
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Haglund-Schinz osteochondropathy.
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
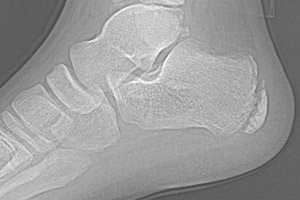
Aseptic necrosis of the calcaneal tuberosity, which is most often encountered by teenage girls, is Haglund-Schinz osteochondropathy. It develops due to constant overload of the foot and repeated heel injuries. In some cases, bilateral damage is observed. It is a disease of childhood and adolescence; it occurs extremely rarely in adults.
The heel bone is the largest bone of the foot with a spongy structure. It bears increased load during walking and running. On the back surface of the bone is the calcaneal tubercle - a protruding area. The Achilles tendon and long plantar ligament are attached to it.
Causes osteochondropathies
Causes of the disease:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Neurotrophic disorders.
- Infectious diseases.
- Frequent foot injuries.
Increased loads lead to a violation of vascular tone, due to which the bone area does not receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. Against this background, bone destruction occurs without the participation of infectious agents and inflammation.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Symptoms osteochondropathies
Symptoms of Haglund-Schinz disease:
- Discomfort when putting weight on the heel and after any load.
- Absence of pain at rest.
- Atrophy of the calf muscles.
- Pain in the foot when bending and unbending.
- Lameness and pain when palpating the calcaneal tuberosity.
The disease does not cause soft tissue swelling, skin atrophy or inflammatory reactions. In some cases, after the foot stops growing, the painful symptoms disappear completely.
Treatment osteochondropathies
Treatment is conservative. It is recommended to limit the load on the leg, wear orthopedic insoles. In case of severe pain, temporary fixation with a plaster splint and taking painkillers are possible.

