
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Mediastinotomy
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 03.07.2025
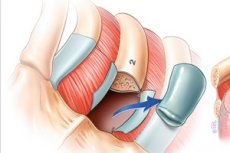
One of the procedures in thoracic surgery is mediastinotomy (Latin mediastinum – mediastinum + Greek tome – section), which consists of opening direct access to the anatomical structures located in the central parts of the chest cavity.
Indications for the procedure
Direct access involves an incision (a surgical cut, a tissue dissection), and mediastinotomy is the making of such an incision in the upper chest, resulting in a small opening leading into the mediastinum.
The main indications for this surgical procedure are related to diagnostics. Firstly, it is necessary to visualize pathological formations and lymph nodes using an endoscope inserted into the mediastinal space or a palpatory examination by a doctor. And such a procedure is called mediastinoscopy. [ 1 ]
Secondly, this is a histological (morphological) examination of tissues - a biopsy, for which it is necessary to take a sample (biopsy). Only a biopsy makes it possible to determine the nature of mediastinal neoplasms, and its implementation by the transthoracic aspiration method is far from always successful. [ 2 ]
Thus, mediastinotomy may be necessary for histological confirmation of the diagnosis or to identify suspected diseases and putative pathological conditions, including:
- lung cancer – with clarification of the stage, degree of metastasis to the lymph nodes and tumor resectability (in accordance with the generally accepted nomenclature of lymph node lesions – the MD-ATS staging map);
- lymphomas localized in the mediastinum (lymphoblastic, T-cell, Hodgkin's);
- bronchogenic carcinoma;
- enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes (which may indicate a malignant neoplasm);
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- widening of the mediastinum of unclear etiology;
- purulent mediastinitis;
- hyperplasia and tumor of the thymus gland;
- neurogenic tumors localized in the paravertebral (near-vertebral) groove.
In addition, the mediastinotomy approach is used to resect affected lymph nodes, as well as treat (by removing suppuration and draining) mediastinal abscesses and infections of the retropharyngeal space, which often spread to the mediastinum – to its anterior and posterior sections. [ 3 ]
Through a mediastinotomy in the neck area, the thymus gland is removed - transcervical thymectomy, and anterior mediastinotomy is used to install pacemaker electrodes.
Preparation
This procedure is carried out on a planned basis, and preparation for it consists of passing a general clinical blood test and a coagulogram. Mediastinotomy is performed under general anesthesia (intubation), so patients undergo electrocardiography.
Preoperative CT or positron emission tomography (PET) of the chest is also performed to clarify the individual characteristics of the location of the anatomical structures of the mediastinum, to determine metastases (if the patient has a malignant neoplasm) and to select the optimal technique for performing in accordance with the diagnosis (established or suspected). [ 4 ]
It is recommended to not take anticoagulants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs a week before the procedure, and to stop eating 6-10 hours before it.
Technique mediastinotomies
There are several basic techniques for surgically opening direct access to the mediastinum.
Anterior or parasternal mediastinotomy: A small transverse incision is made in the upper left parasternal region, above the second intercostal space, with resection of the costal cartilage. This allows access to the extrapleural space (aortopulmonary window) and the anterior mediastinal areas below the aortic arch. Alternatively, an anterior approach in the upper right parasternal area may be used to assess the right-sided, anterior mediastinal, or hilar lymph nodes. [ 5 ]
After all necessary manipulations have been carried out, the incision is sutured layer by layer and a bandage is applied.
Cervical mediastinotomy – suprasternal cervical mediastinotomy according to Razumovsky or collar, that is, colar mediastinotomy – is performed by transverse dissection above the sternum – along the sternocleidomastoid muscle to the anterior surface of the trachea, parallel to the edge of the suprasternal (jugular) fossa. The superficial fascia and the superficial leaflet of the proper fascia of the neck are dissected, the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles are moved apart, and the deep leaflet of the proper fascia is stratified (using a finger or a blunt instrument), entering the slit-like space with loose tissue and moving downwards – directly into the anterior part of the mediastinum. [ 6 ]
Posterior mediastinotomy is most often performed on the right side of the spine - on the side of the paravertebral muscles.
Contraindications to the procedure
Mediastinotomy is contraindicated in patients with a history of:
- aneurysms or dissections of the ascending aorta;
- radiation therapy in the mediastinal area;
- surgical operations involving dissection of the sternum (sternotomy).
Relative contraindications include superior vena cava syndrome; significant enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter); history of mediastinitis; previous mediastinoscopy and tracheostomy. [ 7 ]
Complications after the procedure
Mediastinotomy may be complicated by bleeding, difficulty swallowing, and infection and inflammation – with redness and swelling of the tissue. Infection may be accompanied by fever and the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate, which, when enlarged, can compress the aorta or pulmonary artery.
During the procedure, damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerves is possible, which manifests itself as hoarseness (which passes over time). [ 8 ]
The risk of complications is increased by obesity, diabetes, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
The following possible consequences are noted after the mediastinotomy and mediastinoscopy procedure:
- pneumothorax (if the pleura is damaged and air enters the pleural cavity);
- chylothorax (leakage of lymphatic fluid into the chest due to damage to the thoracic duct and pleura);
- damage to the chest organs - perforation of the trachea or esophagus;
- shortness of breath and paralysis of the diaphragm (in case of irritation or damage to the phrenic nerve of the cervical plexus).
Care after the procedure
Depending on the purpose of mediastinotomy and diagnosis, the duration of the procedure ranges from 30 minutes to two hours.
After its completion – if there are no complications – patients stay in a medical facility for 24-48 hours. Post-procedural care includes hardware monitoring of breathing, pulse and heart rate, as well as body temperature control. In case of severe pain, analgesics or NSAIDs are used. [ 9 ]
At home, according to the instructions given by the doctor, you should follow the rules of antisepsis and keep the bandage clean. Until the suture at the incision site has healed, taking a hot bath, increased physical activity and any sports activities are contraindicated. [ 10 ]
Reviews
Mediastinotomy with biopsy can provide important information about lung and chest diseases that cannot be obtained by other methods. And oncologists' reviews confirm the importance of histological confirmation of regional nodal spread of malignant lung tumor performed during mediastinotomy with mediastinoscopy - for choosing the most adequate treatment strategy.

