
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Hyperechogenic mass: with anechogenic inclusions, acoustic shadow, heterogeneous, avascular
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
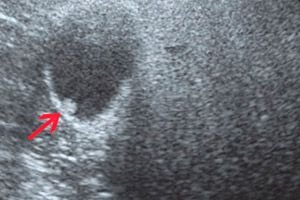
Any tissue area with increased density for ultrasound waves is a hyperechoic formation. Let's consider the causes of this phenomenon, types, diagnostic and treatment methods.
Many patients experience hyperechogenicity after an ultrasound examination. It is not a diagnosis, but only a signal from the body about pathological processes and a reason to conduct a more detailed examination. In most cases, the detected compaction is a calcified tissue area, bone formation, stone or fat.
On the ultrasound monitor, echogenicity looks like a light or almost white spot. Based on this, it can be assumed that this is a compaction. Such tissues are visualized as point, linear or volumetric structures within the examined organs. If the area is darkened, then this is a hypoechoic formation.
Epidemiology
Echopositive compactions occur in both adults and children. Epidemiology, i.e. the pattern of occurrence of echo structures, depends on the general condition of the body. Most often, high acoustic density is detected during examination of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, uterus and ovaries.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Causes hyperechogenic mass
There are many reasons that can provoke echo-positive compactions of internal organs. The reasons for the hyperechoic formation depend on its location, size and general condition of the body. Most often, ultrasound reveals calcifications, which can be both multiple and single with an acoustic shadow. They occur in the following pathologies:
- Infectious lesions of the body and lungs – tuberculosis, flu, bronchitis, pneumonia.
- Diseases of the prostate gland (prostatitis) and some venereal diseases.
- Thyroid gland lesions – nodular, diffuse or toxic goiter, hypothyroidism.
- Cardiovascular diseases – myocardial infarction, endocarditis, pericarditis.
- Liver diseases – chronic viral hepatitis, amebiasis, malaria.
- Endocrine diseases, dermatomyositis, Wagner's disease, can lead to calcium foci on skeletal muscles, joints, lungs and gastrointestinal organs.
If microcalcifications are detected, this most likely indicates the malignancy of the seals. Pathological inclusions occur in chronic nephritis, injuries and other diseases. They do not contain liquid, but have high acoustic density and low sound conductivity. The detected neoplasms may be framework elements of organ tissues.
Risk factors
An accumulation of tissue that is atypical for an organ and is detected during an ultrasound examination is an echo-positive compaction. Risk factors for their development are based on conditions such as:
- Various infectious diseases, especially those with an acute course.
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Long-term negative thermal or chemical exposure, i.e. unfavorable working conditions, etc.
- Acute chronic diseases.
- Poor nutrition and bad habits (smoking, alcoholism).
- A sedentary and inactive lifestyle.
- Injuries.
All the above factors can lead to pathological conditions. Therefore, it is very important to carry out timely prevention of future deviations.
Pathogenesis
Tissues with high density for ultrasound waves can be detected in patients of any age. The pathogenesis of their development is most often associated with previously suffered infectious or inflammatory processes, injuries. That is, such deposits act as a response of the body to the suffered pathological process.
Seals are found in any organs. Most often, they are calcium and salt deposits, i.e. calcifications, tumor neoplasms, lipoma. In any case, they require careful diagnostics and, if necessary, conservative or surgical treatment.
Symptoms hyperechogenic mass
Since echo-positive inclusions can occur on different internal structures, the overall picture of the pathological condition depends on the degree of damage to a particular organ. Symptoms of a hyperechoic formation have a number of similar signs:
- Chronic inflammation: general weakness, headaches, elevated body temperature.
- Loss of muscle mass and sleep disturbances.
- Neurological disorders: dizziness, increased irritability.
Local symptoms depend entirely on which organ has an echo-positive inclusion:
- Lungs - rapid breathing, shortness of breath, specific cyanosis.
- Liver – painful sensations in the right hypochondrium, vomiting and nausea, fluid retention.
- Kidneys - change in urine color, bad breath, symptoms of kidney failure.
- Prostate gland – urinary dysfunction, erectile dysfunction.
- Thyroid gland – deficiency of thyroid hormones, drowsiness and general weakness, enlargement of the organ.
- Cardiovascular system – pain in the heart muscle, irregular heartbeat, cyanosis or blue discoloration of the extremities, lips, ears.
Based on the above symptoms and ultrasound results, the doctor prescribes a set of additional studies and draws up a treatment plan.
 [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
[ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
First signs
In some cases, echo-positive inclusions may be the first signs of malignant processes. The pathological condition is accompanied by progressive symptoms from the affected organs and systems. To confirm oncology, a biopsy and a number of other diagnostic procedures are necessary. If tumor markers are not detected, then monitoring the patient's condition and echo structures is indicated.
Hyperechoic formation in the liver
Very often, the tumor appears as a hyperechoic formation on ultrasound. In the liver, it may indicate cancerous lesions or metastasis from other organs. After such an ultrasound conclusion, the patient is sent for histological verification.
