
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Pituitary prolactinoma in women, pregnancy and men
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
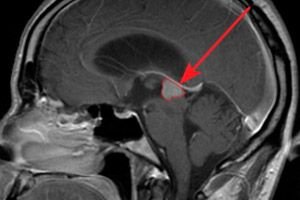
A hormonally active tumor of the anterior pituitary gland is a prolactinoma. Let's consider the reasons for its occurrence, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic and treatment methods.
Prolactinoma is a neoplasm that forms on the endocrine gland – the pituitary gland. It is located deep in the brain and is a benign pathology.
According to the international classification of diseases ICD 10, it falls under the category Neoplasms (C00-D48):
D10-D36 Benign neoplasms.
- D35 Benign neoplasm of other and unspecified endocrine glands.
- D35.2 Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland.
This name of the pituitary gland lesion is associated with one of its symptoms – the production of an increased amount of the hormone prolactin. Normally, it is produced only in women in the last months of pregnancy and continues to be secreted during breastfeeding.
Together with follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, prolactin affects sexual functions. In women, they ensure a regular menstrual cycle and estrogen synthesis. And in men, they ensure sperm activity and testosterone production. With an excess of hormones secreted by a tumor, estrogenogenesis is suppressed in women, which leads to anovulation and infertility. In men, this reduces sexual desire, erectile dysfunction and gynecomastia occur.
Epidemiology
Prolactinomas are benign pituitary adenomas. Statistics indicate that their incidence is about 30%. This lesion very rarely takes a malignant form - in 2% of cases. Such degeneration is most often diagnosed in women of childbearing age. The size of the tumor in women is about 2-3 mm, while in men, adenomas are more than 1 cm in diameter.
Causes prolactinomas
Modern endocrinology and genetics are still continuing research to determine the cause of prolactinoma. Very often, the disease is detected against the background of genetic disorders. For example, multiple endocrine neoplasia type I (hereditary pathology) is characterized by increased production of hormones of the pituitary gland, parathyroid and pancreas.
Many scientists are inclined to believe that damage to the pituitary gland and increased production of prolactin can be caused by the following factors:
Diseases:
- Infections (encephalitis, meningitis).
- Infiltrative and granulomatous processes.
- Trauma (neurosurgery, radiation, cerebral peduncle rupture).
- Metabolic disorders.
- Tumors (germinoma, meningioma).
- Cirrhosis.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Chest injuries and breast stimulation.
- Primary hypothyroidism.
- Ectopic secretion of hormones.
Taking medications:
- Antidepressants.
- H2 blockers prescriptions.
- Opiates and cocaine.
- Dopamine blockers.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Estrogens.
- Adrenergic inhibitors.
When determining the cause of the disease, special attention is paid to the drug history. At the same time, the fact that taking oral contraceptives does not affect the risk of formation or growth of prolactinomas is taken into account.
Microadenoma and prolactinoma
The pituitary gland is a cerebral appendage located on the lower surface of the brain. It is the central organ of the endocrine system and produces hormones that are responsible for growth, metabolism, and the reproductive system. Microadenoma and prolactinoma are tumor lesions of the pituitary gland. Let's consider each of these pathologies in more detail:
- Microadenoma is a neoplasm, usually benign. It provokes uncontrolled growth of glandular cells due to various disorders and anomalies. The tumor volume is about 10 mm.
Reasons:
- Skull and brain injuries.
- Genetic determinants.
- Inadequate blood supply to the pituitary gland.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Neuroinfections involving the structures and membranes of the brain and spinal cord in the pathological process.
In addition to the above factors, the disease can occur due to abortions, pregnancies and breastfeeding, hormonal contraception. According to medical statistics, microadenoma is more often diagnosed in women. In men, it is detected during puberty and treated with hormonal drugs.
- Prolactinoma is a benign lesion of the anterior pituitary gland. It is most often detected in middle-aged people. Women are more susceptible to this disease than men.
The main symptom is increased production of prolactin. This hormone regulates milk secretion, the reproductive system and reproductive capacity. Excess hormone inhibits the synthesis of female estrogen, which leads to suppression of ovarian function, menstrual irregularities and infertility. In men, the disorder manifests itself as decreased testosterone levels and impaired sexual activity.
Pituitary adenoma and prolactinoma
According to medical research, pituitary adenoma and prolactinoma are tumors of the same origin. The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland that is located on the lower surface of the brain. Through an opening in the dura mater, it contacts the hypothalamus, forming a close functioning. Both parts of the brain form the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which regulates and controls the work of the endocrine glands.
There are many tumors of the pituitary gland, which are called adenomas. Let's take a closer look at the features of the organ's structure:
- The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) makes up about 80% of the gland. It consists of glandular cells of different types that secrete a separate type of hormone. It is responsible for the production of the following hormones:
- Prolactin is responsible for the menstrual cycle and metabolism, regulates lactation and milk production.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone – the thyroid gland and the synthesis of its hormones.
- Luteinizing hormone – synthesis of steroid hormones, ovulation, formation of the corpus luteum in the ovaries.
- Adrenocorticotropic – the secretion of steroid hormones by the adrenal glands.
- Follicle-stimulating – responsible for the growth of the endometrium, maturation of follicles and the formation of steroid hormones.
- Somatotropic is a growth hormone, responsible for the breakdown of glucose and fats, and activates protein synthesis.
- The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) produces and accumulates hormones, consists of nerve cells, fibers and neurosecretory bodies. Responsible for the production of the following hormones:
- Vasopressin – affects the brain and blood vessels, regulates kidney function and the amount of water in the body.
- Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and the release of breast milk.
A pituitary adenoma is a benign tumor of glandular tissue that forms only in the anterior lobe of the organ. At the same time, prolactinoma is a hormonally active formation with extremely slow growth.
Risk factors
Hormonally active neoplasm in the pituitary gland occurs for many reasons, some of which have not yet been established. There are risk factors that increase prolactin levels and may lead to the formation of a prolactinoma:
- Improper functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Chest injuries.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Renal failure.
