
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Naboth gland cysts: what are they?
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
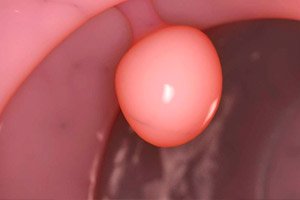
The internal cervical canal of the cervix is covered with cylindrical epithelium. The mucous membrane of this canal contains the so-called nabothian glands, which produce an antibacterial fluid that protects the uterus from pathogens. In some cases, the glandular ducts become clogged, and fluid secretions accumulate in them, which leads to the formation of nabothian cysts - small neoplasms, multiple or single. This pathology is considered quite common. However, the difficulty lies in the fact that most often patients learn about the disease by chance - for example, during a preventive visit to the doctor. [ 1 ]
Epidemiology
More than 20% of the fair sex, belonging to the age category from sixteen to 45 years (childbearing age), are found to have some diseases of the reproductive organs, which do not manifest themselves with any pronounced clinical picture or discomfort. One of such pathologies is nabothian cysts - they are usually diagnosed in 10% of cases. [ 2 ]
Women who have given birth are especially susceptible to the formation of nabothian cysts.
Causes nabotic cysts
Nabothian glands (also called follicles) look like numerous clusters in the lower segment of the cervical canal. They have an external resemblance to small tubes filled with a mucous mass. The openings of the glands are located in the area surrounding the external os. A nabothian cyst is the result of blockage of this opening, which occurs when the evacuation of mucous secretion is disrupted, when it accumulates with simultaneous stretching of the walls of the glandular canal. If one canal is affected, then one nabothian cyst is formed, and if several canals are blocked at once, then we are talking about multiple pathology formation. [ 3 ]
What are the reasons for dysfunction of the glandular canal? The most common reasons are:
- the tissues of the cervix are mechanically injured - for example, during abortions, childbirth, instrumental treatment or diagnostic procedures;
- there are hormonal imbalances that provoke thickening of the mucous secretion, which leads to deterioration of evacuation and blockage of the gland opening;
- an inflammatory process develops, leading to increased glandular secretion and thickening of discharge.
Less common causes include cervical endometriosis, a painful condition in which the opening of the gland becomes blocked by endometriotic tissue. [ 4 ]
Risk factors
The risk factors that contribute to the appearance of nabothian cysts are considered to be the following:
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs, vaginal dysbacteriosis, HPV;
- structural disorders, age-related changes, dysplasia;
- leukoplakia of the cervix;
- endometriosis;
- injuries to the genitals, childbirth, abortions, curettage, miscarriages, etc.;
- specific infectious lesions (chlamydia, ureaplasma, syphilis, trichomonas, etc.);
- atrophy of the mucous tissues of the cervix.
Pathogenesis
Nabothian cysts may have various origins. They can form from unchanged tissue structures, from rudiments, differentiated cells. Some such neoplasms arise against the background of fluid accumulation in the rudiments of mesonephric canals localized in the stromal base of the organ, or during the population growth of germinogenic cell structures.
The most common mechanism of development of nabothian cysts is squamous metaplasia. The cylindrical epithelial tissue that produces mucous secretion is replaced by protective epithelium with a multilayered squamous cell structure, which often contributes to the blockage of the outlets of the cervical glands with their subsequent cystic transformation. In the vast majority of patients, such processes are triggered in ectopic areas, but sometimes they can be observed in the area of the cervical canal, or on the polypous surface. [ 5 ]
In the case of endometrial ectopia, the cavity is formed from structures similar in morphological and functional terms to the inner surface of the uterus. These structures are implanted in the cervical zone. Against the background of cyclic hormonal changes, regular epithelial rejection is observed - as in the body of the uterus, but in endometrioid foci. There is also an accumulation of blood mass in them, the formation of cystic cysts.
