
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
MRI of the joints of the hand
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 03.07.2025
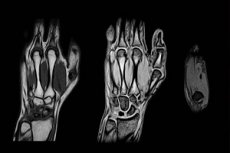
Magnetic resonance imaging of the extremities allows for a thorough diagnosis of the condition of bone and soft tissues, joints. MRI provides a three-dimensional image. This allows the doctor to examine the smallest defects, and also helps to distinguish benign pathology from malignant, predict possible consequences of injuries, and detect inflammatory changes. MRI of the hand plays a significant role before and after surgery on the extremity: often the correctness of the prescribed treatment and the final outcome of the disease depend on this type of examination.
Indications for the procedure
MRI of the hand is almost always prescribed as an additional type of diagnostics – for example, to clarify some information obtained using ultrasound, computed tomography or radiography.
Direct indications for MRI of the hand are:
- the period before surgery, after surgery on the hand;
- injuries, damage to the hand area;
- neuritis, pinched nerve endings in the area of the hand and wrist joint;
- diseases of the ligaments and muscles in the area of the hand - in particular, phlegmon or wrist hygroma;
- joint pathologies – for example, arthritis (including gouty arthritis), arthrosis, osteomyelitis;
- tumor processes - benign and malignant;
- stiffness, pain in the joint with unknown etiology;
- suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Preparation
- If an MRI of the hand with contrast is planned, it is advisable for the patient to go to the procedure on an empty stomach - do not eat for about 5 hours before the diagnosis.
- Immediately before the MRI of the hand, you must remove all metal and metal-coated accessories.
- In some cases, the doctor may ask the patient to change into a special disposable medical gown and cap.
- Before undergoing an MRI of the hand, it is necessary to warn the doctor about the presence of serious chronic pathologies, allergic reactions (especially if the administration of contrast is expected).
Technique MRI of the hand
To perform MRI of the hand, a standard tomographic device is used, consisting of a movable couch for the patient. The couch has built-in belts and rollers to fix the patient's limbs and head. Such devices help prevent involuntary movements during the examination, which can negatively affect the quality of the images.
When the couch is moved into the equipment chamber, the tomographic drum begins to move, which produces a peculiar crackling sound due to the action of the magnet. The patient cannot feel any discomfort - the MRI procedure of the hand is harmless and safe.
Once the scan is complete, the patient leaves the imaging room and waits for the results of the examination in the hallway or in a nearby room.
The contrast component that is injected into the patient for an MRI examination of the hand is, in most cases, gadolinium-based. Gadolinium is absolutely not dangerous for the human body. It is injected into a vein, after making sure that this agent will not cause an allergy in the patient (by the way, this happens very rarely - in about 1% of cases).
The contrast component visually highlights the vascular system during the MRI procedure, which allows the doctor to clarify many details of the image.
MRI of the hand with contrast is often prescribed to diagnose tumor processes, since in the area of tumor growth the network of capillaries grows especially densely.
Otherwise, contrast MRI of the hand proceeds in the same way as a regular non-contrast examination. After the diagnosis, the patient returns to his normal rhythm of life. The injected substance is excreted by the body on its own, naturally, and does not require additional intake of any medications.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist joints is considered to be quite informative and accessible. There are no alternative methods capable of visualizing the wrist joint with the same quality. MRI of the wrist joints is most often prescribed:
- for osteoporosis;
- for gouty joint inflammation;
- for damage to tendons, soft and bone tissues;
- for cysts, tumors;
- for inflammatory joint lesions.
MRI of the hand and wrist can also help determine the cause of pain and stiffness and help diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
The joints of the hand are vulnerable to most systemic inflammations - for example, they are often affected by rheumatic pathologies. X-ray examinations will help assess damage to bones and periarticular soft tissue, especially in the presence of calcifications. If there are no calcifications, then it is quite difficult to clearly imagine the picture of altered structures using X-rays. It is in such cases that MRI of the hand comes to the rescue. Magnetic resonance imaging will help detect painful disorders in the early stages of the disease, when X-ray methods do not yet "see" pathologies. The fact is that the sensitivity of the MRI method is much higher than that of other diagnostic methods.
MRI of the hand in rheumatoid arthritis shows an equivalent picture. There are four diagnostic stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Thus, the earliest sign is considered to be diffuse periarticular thickening and compaction of soft tissue. At the next stage, cystic enlightenment of bone tissue is determined against the background of a decrease in joint spaces. This means that the inflammatory process progresses and passes to a further stage, at which erosive damage to the joint is detected. With further progression, erosions become multiple, incomplete or complete ankylosis of the bone of the intercarpal or carpometacarpal joint develops. All changes in the hand MRI are determined at any stage of the development of the pathology.
MRI of the hand tendons is prescribed if tendinitis and tenosynovitis are suspected.
The inflammatory reaction affects the carpal tendons or the styloid process of the ulna. When conducting diagnostics, such changes are manifested by thickened and compacted ligaments and tendons in the area of their localization and attachment to bone tissue. Calcifications may be detected in soft tissue structures.
Contraindications to the procedure
- MRI of the hand cannot be done during pregnancy. If contrast is used, then the period of breastfeeding is also prohibited.
- MRI of the hand is not performed if the patient has any metal implants. For example, MRI cannot be used in the presence of pacemakers, hearing devices, nerve and cardiac pacemakers, vascular clips and insulin pumps, fixed metal prostheses. Titanium, ceramic and plastic elements are not prohibited.
- MRI of the hand cannot be performed if the patient suffers from hyperkinesis – uncontrolled motor activity
- Closed type MRI of the hand is not performed on people suffering from claustrophobia, mental illness, or obesity.
- The introduction of contrast during MRI of the hand is not practiced for those who have a tendency to allergic reactions or have problems with the liver and kidneys.
Care after the procedure
No additional patient care is required after MRI of the hand. After the diagnosis, the patient can return to their normal rhythm of life.
 [ 17 ]
[ 17 ]
Reviews
Judging by the reviews, MRI of the hand often helps to identify pathology at the earliest stage of development, when other diagnostic methods are not yet able to detect the problem. At the same time, the tomograph provides information not only about the structure of the necessary joint or organ, but also about the features of metabolic processes in the tissues.
The tomograph itself essentially resembles a large magnetic scanner, inside which a person is located. Under the influence of electromagnetic radiation, hydrogen atoms in the body tissues resonate, and the signals from them are recorded by the scanner and converted into a three-dimensional image.
The procedure itself does not cause any pain or other unpleasant sensations. The only condition is that during the session you need to remain completely still: you cannot move or even wiggle your fingers. Otherwise, MRI diagnostics of the hand is comfortable and without any negative aspects for the patient.

