
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Femoral neck fracture in the elderly
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
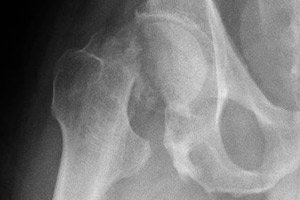
Bone fractures and soft tissue injuries often occur after the age of 50. This is due not only to the fact that a person becomes less active and more clumsy. This age is often characterized by vitamin deficiencies, osteoporosis, and mineral deficiencies. And banal age-related changes make themselves known. A hip fracture in the elderly is especially dangerous. This is an injury that all patients who have crossed the 45-50-year mark should be informed about.
Epidemiology
A hip fracture is probably one of the most unfavorable injuries for older people. Moreover, people receive such an injury not only on the street, but also at home, so even a sedentary elderly person can be injured.
According to statistics, more than half of hip fractures occur in the warm season: about 10% in May, and about the same number between September and October. Moreover, more than 75% of fractures occur indoors.
Elderly people most often get injured when trying to overcome some obstacles or barriers on the way, which can be thresholds, rugs, etc. (about 40% at home, and more than 55% outside). Less often, falls from a chair, bed, steps, etc.
Causes of femoral neck fracture in the elderly.
The femur is a fairly large skeletal element that has to deal with enormous stress on a daily basis, as it is located in the upper segment of the lower limb. According to anatomical data, this bone is divided into three parts: the body, the neck, and the head, which is located in the socket of the joint. It turns out that the neck of the femur is a kind of “weak link” in this area, so corresponding fractures occur quite often. [ 1 ]
Osteoporosis makes a special negative "contribution" to the development of a fracture. This pathology is inherent mainly to elderly people (mainly women), and is associated with demineralization and increased fragility of bones. In addition to osteoporosis, there are other negative factors - for example, in elderly people, the blood supply to the femoral neck is disrupted, which not only affects the quality of bone tissue, but also worsens its recovery if damage already exists.
Most patients experience a hip fracture after a side fall, as this is a powerful, targeted blow directly to the hip joint. But in advanced osteoporosis, even one incorrect turn of the body or an awkward bend is enough to cause injury.
Certain risk factors also increase the likelihood of a fracture.
Risk factors
Predisposing traumatic factors often include:
- menopause, hormonal problems, increased leaching of calcium from bone tissue;
- obesity, physical inactivity;
- prostate hyperplasia;
- alcohol abuse, poor nutrition, impaired absorption of vitamins and minerals.
Many chronic pathologies lead to weakening of bones, in particular, the femoral neck. Thus, the risk of injury increases significantly in elderly people suffering from arthrosis, osteochondrosis, spondylolisthesis or spondyloarthrosis, intervertebral hernia. Bone fragility increases against the background of diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases, thyroid diseases.
Pathogenesis
The neck and head of the femur are supplied with blood mainly through the intraosseous vascular arterial branches. The vascular network of the femoral head ligament is less involved and is often obliterated in older people.
In case of intra-articular fracture of the femoral neck, the basic intraosseous network of arteries is disrupted, which leads to deterioration of trophic processes in the proximal part of the femoral neck and head. At the same time, recovery processes also deteriorate: with a fracture, the risk of avascular necrosis increases.
A femoral neck fracture most often occurs with an adduction injury, that is, during a lateral fall. The peripheral segment is adducted and displaced upward and outward. An abduction injury, i.e. a support and fall with the limbs spread apart, is less common in the elderly. The peripheral segment is in an abducted state, with an upward displacement, and in some cases enters the central fragment, forming an impacted fracture.
Negative conditions for adequate fracture healing in elderly people include insufficient blood supply to the proximal fragment, absence of a periosteal layer in the neck area, vertical fracture plane, complex alignment of fragments and their loose contact, and tissue demineralization.
Symptoms of femoral neck fracture in the elderly.
Because of their extreme prevalence and severity, hip fractures in older adults are well understood, so most health care professionals can readily identify the injury if the following symptoms are present:
- Long-term constant pain in the groin, not intense but continuous. The victim can tolerate such pain for several days, hoping for its self-elimination, or taking it for a manifestation of arthrosis or arthritis. However, without appropriate treatment, the pain syndrome gradually increases and becomes especially noticeable when trying to walk actively or when placing the foot on the heel.
- The foot changes slightly, as if turning outward: this can be easily determined if you compare both feet and compare their position relative to the knee joint.
- Some patients experience a slight shortening of the affected limb, not exceeding 40 mm. The cause of this symptom is the contraction of the muscles in the area of injury, which is especially typical for varus injury.
- A characteristic symptom of a "stuck heel" appears: it is expressed in the fact that the limb cannot be placed from a suspended position onto a horizontal plane, since it seems to slide. At the same time, the function of flexion and extension of the leg is preserved.
The first signs of a hip fracture may manifest themselves as a crunch, which is especially noticeable when trying to turn the leg, which is horizontal. Pain can also be felt when palpating the damaged area: then you can also notice a strong pulsation in the area of the femoral artery.
