
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Dolichosigma in adults and children
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
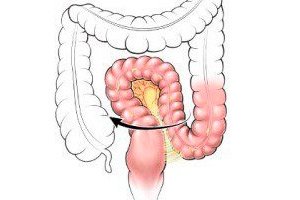
Dolichosigma refers to a pathology in which the sigmoid colon and its mesentery acquire abnormal sizes. Dolichosigma is sharply lengthened, disrupting the normal functioning of the body. All this is accompanied by constant constipation, flatulence. Against this background, severe pain occurs.
Diagnostics is lengthy and includes many studies. You need to be prepared for the fact that if the diagnosis is confirmed, long-term treatment will be required. A special diet is prescribed, which must be followed throughout life. In the chronic form of the disease, conservative therapy may be ineffective, and then surgical intervention may be required. The main methods of treatment are drug therapy, folk and homeopathic remedies. Auxiliary methods are therapeutic exercise, swimming, physiotherapy, massage.
What is this?
The disease is considered as an anomaly of the structure of the sigmoid colon. The essence of this pathology is the enlargement and lengthening of the intestine. Although the morphology of the intestine remains unchanged. Often, the elongated intestine is characterized by a high degree of mobility, leading to a violation of the movement of feces. Often, the pathology is latent, has an erased clinical picture. Normally, the length of the intestine fluctuates between 24 and 46 cm. If the length exceeds 46 cm, they talk about dolichosigma, that is, an elongation of the intestine.
Epidemiology
In 80% of children, dolichosigma is a consequence of the cessation of intestinal neuronal migration and disruption of innervation, in 10%, innervation is disrupted at the level of the large intestine, and in another 10% at the level of the splenic flexure. In 15% of people, the disease is diagnosed, but it is asymptomatic and does not bother patients at all. In 1% of cases, the intestine is affected along its entire length. In newborns, the incidence of this pathology is 1 case per 5,000 people. The disease mainly occurs in boys. The ratio of boys to girls is 4:1. In 7% of people, the disease is burdened by a similar family history. In 3-5% of cases, the disease is associated with various developmental defects, such as Down syndrome.
Causes dolichosigmas
The obvious causes of such anomalies are still unclear. Sometimes children with congenital anomalies were born as a result of exposure to radioactive substances, toxins, various physical and chemical factors during pregnancy. Pathology can develop when the expectant mother has suffered an infectious disease, especially if the pathogen exhibited tropism for intestinal cells. Taking certain medications during pregnancy can provoke abnormal development of the fetus.
Acquired dolichosigma most often manifests itself after prolonged constipation, fermentation, putrefactive processes in the intestine, after prolonged dysbacteriosis or a protracted infectious disease, frequent food poisoning. The cause may be a violation of intestinal motility, which arose as a result of prolonged work in a sitting position, hypodynamia. It can develop against the background of intestinal atony, which occurs with age and is most often found in people aged 45 to 50 years. The cause may be the abuse of meat food, carbohydrates, as well as prolonged stress and constant nervous tension.
Many experts are inclined to believe that dolichosigma is a genetically determined disease, and whether it will manifest itself or not depends on a person’s lifestyle and many other factors.
Origin theories
There are quite controversial theories that shed light on the cause and origin of the pathology. But the question still remains open. Doctors are engaged in numerous debates about whether this anomaly should be considered a normal variant or one of the forms of pathology. The fact that the disease can be considered a normal variant is indicated by the fact that approximately 15% of children diagnosed with this disease do not experience any complaints or symptoms. They have absolutely normal stool, feel great. During examination, no concomitant pathologies or inflammations are found, and such children are not bothered by pain.
On the other hand, there is every reason to consider this anomaly as a pathology, since many people suffering from this pathology develop structural and functional disorders of the intestine, colon and sigmoid colon. In addition, those 15% for whom the anomaly can be considered a normal variant still fall into the risk group, since no one can say with certainty whether the condition will be as stable in the future, or whether pathology may develop over time.
Some specialists consider this anomaly as a degenerative process in the intestine. Dolichosigma is often considered a consequence of intestinal dysfunction. It develops as a result of spasm, stasis, chronic inflammation and vascular damage. Ultimately, secondary degenerative changes and intestinal motor dysfunction develop.
