
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Cracked hand
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
There are quite a few life circumstances in which one can get various injuries. A common occurrence in traumatology is a crack in the hand. It can be obtained both in ordinary everyday conditions and in various disasters, accidents. But in addition, there are a number of conditions that predispose to such injuries. They need to be known and taken into account in order to be able to prevent such accidents.
Epidemiology
According to statistics, a crack in the hand is most often found in elderly and old people. This is due to increased fragility of bones, metabolic disorders that predispose to bone fragility. It is also associated with impaired coordination, blood circulation, due to which elderly people often fall and hit themselves. About 45% of hand fractures occur in old age. About 35% of all hand fractures occur in mature people - from 25 to 45 years old. At the same time, they most often get injured in emergency situations (up to 70% of cases), in connection with professional activities - up to 18% of cases, at home. On vacation - about 10%. Other reasons account for about 2%. At the same time, the number of injuries increases sharply during the holidays, especially on New Year's Eve, from May 1 to 10. During this period, ambulances and traumatology departments work in an enhanced, emergency mode. On average, the frequency of fractures and cracks of the hand during this period increases by 2.5-3 times. Approximately 15% of injuries occur in adolescents and young adults - from 12 to 25 years old, and only 5 percent - in children under 12 years old.
Causes cracks in the hand
A crack in the hand can be obtained at any age and under any circumstances. Naturally, the main cause is traumatic circumstances in which the physical destruction of the bone occurs, its integrity is violated. The main cause is considered to be an injury that can occur with a strong push, compression, impact, stretching, pressure. An injury can occur in normal household conditions, in everyday life, most often due to carelessness, inaccuracy. An injury can be obtained when carrying out various works at home, on a personal plot, in the country.
An injury can also be sustained during professional activity, at work. Injuries are especially common at work, during physical exertion. Cracks often occur in coaches, instructors, and athletes. Injuries can be observed in professional athletes who do physical exercises incorrectly, who train intensively, especially when preparing for competitions, directly at competitions, tournaments, relay races, and performances.
And of course, various accidents, emergencies, accidents, disasters are common causes of hand injuries. A crack can be caused by a fire, flood, earthquake, building collapse, strong hurricanes, tsunamis.
The cause may be osteoporosis - a disease of the skeletal system, in which the structural state of the bones is disrupted, they become fragile, brittle. The cause may be increased fragility of bones, which occurs due to a violation of calcium-phosphorus metabolism in the body, with a lack of vitamins, minerals, especially with a lack of vitamin D. In these conditions, bones also lose elasticity, resilience. Increased fragility can also be observed in connection with past infectious diseases, tuberculosis of bones, after chemotherapy and antibiotic therapy, against the background of rickets, with carbohydrate metabolism disorders, a lack of organic substances in the body.
Bone fragility increases with age, in old age, when degenerative processes, age-related changes in bone and muscle tissue, dystrophy, and malnutrition develop. The cause may be a violation of neuroregulatory, immune, and, less often, hormonal processes.
Risk factors
The main risk factors are environmental conditions under which a damaging factor may affect the human body. The risk increases sharply in emergency situations, accidents, high physical exertion, extreme situations. This may be a war zone, local conflicts, areas with an increased risk of disasters, emergency situations. If a person has a history of osteoporosis, tuberculosis of bones, rickets, other diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Also, the risk group includes elderly people who often suffer from infectious diseases, people with insufficient nutrition, malnutrition, hypovitaminosis.
Cracked wrists are often suffered by tourists, especially those who prefer extreme sports such as surfing, scuba diving, rock climbing, mountaineering, and others. This includes people of various natural science professions, researchers who are often forced to live and work in extreme conditions: geologists, geographers, biologists, ecologists, zoologists, volcanologists, oceanologists. An injury can also be sustained by an ordinary tourist who moves along unfamiliar paths, especially in the mountains, at waterfalls, in caves.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis is based on the actual destruction of the bone, the development of a crack in the area of the hand, and the disruption of the anatomical and morphological integrity of the hand. There are several pathogenesis options. First, the bone may shift, forming fragments. Second, the fracture may be in one place or in several.
Particularly dangerous are multiple injuries with the formation of fragments. With bone displacement (there is a risk of damage to soft tissues, blood vessels, nerves). At the site of the crack of the hand, the skin can break through, which is also dangerous due to complications, in particular, infection, which entails inflammatory, infectious, purulent-septic processes, gangrene. Often cracks of the hand are accompanied by bruises, hematomas, sprains or ruptures of tendons, muscles, ligaments. The formation of exudate (fluid) is dangerous.
