
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Pseudopodagra
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
Pseudogout is a disease characterized by infrequent acute attacks of arthritis and is distinguished by quite severe pain. As a rule, this disease develops due to the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate salts in the joints.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Epidemiology
Causes pseudogout
The most common causes of pseudogout include:
- When the level of calcium in the blood increases due to too much parathyroid hormone in the blood (this condition is called hyperparathyroidism).
- If there is an increased level of iron in the tissues (“hemochromatosis”).
- There is a decreased level of magnesium in the blood (“hypomagnesemia”).
Risk factors
Many cases of pseudogout in older people are idiopathic, but it is also often associated with trauma. Joint surgery, trauma, and metabolic diseases are common risk factors. A genetic predisposition to pseudogout has been proven.
Risk factors for pseudogout also include:
- Use of non-thiazide diuretics and proton pump inhibitors, which cause hypomagnesemia.
- Etidronate therapy and angiography.
Pathogenesis
The early stage of pseudogout is characterized by the fact that calcium pyrophosphate crystals begin to be deposited in the articular cartilage. Inorganic pyrophosphate is synthesized with the participation of phosphodiesterase pyrophosphatase (ENPP1), a catalytic enzyme contained in cartilage chondrocytes.
As a result of the accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joint cavity, the matrix is destroyed.
 [ 10 ]
[ 10 ]
Symptoms pseudogout
Symptoms of this disease can vary from minor pain to an acute attack resembling gout. Some patients suffer from frequent attacks of acute arthritis pain (usually in the knee and wrist joints), while others complain of dull and constant pain that prevents them from moving their arms and legs normally. The latter symptoms are very similar to rheumatoid arthritis.
It should be noted that pseudogout is characterized by less severe attacks than gout. It happens that there are no symptoms between attacks. Also, pseudogout is sometimes asymptomatic.
First signs
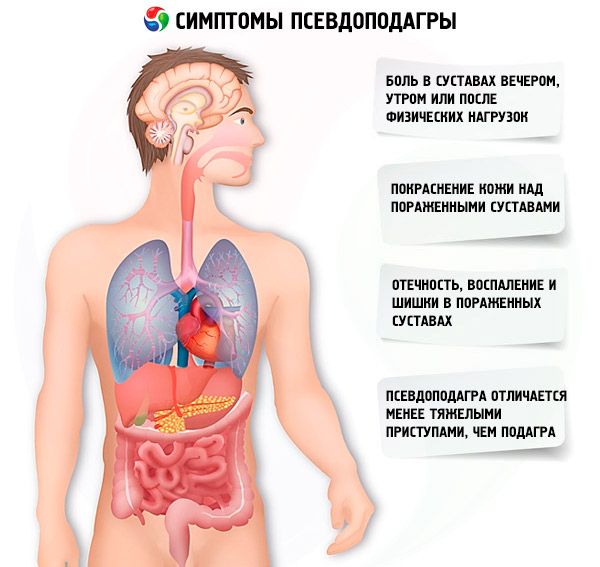
In the early stages, the patient may experience the following signs of the disease:
- Painful sensations arise in the joints, which manifest themselves in the evening, in the morning or after physical exertion.
- The skin in the affected area turns red.
- The skin becomes hot.
- The pain increases when you put pressure on the joint.
- The affected area swells, the joint may enlarge, and bumps often appear at the site of inflammation.
Stages
There are acute and chronic stages of pseudogout. In the acute stage of the disease, as a rule, only one joint is affected (usually the knee). The pain develops rapidly, the joint begins to swell, often accompanied by fever, increased ESR, chills. The acute stage lasts from four to six days, after which all its symptoms disappear completely.
The chronic stage of the disease is characterized by the patient complaining of constant aching pain. In the morning hours, the joints are stiff and slightly swollen. From time to time, acute attacks may occur, which quickly pass. As a rule, the shoulder, hip, wrist, and elbow joints are affected. Sometimes secondary radiculitis may develop against the background of the disease.
Forms
There are two types of pseudogout:
- Primary, idiopathic (familial).
- Secondary.
Primary pseudogout is diagnosed in 90% of patients. Its etiology is still unknown to date.
The development of secondary pseudogout occurs due to various diseases that are associated with improper metabolism of inorganic phosphate and calcium. It is believed that calcium pyrophosphate is deposited in the joints due to a violation of metabolism in cartilage cells, in particular, the enzyme phosphodiesterase pyrophosphatase. Because of this, pyrophosphate crystals begin to accumulate.
 [ 21 ]
[ 21 ]
Diagnostics pseudogout
To diagnose this disease, an X-ray examination of the affected joint is performed. Thanks to it, calcium pyrophosphate deposits in the joints can be detected. It is also important to conduct a microscopic examination of the synovial fluid, which is taken with a special needle from the joint that was inflamed. If calcium pyrophosphate is found in the fluid, and not urates, then the patient has pseudogout.
Tests
In addition to microscopic examination of synovial fluid, to diagnose pseudogout, patients often undergo blood tests for specific markers, hormone tests to rule out other diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gout, hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis).
