
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Chest pain on the left side: aching, stabbing, sharp, pulling, blunt
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
Left-sided chest pain can often be caused by a heart attack. But in 80% of cases, this is far from true. Left-sided chest pain can be caused by diseases of the respiratory system, digestive organs, as well as muscles, skin, and bones. How to understand the causes of left-sided chest pain? What are the symptoms of left-sided chest pain, as well as diagnosis and treatment?
Cardiovascular diseases
Let's start with the most dangerous causes of chest pain on the left. These are cardiovascular diseases. Their list is quite long, but it is important to know all these points in order to call a doctor in time for chest pain on the left. Diseases associated with chest pain due to heart problems are coronary and non-coronary.
Coronarogenic heart diseases include myocardial ischemia and acute myocardial infarction. These are serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels that can cause death if a person does not receive medical care in time.
Heart attack (acute myocardial infarction and ischemia)
A heart attack due to acute myocardial infarction or ischemia occurs when blood flow to the arteries that supply blood to the heart (coronary arteries) is blocked. This prevents the heart muscle from getting enough oxygen. This can cause damage, deterioration, and atrophy of the heart muscle.
Causes of Heart Attack
A heart attack is caused by coronary artery disease, or ischemic heart disease. Heart disease can be caused by a buildup of cholesterol in the coronary arteries (atherosclerosis), blood clots that can interfere with blood flow, or a spasm of the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart.
Risk factors for heart attack
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- smoking
- high cholesterol
- heredity - cardiovascular diseases in close relatives that occur at the age of under 60 years,
- obesity
After menopause, women have a higher risk of heart attack than premenopausal women. This is thought to be due to the loss of the protective effect of the hormone estrogen during menopause. Therefore, premenopausal women need hormone replacement therapy to balance the hormonal balance in the body.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
Typical pain during a heart attack occurs in the middle and left side of the chest and may also spread to the left shoulder, left arm, jaw, abdomen, or back. Be aware that different people may have different symptoms during a heart attack.
Symptoms associated with chest pain include shortness of breath, increased sweating, nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of left-sided chest pain during a heart attack in women may not differ from those in men. However, in women, symptoms may be atypical (not characteristic). With left-sided chest pain in women, the following signs of a heart attack may occur:
- abdominal discomfort,
- heartburn,
- dizziness,
- unexplained fatigue.
Diagnostics
- Chest palpation examination
- Electrocardiogram (ECG), for diagnosing heart function. After the ECG, it is already possible to say which vessels of the heart are blocked or narrowed.
- A study of enzymes that heart muscle cells produce when they don't get enough oxygen. These enzymes can be detected in a blood test.
Treatment
The first thing to do when a heart attack occurs is to call an ambulance. While the patient is waiting for the ambulance, they should take nitroglycerin to relieve chest pain.
Inpatient treatment for infarction or ischemia that caused a heart attack is primarily aimed at increasing blood flow through the arteries. It is important to unblock the blood flow and the arteries themselves, as well as to eliminate the risk of blood clots passing to the heart. Medicines used for this purpose include aspirin, heparin, thrombolytic drugs.
The second goal in treating a heart attack is to slow the heart rate, which reduces the strain on the heart and reduces left chest pain.
Angioplasty is a method of unblocking an artery.
Angiography – This is done primarily to find narrowings or blockages in the arteries. A very thin plastic tube, called a catheter, is inserted into the artery. This widens it, allowing a wider passage for blood. Sometimes a stent (a flexible metal structure) is used to widen the arteries and allow blood to flow freely.
Surgery for left chest pain is used if treatment fails. This may include angioplasty or heart bypass surgery.
Non-coronary heart disease
This group of heart diseases can also cause chest pain on the left. But these diseases are very difficult to diagnose because they have not yet been sufficiently studied by doctors. In addition, many of these diseases have very vague, unclear symptoms. The most common non-coronary cardiovascular lesions are pericarditis, arterial hypertension, also associated with the pericardium, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, heart defects, congenital and acquired, mitral valve prolapse, neurocirculatory dystonia (including 4 types of cardialgia), angina. Let's consider the most life-threatening diseases that cause heart pain in the chest on the left.