 [ 4 ]
[ 4 ]
Risk factors
The risk group includes children whose mothers were exposed to radiation or harmful physical and chemical factors during pregnancy. Especially if such exposure occurred in the first trimester.
People with congenital bowel abnormalities, even in the absence of complaints and symptoms of any disease, are at risk. The risk of developing the disease increases in people suffering from frequent constipation, intestinal atony, as well as those who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis is based on congenital or acquired elongation of the sigmoid colon. In the presence of concomitant pathologies, fibrosis of the intestinal tissue often develops, as a result of which normal tissue is replaced by connective tissue. Edema and hyperemia appear. Muscle fibers grow, which leads to abundant impregnation of the intestinal walls with tissue fluid.
This leads to a disruption of the normal contractile activity of the intestine, weakening of the intestinal tone. Since the intensity of contractile processes decreases, feces pass through the intestine with difficulty, which leads to the development of constipation. In turn, the constant presence of feces in the intestine leads to a disruption of the innervation of intestinal cells, stagnation, pain and intoxication.
Symptoms dolichosigmas
They appear as the intestines fill with fecal matter and the body becomes intoxicated. The severity of the pathology depends on how pronounced the morphological and functional disorders in the intestines are. They are also largely determined by the body's compensatory capabilities, intestinal motility and tone.
The main symptom is long-term or chronic constipation. If constipation becomes long-term, the reaction to defecation gradually decreases, the intestines expand, intestinal tone and contractile activity are lost. Functional disorders are followed by a structural disorder, which already manifests itself in the form of pain, flatulence, bloating. The feces change shape and size, become dense, large and have a foul odor.
Gradually, as the congestion deepens and inflammation develops, recurrent pains in the iliac and umbilical area, flatulence, and pain on palpation appear. The pain syndrome is accompanied by spasms, cicatricial changes in the intestines, and inflammation.
The earliest harbinger is constipation. If a single case of constipation can be ignored, writing it off as an indigestion disorder, then long-term and persistent constipation should be a cause for concern. When the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist or proctologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Pain in dolichosigma
The disease is often accompanied by pain syndrome. Due to dilation of the sigmoid colon, impaired blood circulation and intestinal innervation, accumulation of feces and congestion.
 [ 7 ]
[ 7 ]
Pain in the left side
The pain is most often localized in the left side, since it is in this area that the colon is located and the main inflammatory process develops. Spasms and attacks of acute pain in combination with spasm may be observed.
Pain in the groin
Pain in the groin area can occur for various reasons: spasm, disruption of innervation, severe intoxication, intestinal dilation, inflammatory and infectious processes. Pain can radiate to the groin with inflammation and structural damage to the intestine, especially if nerve fibers are damaged. Cicatricial changes and fibrosis can also be accompanied by pain that radiates to the groin area.
Heaviness in the abdomen and bloating
Heaviness can occur as a result of accumulation of fecal matter, inability to empty the intestines. Bloating is a consequence of accumulation of fecal matter, irritation of the intestinal walls by toxins and bacteria.
Stool with dolichosigma
Constipation develops, the duration and severity of which depend on the stage of the disease. Usually, defecation occurs once every 3-4 days, sometimes even less often. With prolonged constipation, feces acquire a foul odor, sheep feces appear. Frequent use of laxatives is required. Diarrhea is not observed.
Stubborn constipation
Quite often, dolichosigma is accompanied by persistent constipation, which causes sheep feces and a foul odor. Stool is irregular, approximately once every 3-4 days, often after taking laxatives. Over time, constipation becomes chronic and regular. As feces accumulate in the intestine, it expands and its sensitivity decreases. In structural terms, 2-3 additional loops appear. The patient gradually loses innervation and the urge to defecate disappears. Fecal incontinence develops. The feces gradually harden and can damage the intestinal walls during passage, resulting in blood impurities in the feces. The damaged area becomes inflamed, an infectious process develops, and the integrity of the mucous membrane is disrupted. The inflammation can spread to other parts of the digestive tract.
Then intense gas formation occurs, pain and spasms appear. In severe forms of the disease, the spasm becomes relatively stable, the pain does not subside.
Diarrhea
If a person has dolichosigma, he suffers from constipation. The appearance of diarrhea may indicate the presence of concomitant pathology of the digestive tract, as well as the addition of an infection or food poisoning.
