
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Radial nerve neuropathy
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 12.07.2025
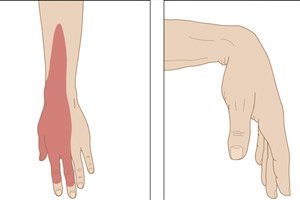
Is it difficult to move your arm in the elbow joint, is it numb, is there weakness in the wrist? Most likely, this is radial neuropathy or neuropathy of the radial nerve - a disease of the peripheral nervous system.
According to ICD-10, this condition is defined as mononeuropathy of the upper limbs and has the code G56.3 – radial nerve damage.
Epidemiology
Among neurological pathologies, almost half of the cases are peripheral neuropathies. And with various injuries to the upper limbs, on average, more than 3.5% are nerve damage.
The incidence of traumatic radial neuropathy in closed humeral shaft fractures is 2.5-18%. A fracture along the lower third of the humerus results in radial neuropathy in 15-25% of patients. Acute compartment syndrome occurs in approximately 6% of forearm fractures. [ 1 ], [ 2 ]
The clinical statistics of compression and ischemic neuropathy of the upper extremities are unknown, but tunnel syndromes account for at least 30% of cases.
Causes radial nerve neuropathy
As in the case of other mononeuropathies of the peripheral nerves, the key causes of neuropathy of the radial nerve (nervus radialis), which comes out of the brachial plexus (plexus brachialis) and follows along the arm to the wrist and fingers, consist of its traumatic or compression-ischemic damage, which leads to certain functional disorders.
And depending on their etiology and nature, the types of radial neuropathy are determined. Thus, traumatic and post-traumatic neuropathy of the radial nerve can be the result of a fracture of the humerus (in particular, its diaphysis at the junction of the medial and distal thirds), as well as a fracture affecting the place where the nerve passes through the intermuscular septum. [ 3 ]
A severe dislocation and fracture of the head of the radial bone (which is part of the elbow joint), as well as a fracture of the bones of the forearm, often cause traumatic damage to the posterior interosseous branch of the radial nerve, which innervates the posterior group of muscles from the elbow to the wrist joint.
In this case, the nerve can be damaged both by the fracture itself and as a result of transposition of bone fragments, installation of fixing devices or traction of the limb. Such consequences are also possible due to iatrogenic injuries during arthroscopy, endoprosthetics or synovectomy of the elbow joint and even during intramuscular injections into the shoulder area.
One of the most common types of neuropathy of the upper extremities is compression neuropathy of the radial nerve when it is pinched and/or compressed:
- in the armpit area (in case of shoulder joint injury or prolonged use of crutches);
- at the level of the middle third of the shoulder, between the humerus and the heads of the triceps brachii muscle - in the spiral groove (brachial canal);
- in the forearm - when the deep-lying posterior interosseous branch passes under the fibrous upper edge of the supinator muscle, known as the arch or arcade of Froese, and also at the exit of the superficial branch of the radial nerve from under the brachioradialis muscle of the forearm - as a complication of trauma to the middle of the forearm.
Associated with insufficient local blood supply and tissue hypoxia, ischemic neuropathy of the radial nerve can be a consequence of any traumatic and compressive impact, including all of those mentioned above.
Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome (branch of the radial nerve) or compartment syndrome of the forearm occurs when the nerve just below the elbow joint is compressed due to increased tissue pressure in the space between the muscle fasciae. This causes local blood circulation and trophism of the nerve tissue to deteriorate with decreased nerve cell function. The same condition can be caused by prolonged compression of the nerve by fibrous or bone neoplasms. [ 4 ]
In essence, tunnel neuropathy of the radial nerve is also compression-ischemic, since it occurs due to compression or impingement of this nerve - its posterior and superficial branches - when passing through narrowed areas (canals or tunnels). And among tunnel neuropathies, the following are distinguished: compression in the brachial canal - spiral canal syndrome; below the elbow joint - supinator syndrome; between the block-shaped humero-ulnar joint (articulated at the elbow joint) and the distal part of the supinator muscle - radial tunnel syndrome; in the radial canal of the wrist - Wartenberg syndrome. [ 5 ]
Also read:
Risk factors
The risk of developing radial nerve neuropathy is increased with constant (in most cases, occupational) overexertion of the upper limbs: actions with increased grip force, frequent changes in forceful supination and pronation, adduction-abduction and vibration.
