
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Itchy eyelids and other symptoms: swelling, redness, peeling
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
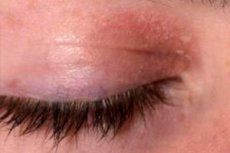
Even a completely healthy person may sometimes experience slight itching of the eyelids - for example, when dust gets into the eyes or when the direction of eyelash growth changes. But most often, itching becomes a sign of some kind of malfunction inside the body. For example, this sometimes happens when an infection gets into the eye, with systemic allergic and viral diseases, with dry eye syndrome, as well as against the background of other pathological conditions.
What can itchy eyelids indicate? What diseases is this symptom most often associated with?
Causes itchy eyelids
When itching begins to bother you to a significant extent, then any person who monitors their health wants to know the reasons for such discomfort.
Eye diseases affect a third of the population of our planet. Pathologies can occur after foreign particles - dust, organic, chemical, etc. - enter the organ of vision. Nutrition, general diseases (for example, acute respiratory viral infections), skin diseases, demodicosis, allergies can also be to blame. Even prolonged contemplation of the screen of a smartphone, computer or TV can lead to itching of the eyelids.
How can we understand the reasons for this uncomfortable state?
- Severe itching of the eyelids occurs with inflammation of the eye conjunctiva. This pathology can be of both infectious and allergic origin. The infectious inflammatory process, in turn, can be provoked by microbes, or viruses, or even fungi. Conjunctivitis can be transmitted by contact - through unwashed hands or household items.
- Another common cause is allergy - the strongest response of the human immune system to the introduction of a certain substance. Most often, allergic eyelid itching has seasonal characteristics and can be associated with the presence of plant pollen particles, animal hair, dust, etc. in the environment.
- Prolonged itching of the upper and lower eyelids is typical of blepharitis, an inflammatory process affecting the edges of the eyelids. Blepharitis, in turn, can be a consequence of infectious and inflammatory reactions in nearby structures, or traumatic and chemical damage.
- Periodically occurring itching and dry eyelids often appear as a result of anemia, vitamin and mineral deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, helminthiasis, dental problems, chronic diseases. Quite often, itching accompanies many other diseases that are not related to ophthalmological pathologies.
- Severe itching and flaking of the eyelids can be caused by scaly blepharitis, and if the scales peel off and ulcers form, then we may be talking about ulcerative blepharitis. This disease requires quite complex and long-term treatment, with initial identification and elimination of the root cause of the pathology.
- Itching under the eyelid or in the upper eyelid area is often the first sign of a maturing stye. Stye is a purulent inflammatory element in the hair follicle. It, in turn, develops as a result of infection getting inside the hair follicle of the eyelash or into the sebaceous gland. The pathology often appears after hypothermia, with a strong decrease in immunity.
- Itching of the eyelids and eyebrows, which intensifies at night, is a consequence of demodicosis, a parasitic disease caused by the introduction of the demodex mite into the skin. Itching can be widespread, all over the face, or from the eyes to the forehead. This disease can be successfully treated, but for this you need to see a dermatologist.
- Glaucoma or cataracts are also sometimes characterized by itching in the corners of the eyes. This symptom occurs along with double vision, the appearance of circles before the eyes, and a feeling of constant discomfort. These diseases, in turn, arise against the background of impaired fluid flow, increased pressure inside the eye. And cataracts, for example, are a common problem in diabetes.
There are other reasons for the appearance of uncomfortable sensations in the eye. For example, itching of the eyelid and rhinitis are symptoms that sometimes manifest themselves in acute respiratory viral infections, flu. After the main pathology is cured, such itching goes away on its own.
Itching of the eyelids and redness can be observed periodically in people who use contact lenses - especially those that are worn for a long time. To help your eyes and eliminate itching, you need to see a doctor and ask about the additional use of special eye drops. No less often, itching and swelling of the eyelids are caused by improperly selected lenses or liquid for them. In this situation, you also need to see a doctor and choose the right accessories.
If a person spends a long time and often at a computer monitor, or does not take his eyes off the smartphone screen, then due to the drying out of the mucous tissues of the eye, itching of the eyelash edge or corners of the eyes may be observed. To avoid such problems, you need to periodically shift your gaze to other objects, perform special "eye" gymnastics.
Itching of the face and eyelids can be caused by taking certain medications, such as antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Hormonal imbalances and thyroid problems cause dry skin and mucous membranes, swelling of the eyelids and itching around the eyes in many people. Health may worsen under the influence of severe stress, nutritional errors, etc.