- Dysfunction of the hypothalamus.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Liver hypofunction.
- Increased physical activity.
- Neuroinfections.
- Long-term drug therapy.
- Taking medications that affect hormone production.
The tumor promotes increased production of prolactin. This hormone is responsible for the normal lactation process. Prolactinoma is one of the most common pituitary tumors.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of prolactinoma development is not fully understood. The pathogenesis of the tumor is associated with two theories:
- Internal defect – a genetic disorder of at least one cell of the pituitary gland provokes the transformation of the organ into a tumor with its further growth.
- Disorder of hormonal regulation of pituitary gland functions – this process is associated with the functioning of hypothalamic releasing hormones – liberins and statins. When they are produced in excess, hyperplasia of glandular tissues occurs, which initiates the tumor process.
The formation of neoplasms is also associated with the influence of certain hereditary factors.
Symptoms prolactinomas
Hormonal-dependent damage to the pituitary gland most often makes itself known with a sharp increase in prolactin levels and compression of the surrounding brain tissue by the tumor. Symptoms of prolactinoma directly depend on its size.
If the tumor is no more than 10 mm, the following symptoms are observed:
- Severe headaches, most often occurring in the temple area and are constant. This symptom is associated with increased intracranial pressure and pressure from the formation on the surrounding structures of the brain.
- Various visual impairments are associated with the pinching of the optic nerves that pass near the pituitary gland. Patients complain of narrowing of the visual field, decreased color perception, diplopia, strabismus, and decreased visual acuity.
- Pain in the face, upper cheeks, wings of the nose, upper lip and outer edge of the eye. Discomfort occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by the tumor. The functioning of the facial muscles is not impaired.
If the tumor is larger than 10 mm, it is called macroprolactinoma. It can cause blindness, pathological symptoms of the central nervous system, and emotional instability. Large tumors lead to disruption of the production of other hormones of the gland.
First signs
The larger the size of the tumor, the more pronounced the symptoms indicating its presence. The first signs of prolactinoma:
- Headaches.
- Increased irritability.
- Anxiety.
- Long-term depressive state.
- Double vision.
- Decreased visual acuity.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms increase. Due to excessive hormone production, the tumor exerts a compressive effect on adjacent tissues. This is manifested by a disruption of the functions of organs located near the pituitary gland.
Symptoms of Prolactinoma in Women
The first symptoms of prolactinoma in women are as follows:
- Changes in the rhythm of the menstrual cycle, up to and including its cessation.
- Lack of ovulation and inability to conceive. This occurs due to a disruption in the formation of hormones (follicle-stimulating and luteinizing) responsible for the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
- Long-lasting headaches.
- Breast size reduction.
- Discharge of a milk-like fluid from the nipples.
- Vaginal dryness.
- Decreased libido due to changes in estrogen levels.
In addition to the above symptoms, the disease provokes psycho-emotional disorders:
- Decreased concentration.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Increased fatigue.
- Nervous excitability.
- Sleep disorders.
- Depressive state.
If pituitary gland lesions are detected in girls, then patients are diagnosed with:
- Underdevelopment of the genitals - reduction in the size of the uterus, labia minora and clitoris.
- In adolescence, the disease manifests itself in male-pattern hair growth. Coarse pigmented hairs appear on the upper lip, chin, chest and around the nipples, abdomen and other parts of the body. Due to the high level of prolactin, the adrenal glands actively work, producing androgens.
- Acne and pimples are associated with increased levels of male sex hormones.
- Obesity – excess weight gain occurs due to a disruption in fat metabolism.
- Multiple caries and frequent fractures are associated with calcium loss due to mineral metabolism disorders. Gradually, bone tissue loses minerals and other useful substances, becoming more fragile.
The above symptoms of the disease can occur both in combination and in isolation.
Symptoms of Prolactinoma in Men
Hormone-dependent pituitary tumors in men are diagnosed much less frequently than in women.
Let's look at the main symptoms of prolactinoma in men, caused by a decrease in testosterone levels and spermatogenesis:
- Weakening of sexual desire.
- Decreased potency.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Infertility.
- Enlargement of the mammary glands.
- Testicular atrophy.
- Reducing facial hair growth.
- Muscle weakness.
- Osteoporosis.
- Severe headaches.
- Impaired visual acuity.
Men are often diagnosed with macroprolactinomas, that is, large tumors.
Prolactinoma in children
According to medical statistics, prolactinoma is rare in children. The disease accounts for about 50% of all pituitary adenomas, which account for 2% of intracranial tumors. Symptoms of the pathological condition in children are scanty and are associated with hormonal changes.
Signs of the disorder in girls:
- Primary or secondary amenorrhea.
- Change in body weight (obesity).
- Galactorrhea is a discharge from the nipples.
In boys, the disease may not have any symptoms. Because of this, the tumor is detected accidentally during CT, MRI of the brain and other studies. In some cases, the only sign of the disorder is delayed puberty.
A long-standing tumor of the anterior pituitary gland disrupts the secretion of gonadotropins, which leads to insufficiency of the functions of the sex glands and disorders in the synthesis of sex hormones. Neuro-ophthalmological symptoms also occur: headaches, dizziness, attention disorders, visual disturbances.
Treatment is aimed at stabilizing the hormonal background in the child's body. Dopamine mimetics are used for this. Such therapy has a quick and long-term effect. Surgical treatment is carried out extremely rarely, and as a rule, when the affected organ is inflamed.
Prolactinoma and pregnancy
A fairly frequently diagnosed pathology in women is prolactinoma. Pregnancy can be its provoking factor. Particular attention is required for patients with adenoma who want to have a child. They are prescribed dopaminergic drugs for a year before the planned conception. At the same time, to reduce the risk of unplanned pregnancy during this period, the use of barrier contraception is recommended.