The Douglas pouch in women is the lowest localized peritoneal pocket, reaching the posterior vaginal wall and lining the anterior rectal surface. It is in this area that many painful reactions are often observed, in particular, endometriosis. The Bartholin gland, the outlets of which are located on both sides of the vagina, is also subject to frequent formation of cysts. Due to the blockage of the outlet glandular channels, accumulation of secretions, formation of edema and cystic neoplasm are observed. [ 6 ]
Symptoms nabotic cysts
In the vast majority of cases, nabothian cysts do not show obvious signs of their existence: they are discovered by chance during an examination by a gynecologist.
The first signs may be noted if the patient has large or multiple nabothian cysts. Such signs include:
- dyspareunia (discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse);
- yellowish or thick mucous vaginal discharge;
- rarely – contact bleeding.
Small, isolated nabothian cysts very rarely cause pain: pain can only be a concern when the formations become purulent. [ 7 ]
The presence or absence of symptoms directly depends on the underlying cause of the neoplasms. If nabothian cysts have formed against the background of an infectious and inflammatory process, then the woman often experiences characteristic symptoms of endocervicitis or colpitis:
- massive serous or purulent-serous discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant odor;
- vaginal burning;
- itching, painful sensations.
However, the clinical picture of nabothian cysts is poor or completely absent. That is why doctors often do not prescribe any treatment for minor and isolated cysts, but simply establish dynamic monitoring of the problem.
Nabothian cysts and pregnancy
It is possible to get pregnant with a diagnosis of "nabothian cysts": in most cases, such neoplasms do not block the cervical canal and do not create obstacles to conception, the course of the process of bearing and the natural birth of a child. However, pregnancy with a nabothian cyst has some peculiarities and requires additional monitoring by a doctor.
Nabothian cysts are often detected at the stage of pregnancy planning. The primary task of the doctor is to verify the correctness of the diagnosis, exclude hormonal imbalances, inflammatory and malignant processes in the cervix. Then the patient is prescribed complex treatment to eliminate the root causes of the pathology, strengthen the immune defense, and prepare the female body for the future process of bearing a child.
If surgical treatment is required, it is performed before pregnancy occurs. In this case, conception should be planned approximately 6 months after the intervention.
Can problems with conception arise due to nabothian cysts? Sometimes this is indeed possible – for example, with numerous or large cysts that block the lumen of the cervical canal. This makes it difficult for sperm to enter the uterine cavity, and further fertilization becomes impossible.
To prevent such problems, multiple or large nabothian cysts are removed by carefully choosing the method of intervention. The less tissue is injured during the procedure, the sooner a woman will be able to plan a pregnancy. The most undesirable method of removing cysts if a woman is planning to become pregnant is instrumental excision of neoplasms. Usually, doctors choose more gentle methods - for example, laser treatment or cryodestruction.
Stages
- Activation of the inflammatory reaction in the vaginal segment of the cervix and in the endocervix.
- Filling of the mouths of the nabothian glands with particles of squamous epithelium.
- Obstruction of the orifices located on the mucous tissue.
- Accumulation of mucous secretion produced by glands.
- Dilation of a blocked gland duct.
- Formation of a capsule-shaped cavity filled with mucous secretion.
Forms
Nabothian cysts are classified by location. According to this classification, neoplasms can be paracervical (located on the vaginal segment of the cervix) and endocervical (located directly in the cervical canal).
In addition, there are single and multiple cysts, small (up to 1 cm) and large (up to 3 cm and more).
According to the type of formation and etiological factor, Nabothian cysts of the cervix are:
- traumatic;
- infectious and inflammatory;
- dysplastic, dystrophic;
- tumor;
- congenital;
- retention.
Nabothian cysts, endocervical cysts, and cervical canal cysts increase in size due to the accumulation of secretory fluid in them, but not due to an increase in the capsule. Such neoplasms do not relate to genetic or hereditary pathologies, do not pose a danger in terms of infection during sexual intercourse, and are not prone to malignancy. [ 8 ]
Nabothian cysts do not affect the ovaries, sometimes accompany cervicitis or cervical ectopia: they are localized exclusively in the area of the cervix, more often in the area of the ectocervix. Determining the type of neoplasm according to the generally accepted classification is necessary for developing the correct treatment tactics.
