
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Erosion of tooth enamel
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
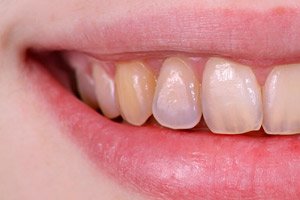
One of the most common non-carious lesions of teeth – erosion of dental enamel – is a gradual and stable destruction of the outer protective dental shell. The pathology affects mainly the convex parts of the tooth surface and manifests itself in the form of rounded defects of varying depth and diameter.
It is worth noting that tooth enamel erosion is not only a cosmetic problem. Without treatment, the damage constantly progresses, worsens, which subsequently leads to the destruction of both the enamel layer and dentin. In addition, other, initially healthy teeth are inevitably involved in the process. [ 1 ]
Treatment of the pathology is complex.
Epidemiology
In the vast majority of cases, enamel erosion is localized in the vestibular surface of the lateral and central maxillary incisors. Premolars and canines on the upper and lower jaws are damaged much less frequently.
Erosions are usually detected as a distinctive defect of a round or oval configuration. The lesion affects at least two symmetrical teeth.
The average diameter of erosive lesions is 1-2 mm, however, some patients experience damage to the entire vestibular surface of the teeth.
Erosion of dental enamel was first described in the 18th century. The pathology can affect both baby and permanent teeth (although permanent teeth are affected much more often). The average age of those affected is 30-50 years. The prevalence of the disease ranges from 2 to 42%, according to various sources. Women and men get sick with approximately the same frequency. [ 2 ]
Causes tooth enamel erosion
Dentists do not yet know absolutely all the reasons for the formation of tooth enamel erosion. Therefore, at the moment, the pathology is being actively studied, and the etiology of its development is being investigated. However, some reasons are already known: they belong to three categories of factors, such as chemical, mechanical and internal irritants:
- use of aggressive oral and dental care products (homemade and whitening pastes, powder, rinse);
- internal diseases (thyroid pathologies, diseases of the stomach and duodenum, frequent vomiting, increased acidity of gastric juice);
- occupational hazards affecting the composition of salivary fluid;
- regular consumption of acidic foods, marinades, vinegar, carbonated drinks;
- excessive load on the dental coating, which is typical for patients with malocclusion, dental and jaw injuries, wearing mouth guards and other factors that affect uneven chewing and distribution of food in the oral cavity;
- systematic use of medications containing acetylsalicylic, ascorbic or folic acids;
- regular inhalation of acid vapors, metal or mineral dust.
In childhood, the appearance of erosions is often associated with the abuse of drinks containing sugar and acids. In particular, we are talking about juices, carbonated drinks, compotes. Other reasons can also be improper dental care or lack thereof, bite disorders. [ 3 ]
Risk factors
Tooth enamel is a strong mineral layer that is virtually indestructible. However, under the influence of certain factors, the process of its self-destruction is launched: it can continue for many years until it reveals itself as obvious pathological changes.
Experts identify several basic factors that can influence the appearance of dental enamel erosion:
- The mechanical factor involves regular use of too strong toothpastes and other preparations for cleaning teeth. The problem may arise with systematic whitening procedures, the use of mouth guards. Such a bad habit as bruxism also makes its contribution – frequent grinding of teeth, especially at night.
- The chemical factor is the regular contact of various acids and alkalis (including food acids, such as fruit juices, vinegar, citric acid, and sweet carbonated drinks such as Coca-Cola or Pepsi) with tooth enamel. [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
- The internal or endocrine factor is caused by the malfunctioning of the thyroid gland. Many people suffering from thyrotoxicosis experience changes in the composition of the salivary fluid, which directly affects the damage to tooth enamel.
Other factors include excessive use of vitamin supplements (especially large doses of vitamin C and folic acid), malocclusion, and infectious lesions of the oral and nasal mucosa. Some patients have been shown to have a genetic predisposition to the development of dental enamel erosion. [ 6 ]
Pathogenesis
Erosion of dental enamel develops according to the following pathological stages:
- The active stage is accompanied by increasing thinning of the protective layer of the tooth, which entails increased sensitivity of the teeth to the effects of various irritants. The destruction of the enamel layer usually occurs intensively, erosions gradually increase.
