
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Facial nerve neuropathy left, right: acute, ischemic
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025

Facial nerve neuropathy is a pathological process that results in disruption of innervation and sensitivity of the facial nerve branches. Statistics show that 75% of all cases of facial nerve neuropathy are Bell's palsy - unilateral paresis of the facial muscles. This disease occurs regardless of the person's gender and age, but is most often observed in people aged 20 to 45 years. This type of peripheral nervous system damage is not an independent disease, with the exception of congenital anomalies or disruption of normal intrauterine development.
Paralysis can be unilateral, for example, neuropathy of the facial nerve on the right. With bilateral damage, another focus appears - neuropathy of the facial nerve on the left. Bilateral damage is considered the most painful and is difficult for patients to bear.
Causes facial neuropathy
The causes of facial neuropathy are not fully understood. It has been proven that acute facial neuropathy is the second link in the pathological process. The first link or trigger mechanism is:
- traumatic brain injuries, especially injuries to the temporal bones, cranial vault bones and mastoid process
- surgical interventions (plastic surgery, mastoid surgery, etc.)
- viral and bacterial infections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis, epidemic parotitis "mumps"), complications after acute respiratory viral infections, flu, otitis and mastoiditis.
- hypothermia and prolonged exposure to drafts
- aneurysms of the cerebral arteries, acute cerebrovascular accident, in some cases – consequences of a stroke.
 [ 5 ]
[ 5 ]
Risk factors
The likelihood of developing neuritis increases in healthy people if they work in cold conditions, near refrigeration units, air conditioners, or in a draft.
Another equally important factor is facial piercing, namely eyebrows, lower lip or the front third of the tongue. Firstly, an unprofessional piercing can cause nerve trauma. Secondly, even a correct piercing does not guarantee complete safety, since inadequate care of the piercing site, contact with insufficiently sterile instruments, dust and dirt can lead to infection with pathogenic microorganisms and cause an acute inflammatory process.
Facial nerve neuropathy in children occurs when there is a burdened heredity for this disease. If one of the parents had a case of neuritis in their medical history, then there is a possibility of its occurrence in the child.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenetic mechanism for the development of Bell's palsy depends on the cause of its occurrence.
Ischemic neuropathy of the facial nerve occurs due to vascular ischemia, which causes damage to the motor neurons of the facial nerve. This condition is often observed during a hypertensive crisis.
Compression ischemic neuropathy of the facial nerve develops as a result of compression of the nerve by nearby structures with subsequent circulatory failure. Bone fragments, hematomas, hemostasis and lymphostasis can negatively affect the branches of the facial nerve and disrupt normal functioning.
Symptoms facial neuropathy
The main source of unpleasant symptoms is weakness or paralysis of muscles. Visually, distortion of facial expressions and asymmetry are observed.
Symptoms of facial neuropathy form a complex that includes:
- Acute pain in the affected half of the face.
- Headaches.
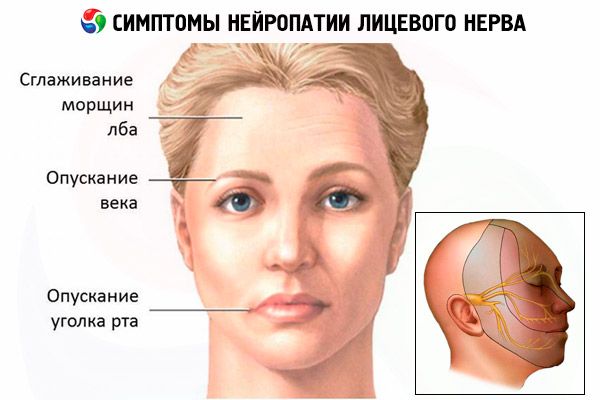
- Inability to moisten the eyelids, the outer corner of the eye and the corner of the mouth are lowered.
- Smoothing of nasolabial triangle folds and forehead wrinkles.
- Lacrimation, which is replaced by dry eyes, a feeling of “sand” in the eyes.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Drooling (in some cases).
- Intolerance to noise and bright light.
- Slurred speech.
- Loss of taste.