Complications and consequences
Nabothian cysts can be almost asymptomatic. But if a woman becomes pregnant, various complications can occur. During pregnancy, significant hormonal changes occur in the female body, which can cause the growth and multiplication of nabothian cysts. These processes, in turn, affect the quality of the cervix: its walls often become deformed, and the lumen becomes blocked. The situation is further aggravated by the fact that with the onset of pregnancy, the vast majority of women experience a decrease in immunity. This threatens relapses of inflammatory diseases.
Here's why nabothian cysts are dangerous:
- violation of the shape and configuration of the cervix;
- changes in the cervical canal;
- creation of favorable conditions for the development of inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs;
- an increased likelihood of early termination of pregnancy or premature birth.
Only a doctor can assess the degree of risk for a specific patient after conducting an examination and other diagnostic tests. Only after conducting diagnostics will the treatment strategy and prognosis of the disease be determined. [ 9 ]
Diagnostics nabotic cysts
Diagnosis of such diseases is carried out in the gynecological department, or in outpatient settings at a gynecologist's appointment. Nabothian cysts with visible localization in the cervix are detected without problems during a standard gynecological examination: the doctor notes the presence of single or multiple dense hemispherical elements of different sizes, with thin walls through which a yellowish secretion is visible. If the nabothian cysts are accompanied by an inflammatory process, then redness of the mucous tissue and their swelling are additionally detected. Pathological vaginal discharge is also present. [ 10 ]
However, even with high-quality external visibility of pathology, each patient is prescribed additional diagnostic procedures:
- Analysis of venous blood for tumor markers (helps determine the risk of developing malignant processes), general clinical blood and urine tests (determine anemia, inflammatory processes).
- Instrumental diagnostics includes ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, magnetic resonance imaging (used to clarify the condition of other organs), and also for differential diagnostics.
Cytology is traditionally used for nabothian cysts: a smear is taken from the patient's cervix, transferred to the surface of a laboratory glass and examined under a microscope for the presence of atypical cells. In more modern clinical conditions, a new method of liquid cytology is used (instead of the usual one), followed by analysis for tumor markers.
The differences of liquid cytology are that the extracted biomaterial is placed in a liquid medium. Then, using centrifugation, smears are formed and transferred to the surface of laboratory glass. Smears after centrifugation differ from ordinary ones in that they include only "washed" structures, presented as an even concentrated layer. This new method makes it possible to obtain more reliable and informative results than with traditional cytology.
The study of tumor markers practically replaces the previously conducted PCR diagnostics for HPV. The desired protein p16ink4α is involved in the mechanism of constant renewal of cells on the surface of the cervix. Its normal concentration indicators are negligible. If the tests indicate an excess of the norm, then the result of the study for the tumor marker is considered positive.
Ultrasound is a well-known method that is indispensable for making this diagnosis. The image obtained during the procedure clearly visualizes the size of the nabothian cysts and their number. The nabothian cyst itself looks like a thickening (focal compaction) of the epithelial tissue of the cervical canal against the background of a small and uneven expansion. If the problem is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then the echographic detection of hypertrophic changes and increased echogenicity of the uterus is revealed. The ultrasound procedure is quite informative regardless of the type of its implementation: both an abdominal and a transvaginal sensor can be used. However, specialists themselves often prefer the latter option. [ 11 ]
In some cases, ultrasound alone may not be enough: the information should be double-checked using magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is prescribed:
- if there are difficulties in making an accurate diagnosis;
- if clinical manifestations and diagnostic results have certain contradictions;
- if it is necessary to know the general condition of the genitourinary organs.
MRI is optimally performed starting from the seventh to the thirteenth day of the cycle. [ 12 ]
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics is carried out after evaluating all diagnostic results: mirror examination of the cervix, colposcopy, cytological examination, bacterioscopic and bacteriological analysis of vaginal and cervical discharge, examination for STIs, targeted biopsy, local spectroscopy, etc. [ 13 ]
Nabothian cysts usually have the appearance of retention neoplasms, the sizes of which vary from 0.2 to 1 cm. The surface of the formations is covered with a different-sized subepithelial vascular network.