Older people with osteoporosis are more likely to have fractures of the shoulder and forearm bones and injuries to the hand joints, so they are also at increased risk of peripheral neuropathies.
Predisposing factors include diseases of the joints and periarticular structures of the upper limbs, cysts, osteomas and tumors of soft tissues in the shoulder, forearm and wrist.
In addition, experts attribute the risks of developing radial compression-ischemic neuropathy to individual anatomical deviations (osteophytes, additional tendons and intermuscular septa), as well as some systemic metabolic diseases and chronic intoxications. [ 6 ]
Pathogenesis
The main mechanism of radial neuropathy in both traumatic and compression-ischemic lesions is blocking the transmission of nerve impulses along the radial nerve, i.e. disruption of the functions of the ion channels of the axon membranes, leading to a decrease in the excitability of neurons in the peripheral nervous system. In addition, nerve damage can negatively affect the condition of its myelin sheath with focal loss of myelin.
The pathogenesis of radiation neuropathy is directly dependent on the degree of nerve damage and can take one of three forms. In the form of neuropraxia, compression occurs without damage to the fibers and nerve sheath - with a temporary interruption in the transmission of nerve signals and loss of function. But with prolonged compression (as with tunnel neuropathies), additional factors appear: ischemic changes with deterioration of blood microcirculation and edema of the endoneurium of the nerve trunk.
More severe damage in the form of axonotmesis – with intra-trunk destruction of axons and their myelin sheath according to the type of post-traumatic degeneration, with the transformation of blood monocytes into macrophages, with the activation of macrophages and increased production of a number of pro-inflammatory cytokines, causing an inflammatory reaction and the appearance of neuropathic pain.
The most severe form of damage is neurotmesis, in which there is complete destruction of a nerve segment (its axons, myelin, endoneurium of the nerve trunk and connective tissue structures).
Symptoms radial nerve neuropathy
Specific clinical manifestations of radial nerve neuropathy are determined by the degree of its alteration and localization.
Injury to the radial nerve typically causes symptoms of numbness and tingling (paresthesia) on the back of the hand, near the first three fingers (thumb, index, and middle), as well as difficulty straightening the hand and neuralgia (burning pain). [ 7 ], [ 8 ], [ 9 ]
If compression neuropathy is caused by compression of a nerve in the upper arm or in the armpit area, the first signs include decreased cutaneous sensitivity of the dorsal surface of the entire upper limb, as well as difficulty in its movement in the sagittal plane - flexion-extension in the elbow and wrist joints with a condition such as wrist drop, that is, weakness of the wrist.
Radial tunnel syndrome also causes numbness on the back of the hand and fingers, a burning sensation and pain on the back of the thumb, pain on the side of the elbow, and pain on the back of the forearm. Pronation of the forearm and flexion of the wrist may increase symptoms. [ 10 ]
More details about the manifestations of this mononeuropathy in the publication - Symptoms of damage to the radial nerve and its branches
Complications and consequences
Traumatic radial neuropathy can result in peripheral paresis (weakness and numbness) or paralysis of the arm, since the deep branch of the radial nerve provides motor innervation to the muscles responsible for extension of the elbow, wrist, and first three fingers.
Denervation and loss of motor function may be complicated by gradual muscle atrophy and myogenic contracture.
In addition, there is a high probability of developing focal inflammation of the radial nerve trunk - neuritis.
Complete destruction of the damaged area of the nerve causes fibrosis of its trunk, which prevents axon regeneration and leads to disability.