Other characteristic features include:
- if you press or tap on the patient's heel bone, you will experience discomfort or even pain;
- If there is a violation on the part of the greater trochanter, then the displacement of the Schemaker line attracts attention - this is an imaginary line connecting the apex of the greater trochanter with the anterior superior iliac spine.
Some time after a hip fracture, a hematoma may form in the injured area, caused by a breach in the integrity of deep-lying vessels.
Forms
Hip fractures in the elderly are divided into several types, depending on the location of the injury, its level, the type of displacement and its nature.
For example, with a varus fracture, the head moves downwards and inwards, with a valgus fracture, the head moves upwards and outwards, and with an impacted fracture, the fragments are displaced into each other.
According to statistics, the impacted form of intra-articular fracture has the most unfavorable prognosis: in the absence of treatment, the damage can transform (bone fragments separate and diverge, which can only be corrected through surgical intervention).
We will look at other common types of fractures in more detail.
- Impacted fracture of the femoral neck in elderly people often has an intra-articular character. Severe pain and limited mobility are not typical for it, so victims do not immediately seek medical help. Often this leads to the fact that fragments and splinters continue to shift, leading to even greater damage, and the impacted fracture is transformed into a non-impacted form. Interestingly, with timely treatment by a doctor, this type of fracture is the most favorable.
- Lateral fracture of the femoral neck in elderly people occurs most rarely: the line of damage runs clearly along the lateral border, piercing the base of the neck and not reaching the trochanteric zone. The damage usually does not provide for displacement; rotational outward bending and varus position are possible. When viewed from the side, the position of the axis is normal, but curvatures forward or backward of varying degrees of severity are possible. Lateral fracture has much in common with trochanteric fractures in terms of clinical presentation and treatment, and some specialists even identify these types of injuries.
- A pertrochanteric fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly is a lesion that involves the bone segment from the subtrochanteric line to the cervical base. The injury usually results from overloading the greater trochanter or a twisting movement of the leg. The fracture may be accompanied by severe blood loss, external tissue edema, and hematoma.
- A basal fracture of the femoral neck in older people is characterized by the location of the fracture line at the base of the neck. The injury occurs as a result of a fall or a direct blow to the hip.
Complications and consequences
According to statistics, hip fractures in older people often cause death, despite the fact that death is not a direct consequence of the injury. Why does this happen?
With prolonged forced lying down, the elderly are at increased risk of developing problems with the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and the risk of vascular thrombosis, infection, and skin diseases increases.
Pneumonia associated with congestion and continuous bed rest is often the killing point for patients.
Other unpleasant consequences of prolonged "lying down" include depression and mental disorders. Many elderly people lose the meaning of life due to trauma and immobility, their perception of reality is impaired, and their consciousness is confused. Often, patients begin to abuse alcohol, take strong medications (for example, tranquilizers, antidepressants), which easily aggravates the deplorable situation. [ 2 ]
Diagnostics of femoral neck fracture in the elderly.
Diagnosis is usually simple, as a hip fracture can be diagnosed if the symptoms are present. However, without confirmation, such a diagnosis is not valid, so an X-ray should be taken first: this type of examination will help to detect a crack or displacement of bones in the hip area.
The following tests are prescribed as a supplement to the main diagnostics:
- clinical blood test, ESR;
- urine analysis;
- if necessary – analysis of joint fluid, examination of tissues taken during biopsy.
As we have already said, the basic diagnostic method for detecting a hip fracture is radiography: the images visualize both cracks and fracture lines. Additional instrumental diagnostics can be used to clarify some details of the damage. For this, computed tomography is used - a diagnostic study that allows for a more accurate and detailed assessment of the bone condition. Magnetic resonance imaging can be an alternative to CT.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnostics should be carried out with a contusion of the hip joint, a dislocation of the hip joint. In case of a dislocation, there are characteristic symptoms: a spring tension of the affected leg, displacement of the femoral head, noticeable shortening of the limb. In case of a contusion, pain, swelling, hematoma are observed; the function of the joint is limited or severely impaired. The final diagnosis is made after an X-ray examination.
Who to contact?
Treatment of femoral neck fracture in the elderly.
You can't let the situation slide and leave a hip fracture without proper treatment: for older people, such an attitude to the problem can be fatal. Treatment is mandatory - be it conservative methods or surgery.
Surgical treatment is considered the most effective and radical, but it is not always necessary. For example, in the case of an impacted fracture or damage to the lower segment of the neck, the help of a surgeon may not be needed. In addition, surgical intervention may simply be contraindicated for an elderly person - for example, due to old age, with severe disorders of the internal organs.
Conservative treatment usually consists of the following mandatory stages:
- Examination of the patient with subsequent placement in a specialized orthopedic or trauma department.
- Implementation of skeletal traction during the first 8 weeks from the moment of fracture.
- Manual therapy, massage procedures.