Endometriosis of the cervix can manifest itself as subepithelial cysts of a crimson hue, with average diameters from 0.3 to 0.7 cm. Common symptoms include bloody discharge outside of menstruation, contact bleeding.
Uterine myoma, especially with vaginal prolapse, is easily detected during a speculum examination. Some types of myomas can be palpated during a bimanual examination. For a more accurate diagnosis, transvaginal ultrasonography is performed, and a blood test is taken for hemoglobin and hematocrit levels (to assess the likelihood of anemia). It is also necessary to exclude a malignant process by taking a smear from the cervix for atypical cells.
Sometimes nabothian cysts are found in patients who have come to the doctor with a completely different problem. For example, dyspareunia is often the cause for female concern – it is a painful symptom indicating that the woman has been experiencing pain during sexual intercourse for some time. As a result, during a clinical examination, the doctor discovers the causes of such discomfort, and in this case they are nabothian cysts.
Since age-related changes often become the causes of gland blockage, involutional changes in the ovaries are also detected against the background of Nabothian cysts - this usually happens in women over 40 years of age. In young women, flat vaginal epithelium turns into cylindrical in the area of the external os. Over the years, the border of the transition shifts deeper into the cervical canal or to the lip of the cervix.
Endocervical cysts also require differentiation. These are benign formations that grow into the cervical canal. Such cysts are filled with liquid contents and often develop under the influence of a chronic inflammatory process. They can be detected at almost any age, but they are most often diagnosed in patients after childbirth and surgical operations in the cervix. The main method for diagnosing endocervical cysts is ultrasound.
Cervical dysplasia, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, is a tissue lesion associated with the action of the human papilloma virus. This disease is precancerous and often becomes a precursor to invasive cancer. If dysplasia is suspected, a thorough and complete diagnosis is mandatory.
Another common female disease is oophoritis, which is rarely encountered as an independent pathology. Usually, oophoritis develops against the background of other infectious and inflammatory processes - for example, salpingitis, and also has an indirect effect on the further formation of nabothian cysts.
Who to contact?
Treatment nabotic cysts
If nabothian cysts do not cause any pathological symptoms and are not combined with infectious or other diseases, the patient is registered and dynamic monitoring is established, with background correction of the monthly cycle. However, some doctors prefer surgical treatment, referring the patient for an operation to remove even uncomplicated neoplasms. There is no consensus on the correctness of such an appointment: this issue is resolved on an individual basis.
More information about the treatment of nabothian cysts can be found here.
Prevention
In the process of formation of nabothian and other cysts, such unfavorable factors as failure of hypothalamic, pituitary and ovarian regulation of various mechanisms occurring in the female reproductive system play a significant role. Such failure is often a consequence of frequent or prolonged stressful situations, infectious diseases, unsatisfactory social, environmental and domestic living conditions. Therefore, the main point of prevention of the development of the cystic process can be called the elimination or minimization of the effect of these factors.
Menstrual dysfunction is always a reason to visit a doctor. In case of any menstrual cycle disorders in women of childbearing age, it is necessary to perform a colposcopy and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. This is done in order to timely detect not only tumor processes, but also other pathologies of the female reproductive system.
Late seeking of medical help may require more complex treatment (including surgical intervention). In addition, the advanced process increases the risk of recurrence of nabothian cysts, and also generally has a negative impact on the patient's reproductive function.
If a woman has already undergone a course of therapy for a nabothian cyst, then in the future she needs to register with a dispensary for early prevention of relapses of the disease.
Forecast
The prognosis for a nabothian cyst can be called favorable. If the disease is not complicated, it is most often not accompanied by significant anxiety for a woman, does not affect sexual activity and the ability to conceive.
However, even after surgical removal of such cystic neoplasms, the risk of recurrence of the disease remains relatively high. This is due to the impossibility of completely eliminating all the underlying causes that contribute to the development of the pathology. [ 14 ]
If a woman is diagnosed with nabothian cysts, then, in addition to the main treatment, she needs to undergo regular preventive examinations, with mandatory colposcopy and bacteriological examination. To prevent relapses of the disease, such examinations should be carried out annually. But if the disease was complicated, visits to the doctor should be more frequent - at least two or three times a year.

