
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Diagnosis of an endometrial polyp
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
Diagnosis of endometrial polyps is one of the most serious problems in gynecology today. At first glance, it seems that it is quite easy to diagnose a polyp - during a gynecological examination, any gynecologist can identify it by its appearance. It has a characteristic appearance of a neoplasm located on a stalk. It is one of the forms of endometrial proliferation, attached to the uterus, gradually growing into its mucous membrane. The sizes can be different, most often vary from 1 to 10 mm, and more.
The most difficult is differential diagnostics. There are many types of endometrial polyps. It is also important to differentiate a malignant tumor from a benign one, to exclude the possibility of malignant degeneration of the polyp. It is necessary to determine the size of the polyp, their multiplicity, or single nature, the presence of concomitant pathologies, such as inflammation, an infectious process. Sometimes there is a need to differentiate the polyp from other similar neoplasms: hyperplasia, edenomyosis, cancer.
Laboratory diagnostics, tests
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo quite a lot of tests. First of all, general clinical blood and urine tests are prescribed. By detecting protein in the urine, it is possible to draw a conclusion about the presence or absence of inflammatory processes in the body, and roughly determine their nature. Also, the presence of leukocytes in the urine can indicate the development of an inflammatory process.
Blood can also be used to determine an approximate picture of the pathology and develop a further examination plan. Thus, the number of red blood cells in the blood can have diagnostic value. Their decrease is often observed against the background of bleeding polyps, hidden bleeding, and in the presence of hidden inflammatory processes. An increase in red blood cells can indicate the development of a malignant process, as well as the likelihood of cancerous transformation of the polyp. With bleeding and intoxication, degenerative processes in polyps, a change in the morphological structure of red blood cells can be observed. Thus, basophilic granularity of red blood cells is quite often a sign of bleeding polyps. In a chronic pathological process, signs of anemia as a consequence of prolonged bleeding or malignancy, a decrease in the amount of hematocrit can be observed. Such a picture can also be observed against the background of trauma to polyps.
A study of the leukocyte formula can be informative. An increase in the number of eosinophils indicates allergic processes, dystrophy of the mucous membrane. It can indicate the development of parasitic and latent infections. Platelets indicate the state of the circulatory system, features of blood coagulation, can indicate latent bleeding and the presence of an active inflammatory process.
A decrease in the number of lymphocytes and leukocytes in the blood indicates the development of an oncological process. Since this may also be a sign of immunodeficiency, it is advisable to conduct an immunogram to clarify the diagnosis. It is based on the results of this study that one can draw a conclusion about how the polyp will behave and what is the probability of its cancerous degeneration.
If there is a suspicion of cancer, the only way to confirm or refute the diagnosis is a histological examination. For this, a biopsy is performed, during which biological material is collected for further examination.
If a viral infection is suspected, a series of virological, immunobiological and serological reactions are carried out, which make it possible to determine the degree of viral load, species composition and degree of activity of viruses. It is also possible to detect a latent infection, which can proceed asymptomatically, while causing numerous pathological processes in the body.
Hormonal analysis may be required, since further growth of polyps depends on the concentration of hormones in the body. Activation of polyp growth occurs with the predominance of estrogens and a lack of progesterone. In this case, re-formation of polyps may also develop after their removal. If hormonal imbalance is detected, corrective therapy is prescribed.
Scraping of endometrial polyp
A scraping from the endometrial walls is a biological material that is necessary for further bacteriological examination. No special preparation is required. The doctor will do everything necessary during the gynecological examination. Special instruments are used to collect the scraping. The procedure is painless and takes several minutes. The only condition that must be observed is to exclude antibiotic therapy 14 days before the study, and several days before collecting the material, do not use any antibacterial agents, especially local ones, do not douche, do not use suppositories.
A bacteriological examination may be required if there is a suspicion of an infectious etiology of polyps, as well as if there is a suspicion of a violation of the vaginal microflora. For this, a standard bacteriological examination is carried out, during which biological material is taken for examination. This is most often a smear or scraping from the vaginal mucosa, which is taken by a doctor during a gynecological examination.
Then, in laboratory conditions, the obtained material is seeded on nutrient media and incubated in a thermostat for 3-5 days. At the same time, the smear is assessed under a microscope, paying attention to the presence of additional inclusions, the nature of the microflora, and the presence of epithelial cells. This may be a sign of an active inflammatory process.
