
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Penicilliellae are the causative agents of penicilliosis
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 06.07.2025
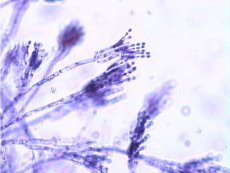
Morphology and physiology of penicillium
Penicillium forms a mycelium of septate branching hyphae. At the end of the fruiting hypha (conidiophore), primary and secondary branches are formed - metulae of the first and second order (multi-whorl brushes). From the tops of the metulae, bunches of bottle-shaped phialides extend, bearing chains of rounded conidia of green, yellow-brown, pink or violet color. The elements of the fungi are different: P. crustaceum has two-, three- and multi-whorl brushes, P. chrysogenum (formerly P. notatum) has asymmetrical, two- and three-whorl brushes, P. expansum (synonym: P. giaucum) has single- and multi-whorl brushes: P. mycetomagenum has single-, two- and three-whorl brushes, and the conidia are smaller than those of the previous ones - up to 2.2 µm in diameter.
Pathogenesis and symptoms of penicillosis
Penicillium causes penicilliosis in patients with weakened immunity. Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations are similar to aspergillosis. The main immunity is cellular. DTH develops. In Southeast Asia, P. mameffci (possible reservoir - bamboo rats) causes a disease similar to gnetoplasmosis. The fungus is dimorphic: at 25 °C, mycelium with a red pigment is formed, and at 37 °C and in infected tissue - yeast.
Microbiological diagnostics of penicilliosis
In preparations (skin, nails, cornea, discharge from the sinuses, external auditory canal, sputum, pus, feces, tissue biopsies) stained with hematoxylin and eosin, according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, according to Wright, long branching septate hyphae and large rounded conidia are detected. It has the appearance of oval cells.


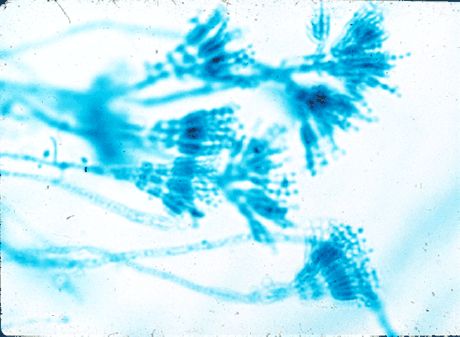
 [
[