, and chronic bronchitis develop. The pressure in the small circle of blood circulation also increases, which causes the right side of the heart to enlarge (so-called pulmonary heart).
Changes in the size of the thorax at a Cobb angle of 60° leads to impaired mechanical function of the ribs and respiratory muscles (intercostal and diaphragm), reduced total lung capacity and clinically expressed pulmonary dysfunction in the form of dyspnea on exercise and a decrease in the amount of oxygen supplied to the body. At a Cobb angle of 80°, hypopnea/sleep apnea is observed.
In addition, consequences and complications of grade 4 scoliosis include: intestinal pain; development of deforming spondyloarthritis; spasms of asymmetrically overloaded muscles; and neuropathies manifested by paresthesia of the extremities.
Scoliosis of grades 1-3 in children or adolescents - until complete ossification of the vertebrae - is considered to be progressive. Although bony fusion of skeletal structures (synestosis) and ossification of vertebrae is complete by about age 25, progression of grade 4 scoliosis into adulthood has been noted. Clinical practice shows that lumbar scoliosis is the least prone to progression; thoracic grade 4 scoliosis is the most likely to progress. Studies have reported an average increase of 2.4° per year over five years, and in adolescents, scoliosis progresses an average of 10-12° over 20 years.
Diagnostics of the fourth-degree scoliosis
For details on how the diagnosis is carried out, see. - scoliosis diagnosis
Instrumental diagnosis see - radiography of the spine in three projections, CT of the spinal column. [9]
Read also:
Treatment of the fourth-degree scoliosis
Conservative treatment of this degree of scoliosis can only be attempted in children before puberty.
Although numerous clinical studies have shown that treatment of scoliosis 4th degree without surgery - physiotherapeutic treatment (lateral electrical muscle stimulation), LFK, massage - are ineffective.
Some experts argue that exercises for scoliosis of the 4th degree are contraindicated due to severe skeletal deformation and serious physical limitations. Others believe that in cases of juvenile curvature of the spine, i.e. In children 4-11 years old, three-dimensional exercises and special breathing techniques according to the method of Katharina Schroth can have a therapeutic effect: strengthening and normalizing the tone of the muscles of the trunk, pelvis, lower extremities; improving the work of the lungs and heart. [10]
Therapeutic massage for scoliosis 4 degree is carried out in courses - in order to correct the load on the paravertebral muscles.
For curvature exceeding 40-50°, surgical treatment by spondylodesis - fusion of several vertebrae with bone grafts and mechanical fixation with specially designed metal structures - is usually recommended; not static structures are used, but techniques of one-stage correction of deformity followed by dynamic fixation with a special endocorrector. Adults with degenerative scoliosis and spinal stenosis may require decompression surgery with spinal fusion; wedge osteotomy is used for lumbar scoliosis.
Read more - scoliosis: surgery
In idiopathic scoliosis of the 4th degree, it is rarely possible to make the spine absolutely flat, but it is possible to provide significant correction of both thoracic and lumbar scoliotic arches: to reduce the main frontal curve by approximately 50%, vertebral torsion by 10%, and the vertical position of the vertebral column by approximately 60% on average. [11]
In the period of postoperative rehabilitation is individually selected gymnastics for scoliosis 4 degree, which is aimed at relieving muscle spasms, restoring joint mobility and normal blood circulation.
On the other hand, early and late complications and consequences after surgery for 4th degree scoliosis cannot be ruled out:
- There may be significant blood loss, venous air embolism, respiratory distress syndrome, and spinal cord injury during surgery;
- The development of a secondary infection;
- Vertebral fixation errors with the development of a false joint;
- Neurological damage with loss of some function.
Correction of scoliosis with successful posterior fusion in children and adolescents may be complicated by continued growth of the anterior part of the vertebral body, which exacerbates its curvature and torsion. [12]
Prevention
If we look at scoliosis of the 4th degree as a neglected case of scoliotic disease, then it immediately becomes clear what its prevention consists in
These are preventive orthopedic examinations of schoolchildren - to identify the initial stage of any curvature of the spine, explaining (both to children and parents) the principles of correct posture and the consequences of their violation, performing posture exercises for children, swimming lessons.
Detected scoliotic deformity must be treated in a timely manner!
Forecast
Scoliosis of this degree can only be controlled, as it is a lifelong diagnosis. And often the prognosis is not very promising, even with all attempts to stop the progression.
Many patients find it difficult to work, so medical and social expertise in the established order can give disability for scoliosis of the 4th degree (with the subsequent registration of appropriate social payments).