After the culture has grown, it is transferred to selective biological media. This is necessary to isolate a pure culture of the pathogen and identify it. If necessary, an antibiotic sensitivity test is performed along with the bacteriological study, which makes it possible to select the optimal antimicrobial agent that will have the greatest effect on the isolated pathogen. The required dosage of the drug is also determined.
If it is necessary to determine the nature of the microflora, a dysbacteriosis analysis is performed, or a special microbiological screening of femoflor, which makes it possible to assess the state of the vaginal microbiocenosis. This study allows you to evaluate the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the microflora, identify the total microbial number, get a general idea of the structure, quantity and ratio of representatives of the obligate and facultative microflora, the percentage of opportunistic microorganisms.
It is also possible to identify absolute pathogens and determine their quantity. Standard analysis for dysbacteriosis is performed by bacteriological seeding, analysis for femoflor is performed by PCR. Each of their methods has both its disadvantages and advantages.
Endometrial polyp biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure that is very often performed when there is a suspicion of an oncological process. It is quite simple, the main thing is to perform it carefully and professionally. In this case, a piece of the tumor (polyp) is taken with the help of special instruments for the purpose of further histological examination. It is necessary to take the sample very carefully so that the piece of tissue does not fall anywhere in the uterus and vagina. In the case of a cancerous tumor, this can become a new site for tumor development (metastases). Also, when taking the material, it is necessary to strive for minimal damage to the polyp so as not to provoke its growth and malignant degeneration.
 [ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
[ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ]
Histology of endometrial polyp
The material obtained during the biopsy is subjected to histological examination. The analysis makes it possible to study the structure and dynamic processes occurring in the tumor cells. Based on the results, a conclusion is made about the nature of the tumor. First of all, it is determined whether it is benign or malignant. Also, based on the results, the nature and direction of further development of the neoplasm are predicted, and the tactics and strategy of treatment are selected.
It has an important diagnostic value. Having determined the nature of the pathology, it is possible to promptly select the optimal treatment, reduce the likelihood of further progression of the disease. If adenomatous polyps are detected, it is recommended to remove them as soon as possible.
The essence of the study is that tissue samples are sown on a nutrient medium intended for growing tissue samples. They are incubated in a thermostat for 10 days to 3 weeks, then transferred to artificial nutrient media and incubated for some more time.
Instrumental diagnostics
It is performed for the purpose of visualizing the polyp and its precise identification, since polyps are practically impossible to palpate and are also difficult to visualize in mirrors. Only instrumental methods make it possible to accurately determine the localization, size, shape, and nature of the polyp. The strategy and tactics of further treatment largely depend on this.
The main methods are ultrasound, which allows assessing processes in dynamics, studying the morphology of the polyp, its size and localization. The main signs of polyp formation are the expansion of the uterus, thickening of its inner layer, and the growth of the mucous membrane.
Colposcopy allows to study and examine the polyp in detail, as well as to determine the approximate cause of the pathology. It is possible to detect inflammation, determine an infectious process, hyperplasia. Colposcopy is mainly used to examine the cervical canal. A gynecological mirror is used, which makes it possible to study the surface, appearance, and structure of polyps.
The exact cause of the pathology can be determined during hysteroscopy, during which the internal cavity of the uterus is examined and inspected. Biological material can be collected for further microscopic or histological examination. X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent is also used. It allows visualizing the polyp, determining the structure, size, shape, and localization.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography allow you to get a complete clinical picture: study the features of localization, development of the polyp, stage, degree of ingrowth. These are expensive procedures, require a longer time for research, so they are used when cancer is suspected. But these methods give the most complete picture.
The combination of several methods is also very informative. For example, hysteroscopy and ultrasound allow a comprehensive assessment of the polyp, studying both anatomical and morphological features in various projections.
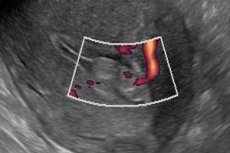
Endometrial polyp on ultrasound
Ultrasound allows visualization of the polyp. There are two ways of conducting the examination: abdominal (external) and transvaginal (internal) method. Most often, endometrial polyps are diagnosed using abdominal ultrasound, since this method is designed to detect polyps localized inside the uterus.
The transvaginal method can provide a lot of useful additional information. Usually, ultrasound can detect fairly large polyps over one centimeter in size. Detection of smaller polyps requires special equipment, and this is a significant drawback of the method. Ultrasound can also be used to calculate how quickly a polyp grows and judge its susceptibility to malignancy.