Hyperechogenicity in the liver most often indicates a hemangioma. The size of this neoplasm depends on its type. Capillary lesions are about 3 cm, and cavernous lesions can exceed 20 cm. According to medical statistics, women are more likely to face this problem. At the same time, its exact causes are unknown, but scientists associate the appearance of seals with hormonal levels. Also, there are a number of cases when tumors were detected in pediatric patients. This may indicate a genetic predisposition.
Signs of a liver tumor may not be apparent. If it grows quickly, the symptoms become pronounced. The patient complains of nausea and vomiting, pain in the side. Treatment depends on the size of the tumor. If it is less than 5 cm, then only medical observation is indicated. But if the compaction interferes with the normal functioning of neighboring organs or its size is more than 5 cm, then surgery is performed.
Hyperechoic formation in the kidney
During an ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands and kidneys, areas of tissue with high acoustic density and altered internal structure may be detected. A hyperechoic formation in the kidney is acellular microstructures represented by accumulations of calcifications, protein-lipid deposits or fibrous-sclerotic areas. On the ultrasound screen, such an area looks lighter in comparison with the rest of the renal tissue.
Types of echo-positive inclusions in the kidney:
- Volumetric formations with acoustic shadowing are observed with large stones and macrocalcifications, sclerotized areas due to a long-term inflammatory process.
- A neoplasm without an acoustic shadow – in most cases indicates atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels, sand, cystic cavities, benign or malignant tumors, small stones or fatty tissue of the renal sinus.
- Bright point inclusions without acoustic shadow indicate the presence of psammoma bodies or microcalcifications. They are observed in malignant and diffusely sclerosing tumors.
Combined variants of the above-described seals in various combinations may be encountered on ultrasound. The appearance of such tissues may indicate kidney stone disease, hemorrhages, cystic growths, scars, oncological tumors, inflammatory processes.
After the ultrasound examination, the patient is sent for additional diagnostics to clarify the diagnosis. A set of laboratory tests of blood for tumor markers, urine, X-ray and MRI are carried out. If the pathology is complex, then a biopsy is indicated. Treatment depends entirely on the type of compaction. If these are stones, then the patient is prescribed diuretics. Benign neoplasms and cysts are removed by partial excision. In case of malignant tumors, complete removal of the kidney and a long course of chemotherapy are indicated.
Hyperechoic formation in the gallbladder
An area of an organ or tissue with high density for ultrasound waves is a hyperechoic formation. In the gallbladder, such a compaction may indicate:
- Stones are dense foci in the lumen of the bladder with an acoustic shadow. The formation is mobile with deep breathing or any movements, but fixed stones are also encountered.
- Bile sludge is an accumulation of bile sediment at the bottom of the organ. It has high echogenicity and does not produce an acoustic shadow, and can change shape when the body moves. In some cases, bile can be so viscous that its structure becomes similar to that of the liver. The patient is prescribed additional studies of the gallbladder and choleretic drugs.
- A cholesterol polyp is a neoplasm that grows from the walls of a high-density organ. It has a small diameter of about 2-4 mm, a wide base, and a smooth outline.
In addition to the above reasons, the lump may be malignant or indicate metastases from other organs.
Hyperechoic formation of the thyroid gland
Poor environmental conditions, ionizing radiation, endocrine diseases, iodine deficiency in the body and a number of other factors can cause hyperechoic formation of the thyroid gland. In most cases, the compaction is a nodule that can grow and divide. Sometimes even increased stress situations and heredity provoke echo-positive inclusions.
Thyroid tissues with increased density may be associated with the following conditions: adenoma of the gland, calcifications, papillary cancer without encapsulation, cartilaginous rings of the trachea, etc. Echogenicity does not always manifest itself in the early stages. Most often, the pathology makes itself known when the compaction reaches large sizes.
Characteristics of fabrics with high acoustic density:
- Increased weakness and constant feeling of drowsiness.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hot and cold flashes.
- Deterioration of hair and nails.
- Sudden changes in weight.
- Irritability and frequent mood swings.
The growth of nodular formations is accompanied by an increase in the gland, constant shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. The voice is impaired, wheezing and pain when swallowing appear, discomfort in the throat.
To clarify the causes of the neoplasm and its type, the patient is prescribed a set of comprehensive studies. In addition to ultrasound, it is necessary to take a hormone test, a general blood test, a chest X-ray and much more. If there is a suspicion of oncology, then a fine-needle biopsy is indicated.
Treatment depends on the course of the disease, the number of seals, their size and the characteristics of the patient's body. If it is a single nodule less than 1 cm, then regular monitoring by a doctor is prescribed. If the nodule causes discomfort, then various methods of suppressing thyroid activity are used for its treatment. This can be laser destruction, the use of radioactive iodine, ethanol sclerotherapy, etc. Surgical intervention is possible if the tumor is large, causes pain and interferes with breathing.
Hyperechoic formation in the uterus
If a hyperechoic formation in the uterus is detected during an ultrasound examination of a woman, this may indicate the following conditions:
- In the middle of the menstrual cycle, the central part of the endometrial tissue becomes hyperechoic with a dark rim. During menstruation, the "rim" becomes lighter and thicker.