Both allergic processes and the herpes virus can cause the simultaneous appearance of symptoms such as a rash around the eyes and itchy eyelids. With herpes, small blisters with liquid inside are formed. In addition, general malaise, chills and other characteristic signs are noted.
Risk factors
The following categories of people are at high risk of developing itchy eyelids:
- those who ignore personal hygiene rules;
- those who ignore safety rules when working with abrasives, sand, chemicals;
- those who had the misfortune of coming into contact with patients suffering from contagious conjunctivitis;
- in patients with immunodeficiency;
- in individuals who are carriers of chlamydial infection;
- in people suffering from any eye diseases, as well as in those who wear contact lenses;
- for those who are forced to look at a monitor screen for a long time;
- in people prone to allergic reactions.
Pathogenesis
According to the etiological factor, itching of the eyelids is divided into the following types:
- bacterially caused itching;
- viral-induced itching;
- allergic itching;
- fungal-induced itching.
In addition, itching sensations can appear under the influence of physical and chemical factors - for example, radiation, bright light, other irritants and conditions.
Bacterial-caused itching is most often caused by staphylococcal, streptococcal flora, as well as gonococcus, chlamydia. Viral-caused itching is provoked by adenovirus, herpesvirus, influenza virus.
Allergic itching is the most common. In the vast majority of patients, itching of the eyelids becomes one of the manifestations of such a pathology as pollinosis. Pollinosis is a specific reaction of the body to allergens that enter not only the eyes, but also the respiratory system. Most often, this allergen is plant pollen and fluff. With pollinosis, such characteristic symptoms as a runny nose and allergic itching of the eyelids in combination with conjunctivitis quickly develop.
If a person has a bacterial, viral or fungal itch, then he is considered contagious: if certain rules are not followed, the infection can spread to other healthy people.
Symptoms
Itching of the eyelids can be detected on its own, or accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of skin scales, peeling of the skin on the eyelids, above the eyes, on the forehead or face;
- the appearance of additional inclusions on the skin or on the cornea;
- increased blinking;
- the release of tears, sometimes the appearance of purulent or other discharge;
- deterioration of vision (double vision, clouding, ripples, circles before the eyes, etc.).
Itchy eyelids are not always a symptom of a disease. For example, the first signs of a banal lack of sleep are reddened eyelids, swelling under the eyes, a feeling of itching and discomfort. And signs of improperly selected cosmetics can be loss of eyelashes against the background of the same unpleasant itching sensations.
With conjunctivitis, itching is also accompanied by other painful symptoms: in particular, it can be a burning sensation, photophobia, a feeling of "sand" or a foreign particle getting in. In the morning, the appearance of discharge is especially noticeable: the eyelids seem to stick together, mucus or pus accumulates in the corners of the eyes.
Viral inflammation and itching of the eyelids may be accompanied by moderate lacrimation, photophobia, runny nose, enlargement of the submandibular or parotid lymph nodes, and blepharospasm.
Itching of an allergic nature is usually severe and can be accompanied by pain, swelling, and in many patients – allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and cough.
If the itching is fungal, catarrhal or purulent inflammation may develop. Candidiasis occurs with the formation of nodular rashes, which are an accumulation of epithelial cells and lymphoid tissue. Aspergillosis is characterized by reddening of the conjunctiva with involvement of the cornea in the process.
If the itching is of toxic origin, after some time, severe pain sensations begin to bother, especially when moving the eyeballs, blinking, or when opening or closing the eyelids.
Diagnostics itchy eyelids
Diagnosis of itchy eyelids should be performed by an ophthalmologist, in a special clinic or equipped office. Basic diagnostic measures are based on collecting patient complaints, on clinical manifestations of the disease. Anamnestic information is also important to determine the origin of the problem: the likelihood of contact with sick people, contact with potential allergens, the presence of other diseases, the presence of a connection with seasonality, the influence of ultraviolet radiation, etc.
During an external examination, the doctor may detect redness and swelling of the conjunctiva, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyeball, discharge and crusts on the eyelids.
A routine doctor's examination may include the following procedures:
- Laboratory tests:
- cytological analysis of a scraping or imprint smear;
- bacteriological analysis of conjunctival smear;
- analysis of the antibody titer (IgA and IgG) to a possible infectious agent (tear fluid or blood serum is examined);
- analysis for demodex.
