
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve branches
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
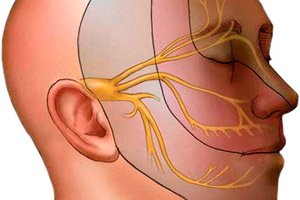
Trigeminal neuropathy is one of the forms of trigeminal system pathology. In this form of pathology, intestinal tissue undergoes degenerative changes. Its multiple transformations, as well as functional changes, are possible. Myelin fibers and axial cylinders are also subject to change. It is a serious problem that modern neurology increasingly faces. It significantly reduces the quality of human life, complicates it. Pain is an unpleasant phenomenon, sensitivity is also significantly reduced, numbness, and loss of many functional capabilities are observed. The most dangerous are facial paresthesia and paralysis.
Nerve damage is fraught with serious consequences, since many structures are damaged. Accordingly, their functions are also damaged. The innervation of many organs and systems is damaged. The trigeminal nerve is formed by three branches that provide transmission of nerve impulses from the innervated organs to the structures responsible for processing the nerve impulse. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for the innervation of the face and oral cavity. The skin, teeth, tongue, nerves, and eyes are also under the innervation zone. This nerve provides motor reflexes and is also responsible for various vegetative reactions.
There can be many causes of neuropathy. These can be both structural and functional disorders. Most often, there is a disorder of a separate branch of the nerve. The disorder of the first branch is a fairly rare form of pathology, while the most common form is the disorder of the second branch. All three branches are extremely rarely disordered. These are isolated cases in all neurological practice. The peculiarity of this form of the disease is that it can develop for quite a long time. Often, the disease develops over several months or more.
Causes trigeminal neuropathy
Primary pathology develops if the nerve is subjected to direct, immediate impact. This may be compression of the nerve by bone protrusions, ligaments, pathological tissue displacements. This may be direct damage to the nerve as a result of a blow, compression, stretching.
Secondary causes are presented by a list of factors that led to inflammation or damage to the nerve. Thus, secondary causes are a consequence of pathological phenomena occurring in the body, which are reflected in the structural and functional state of the nerve.
Leprosy and various neoplasms are considered as secondary causes of pathology development. Both benign and malignant neoplasms have an equally negative effect on the trigeminal nerve, since they exert mechanical pressure on it. Compression of the nerve by pathologically altered vessels, which occurs during tumor development, also has a negative effect. Changes, deposits in the vessels, and blood clots are also dangerous. Atherosclerosis is one of the causes of pathology, since plaques form inside the vessel, which can also exert pressure on the nerve. A plaque that forms in the area of the sensitive nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is especially dangerous.
The main causes include hereditary factors that predispose the nerve to pathological changes. Pathological phenomena observed during pregnancy and intrauterine development have a negative effect. Birth injuries are especially dangerous, as well as various injuries received after birth, especially in early infancy.
Neuropathies are increasingly developing after surgeries, cosmetic procedures, invasive manipulations, during which the nerve is damaged. The nerve is often injured by dentures, as well as during various dental procedures. Craniofacial, craniocerebral injuries also often end in neuropathies. The nerve is often damaged by toxic substances, allergic factors, autoimmune factors. Many viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and even hidden infections can cause nerve damage. Toxic effects can be caused by various plastics, dentures, iron structures that are used in dentistry.
Even simple hypothermia can cause nerve damage. It is especially easy to damage a nerve in a draft, at low temperatures, in the wind. A sharp change in temperature, as well as air conditioners, fans, and heaters operating indoors have a negative effect. The danger is that such effects can reduce the body's immunity and resistance, as a result of which the nerve becomes more vulnerable and susceptible to negative effects. In this state, the nerve is more susceptible to infection, inflammation, and even mechanical damage. Various exhaust gases, toxins from the environment, and nicotine can damage the nerve.
One should not neglect the impact of such severe inflammatory and infectious diseases as typhoid fever, measles, rubella. Nerve damage can develop as a result of inflammation in the ear, nose, and throat. Herpes virus infection, inflammation of the lymph nodes, sinusitis, caries, and sinusitis often lead to nerve damage. Often, the symptoms of these diseases are so close to nerve damage that they are confused with neuropathy. Therefore, differential diagnostics may be required. Trigeminal nerve damage can also be caused by general damage to the nervous system, the brain and spinal cord, as well as other parts of the nervous system, in which the pathological process spreads to other areas and nerves. Paralysis of nerve endings, both the trigeminal nerve and other nerves, paresis, and brain tumors can also lead to nerve damage and other complications. Even a careless attitude to treatment, in which the patient does not follow the doctor's recommendations, self-medicates, can end in inflammation. Even such abstract problems as syphilis, tuberculosis, purulent-septic pathologies can lead to neuropathy.