Acute pericarditis
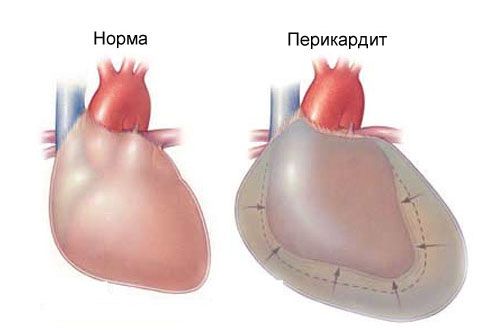
This is an inflammation of the pericardium, a sac that covers the heart. It is called the pericardium or the connective tissue of the heart. The role of the pericardium is to separate the heart from all other organs located in the chest. The pericardium allows the heart to fill better with blood, and during physical exertion, it keeps our "motor" from stretching and moving from its anatomical place.
The pericardium is a cavity between two sheets of connective tissue. Inside, between the walls of the heart and the pericardium, there is a fluid that protects these sheets from friction. There is quite a bit of fluid – 25 ml. When the pericardium becomes inflamed, chest pain occurs on the left.
Causes of Pericarditis
Pericarditis can be caused by a viral infection, a bacterial infection, cancer, uncontrolled use of medications, radiation therapy, and chronic renal failure.
An acute attack due to inflammation of the pericardium can be aggravated by an even more life-threatening condition called cardiac tamponade. This is a buildup of fluid around the heart that prevents it from pumping blood effectively throughout the body. Cardiac tamponade can be characterized by sudden loss of consciousness, severe chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
 [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
[ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
Symptoms of acute pericarditis
Left-sided chest pain with pericarditis is usually described as sharp or stabbing. It also occurs in the middle of the chest and is aggravated by deep breathing.
This pain can easily be confused with the pain of a heart attack because it may radiate to the left side of the back or shoulder.
The distinguishing feature of acute pericarditis compared to infarction or ischemia is that the pain is aggravated in a horizontal position and subsides when the person leans forward. This is explained by the fact that when a person lies down, the inflamed pericardial membrane closely touches the heart, causing pain. When a person leans forward, a space is formed between the pericardium and the heart, and the pain in the chest on the left and in the middle subsides.
Associated symptoms include feeling hot and cold, difficulty breathing, or a sore throat when swallowing.
Treatment of pericarditis
Viral pericarditis usually resolves after 7-21 days of therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen. If there is a risk of tamponade, the doctor will puncture the fluid from the pericardium through the skin. Drainage is also performed along with ultrasound, and excess fluid is pumped out of the pericardium.
Mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse is an abnormality of one of the heart valves. This condition is accompanied by a malfunction of the valve, which is located between the ventricle of the heart and its left atrium. This life-threatening condition can cause severe chest pain on the left side.
Symptoms of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse usually causes no symptoms, but some people may experience rapid heartbeat and chest pain on the left side. This pain may also be accompanied by fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Chest pain associated with mitral valve prolapse differs from the pain of angina in that it is sharp, does not radiate anywhere, and is not associated with physical activity.
Complications can also occur that cause infection of the heart valves, mitral valve regurgitation (abnormal blood flow into the heart chambers), and abnormal heart rhythms, sometimes resulting in sudden death.
Angina pectoris
Angina is chest pain caused by insufficient oxygen reaching the heart through the bloodstream. The lack of blood supply to the heart is caused by blockages or narrowing of blood vessels. Angina differs from a heart attack in that the arteries in angina are not completely blocked, and it does not cause life-threatening damage to the heart.