If the itching is of an allergic nature, an additional skin-allergy, conjunctival, or nasal test may be performed.
- Instrumental diagnostics:
- biomicroscopy of the eye – examination of the conjunctiva, cornea and deeper structures of the eye using a slit lamp;
- tonometry – measurement of intraocular pressure;
- lacrimal duct irrigation is a diagnostic procedure that is performed if there is a suspected obstruction of the lacrimal ducts;
- -Ultrasound of the eyeball – this procedure is performed to determine retinal detachment, tumors, foreign particles;
- electrophysiological study – assessment of the condition of the retina, optic nerves, and the overall functionality of the visual apparatus.
- Additional consultations:
- infectious disease doctor;
- dermatovenerologist;
- phthisiatrician;
- surgeon.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is usually carried out with the following disease states:
- conjunctivitis;
- episcleritis and scleritis;
- keratitis;
- uveitis (iritis, iridocyclitis, choroiditis);
- acute attack of glaucoma;
- foreign particle in the organ of vision;
- canalicular obstruction due to dacryocystitis.
 [ 10 ]
[ 10 ]
Treatment itchy eyelids
The treatment features for itchy eyelids are determined by an ophthalmologist. His task is to identify the root cause of the problem, and in the case of an infectious disease, to identify the pathogen, as well as to assess the severity of the process and the likelihood of complications.
Complications and consequences
If itching of the eyelids is associated with some infectious pathology, then if the problem is ignored for a long time, various unpleasant complications may arise - in particular, the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
In addition, we cannot help but mention other, albeit rare, but very dangerous consequences of untreated eye and eyelid diseases:
- blepharitis;
- astigmatism;
- dry eye syndrome;
- cataract;
- glaucoma;
- keratitis;
- canaliculitis.
Even an experienced doctor will not be able to accurately predict what exactly will happen if infectious itching of the eyelids is not treated. For example, the most dangerous complication of viral itching is often keratitis - an inflammatory reaction in the cornea. The disease manifests itself in its clouding, the appearance of ulcers on it, as well as pain and redness. To avoid such complications, it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible when itching of the eyelids appears - especially if the trouble has affected a child. The superficial form of keratitis can transform into a deep form in a short time, and the inflammation will spread to the internal corneal tissues. As a result - the formation of cicatricial changes, deterioration of vision and even its loss.
Any pathology can negatively affect a person's health. That is why doctors insist: do not be shy about contacting a doctor at the first signs of pain. Timely treatment will help prevent the development of many troubles.
Prevention
Itchy eyelids can be prevented in most cases if you pay attention to the slightest problems with the whole body and the visual organ in particular.
- You must not touch your eyes with dirty hands or rub your eyelids.
- You should only use your personal towel and other hygiene products.
- It is important to be careful and attentive when choosing cosmetics. If possible, it is better to consult a specialist.
- It is necessary to follow a daily routine, ensure adequate and healthy sleep, not to overwork, and not to overload the organs of vision (especially if your professional activity involves spending a long time in front of a computer monitor).
- Contact lenses should be selected in consultation with a doctor.
- Pillows and blankets (especially feather and down ones) should be cleaned and aired regularly. Bed linen should be changed systematically.
- When working with chemicals, abrasives, etc., it is important to wear special protective glasses.
- If any foreign particles get into your eyes, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
- If an allergic reaction occurs, it is advisable to determine its cause and eliminate it (for example, adjust your diet, change cosmetics, etc.).
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to remember several situations in which medical assistance must follow without fail and as quickly as possible:
- if itching of the eyelids is accompanied by even partial deterioration of vision (double vision, change in the quality of perception, fogginess, etc.);
- in case of traumatic eye injury;
- if itching of the eyelids is accompanied by pain, or turns into pain;
- if any light source causes irritation in the eyes;
- if itching is accompanied by swelling and the formation of greenish or yellowish discharge.
Forecast
In the overwhelming majority of cases, itching of the eyelids ends with recovery without the development of adverse consequences for the organ of vision. Of course, provided that timely medical attention is sought and adequate complex treatment is prescribed.
With secondary itching, which appears against the background of other ophthalmological diseases, vision may suffer to varying degrees.
Such a painful symptom as itching of the eyelids relatively rarely transforms into a serious problem that threatens the patient's health and life. However, this symptom cannot be ignored either: the sooner treatment is prescribed and carried out, the faster the disease will be cured.