Primary trigeminal neuropathy
Primary pathology is quite common as a consequence of an infectious and inflammatory process that develops as a result of hypothermia, trauma, compression and mechanical damage to the nerve, against the background of reduced immunity. Primary pathology can also develop as a result of direct damage to the nerve during operations, dental procedures. Congenital anomalies, in which the nerve is damaged, also serve as a factor that causes the direct development of neuropathy. There are no significant differences in the clinical picture between the primary and secondary forms of pathology.
 [ 7 ]
[ 7 ]
Secondary trigeminal neuropathy
The secondary form of neuropathy is also quite common. It is a consequence of the development of various pathological processes in the body. For example, nerve damage can develop as a result of the development of a viral and bacterial infection in the body. Often, brain tumors, various congenital pathologies, atherosclerotic deposits, spasms lead to nerve damage. Neuropathies often develop against the background of diseases such as tuberculosis, syphilis, herpes virus infection. Sinusitis, caries, pulpitis also often lead to nerve damage.
Trigeminal neuropathy after tooth extraction
The most common pathology in dentistry is acute toxic damage to the trigeminal nerve, in which the lower alveolar nerve is injured, as well as the mental nerve, which occurs when filling material gets into the mandibular canal. This happens during the treatment of pulpitis. This pathology is especially common in the treatment of pulpitis of premolars (first and second). Treatment of the teeth of the lower jaw is often accompanied by an inflammatory process in the lower jaw. A characteristic sign of such damage is severe pain, which first occurs during the procedure, and then accompanies a person during the recovery period.
Later, this pain remains dull and aching, however, it is quite exhausting for a person and requires the use of strong painkillers, sometimes even hospitalization for further comprehensive measures. The occurrence of acute pain during dental treatment requires urgent emergency care, during which mandatory canal decompression is performed. For this, dexamethasone, euphyllin solution and glucose solution are used. These drugs are administered intravenously, by jet method. At the same time, diphenhydramine and furosemide are administered intramuscularly. This will prevent the most dangerous nerve damage. Further treatment is required, during which drugs are used to normalize microhemocirculation. Neuroprotectors and desensitizers are also used.
A common consequence of nerve damage during dental procedures is neuropathy of the buccal nerve, which is often intertwined with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve and entails its inflammation. The pain is subacute, relatively constant, and easy to distinguish.
Damage to the superior alveolar nerve is also often observed. It can be recognized by acute pain and numbness in the upper jaw. The mucous membrane of the cheek and gums is also damaged.
Risk factors
The risk group includes people suffering from dental diseases, especially if it is a lesion of deep layers, for example, deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. The risk factor is the presence of a constant source of chronic infection in the body, recent acute infectious diseases, tumors. The risk group also includes people who are constantly exposed to toxic substances, hypothermia, work under air conditioners and hoods.
The risk of developing the disease increases significantly in people suffering from atherosclerosis, tumors, vascular pathologies, congenital anomalies and genetic defects in development.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis is based on the disruption of the normal functioning of body fibers. In this case, it is often their function that is disrupted, not their structure. Pathological phenomena are often observed in the receptors that perceive irritation, as well as numerous pathologies in the area of the reflex arc that supports the path from the innervation zone to the brain, and in the opposite order.
An accompanying factor of such pathology is pain, which in most cases develops subacutely. The pain syndrome can be short-term. It is often accompanied by a spasm of the masticatory muscles. The pain and spasm are constant, increasing in nature, the intensity also constantly increases. Painful sensations are accompanied by numbness and paresthesia, in which a person feels pain and tingling in the corresponding area of innervation. Goosebumps and tingling are also observed.
Symptoms trigeminal neuropathy
Various disorders indicate damage to the trigeminal nerve. Their localization corresponds to the affected area. It is quite easy to recognize the damage, since it is accompanied by a sharp acute reaction of a constant nature and practically does not subside. At night it is aching, burning, during the day it becomes sharp, unbearable. The pain can also radiate to other areas.
A distinctive feature is that it radiates to the hair, chin, ear, and eye area. Often the pain is accompanied by a strong spasm. The chewing muscles suffer from the spasm first. There is a feeling of inability to lower the lower jaw. Over time, a person really cannot lower it. Acute pain may develop, and then an inflammatory process in the ear area. When pressed, pits are formed and the pain increases.