- A lump may indicate a formation in the organ cavity, for example, a polyp or fibroid, but not pregnancy.
- After an abortion, fetal skeletons may remain in the uterus, which calcify and are defined as hyperechogenicity. Very often, such women are diagnosed with secondary infertility, and menstruation is very heavy.
- In chronic endometritis or after surgical curettage, ultrasound shows acoustic-type seals and air bubbles.
- Advanced uterine myoma is another possible cause of high-density tissue for ultrasound waves. Myoma may contain calcifications with a distal shadow. If the neoplasm is multiple, the normal contour is disrupted and the organ cavity is displaced.
- Calcified areas indicate myomatous nodes in the uterine cavity. This is possible after intrauterine surgical interventions or recent labor.
To identify each of the above conditions, the patient is prescribed a set of additional studies. After which treatment or observation by a doctor may be prescribed.
Hyperechoic formation of the cervix
An area with increased density, i.e. a hyperechoic formation of the cervix, may be a polyp or a blood clot that has not come out after menstruation. To differentiate these conditions, an ultrasound examination is performed on the 5th-10th day of the cycle. If echo-positive structures are detected in the muscle tissues of the organ, this may be a sign of a myoma, lipoma or tumor. In this case, the uterus increases in size and changes its contours.
Foci of increased acoustic density in the thickness of the myometrium are observed in women with diabetes during menopause or after endometrial curettage. In the latter case, light areas on ultrasound indicate scarring of the organ walls or remnants of the ovum.
Hyperechoic formation in the mammary gland
Every woman may face the problem of breast tumors. Hyperechoic formation of the mammary gland requires additional research, as it may be a sign of serious pathologies. The echostructure of the tumor may be different and depends on a number of factors: calcifications, fibrosis, areas of necrosis.
The mammary gland consists of stroma and parenchyma. The latter consists of ducts and acini. The stroma supports the breast, i.e. acts as a connective tissue that connects the fatty tissue and parenchyma. The presence of inclusions in these tissues is most often associated with the following diseases:
- Carcinoma - has unclear contours, acoustic shadow and uneven structure.
- A cystic formation is a compacted area with regular and clear contours.
- Atypical cystic formation – has thick walls, which on ultrasound appear as a bright spot with strong growth inside.
Special attention should be paid to additional diagnostic studies if the lump is accompanied by the following symptoms: chest pain not associated with the menstrual cycle, trauma, change in density or nipple retraction, asymmetry, enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes. In some cases, echo-positive inclusions are associated with malignant diseases.
Hyperechoic formation in the bladder
During an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, a hyperechoic formation in the bladder may be detected. This phenomenon is most often associated with stones or parietal polyps. Polyps are less echogenic, but can reach 8-10 mm. Stones have a higher density and acoustic shadow, their sizes vary from multiple small inclusions to large formations. To differentiate these conditions, the patient is asked to change their position. Polyps remain in place, while stones are mobile.
Particular attention should be paid to the structures of the bladder, which are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Painful urination.
- Blood and sediment in the urine.
- Urinary retention.
- Sharp painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
If the above symptoms are present, it is necessary to conduct additional studies, based on the results of which adequate therapy should be administered.
Hyperechoic formation in the ovary
If an ultrasound examination reveals a high-density area that does not allow ultrasound waves to pass through, this indicates a hyperechoic formation. It is as common in the ovary as it is in the uterus or other organs.
The compaction may be a calcium salt deposit, a benign or malignant tumor. In any case, it requires regular monitoring. If an increase in the neoplasm is observed during dynamic monitoring, the patient is prescribed a number of additional studies, one of which is a blood test for the CA 125 tumor marker and an oncologist consultation.
Echo density in the ovary may indicate a dermoid cyst, which includes elements of bone, fat and hair. In this case, surgical intervention and removal of such an inclusion is indicated.
Hyperechoic formation in the heart
Increased brightness of a certain area of the heart muscle on ultrasound examination is a hyperechoic formation. In the heart, it is very often diagnosed in the unborn child at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy. The focus of increased density is not a developmental defect, but simply reflects the nature of the ultrasound. This phenomenon may indicate the deposition of calcium salts in one of the muscles of the organ, which does not affect its functioning in any way.
Echo-positive seals require observation, as they may disappear in the dynamics of ultrasound. In some cases, inclusion indicates chromosomal diseases, for example, Down syndrome. But this marker is a minor marker of this syndrome, so its presence very rarely confirms the disease and does not require additional research.
Hyperechoic formation in the prostate
The main cause of hyperechoic formation in the prostate is inflammatory lesions of the gland. If high-density inclusions were detected during an ultrasound examination, this is a reason to take additional tests. First of all, this is a bacteriological culture of prostate secretion, a smear from the urethra for infections.
Bright light inclusions of the prostate on the ultrasound monitor may indicate neoplasms of phosphorus and calcium. Their size is within 2-20 mm. Prostate calcifications are characterized by a special shape. Stones may indicate benign hyperplasia or chronic prostatitis. In most cases, high-density tissues are detected in men over 50 years of age.