 [ 8 ]
[ 8 ]
Dolichosigma without constipation
Constipation is not observed in only 15% of children diagnosed. In all other cases, dolichosigma is always accompanied by constipation.
Nausea
Nausea may indicate intoxication of the body. Most often it develops if a person has not emptied for a long time, more than 3-4 days. Nausea may also occur with prolonged chronic constipation, in which fecal matter accumulates in the intestine, it is never completely cleansed. As a result, toxins accumulate, fermentation and putrefactive processes develop.
Dolichosigma in adults
The first and main beacon indicating the development of pathology is constipation. They start with rare and short-term. They occur approximately once every 2-3 months, lasting 2-3 days. Constipation gradually occurs more and more often, becomes regular, and can last up to 4-5 days. This already leads to intoxication of the body, since fecal matter accumulates in the body.
A person cannot empty his bowels without an enema. Frequent use of an enema causes the fading of reflexes and urges to defecate. With prolonged constipation, nausea and vomiting develop as a result of intoxication. When palpating the sigmoid colon, a seal or hard lump can be felt. With excessive accumulation of fecal matter, it can spontaneously exit, which is called fecal incontinence.
The disease develops in three stages. In the first stage, you can normalize bowel function by following a diet and taking laxatives.
At the second stage, regular constipation and signs of intoxication appear. Laxatives do not help, cleansing enemas are required.
In the third stage, intoxication increases. It becomes generalized, spreading to the entire body. Inflammation of the digestive tract develops. Constant pains, spasms appear, appetite decreases. Headaches develop. Only siphon enemas are effective.
In most cases, conservative treatment is sufficient. It is necessary to use a strict diet, use laxatives, turn to traditional medicine and homeopathy. Physiotherapy and exercise therapy can be used. If there is no result, surgical intervention is required.
Dolichosigma during pregnancy
If dolichosigma is detected in a pregnant woman, symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating constipation is used. First of all, a special diet is prescribed, which must be followed throughout the pregnancy. In this situation, constipation cannot be allowed to become chronic, since this can be dangerous for both the mother and the fetus. With constipation, toxins and gases accumulate in the body, rotting and fermentation occur. All this is accompanied by a violation of normal microflora, an increase in the bacterial load on the body. Toxins and bacteria enter the blood and spread throughout the body, causing poisoning.
Pregnancy can be the factor that provokes the development of dolichosigma. At this time, the body is rebuilt, hormonal disruptions occur, progesterone is produced, which reduces the tone of smooth muscles and contractile activity of muscles. The same applies to the muscles of the intestines and rectum. This significantly slows down the movement of feces through the intestines. In the later stages, the production of progesterone and other similar changes disappear, but the problem does not go away. The uterus significantly increases in size and provides compression of the rectum and sigmoid colon, which also leads to a decrease in motility. The formation of stagnation is also facilitated by a decrease in peristalsis, which occurs as a result of a decrease in the amount of motilin, a hormone that stimulates motility and peristalsis.
The danger is a long-term retention of feces, which causes toxins and slags to form. They increase toxicosis in a person. Long-term constipation against this background provokes inflammation of the colon, hemorrhoids and anal fissures. All this leads to a change in microflora, the development of a bacterial infection.
The main method of treatment is diet. First, doctors recommend getting rid of fecal congestion on your own, without resorting to herbs, medicines, and enemas. Proper nutrition will help with this. You need to include a large number of products with a laxative effect in your diet. It is also useful to drink a glass of clean water on an empty stomach. Only if this is ineffective can you resort to medications. Any remedy can only be taken after prior consultation with a doctor.
Dolichosigma in children
Often the cause of this pathology in a child is a congenital change in the intestine. In most cases, such a pathology does not require surgical intervention. But such a child requires special attention. Long-term treatment may be required. Parents should monitor the child's diet, the food should include products that have a laxative effect. If pain occurs, an abdominal massage should be performed. Visceral abdominal massage is especially useful, during which the internal organs are worked through the outer wall.
The essence of the pathology is that when it is lengthened, its mobility increases, which results in an obstacle to the movement of secretions through the intestines. With chronic constipation, several additional loops, expansion, and kinks can form. This additionally leads to the formation of gases and bloating.