Mild angina (called stable) may occur during physical exertion, and the chest pain stops after rest. "Unstable" angina results in severe and unpredictable pain that does not completely go away even at rest.
 [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
[ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
Causes of angina
Angina can be caused by a spasm, narrowing, or partial blockage of an artery that supplies blood to the heart.
The most common cause of angina is coronary artery disease, in which a blood clot or cholesterol buildup inside a blood vessel (atherosclerosis) restricts blood flow but does not completely block the blood vessel.
Angina can be caused by physical exertion, emotional stress, or arrhythmia, in which the heart beats very quickly.
 [ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ]
[ 25 ], [ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ]
Symptoms of angina
Angina sometimes resembles a heart attack, but it occurs during physical exertion and goes away after rest, which never happens with a heart attack or ischemic attack. Angina becomes life-threatening when chest pain on the left occurs at rest, the heart rate or intensity increases.
The pain of angina does not go away after taking one nitroglycerin tablet, as it happens with a heart attack. At least three nitroglycerin tablets are needed at five-minute intervals to make the attack less intense.
Diagnostics
Angina is diagnosed using the same methods doctors use to diagnose heart attacks.
The diagnosis of angina is made only after the possibility of a heart attack has been excluded. This is done by analyzing cardiac enzymes, which we wrote about above.
Although an ECG may show abnormalities in the heart's function, these changes are often treatable.
Stress test: Monitoring your ECG during exercise and at rest. The test results are then compared to determine how stress is affecting your heart. This test can detect blockages or congestion in the blood vessels leading to your heart.
Cardiac catheterization (insertion of a catheter) is used to identify blockages in the arteries.
A special type of diagnostic test (angiography or arteriography) is used to detect blockages or other problems with blood vessels.
Treatment of angina
Nitroglycerin tablets under the tongue are the first line of treatment for angina until emergency services arrive. Nitroglycerin can help increase blood flow to blocked or narrowed arteries.
If chest pain continues for the next five minutes, take another nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue. If there is no improvement, repeat the same action after five minutes until the ambulance arrives.
In the inpatient treatment of angina, β-blockers are used to relieve an attack of chest pain on the left and in the middle. Representatives of these blockers are atenolol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol.
Aortic aneurysm (other names: aortic dissection, aortic rupture)
The aorta is the main artery that supplies blood to vital organs such as the brain, heart, kidneys, lungs, and intestines. Aortic dissection means a tear in the lining of the aorta. It can cause severe internal bleeding and stop blood flow to vital organs. Only 20 to 30 percent of people survive. An aneurysm (rupture) can occur in the aorta in the chest or abdomen. Men are at higher risk for aortic rupture than women.
 [ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ]
[ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ]
Causes of aortic dissection
Aortic dissection can be caused by conditions that cause the inner lining of the aorta to break down, including uncontrolled high blood pressure, connective tissue rupture, illness, over-the-counter use of strong drugs, older age, pregnancy, congenital heart defects, and cardiac catheterization for diagnosis.
Symptoms of aortic rupture
Left-sided chest pain associated with aortic dissection occurs suddenly and is described as "tearing, severe." The pain may radiate to the back or between the shoulder blades. Because the aorta supplies blood to the entire body, symptoms of a ruptured aorta may include:
- pain like angina with intermittent breathing
- dyspnea
- fainting
- abdominal pain
- symptoms of a stroke (numbness of the limbs and tongue, loss of motor function in one part of the body)
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of aortic dissection based on the patient's symptoms includes
- Chest X-ray (X-rays will show irregular contours of a torn aorta or its widening).
- Echocardiography (with specialized ultrasound of the heart, when a probe is inserted into the esophagus under local or general anesthesia).
- Aortic dissection can be determined very accurately by a doctor using a CT (computed tomography) scan of the chest or angiography.
 [ 41 ]
[ 41 ]
Treatment of aortic rupture
- Painkillers such as morphine, dopamine, mesaton
- Drugs that lower blood pressure - diuretics, berlipril, anaprilin, diroton and others.