- If the disease is detected at an early stage, there is a high risk of miscarriage. Therefore, the patient should be under the supervision of a gynecologist and endocrinologist throughout the first trimester. The patient is prescribed medicinal analogues of natural progesterone (the drug Utrozhestan).
- If the tumor size is no more than 6 mm, it rarely progresses or complicates the course of pregnancy. Lesions of the pituitary gland more than 6 mm require careful monitoring. Since they provoke a sharp increase in estrogen, visual impairment and frequent headaches.
- Such a study as magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended during pregnancy, so the size of the neoplasm can only be determined by symptoms. Particular attention is paid to determining the level of prolactin in the blood. Since the indicators of this hormone make it possible to draw conclusions about the state of the female body.
Tumor treatment is not performed during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the prescription of drugs that normalize hormonal levels has a negative effect on further gestation and future lactation. A control MRI is performed a couple of months after childbirth. If tumor growth is observed, suppression of milk production is required. According to statistics, an increase in neoplasms occurs in 15-35% of cases of the disease.
Prolactinoma and breastfeeding
The effect of pregnancy on prolactin secretion in women with hormonally active pituitary adenoma manifests itself in different ways. Symptoms and future prognosis depend entirely on the size of the prolactinoma. Breastfeeding is contraindicated when the tumor grows and the patient's condition worsens. In this case, drugs are prescribed that stop milk production, and the woman is sent for additional examination and treatment.
If the size of the neoplasm does not increase, then lactation is allowed for up to 2-3 months with regular MRI, monitoring of visual fields and prolactin levels. With longer breastfeeding, there is a risk of the adenoma becoming malignant.
Stages
Benign pituitary lesions, like many other diseases, have certain stages. Tumors are divided depending on their size and location within the pituitary fossa:
- The first stage is intrasellar microprolactinomas. Their size does not exceed 1 cm, they do not go beyond the boundaries of the sella turcica of the pituitary gland.
- The second stage is extrasellar macroprolactinomas. They grow to more than 1 cm and extend beyond the sella turcica of the pituitary gland, compressing the surrounding tissues and organs.
The size of the tumor affects the symptoms of the disease, which are caused by local pathological changes. In addition, the method of treatment depends on the stage of the disorder.
Forms
Pituitary adenoma can be hormonally inactive or active. The types of the latter depend on the production of hormones by the cells that make it up.
The main classification of pituitary adenomas:
- Somatotropin-producing – promotes increased production of growth hormone.
- Prolactin-secreting – characterized by excessive synthesis of prolactin.
- Adrenocorticopine-producing – secretes adrenocorticotropic hormone.
- Thyrotropin-producing – produces thyroid-stimulating hormone.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone – causes an increase in the level of gonadotropic hormones.
The division of prolactinoma is carried out as follows:
- Functional – occurs during pregnancy and lactation.
- Iatrogenic – provoked by pharmacological drugs.
- Tumor - associated with the development of microadenomas and macroadenomas of the pituitary gland.
Each type of disease can cause infertility, menstrual cycle and potency disorders, CNS disorders and other pathological symptoms.
Complications and consequences
Hormonally active pituitary adenoma, left without medical care, can lead to serious problems. The main consequences and complications of prolactinoma:
- Visual impairment and blindness occur due to the growth of the tumor and its pressure on the optic nerves.
- Osteoporosis – loss of bone mass is associated with decreased production of testosterone and estrogen.
- Hypopituitarism - due to tumor growth and increased prolactin levels in the body, hormonal imbalance, adrenal cortex insufficiency, and hypothyroidism occur.
In addition to the above problems, prolactinoma very often leads to pregnancy complications. During normal pregnancy, a woman's pituitary gland increases in size, which leads to the production of prolactin. But if conception occurs against the background of its high level, there is a risk of miscarriage, especially in the early stages.
Diagnostics prolactinomas
A pituitary tumor can be suspected by characteristic clinical symptoms. Prolactinoma diagnostics consists of:
- Collection of anamnesis and analysis of patient complaints.
- Identification of disease symptoms and assessment of its severity.
- Laboratory research.
- Instrumental diagnostics.
- Complex of differential procedures.
The most informative diagnostic method is considered to be MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent. It is used to determine the location of the tumor and its size. To identify macroprolactinoma, CT is performed, which provides good visualization of the structures of the sphenoid bone. Laboratory tests consist of hormonal studies. If the disease is accompanied by visual impairment, then an ophthalmologist consultation is necessary.
Tests
Laboratory diagnostics of prolactinoma consists of:
- Determination of the level of pituitary hormones in the blood serum.
- Blood test for prolactin.
- Blood tests for other pituitary hormones. An increase in one or more indicators may indicate a pituitary adenoma.
Particular attention is paid to determining the prolactin level. The hormone level depends on the size of the tumor. The presence of a neoplasm is indicated by prolactin above 200 mIU/l. If there is a slight excess of the norm, then a three-fold analysis is prescribed with an interval of 7-10 days. This allows you to exclude fluctuations in the hormone due to stress and psycho-emotional tension.
 [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ], [ 39 ], [ 40 ]
[ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ], [ 39 ], [ 40 ]
Prolactin level in prolactinoma
The hormone that causes milk production in the postpartum period is prolactin (produced by pituitary cells). The level of prolactin in prolactinoma depends on many factors. Its indicators regulate reproductive and sexual functions in the human body. And their violation leads to the development of various pathological symptoms.
The first prolactin is formed in the child's body immediately after birth. In the first weeks of life, its indicators are high - about 2000 mIU / l. With a pronounced increase in the hormone, the mammary glands swell in children and a small amount of milk may be released. In a one-month-old child, the prolactin level stabilizes and is 607 mIU / l in boys and 628 mIU / l in girls. As they grow older, the indicators fluctuate from 40 to 400 mIU / l. In girls, these values are higher than in boys.
- If the prolactin level is higher than normal, it can lead to the development of prolactinoma, hypothyroidism, polycystic formations on the ovaries. Increased values are observed in the last months of pregnancy.