The occurrence of constipation in a child, even a single one, requires special attention. Since the child's intestine is quite elastic, as a result it can easily stretch. Stretching leads to a decrease in tone and motor activity of the intestine, the disappearance of the urge to defecate and deterioration of the innervation of the intestine. As a result, the situation only worsens, constipation becomes chronic. It recurs with greater intensity and pain. The reflex decreases, the urge to empty occurs only if the intestine is completely full.
Treatment comes down to proper nutrition, drinking plenty of fluids. It is important to prevent the compaction of feces. They should remain soft. The diet should include dishes with a high content of pectin, which stimulates the intestines. It is necessary to include in the diet as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible, as well as various cereals, soups, and purees. If there is a need to use laxatives, it is better to resort to vegetable oils. If there has been no bowel movement for 2 days, you need to do an enema. The danger of constipation is that feces accumulate in the intestines, and when they stagnate, rotting and decomposition occur. Toxins are gradually absorbed from the intestines, which leads to poisoning. The microflora changes, the absorption of vitamins and minerals is disrupted, and digestion is completely disrupted.
Dolichosigma in an infant
With it, the sigmoid colon is significantly lengthened, resulting in the development of constipation. The intestine acquires several additional loops. The disease is accompanied by pain, spasm. It is often a congenital anomaly. The reasons for its appearance are not fully understood. Constipation occurs in newborns. Usually, the first signs appear after the introduction of complementary foods. At first, constipation occurs rarely. Alternates with normal bowel movements. After the first year of life, constipation occurs more often.
In case of constipation in a newborn, it is necessary to undergo an examination. For this, a blood test, stool analysis for occult blood, coprogram and stool for detection of worms are carried out. Additionally, instrumental studies are prescribed, such as ultrasound, intestinal X-ray.
The condition is dangerous because it can lead to severe intoxication of the body, the formation of fecal stones, intestinal obstruction, as well as various blood and metabolic disorders. Usually, constipation in a newborn is indicated by the absence of a toilet for several days. The child cries, pulls his legs to his stomach. This means that you need to urgently consult a doctor. The child needs to optimize nutrition, create a regimen, do constant abdominal massage and active-passive gymnastics. Laxatives and enemas are used only in extreme cases, with a long absence of a toilet. Conservative treatment is usually sufficient, the need for surgical interventions rarely arises. Usually, operations are performed only when kinks and loops occur in the intestine, when defecation is impossible for physiological reasons.
Since the causes of the disease are not fully known, preventive measures have not been developed either. In general, prevention can be reduced only to preventing the development of constipation. It is necessary to drink a large amount of water, adhere to a dietary diet and eat only those products that the doctor prescribed. The child needs regular abdominal massage.
Stages
There are only three stages of the disease, which manifest themselves differently. They depend on the severity and extent of the body damage.
The first is compensation, characterized by periodic constipation. Duration up to 3 days. Emptying is achieved by using a laxative. General well-being remains normal.
At the subcompensation stage, regular constipation is observed. The disease is accompanied by painful spasms and flatulence. Laxative enemas are often required.
The last stage is decompensation. At this stage, constipation lasts 5-7 days, and constant abdominal pain occurs. The colon swells and increases in size. There is an accumulation of feces and gases. Against the background of general intoxication of the body, weakness, loss of appetite, and increased fatigue develop. Temperature may rise. Skin rashes of a purulent-inflammatory nature appear. Later, intestinal obstruction develops. Only siphon enemas can help.
Moderate dolichosigma
If it is moderate, it manifests itself in the form of regular constipation, which can be eliminated with medications and enemas. In this case, fecal intoxication does not develop, or is not expressed clearly enough.
 [ 9 ]
[ 9 ]
Forms
There are several types of dolichosigma: acute and chronic. In the acute form, prolonged constipation develops, which lasts 3-5 days. In this case, intoxication of the body and the development of concomitant pathologies are possible. In chronic dolichosigma, constipation becomes a constant problem. Severe pain and intoxication occur.
Depending on the etiological factor that underlies the pathology, a congenital and acquired form are distinguished. Congenital is determined genetically or develops in utero. In the acquired form, the pathology develops as a result of the impact of various external and internal factors on the body.
Depending on the clinical picture of the pathology, an asymptomatic form, dolichosigma with impaired food transit and a complicated form, in which transgulation intestinal obstruction develops, are distinguished.
Depending on the number of additional loops, there are two-loop and multi-loop forms.