Symptoms cracks in the hand
The main symptoms of a crack in the hand are the inability to move the hand, pain in the hand area, swelling. There is a feeling of a violation of the integrity of the hand, fragmentation when palpating. Cracks are accompanied by pain directly at the moment when the crack itself occurred. But there are cases when a person does not feel that the bone has cracked.
Limited mobility is not always a sure sign of a crack. In some cases, on the contrary, an incorrect (excessive mobility of the limb) develops. Displacement, incorrect position of the bone, displacement, swelling, compaction make themselves known. As symptoms of a crack in the hand, curvature of not only the hand, but also the limb itself is considered. Massive hemorrhage is possible when the integrity of the skin is violated, hematomas are formed under the skin (due to damage to soft tissues).
Usually the first sign of a crack is a sharp pain in the wrist area. Often the pain is accompanied by a crunch, the inability to move the wrist, arm. With an open crack of the wrist, the integrity of the skin is damaged, a bone fragment sticks out of the wound, bleeding occurs, and swelling appears. With a closed crack, the skin becomes cold, pale, blue, numb, and sensitivity is impaired.
A fracture of the wrist bone is accompanied by pain, a violation of the integrity of the bone. Sometimes internal soft tissues, nerves and blood vessels are damaged, a hematoma, swelling and redness appear.
Often such injuries are the result of impacts, sudden pressure and are observed in various accidents and crashes.
A person with a fractured wrist bone needs first aid. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the displacement (if any). After that, the bones should be fixed (connected). A splint or tight bandage is applied. It is important that the bones touch and then be immobilized (provide rest). This is why a plaster cast is applied.
 [ 19 ]
[ 19 ]
Complications and consequences
The consequences and complications depend on the type of crack. Thus, with an open crack, complications such as displacement, swelling, and pain shock may occur. With a closed crack of the hand, damage to blood vessels and nerves may develop. Bleeding and neuralgia appear. Progressive neuralgia may end in decreased sensitivity, paralysis, atrophy, and necrosis. If an infection occurs, there is a risk of developing an inflammatory, infectious process, erysipelas, gangrene, bacteremia, and sepsis.
How long does it take for a crack in the hand to heal?
The healing time also differs, depending on the type of crack, the cause, individual characteristics of the person, age. Definitely, in young people, the crack heals faster than in old people. How long it takes for a crack in the hand to heal also depends on the condition of the bones, the presence or absence of complications, concomitant pathologies. On average, if there are no complications, a crack in the hand heals from 1 to 3 months. With complications, this process can drag on for up to six months or more.
 [ 20 ]
[ 20 ]
Diagnostics cracks in the hand
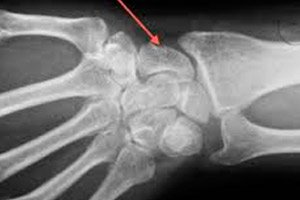
The basis of correct treatment is correct diagnosis. A crack in the hand can be determined during an examination at a trauma center. An experienced traumatologist only needs to palpate the hand to determine the crack, its location, and size. But according to the protocol. No matter how experienced the specialist is, valid and reliable methods of diagnosis are needed. Therefore, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used. For example, an X-ray examination method will help to fully visualize the pathology and view all the features of the crack in the image. Only after receiving the X-ray results, the doctor can finally confirm the diagnosis and has the right to prescribe appropriate treatment. In diagnosing a crack in the hand, X-ray is the main diagnostic method.
 [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ], [ 25 ]
[ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ], [ 25 ]
Tests
Laboratory methods are uninformative, so they are rarely used. Tests are almost never prescribed to diagnose mother-in-law's disease in the hand, except in cases of complications. Also, in rare cases, they can be prescribed to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
Standard tests include clinical blood, urine, and stool analysis. In traumatology, methods such as rheumatic tests, C-reactive protein analysis, and biochemical studies are sometimes used. They mainly have prognostic value and allow one to identify predisposing (aggravating factors) such as osteoporosis, rickets, etc. They also allow one to assess how effective the treatment is or are used in case of complications.
 [ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ]
[ 26 ], [ 27 ], [ 28 ], [ 29 ], [ 30 ]
Instrumental diagnostics
The main method of instrumental diagnostics is X-ray (radiographic) examination. Also used are methods such as computer and magnetic resonance tomography (CT; MRI). These are quite significant informative methods. They make it possible to visualize the crack, to examine its main characteristics. But they are rarely used, due to the high cost. Ultrasound of bones and soft tissues is also used, but rarely.