- Medicines that slow the heart rate and widen the arteries
- Surgery is required to cut (tear) the aorta, which damages the ascending (bottom to top) part of the aorta.
Esophagus Diseases Causing Left Chest Pain
Often, chest pain on the left side occurs due to gastrointestinal diseases. In particular, due to reflux disease, which is commonly called heartburn. The symptoms of this pain may be similar to a heart attack, but this is not the case.
Causes of acid reflux
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Overeating
- Increased acidity
- Gastric sphincter dysfunction
- diabetes mellitus
- scleroderma
Heartburn can be caused by any factor that reduces pressure on the lower esophagus, causes cessation of esophageal activity, or delays gastric emptying. This condition can be caused by:
- eating high-fat foods
- using nicotine
- alcohol consumption
- caffeine intake during pregnancy
- certain medications or hormones (eg, nitrates, calcium channel blockers, anticholinergics, estrogens, progesterone)
- Acid reflux and chest pain on the left side can also be caused by yeast, fungi, viruses, bacteria, or irritation from allergens.
Symptoms
- a sharp pain that bothers a person in the left side of the chest
- pain radiating to the chest, back, neck and shoulder
- pain when swallowing
- bleeding in the esophagus
- heartburn
- salivation
- chest discomfort
- chest pressure
- profuse sweating
- paleness of the face
- nausea and vomiting
- sore throat
- sour or bitter taste in the mouth or throat
- hoarseness
- persistent dry cough.
Diagnostics
- Examination of symptoms and palpation of the chest area
- X-ray
- Bernstein tests (when acid is introduced into the esophagus to study the reaction to it)
- Esophagoscopy (examination of the esophagus using a flexible tube connected to a monitor where the doctor can see the results)
 [ 46 ]
[ 46 ]
Treatment
You can reduce left chest pain from acid reflux in a simple way - raise the head of the bed 15 cm higher or just put a higher pillow under your head. This way, the caustic liquid from the stomach - acid - will not flow into the esophagus.
It is important to take medications that reduce stomach acidity - ranisan, for example cimetidine
You don’t need to smoke, but on the contrary, you need to eat, but only healthy foods: oatmeal, vegetables, fruits, you need to exclude fried and fatty foods, limit chocolate and coffee.
Sometimes your doctor will prescribe antacids, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal medications, medications to relax the muscles of the esophagus, or a combination of these.
Chest pain on the left side caused by respiratory diseases
The most common diseases include pulmonary embolism (artery thrombosis), spontaneous pneumothorax, and pneumonia.
Pulmonary embolism
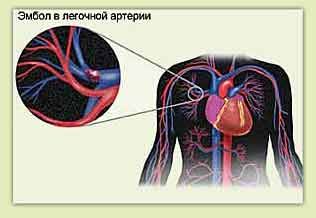
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot in one of the large blood vessels that supplies blood to the lungs. It is a potentially life-threatening condition that is not related to heart or vascular disease.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism
Risk factors for pulmonary embolism include:
- sedentary lifestyle,
- obesity,
- prolonged immobility,
- fracture of the tibia bones of the legs,
- pregnancy,
- Cancer,
- hereditary predisposition to pulmonary embolism,
- heart rhythm disturbance (arrhythmia),
- heart attack
- congestive heart failure.
Women who use birth control pills and smoke frequently are at higher risk of developing pulmonary embolism than women who do not smoke (especially those over 35).
 [ 47 ], [ 48 ], [ 49 ], [ 50 ], [ 51 ], [ 52 ]
[ 47 ], [ 48 ], [ 49 ], [ 50 ], [ 51 ], [ 52 ]
Pulmonary embolism - symptoms
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include
- sudden difficulty breathing
- rapid breathing
- a sharp pain in the middle of the chest that increases with deep breaths
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
- Description of the patient's symptoms when interviewed by a physician
- ECG results
- Chest X-ray
- The doctor may test the blood from the patient's arteries to check the oxygen levels in it. Abnormal blood flow indicates a lung disease that prevents the patient from getting enough oxygen.