Diagnostics radial nerve neuropathy
Radial nerve injuries and peripheral neuropathy are usually diagnosed by physical examination of the patient using specific tests that determine the strength of the innervated muscles, the presence of motor reflexes, the nature of movement disorders, and the level of sensitivity of the upper extremities.[ 11 ]
Instrumental diagnostics are used: electroneuromyography (electrophysiological study of nerve conduction), radiography, ultrasound of nerves, MRI. [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics are performed with neuropathy of other nerves originating in the brachial plexus (musculocutaneous, median, ulnar and medial cutaneous); with radicular syndromes and sensory neuropathies in various neurological disorders of the central nervous system; with diseases of the joints and periarticular structures of the upper limb (including professional tendovaginitis and de Quervain's syndrome); with early manifestations of syringomyelia and neurological symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
Who to contact?
Treatment radial nerve neuropathy
In case of neuropathy of peripheral nerves, including radial, treatment can be conservative and surgical.
To reduce pain, it is recommended to immobilize the limb with a functional splint or orthosis. For the same purpose, medications are taken:
- - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – Ibuprofen, Celecoxib, etc.;
- - anticonvulsants (anticonvulsants), such as Gabapentin (Gabantin, Gabalept).
Locally, it is possible to use gels and ointments with sodium diclofenac, Remisid gel (with nimesulide); ointments that activate local blood circulation with an analgesic effect (Apizartron, Menovazin, Gevkamon, Denebol, etc.).
In extreme cases, they resort to pain relief using novocaine blockade.
More information from the materials:
Injections of glucocorticoids (Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone, Triamcinolone) into the area around the affected nerve are aimed at relieving inflammation.
In case of ischemic neuropathy, microcirculation-activating angioprotectors are prescribed - Agapurin Retard (Pentoxifylline), etc., as well as vitamins B1, B6 and B12.
To improve the transmission of nerve impulses, cholinesterase inhibitors Ipidacrine (Amiridine) or Galantamine (Nivalin) are used parenterally.
In addition, physiotherapy treatment is prescribed, in particular, muscle electrical stimulation and other hardware procedures; more details in the article - Physiotherapy for neuritis and neuralgia of peripheral nerves. [ 14 ]
When the pain is relieved, a dosed physical load on the muscles of the upper extremities is necessary - exercise therapy for radial nerve neuropathy, which helps improve tissue trophism and neuromuscular conduction. Exercises for stretching the muscles of the shoulder, forearm and hands are selected individually, taking into account the general condition and specific diagnosis. [ 15 ]
Many patients find therapeutic massage helpful for radial nerve neuropathy.
Neuropathic pain can be treated with herbs – phytotherapy. The most common plants used to relieve pain symptoms include: ginkgo biloba leaves, which improve blood circulation in capillaries in ischemic tissue damage; calamus and turmeric roots; tarragon, which is rich in zinc (necessary for tissue regeneration); saffron, which reduces pain; extract of sage leaves and madder roots.
If there is no clinical improvement after long-term conservative treatment, depending on the location and extent of damage to the radial nerve – in severe and progressive cases – surgical treatment is performed.
A damaged nerve can be restored by microsurgical transplantation, but most often these are operations aimed at decompressing the radial nerve, for example, when the superficial branch is compressed by a tendon, its stretching incision or displacement is performed. The effectiveness of such an intervention is quite high - up to 50-80%, and the time for restoring nerve conduction ranges from three to four months.
Prevention
The main preventive measures consist of preventing injuries and excessive loads on the upper limbs.
Forecast
Restoration of nerve function and recovery prospects depend on many factors. For example, radial nerve neuropathy due to a closed humeral fracture is cured in 92-95% of cases, although treatment can last from several months to three to five years.
However, partial motor dysfunction and loss of sensitivity due to damage to the axons of the nerve fiber may remain permanently. [ 16 ]
But in the case of acute compression neuropathy, the symptoms of which appear within three to four months, the prognosis is almost always favorable.