- If prolactin is below normal, it causes problems with reproductive function, birth bleeding, post-term pregnancy, tumor lesions of the brain. Also observed are disorders of the central nervous system and excessive hair growth on the body, swelling.
To make a final diagnosis when prolactin levels change, you should undergo a comprehensive examination by the following specialists: gynecologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist.
Instrumental diagnostics
Another way to detect a pituitary tumor and its characteristics (size, location, complications) is instrumental diagnostics. The patient is most often prescribed:
- Magnetic resonance imaging is performed with the introduction of contrast agents that improve the visualization of the tumor. After contrasting, the outlines of the prolactinoma are easily determined against the background of the pituitary tissue, as well as its size and localization.
- Computer tomography – is performed for neoplasms larger than 1 cm to assess the degree of bone destruction. During diagnostics, symptoms of destruction of the sella turcica and dura mater are detected.
- Craniography is an X-ray examination of the skull in direct and lateral projections. The disease is characterized by a change in the shape and size of the sella turcica.
In addition to the above studies, an ophthalmologist consultation is necessary. The doctor determines compression of the optic nerves, decreased visual acuity and disorders of the oculomotor nerves. A mammologist consultation is mandatory to exclude tumors of the mammary gland. The patient undergoes mammography and ultrasound of the glands. An assessment of the density of bone formations is also necessary to exclude the development of osteoporosis.
What do need to examine?
Differential diagnosis
If a benign neoplasm in the pituitary gland is suspected, a comprehensive set of studies is indicated. Differential diagnostics of prolactinoma is carried out with the following diseases:
- Endocrine pathologies.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Adrenogenital syndrome.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Somatic pathologies, for example, renal failure.
- Physiological galactorrhea (may persist in children under 3 years of age and after lactation in women).
- Neuroreflex galactorrhea and hyperprolactinemia.
All possible hormonally active and non-hormonal lesions of the pituitary gland are also taken into account. Based on the results of differentiation, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and draws up a treatment plan.
Who to contact?
Treatment prolactinomas
The choice of treatment method for prolactinoma is individual for each patient. The therapy prescribed by the doctor has the following goals:
- Restoration of pituitary gland functions.
- Reduction of the tumor size or its complete removal.
- Restoring prolactin levels in the blood.
- Elimination of pain symptoms and complications: headaches, visual and central nervous system disorders, galactorrhea.
The treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist and a gynecologist. The patient undergoes drug therapy with drugs that slow tumor growth, reduce prolactin levels and restore sexual function in both men and women.
The main disadvantages of taking medications are that they cause side effects and require a long period of use. In some cases, after stopping taking the pills, the hormone level increases again. If prolactin levels remain normal for 6 months after the start of treatment, then the therapy is suspended. In this case, the doctor recommends preventive courses with taking medications every 2 years. Such treatment allows you to reduce the size of the tumor and avoid surgery.
Medicines
To treat prolactinoma, drugs from the group of dopamine receptor agonists are used. The drugs are necessary to normalize prolactin levels, improve the functioning of the pituitary gland, reduce the size of the tumor (observed after 6-12 weeks of treatment) and eliminate its painful symptoms.
Dopamine agonists:
I generation – Ergot and its derivatives:
- Lysergic acid derivatives: Bromocriptine, Methysergide, Ronalin, Parlodel.
- Aminoergoline derivatives: Lisuride, Tergulide, Mesulergin.
- Clavine derivatives: Pergolide, Methergoline.
The second generation is non-ergot-containing dopamine-mimetic drugs: Quinagolide, Quinagolide.
III generation – selective inhibitors of D2-receptors of pituitary lactotropes: Cabergoline
Most often, patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- Norprolac
A drug from the pharmacotherapeutic group of B2-dopamine receptors. Suppresses prolactin secretion without affecting the state of other pituitary hormones. Clinical reduction of the hormone is observed two hours after taking the drug and reaches a maximum after 4-6 hours with a single dose. It has a prolonged effect, which lasts for about 24 hours. Long-term use of the drug leads to the reverse development of prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors, that is, their reduction or delay in their growth.
- Indications for use: increased blood levels of the pituitary hormone that stimulates milk production, micro or macroadenomas of unknown origin, oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, galactorrhea, infertility, decreased libido.
- Method of administration: the dosage is set individually for each patient. The initial dose is 0.025 mg once a day for three days. The next three days take 0.05 mg. From the seventh day of treatment, the daily dose is 0.075 mg. If necessary, it is possible to gradually increase the dosage to achieve the optimal therapeutic effect. In this case, the interval between dose changes should be at least a week, and the maximum daily dosage should not exceed 0.075-0.15 mg.
- Side effects: headaches and dizziness, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness. In rare cases, acute psychosis develops, which passes after discontinuing the drug. Loss of appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, decreased blood pressure, nasal congestion are also possible. A sharp decrease in blood pressure, i.e. orthostatic collapse, occurs extremely rarely.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. With special caution it is prescribed for patients with a history of mental illnesses. And also for people whose work is associated with rapid motor or mental reactions.
Norprolac is available in tablet form of 0.025; 0.05; 0.075 and 0.15 mg of active ingredient.
- Bromocriptine
A specific stimulator of dopamine receptors. Slows down the secretion of hormones of the anterior pituitary gland, which are responsible for milk production. The use of this drug prevents the lactation process, inflammation of the mammary gland tissue during breastfeeding and its engorgement. Restores ovarian function and the menstrual cycle, promotes conception in women with hyperprolactin amenorrhea.
- Indications for use: suppression of prolactin production and normalization of its levels, galactorrhea, cessation of postpartum lactation.
- Method of administration: the drug is taken orally at 2.5 mg twice a day during meals. Duration of treatment is 10-17 days. Therapy is stopped only on doctor's prescription. This is due to the fact that premature withdrawal of the drug may lead to restoration of lactation.
- Side effects: nausea, vomiting, headaches, decreased blood pressure, whitening of the fingers when exposed to cold.