The first signs may appear a day before neuritis, usually a dull pain in the temporal bone area, which intensifies with active facial expressions. Then the pain becomes acute, which is felt regardless of muscle tension. In parallel, headaches and an inadequate reaction to external stimuli, such as light and noise, occur.
Peripheral neuropathy of the facial nerve, which occurs as a result of otitis or mastoiditis, can begin suddenly against the background of pain and discomfort in the ear area.
Diagnostics facial neuropathy
Primary diagnostics of facial neuropathy includes anamnesis and general examination. Do not neglect questioning the patient, as information about the person's occupation, living conditions, heredity and past illnesses is the basis for making a diagnosis.
During the general examination, the level of nerve damage is assessed using facial tests. The patient is asked to close his eyes and bare his teeth: on the affected side, the eye slit does not close, the corner of the mouth is motionless or slightly mobile.
When trying to puff out the cheeks and hold air in them, the patient experiences discomfort, the air is not retained. Pulling the lips forward and folding them into a tube is difficult.
Based on these tests, the extent of the disease can be determined.
- Mild neuropathy is characterized by slight mobility of the affected side, the eyes close completely, the eyebrows are mobile. In this case, the nerve function is preserved, but it is weakened.
- In moderate neuropathy, the patient cannot close the eyes completely, when trying to raise the eyebrow, slight twitching of the eyelid may be observed, the facial muscles react weakly. At this stage, facial asymmetry is expressed, the patient has difficulty baring his teeth.
- Severe neuropathy is characterized by minimal mobility of the affected side of the face, the eye practically does not close, when trying to frown, smile or raise an eyebrow, the muscles do not react. This degree is accompanied by discomfort in the eye area, chewing food and drinking liquids is very difficult.
What do need to examine?
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics allows distinguishing facial nerve damage from trigeminal nerve diseases. It is performed to clarify the exclusion of other pathologies and to clarify the diagnosis.
Instrumental diagnostics include brain examinations (computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging), electroneuromyography (to assess muscle activity, frequency and speed of nerve impulse conduction) and ultrasound of the parotid gland.
Laboratory blood and urine tests are performed to diagnose the general condition of the body and the presence of metabolic disorders (diabetes). Serological blood tests are prescribed to exclude viral and bacterial infections (herpes, HIV, infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, etc.).
Who to contact?
Treatment facial neuropathy
Treatment of facial neuropathy is carried out exclusively under the supervision of the attending physician. Self-medication can be ineffective and even dangerous. The absence of timely treatment can cause complete paralysis, the outcome of which is extremely unfavorable.
After diagnosis and diagnosis, the doctor prescribes complex therapy. The standard treatment for facial nerve neuropathy includes the use of physiotherapy, medications, massage, facial exercises, and acupuncture.
- Medicines
Prednisolone has an anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect in neuropathy of the facial nerve. The first 2 days, the so-called introductory dose of 20-30 mg (4-6 tablets) is prescribed, after 48 hours, a maintenance dose of 5-10 mg (1-2 tablets) is used. The course of treatment is determined by the attending physician, on average it is 2-3 weeks. Longer treatment with prednisolone is prescribed in severe cases. Long-term treatment with adrenal hormones causes a number of side effects, united under the name Cushing's syndrome (osteoporosis, headaches, obesity, decreased sexual function, decreased secretion of the gastrointestinal tract and weakening of the body's defenses).
Berlition is used for facial nerve neuropathy to normalize the conductivity of peripheral nerves. The main component of the drug is a vitamin-like substance called alpha-lipoic acid. This component is involved in the oxidation-reduction processes of cells and tissues, has a pronounced antioxidant effect, and improves the trophism of nerve tissue. The drug is available in tablets and infusion bottles. The average dose is 600 mg (2 tablets) in the morning 30 minutes before meals.
The infusion solution is intended for intravenous drip administration. An isotonic sodium chloride solution is used as a solvent. The drug is administered slowly, over 30 minutes.
Berlition is generally well tolerated by patients. Individual intolerance may cause allergic reactions (skin itching, urticaria), nausea, vomiting, dizziness.
Euphyllin, nicotinic acid, and sermion are used as circulatory correctors and antispasmodics for facial nerve neuropathy.