- Ventilation-perfusion scanning (V/Q scanning) – allows you to compare blood flow and oxygen supply to different parts of the lungs. Problems in only one segment may indicate an embolism.
- CT scan of the lungs (computed tomography)
Treatment
Anyone diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism requires immediate hospitalization.
Treatment usually involves extra oxygen pumped into the blood and medications to prevent further blood clotting, usually heparin.
If the embolism is very large, in some situations the patient takes medications to dissolve the clot.
For some people, doctors suggest surgery to prevent blood clots.
 [ 53 ], [ 54 ], [ 55 ], [ 56 ], [ 57 ]
[ 53 ], [ 54 ], [ 55 ], [ 56 ], [ 57 ]
Spontaneous pneumothorax
A collapsed lung is a condition that occurs when air enters the space between the chest wall and the lung tissue. Normally, the negative pressure in the chest cavity allows the lungs to expand. When a spontaneous pneumothorax occurs, air enters the chest cavity. When the pressure balance is lost, the lungs are unable to re-expand. This cuts off the body's normal oxygen supply.
Spontaneous pneumothorax - causes
Spontaneous pneumothorax (collapsed lung) occurs when a so-called air cushion forms around the lungs. The area where the air gets in (and it shouldn't get there) is called the pleural area.
Causes of pneumothorax
Chest trauma is the most common cause of this condition. Trauma can occur due to a blow, a fall, an awkward turn, an injury, or surgery.
Some very thin and tall people may suffer from spontaneous pneumothorax due to stretched lung tissue and abnormal air sacs that form at the top of the lungs. It is possible that these air sacs can rupture with simple actions such as sneezing or coughing.
Other risk factors for pneumothorax include AIDS, pneumonia, emphysema, severe asthma, cystic fibrosis, cancer, and antibiotic use.
Symptoms of pneumothorax
- sudden difficulty breathing,
- sharp pains in the chest,
- increased heart rate,
- dizziness,
- weakness
Diagnosis of pneumothorax
- Spontaneous pneumothorax is diagnosed primarily by physical examination and chest X-ray.
- CT (computed tomography) scan may be useful in identifying a small pneumothorax.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity in the left lateral position.
Treatment
Pneumothorax that occurs without an apparent cause does not always require serious treatment. Sometimes a person only needs to spend six hours in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor and have his chest re-examined with an X-ray.
If the size of the pneumothorax does not change during this time, the patient is usually discharged with a recommendation to see a doctor in two days.
If the patient develops new pain symptoms or the volume of the pneumothorax increases, he or she will be admitted for inpatient treatment.
Perforated viscera: A perforated viscera is a hole or tear in the wall of any area of the gastrointestinal tract. This allows air to enter the abdominal cavity, which irritates the diaphragm, and can cause chest pain.
Pneumonia and chest pain on the left
Pneumonia is an infectious disease of the lungs. Chest pain on the left with pneumonia occurs due to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the lungs.
Causes of pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection of the lungs.
Symptoms of pneumonia
Chest pain on the left side due to pneumonia occurs and intensifies during prolonged coughing or deep breathing
Pain in pneumonia is usually one-sided
Other symptoms associated with pain include chills, cough with mucus (phlegm), high fever, and difficulty breathing.
Diagnostics
Pneumonia is diagnosed by physical examination, chest x-ray, and listening to the patient with a stethoscope.
Treatment of pneumonia
Pneumonia is usually treated with antibiotics, and the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve chest pain on the left.
Regardless of the cause of chest pain on the left, mandatory examinations by a doctor are necessary. This will help to determine the diagnosis in time and most importantly - correctly and prescribe the optimal treatment. This will give a person the opportunity to recover and prevent chest pain on the left.