- Contraindications: intolerance to the components of the drug, first trimester of pregnancy, cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, narrowing of the lumen of peripheral vessels, mental illness. During treatment, it is contraindicated to consume alcohol, oral contraceptives and drugs that depress the central nervous system.
Bromocriptine is available as 2.5 mg tablets and 5 and 10 mg capsules.
- Parlodel
A medicinal product with the active component bromocriptine. The active substance binds to dopamine cerebral receptors D2. It has a stimulating effect, inhibiting the processes of prolactin molecule incretion. Due to this, the effect on the pituitary-ovarian system is ensured, the lactation process is suppressed and the menstrual cycle is normalized. The drug reduces the severity of Parkinson's disease symptoms, reduces the concentration of somatotropin, improves the condition in acromegaly. Eliminates the symptoms of depressive disorder.
- Indications for use: prolactinoma, hyperprolactinemia due to drug therapy, infertility in both sexes, menstrual irregularities, polycystic ovary syndrome, decreased libido, impotence, oligospermia. Prescribed for adenomatous lesions of the pituitary gland, acromegaly, postpartum mastitis, and when it is necessary to stop lactation. Used in preparation for surgery as a means of reducing tumors and in postoperative therapy to reduce prolactin levels. The drug is effective in idiopathic Parkinson's disease and postencephalic parkinsonism.
- Method of administration: tablets are used orally. For prolactinoma, the dosage is selected individually for each patient. As a rule, patients are prescribed 2.5-3.75 mg per day. The maximum dosage for children under 12 years old is 5 mg per day, for children over 12 years old - up to 20 mg per day.
- Side effects: dizziness and headaches, dermatological reactions, tachycardia, alopecia, bowel disorders, confusion, sleep and appetite disorders, tinnitus. It is also possible to develop asthenic conditions, hallucinations, various movement disorders, paresthesia, etc.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, gestosis, premenstrual syndrome, arterial hypertension, lactation, benign mammological pathologies, cardiovascular diseases, mental disorders. The use of the drug during pregnancy is possible only if there are justified indications and strictly under medical supervision.
- Overdose: dyspepsia, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, hallucinations, tachycardia, drowsiness, fever, orthostatic hypotension. Gastric lavage is indicated to eliminate the above symptoms. Metoclopramide is recommended to eliminate vomiting and hallucinations.
Parlodel is available in tablet form in packages of 10 and 30 capsules.
- Lisurid
A drug with antiserotonin activity. Belongs to dopamine receptor agonists.
- Indications for use: prolactinoma, hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism, acromegaly. Also prescribed for parkinsonism, allergic diseases and for the treatment of migraine (reduces the frequency and intensity of attacks).
- Method of administration: orally 0.025 mg 1-2 times a day. The duration of treatment is individual for each patient, therefore it is determined by the attending physician.
- Side effects: various dyspeptic symptoms, drowsiness, decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, pregnancy. The tablets are not prescribed to patients with low blood pressure, with peripheral circulatory disorders, ischemia, severe renal and hepatic dysfunction.
Lisuride is available in the form of tablets containing 0.025 mg of the active ingredient.
- Cabergoline
A dopamine D2 receptor agonist, an ergot alkaloid derivative. Stimulates pituitary receptors, causing pronounced and prolonged inhibition of the secretion of the anterior lobe hormone – prolactin. Suppresses and stops physical lactation, has a therapeutic effect in menstrual irregularities, infertility, decreased libido, impotence.
- Indications for use: macro and microadenomas of the pituitary gland, idiopathic hyperprolactinemia, suppression of lactation in the postpartum period.
- Method of administration and dosage: the drug is used orally, the dosage and duration of therapy depend on the stage of the pathological condition and the doctor's prescriptions, therefore they are individual for each patient.
- Contraindications: individual intolerance to the components of the product, pregnancy, severe liver dysfunction, history of postpartum psychosis. The drug is prescribed with special caution to patients with cardiovascular diseases, ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum.
- Side effects: headaches and dizziness, nausea, abdominal pain, decreased blood pressure, increased drowsiness. With systematic use of the drug, soreness of the mammary glands, paresthesia, depression, asthenia are observed.
- Overdose: fainting, hallucinations, nasal congestion. Treatment is symptomatic with monitoring and maintenance of blood pressure.
Cabergoline is available as a powder substance in polyethylene bags.
In addition to the above-mentioned drugs, the following may be prescribed for the treatment of hormonally active pituitary adenoma: Levodopa, Lergotril, Cyrogeptadine, Quinagolide, Abergin, Peritol and other drugs.
If dopamine agonists cause severe side effects in the patient (headaches, dizziness, confusion, increased weakness, nausea and vomiting), then Domperidone is recommended to eliminate them. It should be taken one hour after the main drug. To monitor the effectiveness of the therapy, the level of prolactin in the blood serum should be regularly checked.
Treatment of prolactinoma with Dostinex
An effective drug from the pharmacotherapeutic group of dopamine agonists is Dostinex. Treatment of prolactinoma with Dostinex allows achieving stable therapeutic results in a short period of time.
The active substance of the drug is cabergoline (an ergoline derivative) with pronounced prolonged activity. Its mechanism of action is based on the blockade of hormone secretion by stimulating lactotrophic cells of the pituitary gland D2-dopamine receptors. High doses have a central stimulating dopaminergic effect on D2 receptors.
After oral administration, the drug is rapidly absorbed from the digestive tract. The maximum concentration is observed 1-4 hours after administration. The half-life in urine is 68-115 hours. Due to this half-life, equilibrium concentrations of the drug are reached after 28 days. The level of binding to plasma proteins is about 40%. A decrease in prolactin levels is observed three hours after administration and lasts for 7-28 days. The therapeutic effect during postpartum lactation lasts about 14-21 days.
- Indications for use: prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma, hyperprolactinemia causing infertility, menstrual irregularities, galactorrhea, impotence, decreased libido. Suppression of physiological lactation after childbirth, empty sella syndrome, prevention of lactation after abortion or miscarriage.