Euphyllin reduces the resistance of blood vessels, which helps to normalize blood flow in the affected areas. It is also used as a diuretic to relieve swelling. Tablets are prescribed for oral administration (0.15 g 2-3 times a day after meals) or a solution for intramuscular injections (1 ml of a 24% solution).
Sermion is a cerebral circulation corrector. It is prescribed as a restorative therapy after injuries, strokes, acute and chronic diseases of viral or bacterial etiology. It has a positive effect on cognitive functions and mood, improves transmission in the neuromuscular synapse. The average dosage is 30 mg per day (1 tablet) in the morning 30 minutes before meals or 10 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day at equal intervals. The course of treatment for this pathology is 2-4 months.
Nicotinic acid or vitamin PP is a part of the enzymes of oxidation-reduction processes. Vit. PP has a wide range of effects: it dilates blood vessels, improves cerebral and peripheral blood circulation, normalizes carbohydrate metabolism and reduces the concentration of triglycerides in the blood. It is used for neuritis of the facial nerve as an addition to the main treatment.
In tablet form, the drug is used in a dosage of 0.1 g 2 times a day during meals. Intramuscularly, 1 ml of a 1% solution is administered in the morning and evening. The course of treatment is 1 month.
For diseases of the peripheral nervous system, vitamins of group B (B1, B2, B6) are also used in the form of injections and some fat-soluble vitamins (A and E) in the form of capsules.
- Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment is prescribed with the aim of providing a direct impact on the damaged area, thanks to which blood circulation is restored and tissue trophism is improved.
From the very beginning, it is recommended to conduct treatment in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. Electrophoresis using a 0.02% solution of dibazol has an antispasmodic, vasodilatory effect, improves the functioning and activity of the facial nerve. It is also advisable to prescribe potassium preparations and vitamin B1 for electrophoresis.
To improve facial mobility and reduce the feeling of muscle tension, electrophoresis is used for the cervical-collar zone using sodium oxybutyrate.
Recently, treatment with electromagnetic waves has become widespread. Such electrical stimulation of the facial nerve is prescribed for muscle paralysis.
- Gymnastics
Exercise therapy for facial nerve neuropathy helps improve blood circulation in the face and neck and speeds up the restoration of normal facial expressions. Gymnastic exercises are performed in front of a mirror, and weakened muscles are helped with the hands. It is necessary to perform simple facial movements, such as smiling, pursing the lips, raising the eyelids, and blinking the eyes.
Important! All movements are performed separately from each other. That is, you should not smile and raise your eyebrow at the same time, otherwise the muscle fibers will remember the combination of these actions and it will be very difficult to get rid of them even after recovery.
Facial gymnastics for facial nerve neuropathy should be natural. It is best if, when trying to restore a smile, the patient listens to something cheerful so that a natural reflex is formed in response to the corresponding stimulus.
- Massage
Massage for facial nerve neuropathy is prescribed 1.5 - 2 weeks after the onset of the disease. Any mechanical action is contraindicated in the acute phase, when the patient experiences pain and the inflammatory process persists. Massage is contraindicated if neuritis has developed due to the spread of infection due to injuries and ENT diseases. Under such circumstances, massage will only aggravate the situation and cause further spread of the infection.
It is advisable to prescribe massage after eliminating the underlying cause of the disease.
The massage technique is very simple: light stroking and circular movements clockwise, starting from the neck and ending with the frontal bone area. Before performing the manipulation, hands must be warmed up.
- Acupuncture
Acupuncture for facial nerve neuropathy is performed exclusively by an experienced specialist, taking into account special points on the face and projection points of the facial nerve. First, the needles are placed on the healthy side at the "inhibition" points. The impact on them has a relaxing effect and helps to get rid of the feeling of tension and hypertonicity of the muscles. Next, the needles are placed on the affected area at the "stimulation" points. The needles are on each zone for 15-20 minutes. This technique "balances" the innervation of the face and helps to normalize the conduction of impulses along the nerve fibers.
It is prescribed 2-4 days after the onset of the disease, provided that there is no source of infection.
Folk remedies
Treatment of neuropathies with folk remedies is carried out after consultation with the attending physician. Mild and moderate neuritis can be successfully treated with the following remedies.