Depending on the stage, they are divided into three types: compensatory anomaly, subcompensatory and decompensatory.
Dolichosigma of the large intestine
With this form of pathology, the intestines are lengthened along their entire course, including in the large section. The walls expand and thicken. Usually, the cause of such stretching of the large intestine is a genetic failure, as well as an intense inflammatory and infectious process. The pathology can be provoked by long-term use of certain medications, for example, hormonal agents.
Often, for the pathology to develop, it is necessary to have a genetic predisposition. If such a predisposition is present, the situation may worsen with stress, physical inactivity, upon reaching the age of 45, as well as with improper nutrition and long-term drug therapy.
There is a high risk of developing pathology in the presence of such concomitant pathologies as sclerotic dysfunction, destruction of the mesenteric part of the sigmoid colon, microfibrosis and destruction of nerve ganglia, epithelial dystrophy. All this is accompanied by secondary degenerative processes, disruption of the motor and functional activity of the epithelium and intestinal mucosa.
It manifests itself as chronic stool retention, destructive changes and intoxication of the body, as well as irritation of the intestinal walls. All this leads to the development of an inflammatory process. Fibrosis can gradually develop, in which the mucous membrane gradually becomes thinner and is replaced by connective tissue. The depth of the lesion increases, the inflammatory process affects the muscle layer, submucosa and nervous tissue. The first signs are constipation for 3 days or more, the appearance of pain, spasm.
If dolichosigma is not treated, intestinal ischemia develops, which is accompanied by fecal incontinence. In many people, the disease does not manifest itself for a long time and is detected only during examination. Therefore, it is important to undergo preventive examinations. Diagnosis of the pathology at early stages makes it possible to prescribe treatment in a timely manner and avoid many complications.
Treatment is reduced to normalizing nutrition and drinking regime. Medication therapy and physiotherapy procedures are also prescribed. Enzyme preparations and laxatives are used. This is usually enough to stabilize the condition.
Dolichosigma of the sigmoid colon
This is a pathology in which damage occurs at the level of the sigmoid colon. Constipation causes a delay in fecal matter, the main accumulation of which is located here. An inflammatory process, infection, and intoxication develop. Not only does the quality of digestion decrease, but the general well-being of the body also noticeably worsens. To eliminate this, enemas and laxatives are used.
Dolichosigma and Payr's syndrome
Such combined pathology is accompanied by severe pain, rumbling in the intestines, bloating. The cause of the pathology is a bend. In this case, surgical methods of treatment are used. Most often, laparoscopic surgery is performed, which does not require a cavity incision. During the operation, the sigmoid colon is resected, the splenic flexure of the colon is retracted downwards. After this, the intestines are immobilized, and the mesenteric vessels are clipped. Then a minilaparotomy is performed in the left part of the iliac region, 4-5 cm long. Through this area, the sigmoid colon is resected and an anastomosis is applied.
Complications and consequences
Dolichosigma can be asymptomatic, and then manifest itself with severe complications. Skin rashes of a purulent-inflammatory nature appear. The main place of localization is the face. The accumulation of feces is accompanied by intoxication of the body and the formation of feces. If it is impossible to empty the intestines for a long time, the feces become hard, lose the ability to leave the intestines on their own. Anemia and sudden weight loss may develop.
Since the feces become hard, they can damage the intestinal walls when passing. Inflammation, infection, irritation of the walls, their mechanical damage, anal fissures and hemorrhoids develop. Intestinal obstruction, intestinal ischemia, fibrosis can eventually develop.
Transversoptosis with dolichosigma
The disease is accompanied by pain, a feeling of pressure in the abdomen, bloating, and flatulence. Long-term constipation causes nausea, vomiting, headache, and irritability attacks. Transverse ptosis is accompanied by rapid heartbeat, burning pain in the heart, and pain in the scapular region. If you eat a large portion of food, or if you exercise, the pain increases significantly. The pain may be relieved by lying down. In older patients, the pain is longer lasting and exhausting.
The main diagnostic method is an X-ray analysis performed using irriography. A contrast agent is used - a barium mixture, which is introduced into the intestine. A light abdominal massage is performed, the intestine is gradually displaced. The radioisotope method is also often used. After diagnosis, treatment should be started as soon as possible. The main treatment is aimed at normalizing peristalsis, intestinal motility, and restoring microflora. Gymnastics is important in the treatment of transverse ptosis. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out. For example, when pain occurs, painkillers are prescribed, applications are applied to the abdomen, electrophoresis and abdominal massage are used. It is necessary to include as many fruits, vegetables, and juices in the diet as possible.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, chronic intoxication occurs, and attacks of colon obstruction develop. It is impossible to relieve the pain syndrome. In this case, surgical intervention is required.