Calcifications in the prostate gland are associated with many factors, let's consider them:
- Lack of fulfilling sexual relations over a long period of time.
- Sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Hypodynamia.
- Frequent constipation.
- Chronic infectious diseases of the body.
- Improper nutrition with a predominance of fatty foods.
- Regular hypothermia of the body.
Hyperechogenicity of this nature does not require treatment and is not accompanied by painful symptoms. The main contraindication for calcium salt deposits in the prostate is massage of this organ. This is due to the high risk of injury and stagnation of prostatic secretion. If calcifications have arisen against the background of chronic prostitis, a surgical operation is performed.
Hyperechoic formation in the pancreas
During ultrasound examination of internal organs, special attention is paid to their echogenicity. It allows to evaluate the density and condition of the examined organs. Hyperechoic formation in the pancreas indicates malfunctions of the organ. Echostructures can be associated with inflammatory processes. The pancreas is responsible for digestion and metabolism. It has endocrine and exocrine functions, carries out external and internal secretory activity. Changes in the condition of its tissues can cause serious disorders in the body.
The main reasons for echopositivity of the pancreas:
- Pancreatitis
- Tumor neoplasms
- Increased gas formation
- Tissue calcification
- Necrotic changes in parenchyma tissue
- Fibrous and fibrocystic changes
- Diabetes mellitus
- Lipomatosis
Seals may arise due to reactive inflammation in many infectious diseases, due to food intake or lifestyle changes. In this case, moderate echogenicity is observed. Localized increase in echogenicity is most often associated with calcifications, pseudocysts (fluid formations arising due to pancreatitis), metastatic tumors and fibrous areas.
Treatment depends entirely on the cause of the pathological condition and general well-being. If high acoustic density of tissues is associated with acute pancreatitis, the patient is prescribed drugs to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in the gastrointestinal tract and inhibit the enzymatic activity of the pancreas. In case of lipomatosis, a diet with a reduced amount of animal fats is indicated. If the appearance of inclusions is associated with stones in the ducts, fibrosis or calcifications, a diet is prescribed and the issue of surgical intervention is considered.
Hyperechoic formations in the spleen
If small hyperechoic formations in the spleen were detected during an ultrasound examination, then in most cases these are calcifications. Larger inclusions, triangular in shape and with clear contours are splenic infarctions and old injuries. Neither the former nor the latter require treatment.
If the formations have a heterogeneous structure, unclear boundaries and an acoustic shadow, this indicates abscesses and metastases of malignant tumors. The spleen very often suffers from metastasis from other organs. On ultrasound, metastases look like bright inclusions with an uneven contour. High-density tissues can also indicate benign lesions: lipoma, hemangioma.
Hyperechoic formations in the thalamus
The thalamus is a large paired accumulation of gray matter in the lateral walls of the diencephalon. Hyperechoic formations in the thalami are detected in 4% of people with organic lesions of the nervous system. In most cases, they indicate tumor lesions. This pathology ranks fifth among oncology of other localizations, yielding to neoplasms in the uterus, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract.
Seals in the thalamus are found in patients of any age, but most often in puberty and at the age of 45-50 years. The exact cause of pathological inclusions is unknown. Scientists assume that they are associated with the late active development of cells that were previously dormant. Also, do not forget about exogenous and endogenous factors: infections, hormonal disorders, injuries.
The symptoms of pathological compactions are based on the histostructure of the tumor. Patients experience increased intracranial pressure, which provokes headaches and dizziness, vomiting attacks, changes in the bones of the skull, damage to the cranial nerves and psyche. Treatment of these conditions depends on the patient's age, the characteristics of his body and the volume of hyperechoic compaction.
Forms
There are several types of hyperechoic neoplasms, their types depend on the localization. Let's consider the main types of inclusions:
- Pronounced point compactions of small size and without acoustic shadow.
- Volumetric formations without shadow, but large in size. Such components may indicate both benign and malignant tumors. But most often these are fibrous-sclerotic areas.
- Large tissues with high density and acoustic shadow. They indicate sclerotic zones with a large accumulation of psammoma bodies. In benign tumors, such pathology occurs in 4% of cases, and in malignant tumors in 30%. Most often, large formations are diagnosed as papillary or medullary carcinomas.
Many patients are found to have different types of inclusions, i.e. large and small seals, both with and without acoustic shadow. But only a doctor can determine the danger of hyperechoic neoplasms and their features.
Hyperechoic formation with anechoic inclusions
The echogenicity of tissues depends on their ability to absorb and reflect ultrasound. This is due to the morphological features of the structure of organs. That is, the less liquid the object under study contains, the higher its echogenicity. While the absence of liquid indicates low density - anechoicity.
A hyperechoic formation with anechoic inclusions can occur in the following organs:
- Mammary gland - most often indicates a cyst. In this case, a complex cyst is visualized as a bright area with dark dots. For detailed diagnostics, a biopsy and detailed mammography are performed. In lactating women, this may be a cavity with milk.
- Thyroid gland - this may be a cyst, a false cyst (formations with glandular tissue and a flocculent structure), an adenoma or colloid cysts. Additional studies are carried out to accurately determine the type of compaction.