Echo signs of endometrial polyp
The main indicator that is assessed when diagnosing polyps is the change in M-echo, which reflects the anteroposterior size of the uterine cavity. Its expansion can be observed during menopause, which lasts more than 5 years (normal). In case of pathology, in women of reproductive age, it indicates the presence of some additional structure, regardless of whether it is a polyp, tumor, hyperplastic change in the mucous membrane or other layers of the uterus.
Usually, a polyp can be recognized by its characteristic appearance, which visualizes a fairly dense, outlined structure with a stalk. Additional information that will allow a polyp to be finally identified is Dopplerography, which allows determining the characteristics of blood flow in the vessels of the polyp. This makes it possible to accurately study the vascular bed of the polyp, which is quite independent. Introduction of a physiological solution into the uterine cavity makes it possible to examine the vessels in more detail and clearly.
Sizes of endometrial polyps in the uterus
The minimum size of a polyp that can be visualized using special methods is 1 mm. This is a small polyp. Medium-sized polyps include polyps from 5 to 7 millimeters in size. Large polyps are those 1 cm or larger. They require removal.
Polyps can have different sizes. At an early stage, polyps of fairly small sizes, reaching several millimeters (usually 1-3 mm), are visualized. Detection of such polyps requires special equipment. Such polyps are not detected by ultrasound. Ultrasound can diagnose polyps larger than 1 cm.
Polyps of 4 mm and larger can be diagnosed during colposcopy. Polyps of 5-7 mm are considered average. They can be treated or removed. They usually respond well to drug treatment, so do not rush to remove them. Polyps of 8-9 mm are almost not amenable to conservative therapy. If the size reaches 1 centimeter or more, it must be removed, these are fairly large polyps. They are visualized using ultrasound.
 [ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
[ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
Multiple endometrial polyps
Polyps can be not only single, but also multiple. When multiple polyps are detected, a diagnosis of polyliposis is made. This means that initially a single polyp was formed, which gradually began to undergo hyperplastic processes. Multiple polyps can mainly be glandular or fibrous, since they tend to grow rather than transform into a malignant neoplasm.
Polyps are quite easy to recognize by their characteristic external signs. They often occur in women who have not given birth, after the age of 27, since the natural hormonal cycle is disrupted. Multiple polyps can be detected quite easily either during a routine gynecological examination or with the help of simple laboratory and instrumental methods. Among the main methods of treatment - one can name resection (the polyp is removed, and its bed is cauterized).
Endometrial polyp on MRI
Magnetic resonance therapy allows to detect a polyp, study its main characteristics, localization, note tissue malignancy. It makes it possible to detect a cancerous tumor and the probability of polyp transformation (the presence of atypical cells in them) as quickly as possible, even at the stage of tumor formation. It is used when cancer is suspected.
Differential diagnostics
The purpose of differential diagnostics is to differentiate a polyp from other neoplasms that have similar signs. It is often necessary to differentiate a polyp from an ovarian cyst, endometriosis, blood clots, uterine fibroids, and cancerous tumors.
A cyst can be differentiated primarily by its appearance and location. A cyst is usually located behind and to the side of the uterus, while a polyp is located directly in the uterine cavity or on its cervix. A characteristic feature of a cyst is adhesions that cover the entire endometrium quite intensively: the adhesion process covers the walls of the uterus and the cervix. With polyps, there is no adhesion process.
The polyp is smooth, has clearly defined contours, and is located on a stalk. The walls of the cyst are unevenly thickened, the contours are uneven. A characteristic specific feature of an ovarian cyst is the effect of uniform darkening. The shape of the cyst is often round, oval, the polyp - absolutely any shape.
In some cases, a woman may not even know that she has polyps, since they develop over a long period of time and without symptoms. They are often discovered by chance, during a routine examination. A cyst often makes a woman see a doctor with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen. If the cyst has reached a large enough size, it can press on neighboring organs, while polyps, even large ones, may not manifest themselves in any way.
It is also often necessary to differentiate polyps from endometriosis. Endometriosis is a disease that is accompanied by the proliferation of the endometrium and the formation of endometrial polyps. These are quite dangerous polyps, since they have changed their cellular structure and, in fact, represent a precancerous condition. Sometimes endometriosis is not accompanied by the formation of polyps. The main method of differential diagnostics is histological and cytological examination. During these studies, the structure of tissues and cells is studied. The detection of atypical cells indicates the development of endometriosis.