- Method of application: in case of tumor damage of the anterior pituitary gland, patients are prescribed 0.25-0.5 mg 1-2 times a week on certain days. For example, every Tuesday or Tuesday and Friday. If necessary, the dosage is increased by 0.5 mg every month of treatment. As soon as the optimal dosage regimen is selected, the hormone level in the blood should be determined. In most cases, a stable therapeutic effect is achieved after 0.5-1 month of treatment.
- Side effects: headaches and dizziness, hypotension, insomnia, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain. Various dyspeptic phenomena, abdominal pain, hot flashes to the face, paresthesia are also possible. The most pronounced side effects make themselves known during the first two weeks of treatment. Pronounced adverse symptoms require discontinuation of the drug.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, liver failure, late gestosis, postpartum psychosis in the anamnesis. The drug is not intended for use during pregnancy. If conception occurs while taking it, Dostinex is canceled.
- Overdose: nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, arterial hypotension, various dyspeptic disorders. To eliminate them, gastric lavage and further symptomatic therapy with normalization of arterial pressure are indicated.
- Drug interactions: avoid concomitant use with ergot alkaloids. Also not recommended is the use of Butyrophenone, Phenothiazine, Metoclopramide, Thioxanthene, as Dostinex stimulates dopamine receptors, which may cause the ineffectiveness of the therapy. Medicines with a hypotensive effect are prohibited, as they can cause arterial hypotension.
Dostinex is available in tablet form – 8 tablets per package with 0.5 mg of active substance each.
Vitamins
One of the methods of prevention, successful treatment and recovery after prolactinoma and other tumor lesions of the body is vitamins. You should take useful substances after consulting with your doctor. Since some of them affect blood circulation in tissues, therefore, they can aggravate the painful condition.
The most useful vitamins for pituitary adenomas are A, E, C, as well as antitumor products based on cruciferous vegetables and flavonoids. In addition, there are ready-made pharmacy vitamin complexes to maintain brain health.
Let's look at the effects of certain vitamins on brain function:
- B1 – thiamine reduces fatigue and anxiety, improves sleep quality and coordination. Its deficiency leads to the development of anxiety and depression. Contained in oatmeal, nuts, buckwheat, pork and beef, fish.
- B2 – riboflavin accelerates mental reactions. It is a preventive measure against headaches, weakness and drowsiness. It is found in meat and dairy products.
- B3 – nicotinic acid is responsible for a cheerful state, good memory and the ability to concentrate. It is found in milk, fresh greens, nuts, buckwheat, egg yolk.
- B6 – pyridoxine fights anxiety and irritability, speeds up thought processes and increases intelligence. The substance is synthesized in the body and is found in the following products: potatoes, bananas, beans, milk, cabbage, eggs.
- B9 – folic acid helps eliminate insomnia, increased fatigue and apathy. It is present in fresh vegetables, hard cheeses, mushrooms, milk, apricots, meat. The synthesis of this vitamin is accelerated by eating bifidobacteria.
- B12 – cyanocobalamin is responsible for the normal switching of the body between sleep and wakefulness. Contained in seaweed, milk, shellfish, meat.
- C – ascorbic acid has antioxidant properties, protects the body from increased emotional and physical stress. Helps to better absorb vitamins from group B. It is found in large quantities in citrus fruits, vegetables and fruits.
- D – calciferol protects the body from malignant lesions, maintains the elasticity of the walls of capillaries and large vessels. Stops oxidative processes. It is formed in the body under the influence of solar radiation, in small quantities it is contained in dairy products, eggs, fish oil, fresh parsley.
- E-tocopherol acetate fights destructive processes in the body, strengthens the walls of blood vessels and prevents Alzheimer's disease. It is present in unrefined sunflower oil, milk, beans, beef and pork liver.
- P - bioflavonoid protects the brain from hemorrhages, as it prevents capillary fragility. It is found in green tea leaves, rowan, rose hips, black currants, lemon.
Each of the above vitamins plays an important role in the normal functioning of the body, but has the most pronounced effect in combination with other beneficial substances.
Physiotherapy treatment
Tumor lesions of the brain, including hormonally active neoplasms of the pituitary gland, are a direct contraindication for most physiotherapy procedures. Physiotherapy treatment can begin to stimulate tumor growth, so it is selected extremely carefully, taking into account all possible risks and complications.
Most often, patients are prescribed UHF - this is extremely high-frequency therapy using millimeter-range waves. The radiation has a moderate penetrating ability into biological tissues and acts in the superficial layers of the skin. It has a therapeutic effect on the body by activating internal energy sources.
When applied to a local painful area or biologically active points, it changes and stimulates the functioning of the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems. Increases the body's resistance to negative environmental factors.
Therapeutic effects:
- Stimulation of the nervous system.
- Improving the functioning of the immune system.
- Improving tissue trophism.
- Stimulation of regeneration and repair processes.
The types of UHF therapy are selected by a physiotherapist individually for each patient. Other physiotherapy procedures, such as massage of the collar zone or darsanval of the scalp (most often prescribed for severe headaches and dizziness) are contraindicated.
UHF is prescribed for immunodeficiency conditions, endocrine system diseases, cardiac pathologies, long-term non-healing wounds and ulcers. It helps with diseases of the ENT organs, lesions of the genitourinary and nervous systems, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Physiotherapy is contraindicated in cases of severe cardiac, renal or hepatic insufficiency, infectious diseases in the acute period, severe mental disorders, and during pregnancy.
Folk remedies
At the initial stages of prolactinoma development, many patients resort to using unconventional methods. Folk treatment is possible only with the consent of the attending physician, since some recipes can worsen the painful condition.
- Take equal proportions of lemon balm, valerian, plantain, sage and rowan berries. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over the ingredients and let it brew until it cools. Strain and take ½ cup during the day before each meal.
- Pour 10 g of dry St. John's wort with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for 30 minutes. Take the remedy 3-5 times a day, one tablespoon at a time.