- Uterus and ovaries - echostructures with anechoic areas occur during ovulation and before menstruation, with degenerative pathologies. If a seal is detected in the cervix, this may indicate an endometrial cyst, malignant processes or ectopia.
- Kidneys and liver – inflammatory processes, cysts, polycystic disease, nephropathy. If the compaction is detected near the kidney, it may be a perirenal hematoma.
That is, in most cases, a formation with anechoic areas indicates the presence of a cyst or malignant processes in the body. Additional studies are needed to determine the type of echostructure and its danger in more detail.
Hyperechoic formation with acoustic shadow
Very often, after an ultrasound examination of internal organs, the conclusion indicates the presence of a hyperechoic formation with an acoustic shadow. An acoustic shadow is formed from stones, air bubbles, bone tissue, connective tissue and dense formations.
The shadow is formed at the boundary of tissues that reflect ultrasound. During passage through such structures, the ultrasound beam is completely interrupted, forming a reflection. That is, such tissues have a high acoustic density.
Heterogeneous hyperechoic formation
If an ultrasound examination reveals a non-uniform hyperechoic formation, this may indicate acute inflammatory or malignant processes in the body. If we consider this condition using the pancreas as an example, a non-uniform compaction in most cases is associated with pathologies such as:
- Subacute and chronic pancreatitis - this condition is associated with an exacerbation of the disease at any stage. The pathological process can last from a week to several months. Treatment depends on the degree of heterogeneity. If the changes are not strong, then replacement therapy and diet are indicated.
- Cystic formations – most often, several such inclusions are formed on the pancreas. Some of them can be filled with liquid and change their location within the organ.
- Malignant and benign tumors – these pathologies change the structure of the organ at any stage. Complex diagnostics are necessary to differentiate such conditions.
Heterogeneous hyperechogenicity may indicate inflammation, digestive system disorders, enzyme deficiency. In a healthy person, the echostructure of the pancreas is smooth and uniform. Its clear contours are visible on ultrasound examination, indicating normal functioning of the body.
Avascular hyperechoic formation
Non-vascular seals are most often detected in the ovaries. An avascular hyperechoic formation may indicate a functional cyst. This is a benign tumor that forms both in the ovary itself and on its surface. The hollow formation arises from the natural structures of the ovary. As a rule, it appears due to a violation of ovulation and follicle growth. Most often, this pathology is diagnosed in women of childbearing age. Frequent stress, hormonal imbalances, bad habits and the presence of chronic diseases can lead to avascular seals.
Another possible variant of a dense non-vascular tumor is a dermoid cyst. This avascular echostructure is benign and consists of epidermal tissue, dermis, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands. It is formed during embryogenesis, so it is congenital. Surgical intervention aimed at removing the neoplasm is indicated for treatment.
 [ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ]
[ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ]
Homogeneous hyperechoic formation
A homogeneous hyperechoic formation detected during an ultrasound examination occurs for many reasons. The neoplasm may be associated with inflammatory and infectious processes in the body, progression of existing diseases. With more detailed diagnostics, a homogeneous seal may turn out to be a salt deposit, a cyst, a lipoma or a tumor.
Complications and consequences
The consequences and complications for the body depend on the type of hyperechoic formation and its localization. If the compaction is a calcification, then patients most often suffer from cardiovascular, renal, hepatic and respiratory failure, hypothyroid crisis.
If a malignant tumor is confirmed, the main danger is metastases and uncontrolled growth of the tumor. Even after successful treatment, there is still a risk of relapse, so the patient is prescribed regular examinations to monitor the body's condition.
An echo-positive seal may be a lipoma (fatty tumor), i.e. a benign neoplasm of adipose tissue. In this case, the patient will face complications such as: inflammation, painful sensations at the site of the growth, displacement and deformation of surrounding tissues, and even malignant degeneration.
Diagnostics hyperechogenic mass
Ultrasound examination is the main method of diagnosing a hyperechoic formation. The first thing to do when such a compaction is detected is to determine the nature of its occurrence. Particular attention is paid to the general condition of the body and the accompanying symptoms. Additional diagnostic procedures depend on the localization of the inclusions.
- Kidneys - after the ultrasound, the patient is prescribed a set of laboratory tests (blood and urine tests, blood for biochemistry, immunology), as well as magnetic resonance imaging and a set of tests to detect a tumor (angiography, cavagraphy).
- Liver – ultrasound examination is combined with computed tomography, hepatoscintigraphy, hepatoangiography, diagnostic biopsy and laparoscopy with morphological examination of tissues.
- Uterus and ovaries – general gynecological examination, CT, MRI, ultrasound, laboratory tests (blood, urine, smears). Transvaginal diagnostics, hydrosonography, angiography and others are also used.
- Brain (thalami) – computed tomography, magnetic resonance and ultrasound diagnostics, radiography. To differentiate malignant neoplasms, endoscopic examinations, biopsy with histology and cytology, radioimmune and immunoenzyme methods are used to determine tumor markers.