Differential diagnosis
The essence of differential diagnostics is the need to accurately determine the type of crack and its location. There are many types of cracks that manifest themselves in approximately the same way, but require different approaches to treatment. The more accurately the fracture is differentiated, the easier and more effective the treatment will be.
Who to contact?
Treatment cracks in the hand
The treatment is carried out in several stages. Thus, at the first stage, standard symptomatic treatment is prescribed. In fact, this is emergency care for the patient. The main symptoms, such as pain, swelling, rupture of soft tissues, vessels, should be removed. The likelihood of complications, such as damage to the integrity of the skin, inflammation, infection, should be prevented.
Then, at the second stage, bone immobilization is performed. Measures aimed at fusion of cracked hand bones are important. In this case, plaster is used. The essence is to ensure a fixed position of the bone for its further fusion.
If necessary, drug therapy is also used: painkillers, anti-inflammatory, anti-infective agents.
After the plaster cast is removed, rehabilitation (restorative therapy) may be required to restore sensitivity and mobility. This is mainly drug therapy combined with physical activity, massage, and exercise therapy.
Medicines
- Chondroitin ointment
Dosage: squeeze out a pea-sized amount of ointment, apply to the cracked area, onto the hand. Rub until completely absorbed.
Directions for use: For external use only, on skin.
Precautions: Do not apply to mucous membranes. Also, do not apply to damaged skin (not allowed in case of open fractures or wounds).
Side effects: possible allergic reactions. In case of overdose – burning, redness.
- Analgin
Dosage: one tablet 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is from 3 to 7 days, depending on the severity of the pathology.
Directions for use: swallow, wash down with water.
Precautions: should be taken with caution by patients with a tendency to bleeding, since analgin is a strong blood thinner. It is not compatible with anticoagulants.
Side effects: bleeding due to decreased blood clotting.
- Spazmalgon
Dosage: one tablet 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is from 5 to 10 days.
Directions for use: swallow, wash down with water.
Precautions: Consult your doctor before starting treatment.
Side effects: none known.
- Suprastin
Dosage: one tablet 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is from 5 to 10 days.
Directions for use: swallow, wash down with water. Can be chewed, sucked, held under the tongue (this way the drug works faster).
Precautions: Consult your doctor before starting treatment.
Side effects: drowsiness, decreased concentration.
Vitamins are used mainly after the plaster is removed, during the rehabilitation process. Vitamins of group B are prescribed - 60 mg per day, C - 1000 mg, A - 420 mg, E - 45 mg. Vitamin C is especially important, since it relieves the effects of the fracture, accelerates the recovery processes.
Physiotherapy treatment
Various methods of physiotherapeutic treatment are used. They are most effective during the rehabilitation process, after the plaster cast is removed. They allow metabolic processes, tissue nutrition, return sensitivity, and normalize blood circulation. The main methods of physiotherapeutic treatment are ultrasound, microcurrents, waves of various lengths, electrophoresis, massage, cryotherapy, thermal procedures, and electrical procedures.
One of the main rehabilitation methods is electromyostimulation (increases the electrical activity of skeletal and smooth muscles, normalizes the electrical potential, which is important for restoring sensitivity and mobility after prolonged immobilization). Acupuncture has similar properties, only it additionally relieves pain.
It is necessary to take into account that no procedure will be effective without therapeutic physical training. It is necessary to use means of active and passive gymnastics.
Folk remedies
With the help of numerous and varied methods of traditional medicine, standard therapy can be effectively supplemented.
- Recipe No. 1.
Take about 30-40 grams of white clay as a base. Add baby cream (about the same amount). Prepare a mass of uniform consistency. The mass should be such that it is easy to apply to the skin and harden (approximately the consistency of sour cream). Apply for 15-20 minutes on the brush, in the place where there is a crack, then wash off and apply a greasy cream (any) or anti-inflammatory ointment.
- Recipe No. 2.
As a base, take about 20-30 grams of blue clay and cleaned fried sand, mix together. Pour in a small amount of pre-prepared warm herbal decoction (birch buds and leaves, linden flowers, nettle leaves). Prepare a mass of uniform consistency (like sour cream). Immediately before applying to the crack of the brush, add 2-3 drops of concentrated eucalyptus essential oil. Apply for 15-20 minutes, then wash off and apply a greasy cream (any), or ointment.