First signs
First of all, there is a feeling of pain, which is of a nagging nature. The pain is initially localized in the eyebrow area, above the eyes. Gradually, it can spread to other areas. The pain especially intensifies in the cold season. A distinctive feature of such pain is its development by short-term attacks of acute pain, which are accompanied by a lull, a nagging pain. Most often, the pain is localized only on one side. In this case, it becomes more intense at night, shooting. Later, a spasm of the face and lips develops. The pain intensifies during movements.
Many people also report pressure in the cheeks, ears, nose, and eyes. Gradually, the sensations may spread to the back of the head. Some even feel pain in the thumb, which often includes the index finger.
 [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
[ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
Swelling in trigeminal neuropathy
Neuropathy may be accompanied by edema, since normal metabolism is disrupted both in the nerve itself and in the surrounding tissues. Hyperemia appears, blood circulation is disrupted in the compressed and inflamed area, edema and swelling of the tissues develop. The cause is also fluid retention and disruption of the removal of metabolic products from damaged tissues.
Neuropathy of the 1st branch of the trigeminal nerve
Cases of damage to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve are extremely rare. This is almost never seen in medical practice. More often, there is a combined damage to the 1st and 2nd branches of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the damage is most often accompanied by an inflammatory process that occurs in the brain. In this case, an adhesive process develops. Other structures are often involved in the inflammatory process, for example, the maxillary and frontal sinuses.
Constant aching pain that pulsates is often observed. The pulsation develops especially strongly in the area of innervation of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the process is accompanied by numbness, a feeling of crawling ants. Many people have teeth aching, which is often explained by damage to the motor part of the nerve. Patients cannot perceive jaw movements. They either become involuntary, or the person practically stops moving the jaw altogether. It also becomes difficult to eat and talk. In the oral cavity and on the face, it is impossible to determine the trigger zones of this process.
Diagnosing the pathology is not difficult. In most cases, a high-quality objective and subjective examination is required to establish a diagnosis. Often, the diagnosis is made based on the medical history - the main diagnostic sign indicating the development of the pathology is the very fact of severe pain in the dental system, which arose during dental and surgical intervention.
This disease is characterized by a long clinical course, as well as a significant duration of pain, its high intensity. A high level of clinical polymorphism is also characteristic. Exacerbation is often observed against the background of hypothermia, in the cold winter season, as well as after fatigue, stress and nervous strain. Exacerbation can also occur against the background of other somatic pathologies.
A rather dangerous sign is considered to be the formation of scars on the nerve, or its retraction into soft tissues, which occurs during the healing of injuries and traumas. The risk of such lesions is especially high in the presence of congenital or acquired defects and anomalies of the jaw, bones.
Neuropathy of the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve
Pain of a short-term nature is noted, which manifests itself in strong attacks lasting approximately 1-2 minutes. Between pain attacks, a painless period occurs, which is then replaced by intense pain of an acute nature. Often, there is an unexpected, shooting pain, which many compare to a knife blow or a strong electric discharge.
Pain can occur spontaneously and unexpectedly, or be provoked by other factors, such as sudden movements or pressure. Also, an attack of pain can occur during meals, running, moving, swallowing, talking, and even during touching. It is worth noting that all zones that trigger pain sensations are localized in the face, especially in its central parts. The pain wave spreads to the area of anatomical innervation of the nerve. In this case, the spread occurs to the area of 1,2,3 branches of the nerve.
A characteristic sign of damage to the second branch is the irradiation of pain along the entire reflex arc of the trigeminal nerve. The pain wave spreads quite quickly. In this case, the pain has the character of a multineuronal process. In this case, the entire nerve system is affected. There is a certain polymorphism, within which various clinical forms are distinguished. Basically, significant differences are observed between neuralgia of central and peripheral genesis.
Important importance is given to the topical diagnosis, since it is the basis for selecting the optimal treatment method. It should be noted that the pain is always one-sided and intensifies during the day. Most often, the pain is paroxysmal. Outside of an attack, the pain does not bother a person. Trismus often occurs, which is often confused with symptoms of tetanus, rabies.
The second branch is most susceptible to damage in elderly people. Their pain can be long-lasting and constant. It is characterized as dull and aching, which spreads over the entire area of the affected nerve. It is often accompanied by a disturbance of taste and smell. During an objective examination, it is possible to detect the absence or partial reduction of sensitivity in the facial area, as well as along the entire length of the nerve.