- Mandatory use of crutches after removal of skeletal traction.
- Attempts to involve the affected limb in walking and movement under strict medical supervision, not earlier than 4 months after the injury.
If surgery is not an option, the first thing the doctor will suggest is immobilization and skeletal traction of the affected leg. How does this procedure work?
- The damaged joint area is injected with local anesthetics (for example, based on novocaine).
- Traction is installed for a period of up to ten days.
- After the specified time has elapsed, the pulling structure is removed.
- The patient is turned first to one side, then to the other, the head of the bed is raised, and a semi-sitting and sitting position is provided.
- After about three weeks, under the supervision of a doctor, an attempt is made to move the patient on crutches.
Then, if the patient's condition is satisfactory, they prepare him for discharge. However, he should only move around on crutches, accompanied by an assistant. Only the attending physician should decide whether to cancel the crutches.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is an important decision for both the doctor and the patient. The doctor must be sure that the elderly person will tolerate the anesthesia and the intervention itself.
In many cases of hip fractures, the help of a surgeon is mandatory. The nature of the operation itself depends on the type of bone damage and its scale. Most often, the fracture site is reinforced with a special structure that includes spoke-like or rod-like fasteners and/or screws. In severe cases, joint prosthetics may be required.
If the question of surgery is raised, it is recommended to perform it as soon as possible. The only factor in which the intervention can be postponed is the presence of temporary contraindications.
The following are considered to be the general principles of surgical treatment:
- such treatment is always performed under anesthesia;
- if there are bone fragments, they are first repositioned;
- in case of uncomplicated fractures of the femoral neck, intervention can be carried out without resorting to joint opening, using X-ray control;
- In case of complex fractures, the joint capsule is opened.
Endoprosthetics is used mainly in elderly patients whose injuries were accompanied by displacement of fragments, as well as in cases of necrosis of the bone head.
Care for a Hip Fracture in the Elderly
Proper care and a kind attitude of loved ones are important conditions for the speedy recovery of an elderly person who has suffered a hip fracture. In addition to stabilizing the mental state, special therapeutic exercises must also be performed to speed up the restoration of bone tissue. It is important to prevent and eradicate the development of depression, oppression: if necessary, a psychotherapist can be additionally involved in the treatment.
Close people should provide the victim with healthy sleep and a full diet. It is also recommended to undergo a course of massage procedures and treat existing chronic pathologies. All measures taken together will help to cope with the problem faster.
A sick person should not be left alone: he should always feel the support and participation of his family. To prevent the development of depression, doctors recommend spending time together and making plans for the future. It is good if the patient can do feasible housework and also take care of himself independently (for example, on crutches or sitting on a bed). And doing simple physical exercises to music will allow the patient to distract himself and improve his mood.
Rehabilitation
The length of the rehabilitation period for a hip fracture in the elderly is quite difficult to determine accurately. This period depends on many factors, such as the complexity, type of fracture, age and general health of the victim. However, doctors believe that the duration of rehabilitation cannot be less than six months.
In general, the recovery period can be figuratively divided into the following stages:
- Starting from the third day after the plaster is applied, the patient is recommended to start massage procedures: first, massage the lumbar region, gradually moving to the healthy leg. Only after 7-10 days do they start massaging the injured limb, not forgetting about caution and accuracy.
- After the plaster cast is removed, you are allowed to move your knee joint a little, making light movements under the supervision of a medical specialist. After 4 weeks, you can do such exercises on your own, bending and unbending your leg at the knee. You should not perform unnecessary movements not provided for by the doctor's instructions.
- After about three months, the doctor may allow the patient to get out of bed using crutches. However, putting weight on the injured leg is still not allowed.
- The load is gradually increased, and after six months the patient is allowed to try walking without crutches.
Prevention
To prevent such serious injuries as a hip fracture, it is first necessary to:
- ensure that you get enough calcium from your food (for older people, the daily requirement is 1200-1500 mg of calcium, taking into account possible impaired absorption);
- provide the body with the necessary vitamins and mineral components - in particular, retinol, ascorbic acid, vitamins D and K, zinc, phosphorus and magnesium are necessary;
- provide the body with regular and feasible physical exercise, ensure physical activity, and strengthen muscles.
In addition to general strengthening of the body, it is necessary to minimize the possibility of falls and injuries. For example, at home, it is necessary to take measures to prevent an elderly person from falling and hurting himself. Floors and floor coverings should be non-slip, thresholds should be low (or better yet, get rid of them altogether). In the bathroom, it is advisable to install special handrails that a person can hold on to.
If the injury already exists, then efforts must be made to avoid complications and speed up recovery. Consultation with a doctor and treatment should follow as soon as possible.
Forecast
Although a hip fracture in the elderly is considered a very complex injury, the chances of recovery are still high. The pathology is completely curable, but rehabilitation will take more than one month. It is important that the effectiveness of treatment and the quality of recovery largely depend on the positive attitude of the patient and his environment. An injured old man cannot do without the help of loved ones.

