
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Blastocysts in feces in humans: symptoms, classification, analysis, how to treat
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
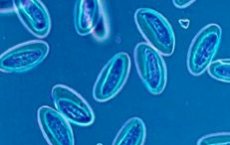
What are blastocysts? This is one of the varieties of protozoa that live and develop in the human intestinal cavity. This type of microorganism can cause a disease called blastocytosis. The pathogenic effect of blastocysts on the human body has been little studied. However, some information about microorganisms is still available.
Protozoan blastocysts
In modern times, the simplest blastocysts are quite widespread: it has been proven that this protozoan infection can easily live in the large intestine of completely healthy people.
Research on blastocysts has been conducted since the sixties of the last century, so it is impossible to call these microorganisms "new". The role of protozoa in the development of infectious diseases, especially in patients with weakened immune defenses, has been studied for a long time. Initially, experiments were conducted on some species of wild and domestic animals, since blastocysts can live not only in the human body. However, for a long time, it was impossible to prove the facts that the simplest blastocysts can cause an infectious disease: blastocysts hominis were considered non-pathogenic microorganisms that act only as harmless transitory carriers. Only a few scientists insisted that blastocysts have the ability to spread, multiply and provoke the development of protozoan infectious diseases.
Meanwhile, in recent years, a lot of epidemiological and clinical information has appeared that confirms the importance of blastocyst hominis in the formation of intestinal pathology.
What does a blastocyst look like?
It is impossible to give a clear answer to the question of what a blastocyst looks like, since there is a certain classification of blastocysts that describes each form of unicellular microorganism separately.
The classification of blastocysts is as follows:
- Vacuolar form – has a characteristic appearance. The outer diameter is from 5 to 20 µm, contains 1-4 nuclei, mitochondria and other components are in the thinnest cytoplasmic layer surrounding a large centered vacuole. Presumably, the vacuole is intended for storing nutrients.
- Granular form - at first glance resembles vacuolar, but in this case the contents of the vacuole and (or) cytoplasm are a granular substance with inclusions of lipids, glycogen, myelin-like structures, etc. Some scientists believe that the appearance of granules is associated with the approaching death of the microorganism.
- Microscopic avacuolar and amoebic forms are protozoa that live in the large intestine. These forms often do not fall into the laboratory's field of vision due to their small size (up to 5 microns), in addition, microorganisms of this form are quickly destroyed when outside the intestine. The amoebic form is not mobile, but it perfectly and tightly contacts the wall of the large intestine.
- Multivacuolar form – is formed from a group of avacuolar forms in the intestinal cavity. The cytoplasm contains a number of vacuoles, while the largest vacuole, occupying the central position, is absent. The structures have a dense outer shell, which acts as a protection against adverse effects.
Under adverse external influences, all of the above forms are capable of transforming into cysts – cells with a multi-layered wall.
Blastocyst Symptoms
In healthy people, blastocyst symptoms may not manifest. The disease makes itself known only when the body's defenses are weakened. In some cases, the disease proceeds covertly with weakly expressed symptoms: in such cases, the patient often does not pay attention to minor periodic manifestations of the disease.
You can become infected with blastocysts by drinking dirty water, eating unwashed fruits and vegetables, or by dirty hands and objects. The blastocyst enters the digestive system and ends up in the large intestine, where it begins its active life. Microorganisms multiply, their life cycle occurs, and some cells die. The waste products of blastocysts can enter the blood, causing symptoms of intoxication. This is mainly reflected in the condition of the skin.
However, most often the intestines themselves suffer. In this case, the symptoms of blastocysts manifest themselves to varying degrees depending on the degree of resistance of the body, that is, on the state of the immune system. What symptoms are most characteristic of the disease:
- abdominal cramps and pain;
- loose stools;
- emaciation;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting attacks;
- fever;
- rashes on the skin, including itchy ones.
Blastocysts in a child
If blastocysts are detected in a child and the child does not present any complaints, then treatment is often not carried out. This is due to the fact that many specialists tend to classify blastocysts as opportunistic microflora of the large intestine of a healthy person. Microorganisms do not cause harm and are not activated until favorable conditions occur, that is, a decrease in the body's immune defense. Only in this case, in the presence of pronounced symptoms of the disease, is appropriate treatment prescribed and carried out.