 [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ]
[ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ]
Instrumental diagnostics
The most popular method of instrumental diagnostics of pseudogout is radiography of the affected joint. With the help of this study, the doctor can make a correct diagnosis, exclude other diseases with similar symptoms, identify possible complications, and determine the treatment method.
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
Differential diagnosis
This disease should be differentiated from the following diseases:
- Hydroxyapatite atropatheia.
- Gout.
- Septic arthritis.
- Reiter's syndrome.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Lyme disease.
- Joint injuries.
Who to contact?
Treatment pseudogout
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure pseudogout, since calcium pyrophosphate crystals cannot be removed from the joint. But modern methods of treatment help make attacks less painful and not so long. There are such directions in pseudogout therapy:
- Inflammation is relieved by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If their effect is insufficient, corticosteroid drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections into the joint (for example, hydrocortisone).
- To relieve pain, you can use popular painkillers.
- Sudden movements should be avoided.
- Physiotherapy procedures bring some effectiveness.
- In rare cases, surgery may be required.
- During remission, you can do special physical exercises and therapeutic gymnastics.
Medicines
- Indomethacin. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is a derivative of indoleacetic acid. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects. When used as tablets or injections, it helps reduce pain, especially in the joints.
The dosage is determined by the doctor individually. It depends on the severity of the disease. The standard dose is no more than 25 mg of the drug two or three times a day. When using the drug, the following side effects are possible: vomiting, headaches, dizziness, allergic reactions, convulsions, drowsiness, and a feeling of fatigue.
The drug is not recommended for use in case of intolerance to its components, stomach ulcers, hematopoiesis disorders and liver failure.
- Cortisone. A hormonal steroid drug that affects electrolyte, carbohydrate and water metabolism. It has a powerful anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and desensitizing effect. Increases the excretion of calcium from the body.
The dosage is individual. But the daily dose should not exceed 300 ml calculated for several injections. Children need to reduce the dose.
Taking this medicine may cause the following side effects: osteoporosis, increased appetite, weight gain, swelling, stomach ulcers, mental illness, hyperhidrosis. The drug is contraindicated in: ulcers of the duodenum and stomach, Cushing's disease, thromboembolism, osteoporosis, glaucoma, systemic mycosis, pregnancy.
- Ibuprofen. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. The active ingredient is ibuprofen. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
Prescribed from 12 years. The standard dosage is as follows: two to three tablets per day. To achieve a therapeutic effect faster, the dose can be increased to two tablets at a time. The therapy lasts no more than five days.
When taking the drug, the following side effects are possible: bronchospasms, toxic hepatitis, hearing loss, vomiting, headaches, allergies, cystitis.
The drug is contraindicated in: stomach ulcers, hemophilia, inflammatory bowel diseases, internal bleeding, kidney diseases, intolerance to components, during pregnancy, children under 12 years of age.
- Diprospan. The active ingredients are betamethasone sodium phosphate and betamethasone dipropionate. This is a hormonal steroid drug that is used for injections. It can be used intra-articularly or periarticularly. If injected into large joints, the dosage can be up to 2 ml. In small joints - up to 0.5 ml.
Side effects from using the product: chronic heart failure, stomach ulcer, muscle weakness, tendon rupture, cramps, limb atrophy, allergy. The drug is contraindicated in: systemic mycoses, infectious arthritis, intolerance to components, children under 6 years old, pregnant women.
Traditional and herbal medicine
One of the folk remedies is to apply heat to the affected joint. For this purpose, it is recommended to use special compresses of birch leaves (dry or fresh will do). To prepare a decoction, you need to brew them in boiling water and then let them cool. These leaves need to be applied to the joint and carefully secured with a bandage. To achieve a therapeutic effect, hold the compress for at least half an hour. Repeat the procedure every ten days.
The following recipes will be no less effective in this case:
- Nettle leaves, corn silk, beans, wild pansy flowers. These plants are used to make decoctions and compresses.
- Tinctures are made from elderberry flowers or blackcurrant leaves.
- You can make an infusion of St. John's wort, oregano, yarrow, elecampane root, linden and calendula. Drink it twice a day.
 [ 37 ]
[ 37 ]
Surgical treatment
In severe cases, when other conservative treatment methods are not effective, surgical treatment of pseudogout is performed, which involves replacing damaged joints with artificial ones.
Diet for pseudogout
Diet for pseudogout has no noticeable effect. Despite the fact that the basis of the crystals that damage the patient's joints is inorganic calcium, the use of products with a high calcium content (cottage cheese, milk) does not affect the clinical picture of the disease.
 [ 38 ]
[ 38 ]
Prevention
Doctors recommend following these guidelines to avoid pseudogout:
- You should avoid rapid weight gain, so make sure you eat right.
- You need to lead an active lifestyle and do physical exercise.
- You shouldn't put too much stress on your joints.
- If you notice the first signs, immediately contact a rheumatologist.