The operation is urgently performed in case of severe pain, bloating and flatulence, as well as in case of risk of intestinal obstruction. Only a surgeon can develop tactics based on laboratory and instrumental examination data. It is necessary to differentiate the disease from cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
The nature of surgical intervention depends on the severity of the disease, its form, and the localization of the main area of damage. According to statistics, transverse ptosis mainly affects elderly people. It develops against the background of a physiological decrease in muscle tone and an increase in pressure inside the peritoneum and chest. In the area of the liver and spleen, a kink in the intestine may occur, as a result of which the pathology worsens and requires surgical intervention.
Transvertoptosis begins with minor abdominal pain. Often they are not even taken for a serious pathology. Sometimes they can be taken for a mild dysfunction of the digestive tract. Gradually nausea and vomiting join in. When constipation occurs, feces are retained in the intestine for a long time, intoxication develops: headache, irritability, dizziness, weakness, sweating.
Colonoptosis with dolichosigma
Colonoptosis is a disease in which the internal organs, namely the colon, descend. It often develops as a complication of dolichosigma and chronic constipation. Most often, the intestine descends as a result of a defect that developed in utero. There is a hereditary predisposition to this pathology. It can also be a consequence of various abdominal surgeries, heavy physical exertion, complicated pregnancy. The pathology is also facilitated by a sharp loss of body weight, abnormal structure of other internal organs, spinal deformities, and injuries.
It manifests itself as stagnation of feces, constant constipation, nausea and vomiting. The bladder may be affected as a result of pressure on it. Right-sided inflammation is more common, and nearby organs are also involved in the inflammatory process. In the absence of treatment, intestinal obstruction may develop.
Colonoscopy and irrigography are used as the main diagnostic methods. These methods can be used to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, determine the diameter of the lumen and make a diagnosis. After that, appropriate treatment is selected. Conservative methods and diet are used.
Dolichosigma and hypotonia of the colon
Hypotonia of the intestine is understood as a decrease in the tone of smooth muscles, which disrupts the motility and contractile activity of the intestine. As a result, the processes of emptying and excretion of feces are disrupted. Normally, feces should be excreted at intervals of no more than 48 hours. With hypotonia, this interval is significantly extended. When combined with dolichosigma, intoxication occurs. The intestine can be affected completely, or only a separate section.
Hypotension most often occurs in old age, when the tone of smooth muscles is significantly reduced. This is facilitated by bad habits, poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, stress, prolonged fasting, and abdominal weakness. Often, weakening of the intestinal tone occurs against the background of diseases of other organs, hormonal dysfunction, congenital anomalies, adhesions and stenosis. It can be a consequence of toxic damage to the walls of the digestive tract, long-term use of drugs. The pathology is accompanied by circulatory disorders and damage to the nervous system, intestinal dysbacteriosis.
In order to choose the right treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that caused this condition. To do this, first of all, it is necessary to conduct diagnostics, then prescribe the appropriate treatment regimen. It is necessary to follow a diet, drink plenty of water, especially on an empty stomach. In the morning, you need to do physical exercises. During recovery, physiotherapy procedures, exercise therapy, yoga, breathing and relaxation practices are used.
Dolichosigma volvulus
With dolichosigma, the sigmoid colon is significantly lengthened. Its size exceeds the normal values. In addition, as a result of the accumulation of fecal matter, it expands. This leads to the appearance of an additional 1-2 segments in the intestine. In some areas, the intestine can twist, forming a bend or volvulus. In this case, surgical intervention is required to eliminate the bend.
Colitis in dolichosigma
Colitis is an inflammation of the intestinal wall that occurs as a result of exposure to exogenous and endogenous factors. Often, inflammation develops against the background of constipation, since feces cannot leave the intestines and accumulate in the intestines. As a result, toxins are produced, intoxication of the body develops, and the walls are also irritated. The mucous membrane swells, hyperemia and irritation develop. The feces become dark and acquire a foul odor.