- Mammary gland – mammography, ultrasound, positron emission tomography, laboratory tests to detect oncology, ductography. If malignant seals are suspected, a biopsy is performed with subsequent examination of the biopsy.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor makes a treatment plan. Therapy can be either medicinal (kidney stones) or surgical (malignant seals). If the detected inclusions are small in size and are not accompanied by pathological symptoms, then monitoring their condition with regular ultrasound is indicated.
 [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ]
[ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ]
Tests
Diagnostics of hyperechoic formations involves the use of laboratory research methods. Tests are prescribed to clarify the state of the body and identify pathological deviations.
Let's look at an approximate list of tests that need to be taken when detecting tissues with high acoustic density:
- Clinical blood test (anemia, neutrophil formula, leukocytosis).
- Biochemical blood tests (tumor markers, uric acid, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium levels).
- General and biochemical analysis of urine (erythrocytes, leukocytes, salts), bacterial culture.
Based on the results of the above studies, a plan for further diagnostic procedures is drawn up.
 [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ]
[ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ]
Instrumental diagnostics
When echo structures are detected in different organs or tissues, various diagnostic methods are used to clarify their origin. Instrumental diagnostics is aimed at determining the nature of inclusions, their exact localization, volume and other features.
Let's consider the main instrumental examination methods:
- Ultrasound examination is a safe, non-invasive method that uses ultrasound waves. It is with its help that hyperechoic formations are most often detected.
- Radiography – allows to determine the localization of the compaction and its structure. Most often used with contrast
- Computer tomography is a method of radiation diagnostics based on obtaining a layered image of any organ or tissue. It determines the localization of the echo structure and its features.
- Magnetic resonance imaging – visualizes deep-seated seals. Used to study inclusions in the brain.
- Puncture biopsy – is used if the above methods have confirmed the presence of calcifications or lipoma. The tissues obtained as a result of the biopsy are sent for cytology and histology.
All the above-described diagnostic procedures allow for a comprehensive assessment of the degree of danger of the identified echostructures.
Differential diagnosis
A hyperechoic formation can occur on any organ or tissue. Differential diagnostics is necessary to determine the pathological process and other changes in the body. Calcinates, bone formations, fatty deposits, stones or tumors may be hidden under the compaction.
In the process of differentiation, the neoplasm is compared with inflammatory processes (abscess, nephritis, carbuncle), scar tissue, hemorrhages and hematomas, stones and sand (urolithiasis) and seals of a different nature (malignant tumors, cysts).
Ultrasound examination and laboratory tests (blood test for tumor markers and urine test for mineral salt levels) are used for diagnostics. Magnetic resonance imaging is also performed, and, if necessary, endoscopic examination with tissue examination. The results of differential diagnostics allow for a treatment plan or monitoring of echo-positive inclusions.
Who to contact?
Treatment hyperechogenic mass
Depending on the type of the detected echostructure, the doctor makes a plan for further diagnostics. Treatment of hyperechoic formation is based on the results of the studies.
- Calcifications - if salt deposits are detected in the kidneys, the patient is prescribed special diuretics to help remove the stones. It is also possible to perform lithotripsy to destroy the seals using shock waves. After crushing, the stones are removed from the body through urination. In particularly severe cases, surgery is indicated. If calcifications are detected in the mammary gland, and they do not indicate a malignant process, then regular medical monitoring is recommended.
- Inflammatory diseases – antibiotics are indicated for the treatment of seals caused by various types of diseases and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Tumor formations - treatment of hyperechoic structures of benign and malignant nature is carried out by surgical intervention. Benign tumors are removed by laparoscopy or resection, and malignant ones are removed surgically followed by chemotherapy.
In case of multiple echo-positive inclusions, medical observation is indicated, regardless of the localization of the foci.
Medicines
Treatment of echostructures depends entirely on the cause that provoked their appearance. The doctor selects medications based on the patient's condition. Since in most cases hyperechoic formations are stones and are found in the kidneys, urinary and gall bladder, prostate, we will consider the most effective medications for their elimination.
- Blemaren is a drug with nephrolitholytic properties. It promotes alkalization of urine, dissolves and prevents the formation of uric acid stones. Neutralizes urine due to citrate metabolism, excess alkali is excreted by the kidneys. It is used to dissolve and prevent uric acid and calcium oxalate stones in the urinary tract. The tablets are contraindicated in acute or chronic renal failure, intolerance to the components of the drug and infectious lesions of the urinary tract.
- Magurlite is a diuretic drug. Its action is based on shifting the pH of urine towards an alkaline reaction and inhibiting the formation of stones. It is used to remove stones from the kidneys and urinary tract. It is available in 2 g sachets. The drug is taken in the morning and evening, 6-8 g per day. The main contraindication is chronic urinary tract infections and circulatory failure.
Another possible reason for the appearance of tissues with high density for ultrasound waves is an inflammatory process. Let's consider effective anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic properties. It is used for traumatic inflammation of soft tissues and the musculoskeletal system, bursitis, gout, neuralgia, osteoarthrosis and other pathologies. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the pathological process. Tablets can cause side effects: nausea, vomiting, headaches and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. The main contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, ulcerative colitis, hematopoiesis disorders, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ketorol is an anti-inflammatory drug with antipyretic and analgesic properties. It is used for severe pain syndrome and various inflammatory processes in the body. Tablets are taken 1 pc. 2-4 times a day. Side effects are manifested in the form of digestive disorders, swelling of the face and limbs. The drug is contraindicated in case of intolerance to its components, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory bowel disease, renal or hepatic insufficiency.