- Recipe #1
Make a small bag from thick natural fabric (linen, cotton, chintz). Pour 400-500 g of salt into a dry frying pan and heat it well. Pour the salt into the bag, tie it up and apply it to the affected half of the face. It is necessary to do 3 warmings per day, the last one must be done immediately before going to bed. As practice shows, within 2-3 weeks there should be a significant improvement up to a complete cure.
- Recipe #2
Apply 1-2 drops of natural fir essential oil to the face and rub it over the entire affected area with light massage movements. The procedure is carried out in the morning and evening, starting from the first day of the disease for a week.
- Recipe #3
Treatment with special mud masks, which are sold in pharmacies. They contain a set of natural minerals and microelements that have a beneficial effect on facial tissues. The mud is heated to 35-40 degrees and applied to the neuritis area for 20 minutes. The procedure is carried out once every two days.
Herbal treatment
The healing properties of herbs help to combat not only the consequences and symptoms of neuritis, but also the cause of inflammation.
- Recipe #1
Pour a glass of boiling water over 3 tablespoons of crushed marshmallow root, cover and leave for 2 hours. Squeeze the root through cheesecloth, drain all the liquid into a separate glass container and store in a closed container in the refrigerator.
Apply the infusion heated to 30 degrees. Take internally (a quarter of a glass half an hour before meals 3 times a day) and externally as a compress (soak a gauze bandage in warm infusion and apply to the site of neuritis for 20-30 minutes 3 times a day). The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Recipe #2
Pour a glass of warm water over a handful of chamomile flowers and place in a water bath. After 30 minutes, squeeze out the flowers and drain the liquid into a separate container. The decoction is used for internal use (half a glass half an hour before meals 3 times a day), as well as for rinsing the mouth (take the decoction in your mouth and hold it on the side of the neuritis as long as possible). The course of treatment is 1.5 - 2 months.
- Recipe #3
Pour 3 tablespoons of sage with a glass of boiling water, infuse according to the above scheme and drink 100 g 3 times a day 40 minutes before meals.
All of the listed herbs have a calming, analgesic, antispasmodic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Homeopathy
For treatment, use Athlete's wort, magnesium chloride and thuja in the form of granules, powders and tinctures.
Aconite is prescribed for neuritis and neuralgia of various origins. Chronic neuropathy requires long-term treatment with small doses, while acute neuropathy requires high doses, which are given every half hour until the patient begins to sweat (a sign of a drop in temperature). The plant is poisonous, so the tincture must be used under the supervision of a doctor.
Magnesium chloride has an antiallergic, bactericidal, and analgesic effect. Magnesium preparations are widely used to treat diseases of the nervous system. Magnesium chloride in powder form is diluted 25 g per 1 liter of water. Adults and children over 5 years old are prescribed 125 ml 2-3 times a day for 1 month.
Thuja is a good addition to the main treatment. Thuja granules can be purchased in homeopathic pharmacies. The standard dosage is 6-8 granules 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day.
Side effects may occur in case of overdose. The main symptoms are: abdominal pain, nausea, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, allergic rashes. If you have the above symptoms, you should stop taking the drug and immediately consult a doctor.
Surgical treatment
In particularly complex cases, the anatomical integrity of the nerve is restored surgically by suturing, moving, or connecting it to another nerve. The main indication for surgery is a tumor of the nerve, a tumor of nearby structures, and traumatic damage by bone fragments in craniocerebral injuries.
Prevention
General strengthening procedures, a balanced diet, moderate physical activity and gradual hardening help to increase the body's resistance.
It is necessary to avoid sudden changes in temperature, avoid overcooling, avoid drafts and prolonged exposure to air conditioning in the summer.
Another mandatory point is timely treatment of diseases of the ear, throat and nose. Treatment should be comprehensive and effective, otherwise a partially cured disease can become chronic. Observing bed rest during illness will not only speed up recovery, but also prevent complications.
Forecast
With proper treatment and adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician, the prognosis for facial nerve neuropathy is favorable. It is important to remember that repeated cases of neuropathy are much worse tolerated by the body and cause irreversible processes in the nervous and muscle tissue. To avoid relapses of the disease, it is important to adhere to prevention.