During the examination, abdominal distension, pain on palpation, and distension of intestinal loops, which becomes visible to the naked eye, are detected. In children, this causes a slowdown in growth and development.
 [ 16 ]
[ 16 ]
Dolichosigma and dolichocolon
Dolichocolon is considered a complication of dolichosigma. It is often detected if the disease is not treated. It is accompanied by severe intoxication. It manifests itself in the form of increasing bloating, rumbling, and foul-smelling diarrhea. If the disease progresses, the temperature rises, nausea and vomiting appear, and abdominal pain appears. Then watery diarrhea in the form of a fountain may appear, which follows prolonged constipation. Against this background, dehydration occurs, intestinal cells lose fluid (it comes out into the intestinal lumen and intensifies diarrhea). It can end in vascular collapse, sepsis, and death.
Diagnostics dolichosigmas
In order to prescribe the right treatment, you must first make the right diagnosis. For this, various research methods are used. First of all, the patient is examined and questioned. The doctor receives the necessary information about the patient.
When collecting a life history, the doctor will find out the conditions in which the person lives and works, determine the diet, diet, susceptibility to stress, and the degree of nervous and mental stress. The doctor will need information about preventive vaccinations, previous illnesses, including infectious diseases and food poisoning. Information is needed about whether the person has traveled abroad, especially to exotic countries, which will make it possible to exclude the risk of developing helminthic and invasive diseases. Data is needed about concomitant pathologies and possible allergic and other reactions.
When collecting the anamnesis of the disease, information will be required on when the signs of the disease first appeared, how they manifested themselves, how the pathology developed. What complaints and subjective sensations the patient has at the moment. The reasons that alleviate the condition and aggravate it are found out. The doctor finds out what treatment was undertaken, what pills the patient takes.
Then, the patient is examined. The abdomen, intestines, and sigmoid colon area are carefully palpated. Percussion is used to tap the areas where the compaction is detected. Also, sounds that are observed in the intestines are listened to by auscultation, which makes it possible to determine the approximate direction of the dynamic processes occurring in the intestines. Thermometry is performed if necessary.
Thus, the doctor receives the necessary information that enables him to assume and make a preliminary diagnosis. But this information is not enough to make a diagnosis; additional laboratory and instrumental studies are required.
Tests
A number of tests are required to establish a diagnosis. You cannot do without a traditional blood and urine test. They can reveal signs indicating the nature and stage of the pathology: inflammation, infection, intoxication. A biochemical analysis provides a comprehensive picture, establishes the characteristics of metabolism, and the main processes occurring in the body.
A stool test for hidden blood is prescribed, which makes it possible to determine internal pathologies, to assume the presence of bleeding in the stomach or intestines. Sometimes the presence of hidden blood in the stool can indicate an early stage of cancer development.
A coprogram is performed, which makes it possible to assess how completely food is digested. A mandatory stool test for helminth eggs is performed; if necessary, a dysbacteriosis test is prescribed.
 [ 17 ]
[ 17 ]
Feces with dolichosigma
Since dolichosigma is accompanied by constipation, the stool becomes harder. Christmas tree-shaped stool, sheep stool may be observed. With prolonged constipation, it acquires a foul odor.
One of the most effective methods of instrumental examination is colonoscopy.
Instrumental diagnostics
In order to detect dolichosigma and fully confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct instrumental studies. Instrumental methods are the most informative. There is a wide variety of methods. Let's consider each one separately.
Irrigography. This method can detect additional loops in the sigmoid colon, volvulus or extensions. Barium mixtures are used for the study. X-rays are used for transillumination.
Using ultrasound of the abdominal organs, it is possible to detect extra loops, expansions, and other anatomical features of the intestine.
Rectomanoscopy is an endoscopic method that makes it possible to visualize and examine sections of the colon.
X-ray examination allows to detect on the image the expansion and additional loops in the sigmoid section. Ineffective in diagnostics of disorders in newborns.
Colonoscopy – allows to evaluate the condition of the walls of the large intestine using endoscopic equipment. During the procedure, a biopsy is taken for further histological examination.
Some other specific methods are used in children, such as rectal manometry, which uses a balloon catheter to measure the diameter of the lumen.