- The stabilized stage proceeds more slowly than the active one. The pain is moderate, which is due to the formation of tertiary dentin - a product of the pulp's vital activity, which becomes a kind of protective layer.
The indicated stages can be repeated, alternating with each other.
In addition to the stages, there are four main phases of development of dental enamel erosion:
- The initial phase is characterized by damage to only the upper enamel layer.
- The middle phase is accompanied by deep damage to the enamel, right down to the dentin.
- Deep phase – represents complete damage to the enamel layer and the upper layer of dentin, with the formation of secondary dentin.
- Involvement of the dental pulp in the pathological process.
Erosion of dental enamel is divided into endogenous and exogenous, depending on the etiology of the disease.
Endogenous erosion is said to occur as a result of regular, repeated vomiting (for example, with eating disorders), increased acidity of gastric juice, gastroesophageal reflux, etc. [ 7 ]
Exogenous erosions are formed when consuming foods and liquids with a pH of less than 5.5. [ 8 ]
Symptoms tooth enamel erosion
The symptoms of the pathology are not sufficiently expressed at first and attract attention only at the moment of damage to the internal layers of the tooth. In general, the clinical picture depends on the stage of erosion development.
Typically, erosion is a round-oval enamel defect, which is located transversely on a more protruding section of the vestibular surface of the dental crown. As the pathology worsens, the erosion boundaries deepen and expand, pain appears due to exposure of dentin and the impact of chemical and thermal irritants.
At the first stage, the enamel coating darkens slightly or becomes matte: to detect the affected area, you can apply a drop of iodine to the tooth, which will allow you to see the damaged area more clearly. There is no pain at the first stage.
The erosive defect itself looks like a rounded cup-shaped lesion with a hard, smooth and glossy bottom. The lesion gradually expands, becomes deeper, the enamel layer becomes thinner with further exposure of dentin. The patient experiences discomfort when hot and cold irritants hit the tooth.
At first, the defect has light shades, but as the process deepens, it becomes light yellow, then brownish.
At a late stage of development, pain appears - during meals, when brushing teeth. The affected areas look like brown deep defects.
Erosion can develop at different rates, which depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the general condition of the teeth, and the degree and frequency of exposure to provoking factors.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course, gradual progression and further spread to healthy teeth.
Each stage of erosion development is characterized by the following initial signs:
- The affected area of tooth enamel becomes matte (loses its shine), which rarely attracts the attention of the patient or even the dentist. The defect can be clearly visualized only by thoroughly drying the tooth surface with a stream of air, or by dropping a drop of iodine tincture on the tooth (the affected area is colored and turns brown). The usual initial form of the defect is round-oval, the bottom is smooth, the color shade is light. There is no pain at the first stage.
- Then, discomfort gradually appears (especially during eating), and the affected area darkens.
- The pain intensifies and the brown spots deepen.
Complications and consequences
The process of tooth enamel erosion formation can last for several years. However, after the first pathological signs appear, changes on the enamel surface occur quite quickly:
- crowns wear out;
- the color darkens;
- the edges of the teeth become thinner;
- sensitivity increases, problems with food consumption arise.
If the pathology is not detected in time and treatment is not started, then the development of serious complications is quite likely, in particular, the following:
- spread of erosion to the entire tooth and to other healthy teeth;
- loss of uniformity of the enamel layer color (the cutting edge may become transparent);
- accelerated wear of the enamel layer, increased wear of teeth;
- increased sensitivity to taste and temperature stimuli, the appearance of pain.
When the pathological process spreads to the hard tissue of the tooth (dentin), its intensive destruction occurs. As a result, other dental pathologies develop. [ 9 ]
Diagnostics tooth enamel erosion
Diagnostic measures for suspected enamel erosion begin with an examination and consultation with a dentist. Standard diagnostics include the following procedures:
- An external examination of the oral cavity and dentition allows the doctor to determine the presence of disorders, to distinguish them from other dental diseases. In some cases, the doctor manages to identify the causes of the pathology already during the first visit.