In most cases, a polyp is differentiated from a cancerous tumor. Sometimes this can be done without special studies, by visualization. Thus, a polyp can be recognized by its dense structure, the formation of a stalk. Cancer is characterized by a loose structure, loose adherence of cells and the ability to grow without limit. Polyps may not grow at all for a long time.
However, it is necessary to take into account that only a histological examination, during which a tissue sample obtained from the tumor is cultured and its properties are studied, is a reliable and accurate confirmation of the diagnosis. The type of tumor is determined by the nature of growth: benign or malignant. This allows a final diagnosis to be made: the polyp is a benign neoplasm.
In some cases, blood clots may be so similar in appearance to polyps that differential diagnostics must be used. It is necessary to carefully examine the detected structure: a polyp has the appearance of a new growth, with smooth, clearly defined walls, located on a stalk.
A clot differs from a polyp in that it can be amorphous, often changing its shape. Often red in color, it can have different consistencies. In the middle, the clot is filled with various contents, which vary widely: from light mucus to hemorrhagic fluid. It can be quite dense and thick, quite large in size.
Another formation from which it is necessary to differentiate a polyp is a myoma. It has the appearance of nodes that have clear boundaries and smooth, slightly bumpy contours. The simplest method of differentiation is MRI. Myoma has a low intensity of magnetic resonance signal in MRI. The signal is very similar to the signal of skeletal muscles.
 [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ]
[ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ]
Is it possible to confuse endometrial polyp?
Endometrial polyps can be confused with some other pathologies. But this does not happen often, since differential diagnostics allows you to exclude all other diseases and neoplasms that have similar symptoms and manifestations. Confusion is possible only during the initial examination, but differential diagnostics exists precisely to exclude such confusion. Theoretically, polyps can be confused with a cancerous tumor, cyst, myoma, endometriosis and blood clots.
Endometrial polyp and cancer
Polyps are pathological formations of the mucous membrane, protruding above its surface and connected to it by a stalk or their base; they are single or multiple formations of an irregular round or oval shape.
A polyp can also be recognized by its dense structure, the formation of a stalk, while cancer can be recognized by its loose structure, loose adherence of cells and the ability to grow without limit.
Despite the fact that cancer and polyps are quite easy to distinguish externally, you should not rely on this diagnostic method. These two diseases can only be differentiated using histological examination. In this case, a targeted biopsy is performed, with the help of which biological material (a piece of the tumor) is taken for examination in laboratory conditions. The essence of the study is to grow a tissue culture from the sample on artificial nutrient media. Then, based on the nature of growth, the type of tumor is determined: benign or malignant.
It is also necessary to take into account that a polyp in its composition may contain atypical cells, which may eventually undergo malignancy and degenerate into cancer. First, the endometrium grows, then the epithelial tissue is transformed. It acquires the ability to grow unlimitedly, turns into a cancerous tumor, the cells of which continue to divide and multiply uncontrollably. The degeneration of a polyp into cancer can occur under the influence of various factors, including as a result of its injury.
Uterine fibroids and endometrial polyps
Myomas are very small in size: on average 0.3-0.4 cm. They are much smaller in size than polyps, and also do not have a stalk. Also, during magnetic resonance imaging, large uterine vessels and large nodes are noticeable. The appearance of heterogeneous areas may indicate the process of transformation of the myoma into a cyst, or profuse hemorrhage.
Myoma can also be recognized by a person's well-being. Polyps do not affect well-being in any way and do not cause any inconvenience to a person, while myoma manifests itself as severe weakness and malaise, frequent inflammatory processes and the development of an infectious process. The main symptom is severe pain in the abdomen, menstruation is accompanied by severe blood loss. Myoma is also characterized by a feeling of pressure on the internal organs, anemia, frequent urination. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the groin area and other areas.
Endometrial polyp and adenomyosis
It is quite easy to recognize a polyp by its appearance. The main method used for differential diagnostics is hysteroscopy. With this method, you can notice the differences - an endometrial polyp is located in the uterine lining, adenomyosis affects the inner deep layers.
Uterine polyps and endometrial hyperplasia
Differential diagnostics of endometrial polyps and endometrial hyperplasia is quite simple. In hyperplasia, the endometrium looks like a protruding hyperplastic mucous membrane of the uterus, which, increasing in size, can extend far beyond the uterus, into the vagina. Polyps are strictly localized areas of the endometrium, which are located on a stalk. Multiple endometriotic polyps are characterized by the formation of numerous nodules.