Colonoscopy for dolichosigma
The method allows to examine the inner surface of the intestine, to assess the condition of the large intestine, sigmoid and rectum. The walls and mucous membranes are assessed. The advantage of the method is that it is endoscopic, and during the examination it is possible to take a biopsy for further histological analysis. This method can diagnose the expansion and lengthening of the intestine, the presence of fecal stones and fecal masses, it is possible to identify the source of inflammation, infection, damage and cancerous tumors. It is used for early diagnostics.
Endoscopic signs of dolichosigma
Endoscopic examination reveals an increase in the lumen of the sigmoid colon, its size also lengthens. Dolichosigma is indicated by a length of over 46 cm. There is an accumulation of fecal matter, as a result of which the intestine expands. There may be signs of irritation: hyperemia, edema, redness of the mucous membrane and intestinal walls.
X-ray for dolichosigma
In diagnostics, an X-ray of the intestine is used, with the help of which it is possible to assess the condition of the sigmoid and other intestines.
Irrigography is a method of X-ray examination, in which a contrast agent is introduced into the intestine, then illuminated with X-rays. The method makes it possible to accurately determine how much the intestine is elongated and expanded, in which area the pathological process is localized. X-rays are not prescribed for children, since it is impossible to distinguish the natural length of the intestine from the pathological one in the image.
Radiographic signs
X-rays reveal dilated areas of the sigmoid colon, possible loops and volvulus. Excessive length of the intestine is also visualized. If fecal stones are present, they can also be detected during the examination.
Dolichosigma on ultrasound
Using ultrasound examination, it is possible to detect additional loops and expansion of the sigmoid loop. It also makes it possible to track the main processes occurring in the intestine.
Differential diagnosis
In order to confirm the diagnosis of dolichosigma, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out. First of all, the pathology must be differentiated from a common functional disorder of the intestine, which arose against the background of inflammation or improper nutrition. Then it is differentiated from food poisoning, intestinal obstruction, atony and ischemia of the intestine, cancerous tumors.
Who to contact?
Treatment dolichosigmas
Conservative treatment of dolichosigma is always carried out first, and only if it is ineffective radical methods are used. Any treatment begins with dietary nutrition, establishing a regime. You also need to drink plenty of water.
Prevention
There are no measures to prevent dolichosigma, since it is a genetic anomaly in which the sigmoid colon increases in size. It develops mainly in utero. You can try to prevent the development of constipation by following a diet and optimal drinking regime. It is important to take vitamins, have a complete diet, and include a large number of products with cellulose in the diet. If a pregnant woman knows about the presence of dolichosigma in her medical history, she should register as soon as possible and follow all recommendations for the prevention of this disease. It is necessary to do regular abdominal massage and exercise.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the severity of the disease, as well as on how well the patient follows the doctor's recommendations. If all necessary treatment measures are taken, the prognosis can be favorable. Usually, it is possible to achieve stool stabilization and regularity. If the child has dolichosigma, it is necessary to visit the doctor regularly, undergo preventive examinations, and adhere to the diet. If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical intervention is performed, the prognosis of which is usually favorable.
Disability in dolichosigma
The diagnosis itself is not an absolute basis for establishing disability. It is established by a medical examination, expert doctors who assess the severity of the disease, prognosis, and the presence of concomitant diseases. The decisive factor for establishing disability in dolichosigma is the degree of muscle hypotrophy and the presence of protein-calorie malnutrition (PCM). With PCM of the 1st degree, disability is not issued, with the 2nd and 3rd degrees - it is issued.
It should be taken into account that in accordance with the rules for recognizing a patient as disabled, three categories are distinguished. The first category includes people with a violation of the structure and functions of the body, which do not allow the patient to take care of himself independently. The main condition is the need for outside care. In most cases, dolichosigma does not apply to such conditions, since even in the most severe case, the person remains capable of action.
The second group includes people who do not need outside care, but require special conditions for life and activity. The third group includes people with limited ability to work, which arose as a result of illness or congenital anomalies. A person can work, but heavy physical work should be excluded. It is believed that dolichosigma does not cause irreversible consequences in the body, does not affect the ability to work, therefore it is not a diagnosis that provides for disability.
But it is important to understand that only the commission can make the final decision.
Do they take people into the army with dolichosigma?
Dolichosigma is not a reason for exemption from military service. The regulations on military medical examination do not include this diagnosis as a reason for recognizing a person as unfit for service, and do not provide grounds for deferring conscription.