If the echostructure is a tumor, the choice of medications depends on the localization of the neoplasm, therefore it is selected by the attending physician. In case of calcifications in various organs and tissues, medical supervision with regular ultrasound examination is indicated.
Vitamins
The human body functions fully due to the coordinated work of all organs and systems. Particular attention is paid to the immune system, since when it is weakened, the risk of various diseases increases. Vitamins are necessary to strengthen and maintain the body's defenses. Since one of the causes of hyperechoic inclusions is inflammatory processes, useful micro and macroelements help prevent this pathology. Vitamins are also used as a preventive measure against various types of neoplasms.
Let's look at the most essential vitamins for the body:
- A – participates in the formation of healthy tissues, maintains normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Group B – improves metabolic processes and carbohydrate metabolism, has a positive effect on the nervous and muscular systems. Accelerates the recovery process after illnesses.
- C – regulates salt metabolism in the body, fights infections, increases iron absorption, prevents the accumulation of carcinogens.
- D – regulates phosphorus-calcium metabolism, improves intestinal function.
- E – participates in cellular metabolism processes, slows down the aging process, improves blood circulation and muscle function.
- H – is responsible for the normal formation and growth of tissues.
- K – improves blood clotting, protects the liver.
- M – folic acid is necessary for the normal development of the spinal cord and brain. Participates in protein metabolism.
In addition to vitamins, the body also needs minerals:
- Iodine – maintains normal hemoglobin levels, destroys harmful microorganisms, normalizes thyroid function.
- Magnesium – normalizes blood circulation, cleanses the body, removes toxins.
- Selenium – prevents the development of tumors, maintains thyroid health.
- Iron – supplies cells with oxygen, activates cellular respiration and prevents hypoxia.
There are also ready-made vitamin and mineral complexes that are excellent preventatives for various seals. To prevent neoplasms and maintain normal functioning of the body, you can use:
- Immunal Forte is a vitamin complex based on plant components that increases the protective properties of the immune system and resistance to various diseases.
- Alphabet – removes toxins and harmful substances from the body, normalizing its functioning.
- Multi Tabs – the action of this complex is aimed at restoring protective forces and energy.
- Supradin – provides the body with all necessary vitamins and minerals, ensuring the normal functioning of internal organs and systems.
Before using any useful microelements, you should consult with your doctor. The doctor will help you choose the optimal complex that will meet your body's needs.
Physiotherapy treatment
Therapy using physical or natural factors is physiotherapeutic treatment. It involves influencing the body with: heat or cold, electric current, ultrasound, infrared, laser or ultraviolet radiation, magnetic field. It is also possible to use massages, hirudotherapy and much more.
The main advantage of physiotherapy is that it is safe and effective. It does not require additional medications, as it increases the body's defenses, reduces the time of treatment of various pathologies, activates biochemical processes, promoting recovery.
Depending on the cause of hyperechoic inclusions, their location and types, the following physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed:
- Cryotherapy – this method is based on the effect of low temperatures on the body, for example, liquid nitrogen. This stimulates the endocrine and immune systems, relieves pain, has an anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect.
- Laser therapy is a biostimulating method based on the impact of a laser on living tissue. It activates important biochemical processes, promotes cell and tissue renewal. It improves blood microcirculation, accelerates the healing of various types of lesions, and stops inflammatory processes.
- Magnetotherapy is a method of influencing the body with the help of a magnetic field. It has a healing effect, improves blood supply and saturation of tissues and organs with oxygen, reduces blood sugar levels, and normalizes the functioning of internal organs. This method simultaneously affects all body systems and metabolic processes.
If echogenic inclusions in the form of stones are detected in a patient, then electrophoresis with antibiotics or other metabolic agents is used for their treatment. During the physiotherapy procedure, drugs penetrate into the affected tissues, improve blood flow and promote the resorption of formations.
Despite all the positive properties, physiotherapy treatment has a number of contraindications: bleeding, malignant tumors and general severe condition of the body. It is an excellent preventive measure for many diseases, very often it is combined with the main course of treatment.
Folk remedies
After a series of diagnostic measures and determination of the type of echo-positive inclusions, the patient is prescribed a course of therapy. This may be taking medications in combination with physiotherapy, a special diet or surgery. Traditional medicine is used to reduce the size of the identified echo structures and prevent their growth. It helps to stop inflammatory processes and promotes the acceleration of metabolic processes in the body.
Let's look at several traditional medicine recipes aimed at strengthening the body and removing compacted stones:
- Take the rose hip rhizome, grind it thoroughly and pour out 20 g. Pour boiling water over the plant material and let it brew for 5-7 minutes. The drink should be taken before meals, 50-70 ml at a time. Positive results are observed with regular use of the product for 6 months.