Pain is detected upon palpation. The nerve exit points are especially sensitive in this regard. The main cause is primary nerve damage by various factors, including mechanical damage. It often results from vibration disease and chronic poisoning. Diabetes mellitus can also result in nerve damage. Inflammation in adjacent organs and infection often involve the nerve itself in the inflammatory process. It can also develop as a consequence of brain inflammation, tumors, or inflammation in other peripheral nerves.
Often, a long course of the disease leads to a change in the main symptom complex. Nerve damage requires emergency care. During the provision of care, it is necessary to use anticonvulsants, which eliminate convulsive tension and promote relaxation. Antineurotic therapy is used.
For prevention, timely oral hygiene is performed, immunity is increased, daily routine is observed, stress and overwork are avoided. Trigeminal neuropathy can be completely cured only if all doctor's recommendations are followed and with complex impact on the body.
Complications and consequences
The consequences are severe pain, loss of sensitivity, up to complete muscle atrophy. Gradually, the atrophic process can affect other nerves. Plexia, paresis, paralysis develop, which are accompanied by a pronounced loss of sensitivity and innervation disorder. The final stage is complete paralysis and brain damage.
Diagnostics trigeminal neuropathy
A mandatory examination by a doctor is required to establish a diagnosis. The doctor examines and questions the patient, conducts a general and specific physical examination, during which both traditional clinical examination methods (palpation, auscultation, percussion) and special ones (determination of sensitivity, functional tests, assessment of basic reflexes) are used. In most cases, a diagnosis can be made based on the examination and questioning data. It is also easy to determine the cause of the pathology and eliminate it. But sometimes this is not enough, then the doctor prescribes laboratory and instrumental studies.
Tests
In general, laboratory tests are used extremely rarely, since they are not informative in this case. Instrumental methods and functional tests can be more informative. In rare cases, a clinical or biochemical blood test is prescribed, which can indicate the presence of an inflammatory process or an allergic reaction. An immunogram or rheumatic tests can be prescribed, which will help confirm or refute the autoimmune nature of the pathological process.
In a routine clinical blood test, the white blood cell count may be significant. Thus, an increase in eosinophils in the blood may indicate the development of an allergic reaction, helminthiasis, the action of toxic substances, rheumatism, neuroses, which may cause the development of neuropathy. A decrease in the number of basophils may occur with acute infections, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, stress, Cushing's syndrome, which may also entail damage to the trigeminal nerve. An increase in the number of monocytes may indicate the development of tumors, sarcoidosis.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental methods are the main ones. They are prescribed when it is necessary to obtain additional information, and if the diagnosis was not made during the examination. The main methods of instrumental examination include X-ray examination, computer or magnetic resonance imaging. They are very informative and complementary.
Thus, X-rays are the easiest way to diagnose bone pathologies, since they show bone tissues well. You can find out the cause of neuropathy. This could be a pinched nerve, its inflammation, displacement, damage as a result of a fracture or dislocation of the bone, which is very clearly displayed on the image. You can also notice a pinched nerve, a bone spur, arthritis, and even an inflammatory process in the nerve. With the help of computer and magnetic resonance imaging, you can examine soft tissues. Muscles, ligaments, tendons, and even cartilage are also well visualized. In rare cases, there is a need to use ultrasound (ultrasound). This method makes it possible to track processes in dynamics.
Differential diagnosis
In most cases, neuropathies are differentiated quite clearly after examination and instrumental diagnostics. The further essence of differential diagnostics consists in identifying the cause of the pathology, on the basis of which the belonging to one or another type of neuropathy is identified. Most often, traumatic, inflammatory compression neuropathy is differentiated.
Prevention
To prevent neuropathies, it is necessary to maintain a high level of physical activity: perform dynamic exercises, and, if possible, exclude static and monotonous work. It is also necessary to ensure that the body receives everything it needs for full functioning: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins and minerals. This is especially true for professional athletes: you need to carefully monitor the hygiene of the joints, periodically change the types of loads, take the necessary complexes and vitamins. It is necessary to undergo medical examinations in a timely manner, and if any pathologies are detected, treat them.
Forecast
If the pathology is detected in time and treatment is started, the prognosis can be favorable. Usually, trigeminal neuropathy is completely cured. But the treatment is quite labor-intensive and lengthy, so you will have to be patient. If left untreated, the disease progresses, and then the prognosis will be unfavorable, up to paralysis and complete disability.
 [ 35 ]
[ 35 ]