- Testing with drying the affected area with a stream of air and applying iodine helps to clearly visualize the areas of erosion.
- Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland and examination of hormonal levels, diagnostics of the digestive system help to clarify the connection between the appearance of erosions and other pathologies in the body. [ 10 ]
Differential diagnosis
Diagnostic measures must be complete and thorough, since the disease is often confused with other dental pathologies.
Erosion of dental enamel is distinguished, first of all, from necrosis of hard dental tissues, from caries and wedge-shaped defects.
In caries, the enamel layer is rough, whereas in erosion it is smooth.
A wedge-shaped defect occurs in the root area of the teeth, causing the crowns to change their shape.
Necrosis of hard tissues is characterized by the appearance of chalky spots on the enamel and peeling off of some areas when using a probe.
Who to contact?
Treatment tooth enamel erosion
In general, treatment of patients with dental enamel erosion is carried out taking into account the following mandatory principles:
- Consultations with a gastroenterologist, neurologist, endocrinologist with further appropriate treatment of the detected disorders.
- Dental treatment using measures that increase the resistance of tooth enamel to acidic influences.
- Professional treatment of the oral cavity without the use of aggressive and abrasive agents (twice a year).
- A course of remineralizing therapy with subsequent fluoridation (two courses of treatment with 15 procedures each). Between courses, chewable vitamin-mineral complex preparations are prescribed (ROCS Medical, three tablets per day for a month).
- Direct and indirect restorative restoration of visible dental defects.
- Outpatient monitoring by specialized specialists (dentist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, endocrinologist).
In addition to the main treatment, the patient's diet must be adjusted. Fruits and citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and sour berries are excluded. After consuming any sour foods, it is recommended to rinse the mouth (without brushing your teeth). Teeth are brushed in the morning and evening using a soft brush and toothpaste with a low RDA index. [ 11 ]
How to restore enamel in case of dental erosion?
At the early stage of the appearance of tooth enamel erosion, remineralizing measures are carried out. They involve applying calcium and fluoride-containing preparations to the affected areas. In general, ten to fifteen such procedures are performed, after which pigmentation is eliminated.
At a late stage of the pathology development, the course of remineralization and removal of pigmentation is completed by filling the defect with composite materials. In this case, remineralization is considered mandatory, since without this link, the filling will be unreliable, and the erosive area will continue to increase. [ 12 ]
The scheme for restoration of crowns is drawn up by the doctor individually, depending on the stage of the pathological process and the number of affected teeth.
Medicines
The following medications may be used as part of complex therapy:
- Elmex gel is used for remineralization of damaged areas of crowns, for desensitization of sensitive tissues. It is recommended to brush teeth with gel once a week (like with regular toothpaste), applying 1 cm of gel to a soft brush. Do not swallow the gel! The product is intended for adults and children from six years of age.
- ApaCare Repair Liquid Enamel Gel is a strong restorative agent that is applied to the teeth for 1 hour (for pediatric patients - for 15 minutes). During the action of the drug, you cannot eat or drink. The procedure is repeated in the mornings and evenings for four weeks. The product is well tolerated, hypoallergenic, does not contain fluoride.
- GC Tooth Mousse is a restorative gel in the form of a water-soluble cream containing casein-phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate. When applied superficially, the gel provides additional protection for hard dental tissues and neutralizes increased acidity in the oral cavity. The product is applied in a thick layer to the surface of the crowns, left for three minutes, and then spread with the tongue over the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Try not to swallow as long as possible (at least 10-12 minutes) - the result depends on this. Then refrain from eating and drinking for half an hour after the procedure.
Dental health, like the health of other systems and organs, is impossible without sufficient intake of vitamin and mineral components into the body. Therefore, doctors often prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes containing calcium and vitamin D to patients: [ 13 ]
- Calcimin is prescribed to adults and children over 12 years old, 1 tablet with food 2 times a day. The duration of administration is determined by the doctor. With prolonged use, dyspepsia and allergic reactions are possible.