- Grind a tablespoon of fresh lemon balm and pour 500 ml of boiling water over it. After cooling, strain and take a couple of sips throughout the day. This infusion can be added to tea.
- Hemlock tincture, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, has a healing effect. Dilute 10 drops of 10% alcohol tincture in ½ glass of water and divide into three doses during the day.
Before using folk recipes, you should carefully check the tolerance of all herbal components to exclude the risk of developing allergic reactions.
Herbal treatment
Since increased production of prolactin is often associated with stress and emotional experiences, the following herbal treatment recipes are recommended to reduce its level:
- Take 100 g of hop cones and grind them. Pour water at a rate of 30 g of raw material per 500 ml of water and bring to a boil over medium heat. After cooling, the decoction should be filtered and can be taken by tablespoon 3-5 times a day.
- Take equal proportions of lemon balm, St. John's wort tops, hawthorn berries, passionflower and hop cones. Grind all ingredients thoroughly. Pour 1.5 liters of boiling water over 100 g of dry raw materials and let it brew until completely cool. Strain and take a glass 30 minutes before meals throughout the day.
- Take equal proportions of sesame seeds, pumpkin, young ginger, primrose grass and honey. Grind and mix all the ingredients thoroughly until a uniform consistency is obtained. Take the remedy 1 teaspoon 3-4 times a day, regardless of food.
Treatment of hormonally active pituitary adenoma by this method is possible only with the appropriate medical permission. Herbal therapy is carried out in combination with traditional medicinal methods.
Homeopathy
Another alternative method of treating prolactinoma is homeopathy. The choice of drug depends on the nature of the disease and the characteristics of the patient's body.
In case of hormonally active pituitary adenoma and increased production of prolactin, the following medications may be prescribed:
- Aconitum – the disease is caused by emotional and stressful overexertion, there are symptoms of hyperemia, increased irritability, and circulatory stimulation.
- Belladonna – used as an analogue of Aconitum, can be used to treat children.
- Glonoinum – frequent headaches and dizziness, feverish state.
- Nux vomica – headaches, confusion, apathy.
- Arnica – frequent dizziness, hallucinations, visual impairment.
- Uranium – increased milk production, pain in the temples, back of the head and forehead. Spasms in the throat, vomiting, purulent discharge from the nose.
- Iodatum – atrophy of the mammary glands, inflamed lymph nodes. Atrophy of the testicles, sexual dysfunction.
All medications are selected by a homeopath, individually for each patient. As a rule, patients are prescribed several medications at the same time to effectively relieve the pathological symptoms of the disorder.
Surgical treatment
If the detected neoplasm is large, then surgical treatment is recommended. Before surgery, the patient is prescribed dopamine agonists, which make the pituitary adenoma more operable. The risk of frequent tumor recurrence is also taken into account, so long-term medication is required after surgery.
Today, microsurgical operations give good results and are carried out in a gentle mode. Patients may be prescribed one of the following treatment methods:
- External beam radiation therapy.
- Proton therapy.
- Radiosurgical treatment.
- Gamma therapy.
The entire treatment process is controlled by a tomograph. Neurosurgery is indicated for patients with pressure from an enlarged tumor on adjacent tissues, and visual impairment. Surgical treatment is also performed for complications of adenoma, such as cysts or hemorrhages.
Prolactinoma removal
If the size of the benign tumor of the anterior pituitary gland does not decrease, then surgical intervention is recommended. Removal of prolactinoma is indicated in the following cases:
- Lack of effectiveness of drug therapy.
- Individual intolerance to drugs used to treat neoplasms.
- Growth of tumors against the background of the use of dopamine agonists.
- Increased growth of pathology during pregnancy.
- Apoplexy (cell necrosis) of prolactinoma due to hemorrhage.
- Optic nerve damage and severe visual impairment.
Removal of a tumor is not performed in the case of a patient’s serious condition, inflammatory processes in the area of the operation (nasal, frontal sinuses), severe forms of cardiovascular, renal or respiratory failure.
About 70% of operations are performed using transsphenoidal access, i.e. removal through the nasal sinuses. This method does not injure the brain and has a minimum of complications. Operations with craniotomy are performed extremely rarely, for example, with giant or atypically located tumors, atypical structure of the facial bones
Let's look at the main methods of removing prolactinoma:
- Radiosurgery
The accuracy of this method is 0.5 mm, which allows you to act only on the adenoma, without affecting the surrounding nerve tissue. Radiosurgery is performed in the following cases:
- The optic nerves are not damaged.
- The tumor is accompanied by neuroendocrine syndrome.
- The size of the neoplasm is no more than 30 mm.
- The sella turcica is of normal or slightly enlarged size, and the adenoma does not extend beyond its boundaries.
Before the procedure, the patient is sent to MRI or CT to create an accurate three-dimensional model of the tumor. During the operation, the patient is placed on a couch and the head is fixed. The CyberKnife operates remotely, it emits waves to the location of the adenoma. During the operation, the patient does not experience discomfort, hospitalization is not performed. Radiosurgical methods are used to remove the remains of prolactinoma after classical surgery or radiation therapy.
- Transnasal removal
This method is recommended if the tumor extends slightly beyond the sella turcica. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon inserts an endoscope with a camera into the nasal cavity. The doctor exposes the bone of the anterior sinus and uses a drill to access the sella turcica. After this, a gradual, step-by-step removal of parts of the tumor is performed. After the operation, the sella turcica is sealed using the patient's tissues. After the procedure, the patient remains in the hospital for 2-4 days.
- Craniotomy
This is the most radical method of treatment. The operation involves opening the skull and is prescribed in the following cases:
- Asymmetric growth of adenoma.
- The presence of secondary nodes in the tumor.
- The tumor extends beyond the sella turcica.
Access to the affected organ is performed frontally (opening the frontal bones of the skull) or under the temporal bone. During the operation, the patient must lie on his side to avoid compression of the jugular veins and arteries that supply the brain with blood.