- Take 10-15 g of crushed birch bark and pour 200 ml of boiling water. After 30 minutes, strain, add 10 ml of lemon juice and water. Take the infusion 3 times a day before meals.
- Squeeze the juice from the rhizomes of fresh parsley and add 10 g of honey and lemon juice. Take the medicine before meals. You can make a healing tincture from parsley. To do this, chop the roots and stems of the plant, pour 20 g of raw materials into a thermos and pour 200 ml of hot water. The remedy should be infused for 6-8 hours, but it is better to leave it overnight. You need to take 50 ml of the prepared infusion daily. The plant eliminates inflammation, improves metabolism, and fights stones.
- If the detected formation is a phosphate stone, then this recipe is suitable for its treatment. Take in equal proportions: St. John's wort, dandelion roots, knotweed, larkspur and wild pansy. Pour 1 liter of boiling water over five tablespoons of the mixture and let it brew until it cools completely. Take 250 ml 2-3 times a day.
Traditional medicine is a form of alternative medicine and is most often used to remove and dissolve stones in the prostate, urinary or gall bladder, and kidneys.
Herbal treatment
Traditional medicine involves treatment with herbs. Medicinal plants of varying effectiveness have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the body, strengthen the immune system and improve metabolic processes.
Let's look at effective recipes for herbal treatment of hyperechoic inclusions (calculi, calcifications):
- Take a handful of oats in the husk, rinse thoroughly, pour into a thermos and pour boiling water. The remedy should be infused for 10-12 hours, after which the settled oats should be rubbed through a fine sieve. The resulting gruel should be consumed for breakfast, without adding spices or oil.
- If the seals appeared due to excess uric acid, then for treatment use an infusion of a mixture of knotweed grass, currant leaves and strawberries in a ratio of 1:2:2. 20 g of the herbal mixture must be poured with boiling water and left to brew. The resulting drink must be filtered and taken 15 ml an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
- Pour 200 ml of hot water over 20 g of crushed goldenrod and place in a boiling water bath for 5-7 minutes. Once the decoction has boiled, it must be infused for 3 hours and filtered. Take 30 ml of the medicine 2-3 times a day. Helps with kidney stones.
- Mix equal parts of sage, rose hips and sage. Pour 20 g of plant material into 500 ml of warm water and boil for 15 minutes. As soon as the decoction cools down, add 10 g of honey. Take ½ cup daily.
Before using the above recipes, you must consult your doctor.
Homeopathy
Another unconventional method of treating tissues with high acoustic density of various origins is homeopathy. Let's consider the options of alternative medicine:
- Calcifications - for these formations, Calcium carbonicum and Calcium fluoricum 6 are used - 2-3 granules under the tongue before meals every morning, over a long period of time.
- Stones - to slow down their formation, it is recommended to use the following homeopathic preparations: Calcarea carbonica, Nux Vomica, Sulphur and Berberis in the 30th dilution. If stones are found in the kidneys and they cause painful sensations, it is recommended to take Dioscorea, Berberis, Cantharis in the 6th dilution.
- Cystic formations – Lachesis 12, Medorrhinum, Arsenicum album, Kalium bichromicum 3-5 granules regardless of food intake in the morning and evening.
All homeopathic medicines should be selected by a homeopathic physician after a comprehensive diagnosis of the body.
Surgical treatment
A radical method of getting rid of echo-positive formations is surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is indicated for large calcifications in various organs and tissues. Very often, such therapy is carried out for inclusions in the prostate. The operation can be open, using laparoscopy or transurethrally. If the gland has pathological lesions, then prostatectomy is indicated, that is, complete removal.
Surgical treatment is necessary for multiple concretions and stones with sharp edges. Such compactions are dangerous due to the risk of tissue and organ injury due to the movement of inclusions. Removal of malignant neoplasms is also possible. The operation is combined with drug therapy (chemotherapy) and various physiotherapeutic methods.
Prevention
There are many reasons for the formation of echo structures of internal organs and tissues. Their prevention consists in preventing provoking factors, i.e. possible diseases.
Let's look at the main preventive recommendations:
- Timely treatment of chronic diseases. Particular attention should be paid to the correct treatment of inflammatory and infectious processes, which most often provoke pathological changes.
- Proper nutrition and physical activity are the key to a healthy body and a beautiful body. Diet therapy and adherence to a drinking regimen keep the body in good shape, and sports give a boost of energy.
- Vitaminization – regular consumption of products or medicinal complexes with vitamins C, A and E increases the protective properties of the immune system. This protects the body from various infectious and bacterial pathogens.
In addition to the above recommendations, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations by a doctor. And if pathological symptoms appear, do not self-medicate, but immediately seek medical help.
Forecast
A hyperechoic formation is not a diagnosis, so it requires more detailed diagnostics. The prognosis depends on its results. If the detected seals are small in size and do not affect the functioning of the body, then only medical observation of them is indicated. In case of concretions, calcifications, benign or malignant neoplasms, a treatment plan is drawn up. Therapy can be both radical and conservative. In any case, echo-positive seals require a comprehensive examination.
 [ 46 ]
[ 46 ]