- Procitracal is a drug that is an additional source of calcium, magnesium, zinc and vitamin D 3. The treatment regimen is individual.
Toothpaste for dental enamel erosion
Damage to tooth enamel and increased tooth sensitivity are common disorders. That is why the pharmaceutical market is increasingly filled with toothpastes and toothpastes that are positioned as protecting the enamel coating and restoring its structure.
Swiss scientists tested nine toothpastes, eight of which were supposed to help with erosion, and one was a regular hygienic paste (control). The results of the experiment led to a disappointing conclusion: none of the pastes affected the wear of the enamel layer, which is a key link in the development of erosion. [ 14 ]
Dentists explain: oral hygiene products need to be used regularly and it is important. However, pastes are only one addition to a comprehensive approach. As a preventive factor, you can use the following products for cleaning teeth:
- EMOFORM-F for sensitive teeth.
- GUM SensiVital.
- Sensodyne Instant Effect
- Parodontax with fluoride.
- ROCS
- Elmex Zahnschmelz Schultz Professional.
In general, regular consultation with a dentist is necessary to monitor your oral health. Only a dentist can give recommendations on choosing a toothpaste after an examination. If you choose the wrong hygiene product, you can not only fail to achieve the expected result, but also harm your teeth and significantly complicate subsequent treatment. [ 15 ]
Herbal treatment
In most cases, experts do not recommend resorting to folk remedies for treating tooth enamel erosion. Although some patients still try to be treated - for example, with the following methods:
- Take 1 tbsp. of oak bark, pour 200 ml of boiling water, keep on low heat for 6-7 minutes. Cool the resulting decoction and use to rinse the mouth three times a day.
- Pour 1 tbsp of chamomile flowers into 200 ml of boiling water, leave to infuse under a lid for 1-1.5 hours. Then filter the infusion and use for rinsing at least 5 times a day.
- Take 1 teaspoon of dry burdock herb, pour 250 g of boiling water and boil on low heat for three minutes. Infuse under the lid for an hour, filter. Use for rinsing up to five times a day.
Dentists point out the low efficiency of such methods. Some medicinal plants do help relieve pain and soothe increased tooth sensitivity. However, they are not able to rid a person of the problem: in the meantime, precious time will be lost, during which the situation may worsen. [ 16 ]
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of dental enamel erosion come down to following the following rules:
- It is advisable to use a toothbrush of medium hardness: too hard brushes can damage both the gums and the enamel protective surface of the teeth.
- Bleaching and abrasive products are not intended for regular use. Long-term or systematic use of such products may cause the development of erosions.
- Sour juices and carbonated drinks have an adverse effect on tooth enamel. If you can’t give up drinking them, you can try drinking them through a cocktail straw, which will reduce the amount of acid that gets onto the surface of your teeth.
- To reduce the adverse effects of acid, rinse your mouth with warm water after each meal. You can't brush your teeth with toothpaste immediately after eating acidic food - you need to rinse your mouth and use the brush after 40-60 minutes.
- It is not recommended to chew gum for more than five minutes.
- It is advisable to use special fluoride-containing pastes periodically.
In addition to all of the above, it is imperative to visit the dentist at least every 6 months for a preventive examination. This will help prevent the development of pathology, or stop it at the earliest stage. [ 17 ], [ 18 ]
Forecast
The prognosis with timely medical intervention is conditionally favorable. If all doctor's instructions are followed, the development of the erosive process is slowed down and stopped, patients note the absence of pain and an improved quality of life. The dentist selects suitable means to improve the aesthetic appearance of teeth, performs procedures to restore the shape of crowns, and ensures reliable protection of their surface from adverse factors.
Erosion of dental enamel detected at early stages has a much more favorable effect. Thanks to complex treatment, it is possible to eliminate the formed defect, restore the aesthetics and functional capacity of damaged teeth.