Prolactinoma removal is performed under general anesthesia. Electric tweezers or an aspirator are used to extract the adenoma. In rare cases, the tumor is removed together with the pituitary gland due to its deep penetration into healthy tissue. After this, the doctor returns the skin flap to its place and applies stitches. The patient spends 2-3 days in intensive care, where his condition is constantly monitored. After this, the patient is transferred to a ward with hospitalization for up to 20 days.
- Radiation therapy
The treatment is carried out in one course of 4-5 sessions with an interval of 7-10 days. The duration of therapy is about 5 weeks. During each procedure, the patient receives a radiation dose of about 180-200 rad, that is, about 5000 rad per course, depending on the size of the neoplasm. The effectiveness of this method is controversial, since an improvement in the condition was noted only in a third of patients.
When choosing radiation therapy, the risk of possible complications is taken into account. Most often, patients experience baldness, damage to the optic nerves, necrosis of the brain substance, hypopituitarism, neoplasia. Complications can make themselves known several months, and in some cases several years after the procedure.
The main indicator of the effectiveness of the operation is the reduction of prolactin levels to normal values within 24 hours after the procedure. According to medical statistics, the success of removing microadenomas is 100%, and for tumors of 1-3 cm up to 80%. At the same time, 65% of patients have complete restoration of visual functions, and 20% have endocrine functions. If the neoplasm is gigantic in size or is characterized by atypical growth, then the surgeon's task is to reduce the pressure on the surrounding tissues.
Removal of prolactinoma, like any surgery, has certain risks. Possible consequences and complications of the surgery:
- Bleeding.
- Visual impairment due to nerve damage.
- Meningitis due to infection.
- Cerebrospinal fluid leak.
In 13% of patients, the disease relapses, and in 5% of cases, death occurs during surgery. In this case, prolactinomas that do not cause symptoms are not subject to removal. It is necessary to regularly check the hormone in the blood and do a planned magnetic resonance imaging every year.
Diet and lifestyle for prolactinoma
For the normal functioning of the pituitary gland and the entire body, a healthy diet is necessary. The diet for prolactinoma should consist of foods rich in folic acid. This substance stimulates hematopoiesis and testosterone production, increases estrogen levels and improves the digestibility of protein foods.
Useful products for the pituitary gland:
- Chicken eggs are a source of lutein and contain a large amount of vitamins and microelements.
- Chicken meat is rich in protein, which is a building material for new cells. Contains B vitamins and selenium.
- Fatty fish - herring, salmon, mackerel are good for the pituitary gland. They stimulate hormone production, maintain the balance of endocrine glands, and prevent cholesterol deposition.
- Walnuts – contain vitamins A, B, C, as well as iron, zinc, cobalt, magnesium and iodine. Stimulate normal functioning of the brain and slow down the aging process.
- Spinach - contains a large amount of iron, which maintains normal blood circulation in the pituitary gland. And the antioxidant effect prevents the development of adenoma.
- Seaweed is a source of iodine. It fights irritation, sleep disorders, fatigue. It helps to supply the brain with oxygen.
- Dark chocolate – stimulates the brain and processes in the pituitary gland. Activates nerve cells, stimulates blood vessels.
Products that increase the level of prolactin in the blood should be excluded from the diet - gluten-containing products. White bread, pastries, cakes, smoked meats, sausages and cold cuts, alcohol, fatty meat and salt are prohibited. During treatment, the use of preservatives, dyes, flavor enhancers should be limited as much as possible. They can cause disturbances in the osmotic state of brain cells and the conductivity of nerve fibers.
Prolactinoma and sports, weightlifting
The possibility of physical activity in case of brain tumor lesions depends entirely on the type of neoplasm, the mechanism of its origin and symptoms. Prolactinoma and sports, weightlifting, swimming and much more are recommended only if the doctor gives the appropriate permission.
As a rule, there are certain restrictions for patients whose tumor has not been removed. This is due to the fact that accelerated metabolism and increased blood supply can cause an increase in the size of the adenoma. Many physiotherapy procedures with a stimulating effect are also prohibited.
As for patients in the postoperative period, minor physical activity is allowed during recovery. It promotes normal functioning of the body. But caution should still be exercised, as excessive overexertion can become a trigger for a relapse of the disease.
Is it possible to sunbathe if you have prolactinoma?
Many patients who have been diagnosed with a tumor of the anterior pituitary gland wonder whether they can sunbathe. With prolactinoma, sunbathing is allowed, but only if all safety rules are observed:
- Sunbathing should be done in the morning or evening hours; it is better to spend lunchtime from 11:00 to 16:00 in a cool room.
- It is necessary to provide the skin with the necessary protection from ultraviolet radiation in the form of a special cream.
- To protect yourself from sunstroke, you should put on a hat, cap or panama hat. Sunglasses will also be useful.
- Stock up on clean, cool water to maintain your hydration balance while you rest. Do not drink alcohol or cold drinks while sunbathing.
- Don't lie in the sun in one position. To get a beautiful tan, it's better to move.
- Avoid all kinds of injuries, especially traumatic brain injuries.
The above recommendations will allow you to safely and usefully spend your vacation in the sun. Sunbathing is useful, as it supplies the body with vitamin D, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the brain.
 [ 52 ]
[ 52 ]
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of hormonally active pituitary tumor, since the etiology of its origin has not been fully studied. To reduce the risk of this disease, one should avoid craniocerebral injuries, as well as long-term use of oral contraceptives. During pregnancy, it is necessary to create all the conditions for its normal course. It is also recommended to undergo a CT scan and ophthalmological examination annually, and take tests every six months to determine hormone levels.
Forecast
Prolactinoma has a favorable prognosis in only a third of all cases of the disease. Prognostic indicators depend on the size, hormonal activity and symptoms of the pathological condition. Relapse occurs in half of the cases within five years after the first treatment. Also, the risk of tumor degeneration into malignancy should not be excluded, which has a very unfavorable outcome.