- Recipe No. 3.
Take approximately equal parts of ground dry seaweed and purified edible sulfur, mix with honey until a uniform consistency is formed. Mix well so that no lumps remain. If you can’t stir, you can pre-melt the honey over low heat or in a water bath.
Before applying, add 2-3 drops of clove essential oil to the brush, mix thoroughly again, and apply for 10-15 minutes. It is also recommended to apply dry heat on top. Rinse with warm water, apply moisturizing cream on top.
- Recipe No. 4.
Mix equal parts blue clay and ground bone meal powder (about a tablespoon of each component), add about 2 tablespoons of cream and 1 tablespoon of glycerin. Mix everything thoroughly until smooth, apply to the brush. It is best used under a compress. After about 40-50 minutes, wash off with warm water.
 [ 31 ]
[ 31 ]
Herbal treatment
Usually, medication is used first, a plaster cast is applied. And herbal treatment is used when the plaster has already been removed and recovery is required.
Chamomile is used internally in the form of decoctions and infusions, increases immunity, eliminates viral infections, prevents infections. It is also used in creams, ointments, masks, for compresses and medicinal baths.
A decoction of cardamom is used. It has a calming and strengthening effect, is responsible for relieving irritation, inflammation, relieves pain, increases muscle and skin sensitivity. A tablespoon of seeds is poured with a glass of boiling water. An infusion is used (pour alcohol, insist for a day and drink a tablespoon three times a day). The decoction is drunk in a glass per day. It can be used in the form of applications, compresses, lotions, baths.
To eliminate inflammation and swelling, use calendula. Mix equal parts of flowers, inflorescences (seeds) and leaves of common calendula, pour boiling water (200-250 ml), leave for at least an hour, use for local baths and compresses during the day. You can add honey or sugar to taste and drink. Relieves inflammation and pain. Prevents infection, alleviates the condition.
Homeopathy
For treatment and recovery after a crack in the hand, not only traditional medications are used, but also homeopathy. Various essential oils have found wide application, which are used mainly in the form of applications and local baths.
To make an applique, you need to prepare a warm solution, then dip the fabric in it, squeeze it out and apply it to the brush. A layer of dry fabric is applied on top, and dry heat is applied on top.
To carry out the baths, prepare a solution, make it warm, maybe slightly hot. Dip the hand with the crack into it. Hold for at least 15 minutes. Then pull the hand out, do not wipe, but only lightly blot. It is recommended to apply dry heat on top. It is recommended to use the following solutions, listed below.
- Recipe No. 1.
Add about 3-5 drops of orange essential oil to a liter of warm water. Relieves pain, redness, stimulates skin sensitivity. Eliminates spasms, increases the tone of weakened muscles, relaxes tense areas.
- Recipe No. 2.
Add about 3-4 drops of vanilla and gardenia essential oil per liter of water. Use to relieve pain and increase skeletal muscle tone.
- Recipe No. 3.
Add 1-2 drops of jasmine, hyacinth and neroli oils to a liter of water. Relaxes, normalizes muscle tone, normalizes blood circulation, increases muscle and skin sensitivity. Has an anti-inflammatory effect, prevents the risk of infection.
- Recipe No. 4.
Approximately 2 drops of sandalwood essential oil, 2 drops of rose oil and 3 drops of cedar oil are required per liter of warm water. Reduces inflammation, increases sensitivity, tones. Cools, relieves burning, itching, which often occur after removing a plaster cast.
- Recipe No. 5.
Add 2-3 drops of saffron, lavender and frankincense oils to a liter of water. Prevents the development of allergic and inflammatory reactions, normalizes blood circulation, stimulates normal vascular tone, skin sensitivity, muscle tone.
Surgical treatment
Basically, cracks and fractures are treated with plaster. Surgical treatment methods are used if the crack has not healed properly, or if the pubis affects nerves, vessels, soft tissues. The need also arises when complications develop, such as necrosis, inflammatory, infectious processes.
Prevention
Prevention is based on a normal balanced diet, taking vitamins and minerals. It is also important to avoid exposure to all possible risk factors that can lead to a crack. In addition, to increase bone strength, regular exercise, an active lifestyle, and, if necessary, taking calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D supplements are required.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the severity of the condition, location and size of the crack, as well as individual characteristics: bone condition, age of the victim. If the crack is detected in time and a plaster cast is applied, the prognosis will be favorable. Usually, a crack in the hand can be treated and does not leave any adverse effects.