Blastocysts in a child can cause the same symptoms as in an adult. The clinical picture can be expressed depending on the degree of weakness of the child's body. Often, with predominantly skin lesions, the child may not have signs of intestinal disease. Blastocysts can reveal themselves as persistent allergic conditions, when the child begins to suffer from allergies to many or some products, and anti-allergic treatment often does not bring the desired effect.
Blastocyst diagnostics
Symptoms alone are not enough to diagnose blastocysts. Clinical manifestations of blastocysts must be confirmed in the laboratory. The material for analysis is feces. This is the only way to prove the presence of a single-celled parasite in the body.
In order to establish a diagnosis, at least five blastocysts must be present in the field of view (using an immersion lens). In this case, the pathogen must be detected multiple times. In order to detect blastocysts in feces, the following study is carried out: feces are collected after an independent act of defecation in a clean special container. After this, the material is delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Sometimes the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is used, which allows detecting the DNA element of the pathogenic microorganism. Blastocysts in feces during this method of research are detected over several days.
Along with laboratory testing, the following are taken into account:
- the presence of obvious and indirect symptoms of an inflammatory process in the intestine;
- increased levels of leukocytes in the blood;
- imbalance of microflora in the large intestine;
- pathomorphological changes in the large intestine.
Based on all the results obtained, the diagnosis of blastocysts is confirmed and further treatment tactics are determined.
How to treat blastocysts?
Before answering the question "how to treat blastocysts?", we should answer the question "is it really necessary?" The fact is that in cases where blastocysts are found in the feces, but the clinical picture of the disease is not expressed, it is not at all necessary to take measures to eliminate the parasites. Blastocyst treatment is prescribed if the patient complains of signs of the disease, if he has persistent allergic reactions, and a constant stable concentration of the pathogen is found in the feces.
Treatment of blastocysts involves the administration of antimicrobial agents that have a depressing effect on single-celled microorganisms. Such medications include:
- metronidazole – 0.5 g twice a day for 5 days;
- furazolidone – 0.1 g four times a day for 7-10 days;
- nimorazole – 0.5 g twice a day.
Some specialists prefer to use Nifuratel (0.4 g up to 3 times a day for 5 days), Tiberal (in the form of 3 tablets at a time in the evening, treatment duration 1-2 days) or Tinidazole (in the form of 4 tablets at a time).
In addition to antibacterial treatment, your doctor may prescribe medications to stimulate the body's defenses to activate the body's own defenses against pathogenic bacteria.
Treatment of blastocysts with folk remedies
It is known that blastocysts die when boiled. This means that these microorganisms are sensitive to high temperatures. Treatment of blastocysts with folk remedies is based primarily on creating conditions in the large intestine under which blastocysts either die or slow down their development and vital activity.
First of all, traditional medicine experts recommend making some changes to your diet. This should be done carefully: if there are other diseases of the digestive system, then the possible harm from this method of treatment should be compared.
- Blastocysts do not like spicy foods, so adding moderate amounts of hot pepper (chili) to the diet will help get rid of the problem.
- It is encouraged to add spices to dishes such as ginger, cloves, mustard, as well as to consume onions, garlic, and horseradish.
- Creating an acidic environment in the intestines also has a negative effect on pathogenic flora, so you can add products such as natural vinegar, sauerkraut, sour juices and fruits to the menu.
- The bitter environment is also unacceptable for blastocysts, so it is recommended to take decoctions and infusions of wormwood.
Among other things, it is recommended to eliminate dysbacteriosis and establish normal bowel function. For this purpose, you should consume fresh fermented milk products: kefir, sourdough, curdled milk, cottage cheese, natural yogurt.
Blastocyst prevention
Blastocyst prevention involves compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules and timely detection of carriers of these microorganisms.
What personal hygiene standards are important as preventive measures:
- washing hands, especially before eating and after using the toilet or being outside;
- washing fruits and vegetables, eating only clean products;
- control of flies and other insects indoors, especially in the kitchen;
- drinking only clean water, preferably boiled;
- Maintaining cleanliness in the kitchen and toilet, cleaning them regularly using special disinfectants and household chemicals.
In addition to the above-mentioned essential preventive measures, it is also necessary to maintain a good state of immunity in the body. To do this, it is necessary to eat right, lead an active lifestyle, play sports, and harden yourself. It is necessary to remember that microorganisms such as blastocysts affect only a weakened and susceptible to infection organism.


 [
[